2D video three-dimensional method based on sample learning and depth image transmission
A technology of depth image and sample learning, applied in the field of video processing, can solve the problems of inability to maintain depth image boundary information, difficulty in ensuring 3D image continuity, image boundary distortion, etc., to reduce computational complexity and improve edge texture clarity. degree, the effect of internal smoothing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
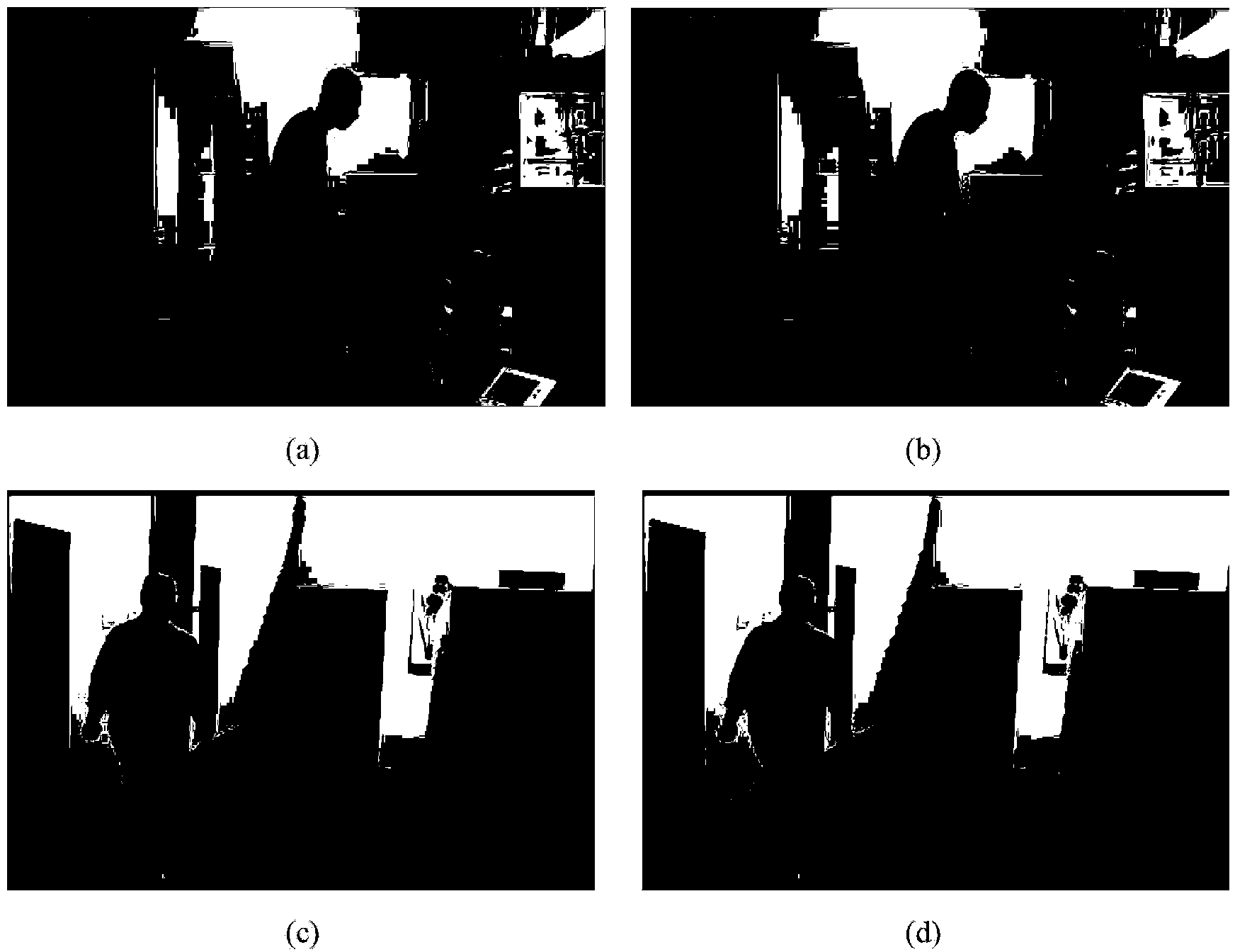
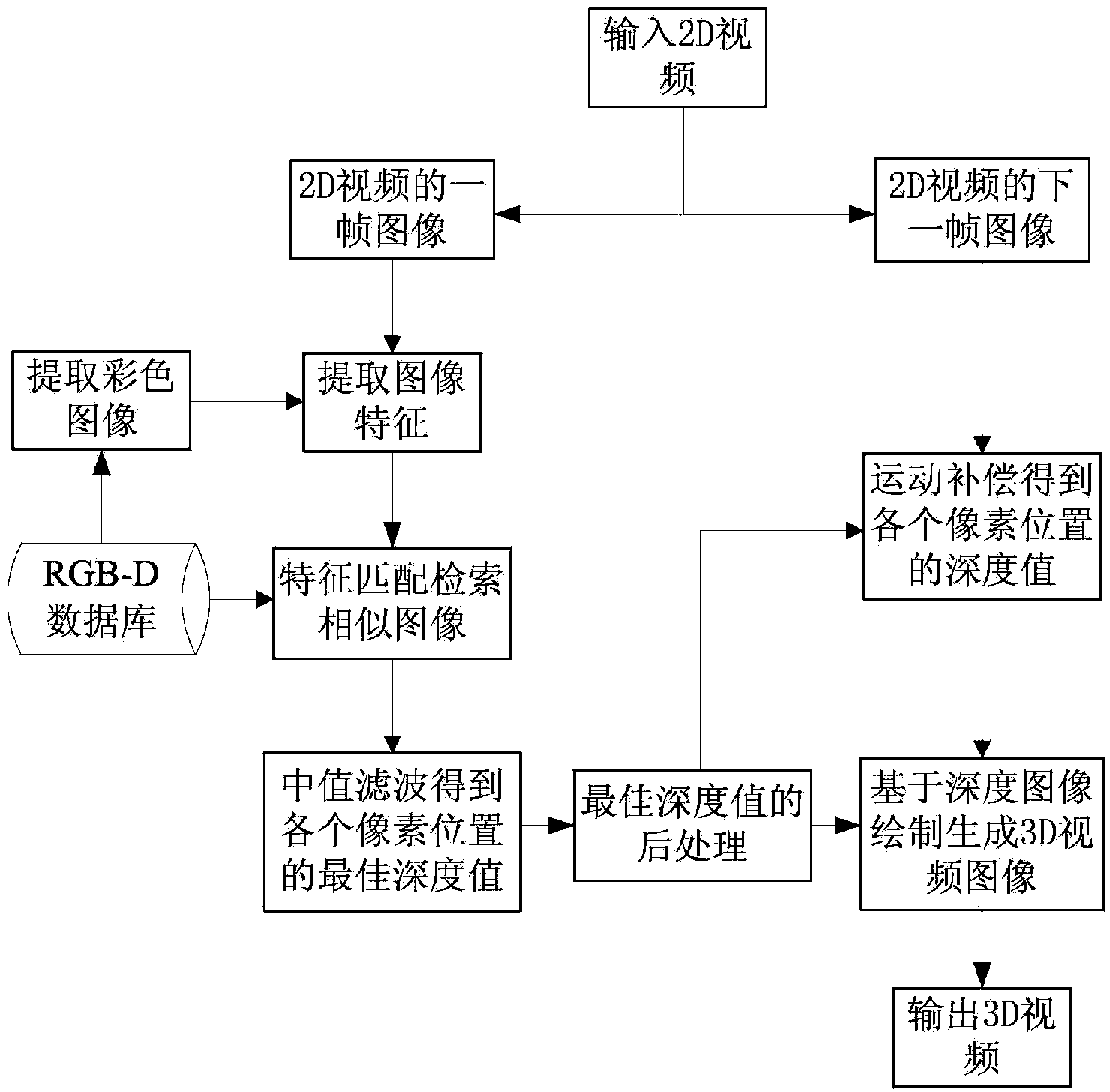
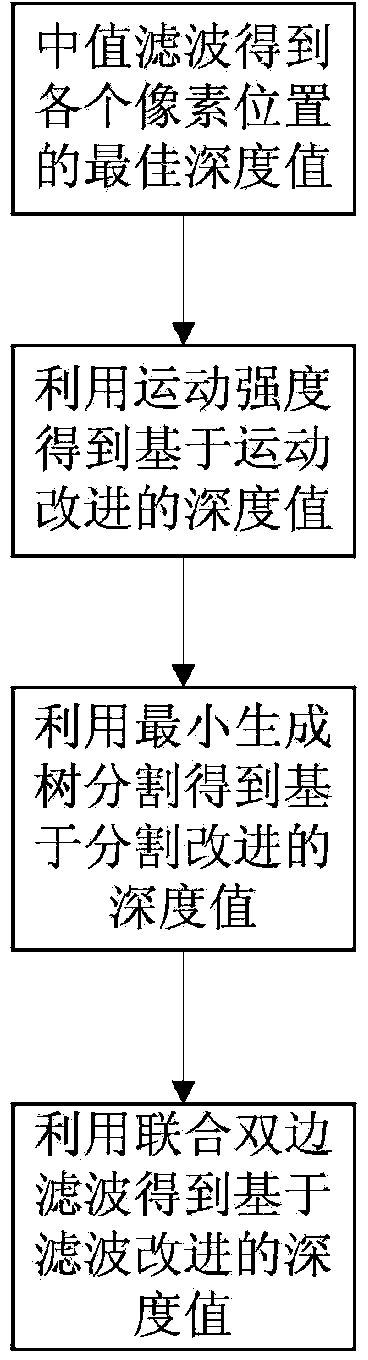
[0041] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0042] Step 1. Extract image features
[0043] 1a) Input two 2D video images I with a size of 320×240 1 and I 2 , and extract the video image I 1 Histogram eigenvectors of oriented gradients Specific steps are as follows:
[0044] (1a1) convert the video image I 1 It is divided into units with a size of 40×40, and the gradient histograms of 9 directions are counted in each unit, and four adjacent units form a block with a size of 80×80, and the gradient histograms of the four units in a block are connected to obtain The gradient histogram feature vector of the block;
[0045] (1a2) Concatenating the gradient histogram feature vectors of all blocks, the resulting video image I 1 Histogram eigenvectors of oriented gradients
[0046] 1b) Extract all color images of size 320×240 from color-depth image pair RGB-D database 1≤i≤N, N is the number of color images in the databas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com