Electric current balancing method and system for multi-battery or multi-battery-pack parallel connection charging or discharging
A current balancing and charging current technology, applied in battery energy storage and application, in the field of current balancing in parallel charging or discharging of multiple batteries or multiple battery packs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
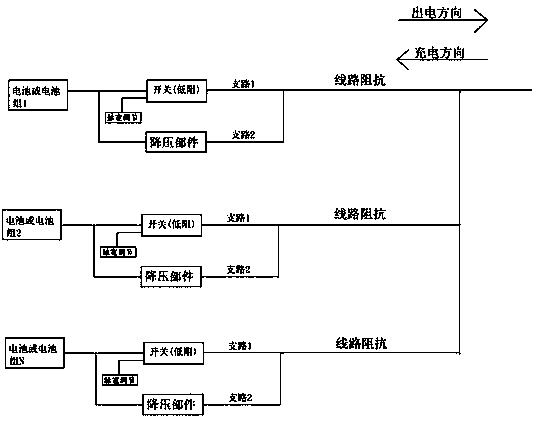
[0020] (1) Embodiment 1: Each battery pack or battery packs are discharged in parallel
[0021] Assume cells or packs 1 through N are all 10V, and only pack 2 is at 10.5V. When discharging in parallel, the discharge currents of the branches 1 of the batteries or battery packs 1, 3, 4, ... N are all equal, equal to 100A. The voltage of the battery or battery pack 2 is relatively high, so its branch 1 discharge current will be higher than 100A, let's say 120A. At this time, the method of current sharing is: to control the branch 1 switch of the battery or battery pack 2 with a certain pulse width, such as 80%, and the switch is disconnected for 20% of the time, thereby forcing the current to flow through the branch. 2. Assume that the voltage drop of the step-down component is 1V, so that during the time when 20% of the current in branch 2 flows, the current in branch 2 is actually relatively small, for example, only 10A. Then the actual output current of the battery or the b...
Embodiment 2
[0022] (2) Embodiment 2: Each battery pack or battery packs are charged in parallel
[0023] Assume cells or packs 1 to N are all 10V, and only pack 2 is 9.5V. When charging in parallel, the charging currents of the branches 1 of the batteries or battery packs 1, 3, 4, ... N are all equal, equal to 100A. The voltage of the battery or battery pack 2 is relatively low, so its branch 1 charging current will be higher than 100A, let's say 120A. At this time, the method of current sharing is: to control the branch 1 switch of the battery or battery pack 2 with a certain pulse width, such as 80%, and the switch is disconnected for 20% of the time, thereby forcing the current to flow through the branch. 2. Assume that the voltage drop of the step-down component is 1V, so that during the time when 20% of the current in branch 2 flows, the current in branch 2 is actually relatively small, for example, only 10A. Then the actual charging current of the battery or the battery pack 2 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com