Emergency call based authentication method, device and system
An emergency call and equipment technology, which is applied in the transmission system, emergency/dangerous communication service, connection management, etc., can solve the problems of poor security of emergency calls, and achieve the effect of improving and ensuring safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
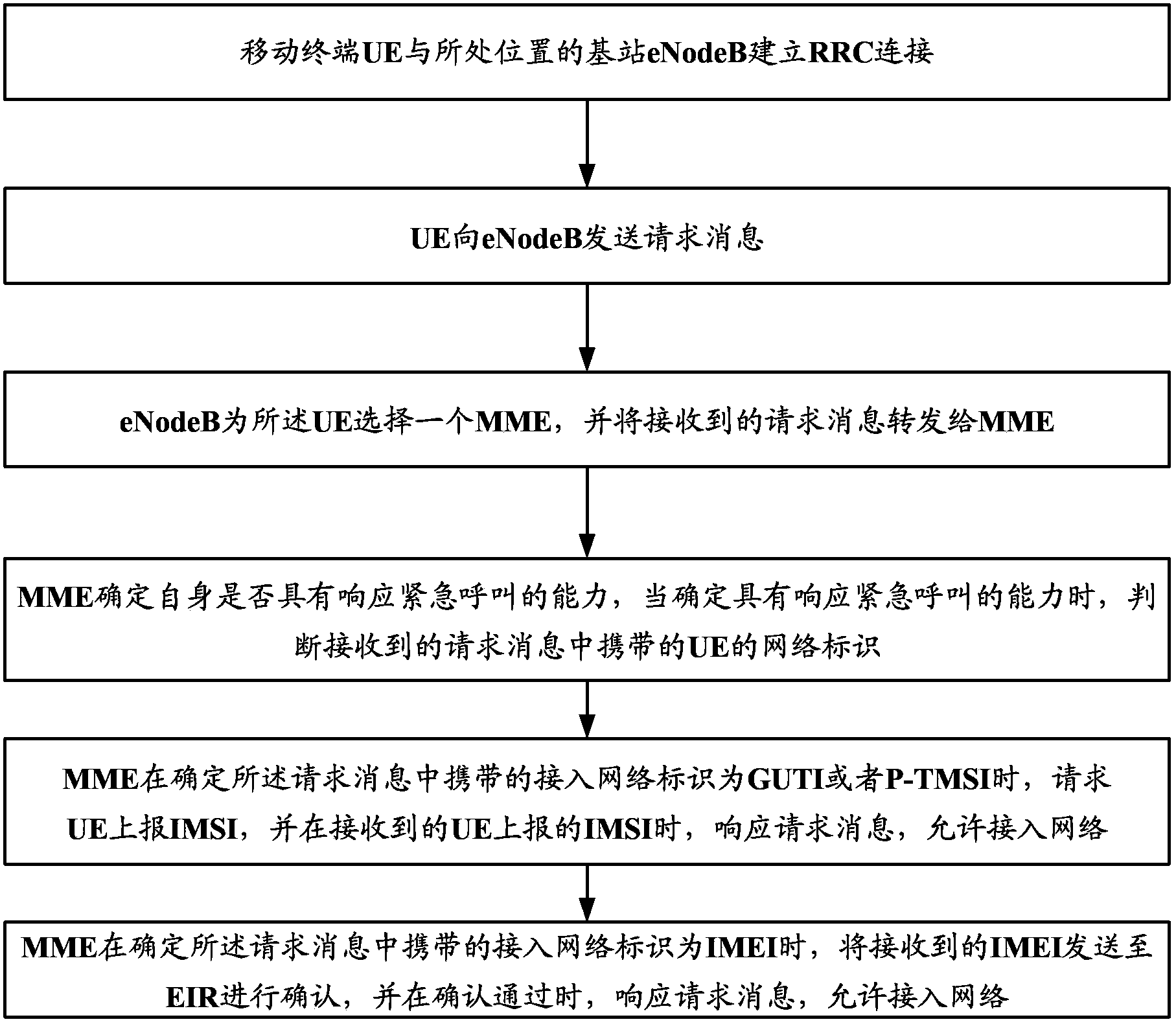
[0048] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a flow chart of an emergency call-based authentication method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and the method includes:
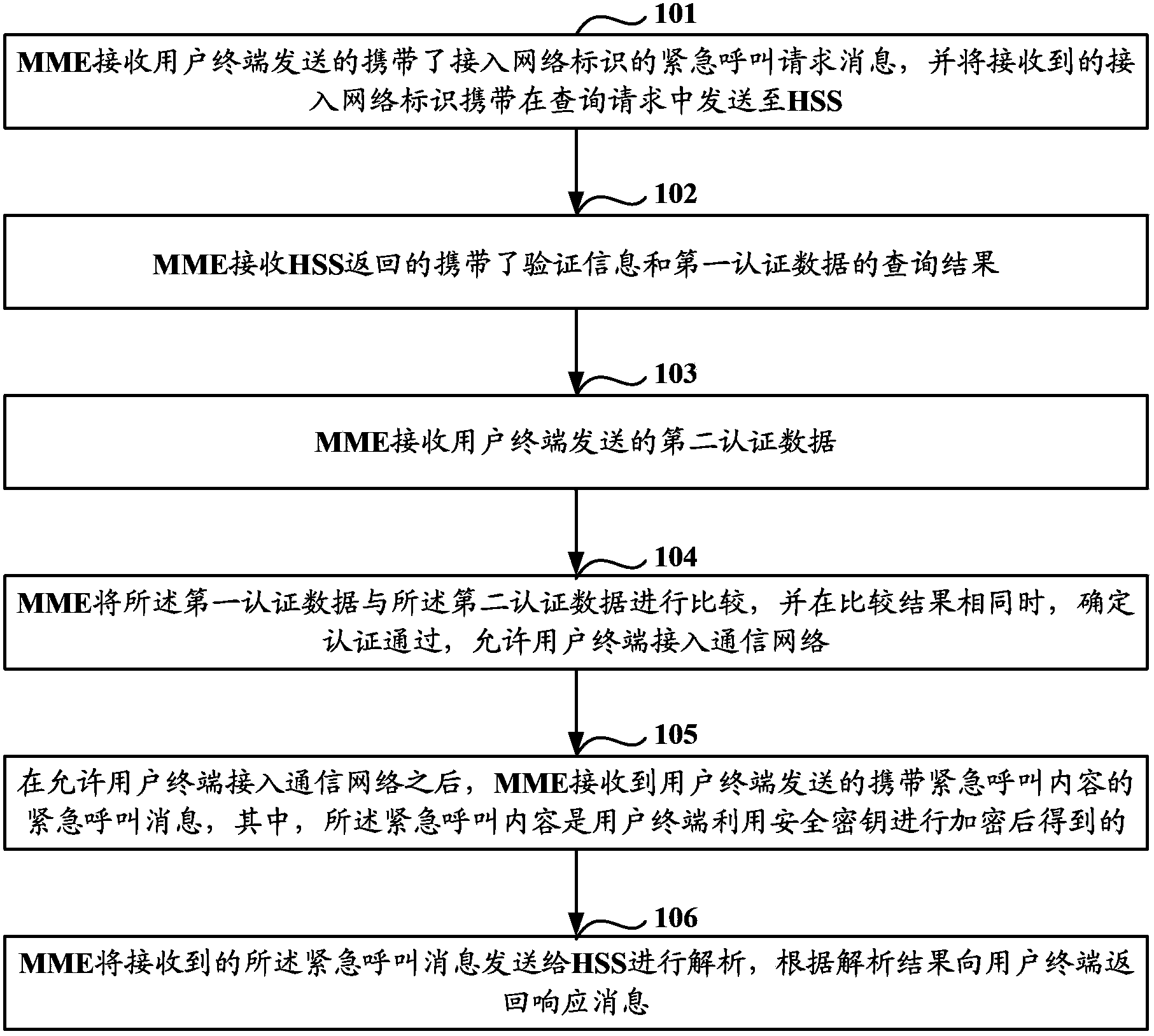
[0049] Step 101: The MME receives the emergency call request message carrying the access network identifier sent by the user terminal, and sends the received access network identifier in the query request to the HSS.
[0050] Wherein, the access network identifier is the IMEI identifier of the user terminal.
[0051] In step 101, when the user terminal is under call restriction or does not have a SIM card / USIM card inserted, and needs to initiate an emergency call request, the user terminal carries its own IMEI identifier as the access network identifier in the emergency call request message and sends it to the MME .
[0052] Preferably, when receiving the emergency call request message sent by the user, the MME instructs the user terminal to report the access network identifier, so as to identif...
