Control method for cluster timing scheduling tasks
A timing scheduling and control method technology, applied in the direction of program startup/switching, program synchronization, multi-program device, etc., can solve problems such as complex configuration, multiple execution of timing scheduling tasks, and inability to take advantage of the high stability of the cluster system. To achieve the effect of reducing the degree of embedding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
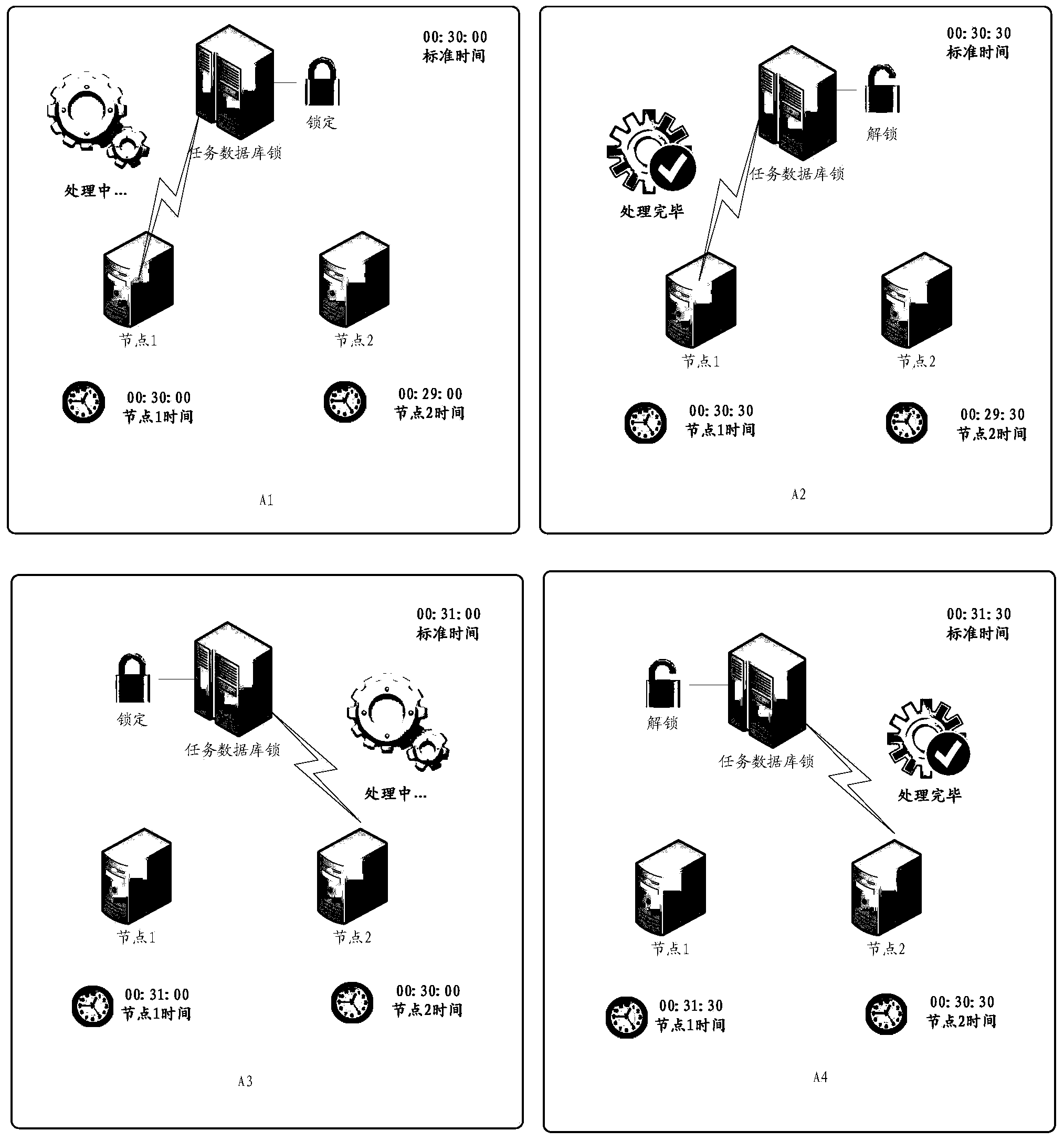
[0026] The core idea of the present invention is: when the cluster node arrives at the execution time of the scheduled task, the database determines whether the task is currently locked, if it is not locked, only the time difference between the current time and the time when the task was executed last time When it is greater than the minimum time interval, the execution of the scheduled task is triggered. In this way, it can be ensured that the cluster timing scheduling task will not cause multiple execution problems due to the time of different nodes not being synchronized. In addition, the database only needs to maintain information such as the scheduling time and lock status information for each timing scheduling task. The maintenance...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com