Embodiment 2
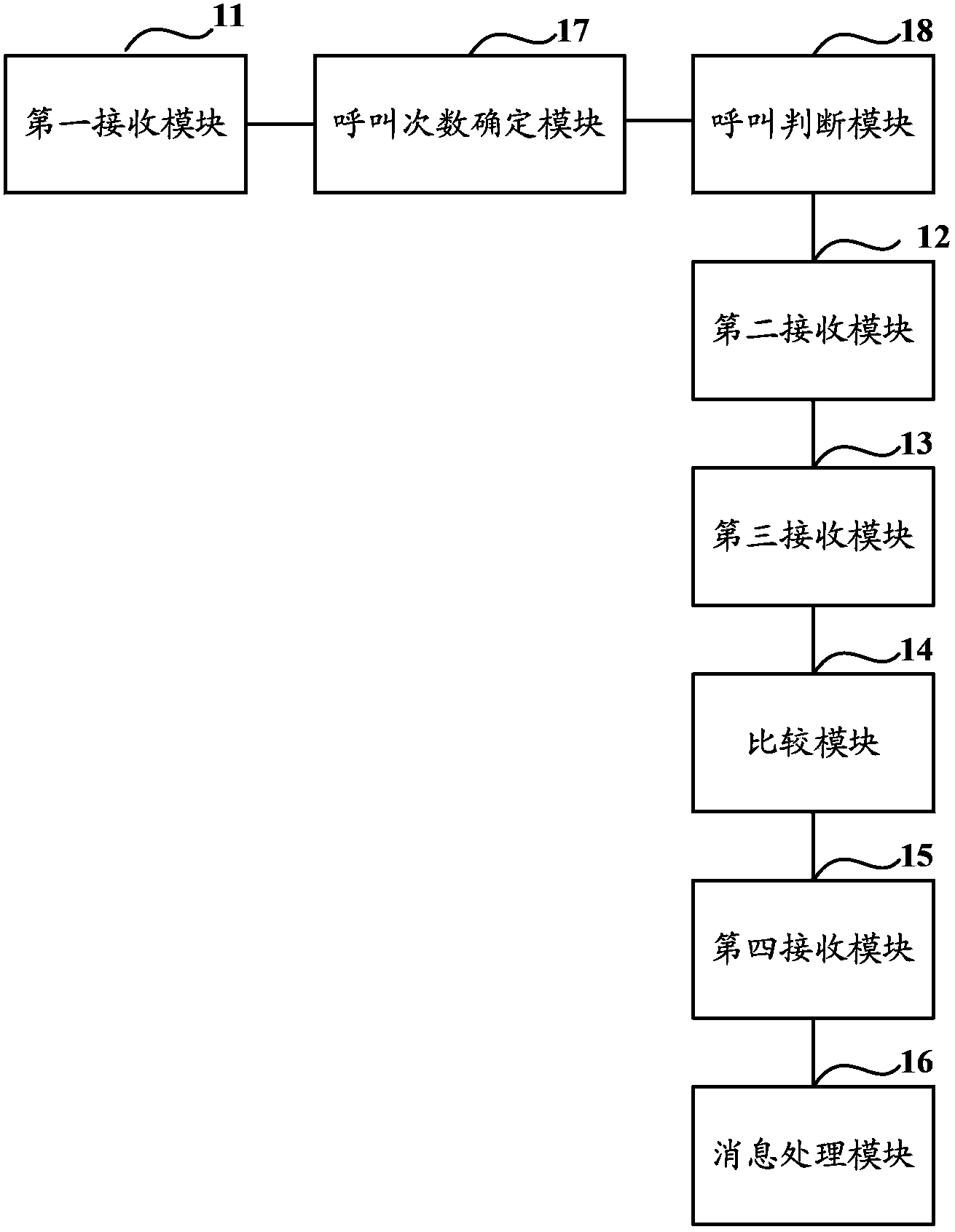
[0084] Such as image 3 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of an emergency call-based authentication device according to Embodiment 2. The device includes: a first receiving module 11, a second receiving module 12, a third receiving module 13 and a comparison module 14, wherein:
[0085] The first receiving module 11 is configured to receive the emergency call request message carrying the access network identifier sent by the user terminal, and carry the received access network identifier in the query request and send it to the HSS;
[0086]The second receiving module 12 is configured to receive the query result returned by the HSS that carries the verification information and the first authentication data, and the first authentication data is calculated by the HSS from the searched security key and the generated verification information, wherein , the security key includes a device key, and the device key is determined by the HSS according to the correspondence be...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Such as Figure 4 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of an HSS according to the third embodiment. The HSS includes: a receiving module 21, a first authentication data calculation module 22 and a sending module 23, wherein:
[0099] The receiving module 21 is configured to receive a query request sent by the MME, the query request includes an access network identifier, and the access network identifier is carried when the user terminal sends an emergency call request message to the MME;
[0100] The first authentication data calculation module 22 is configured to determine the device key corresponding to the access network identifier contained in the query request according to the correspondence between the locally stored access network identifier and the device key, and use the The security key of the key and the randomly generated verification information are calculated to obtain the first authentication data;
[0101] The sending module 23 is configured t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com