Several-for-one collaborative guidance method based on target probability distribution information
A probability distribution and target technology, applied in the field of many-to-one cooperative guidance, can solve the problems of interceptor overload response speed requirements too high, low ballistic prediction accuracy, low target detection accuracy, etc., to reduce overload response speed requirements, reduce ballistic Forecast accuracy requirements, effects of relaxed requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
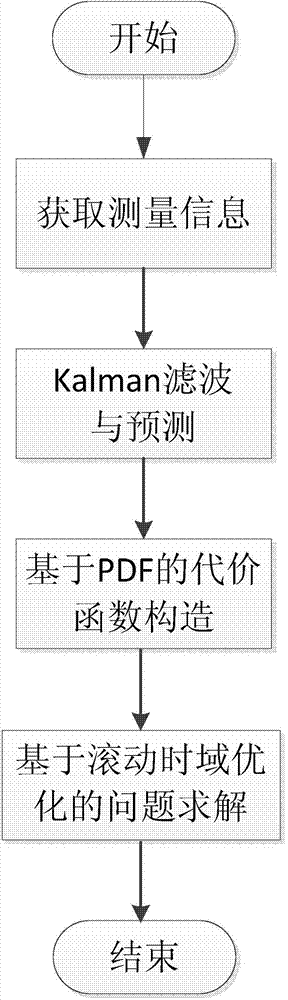
[0023] Specific implementation mode 1: The many-to-one cooperative guidance method based on target probability distribution information described in this implementation mode is characterized in that it specifically includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1, obtaining relative motion measurement information between the interceptor and the target;
[0025] Step 2 (1) Combine the state value of the interceptor and apply Kalman filter to process the above relative motion measurement information to obtain the estimated value of the target state at the current moment; Step 2 (2) Combine the dynamic equation of the target motion to obtain the target terminal time The position probability density function is used to predict the position of the target at the terminal moment;
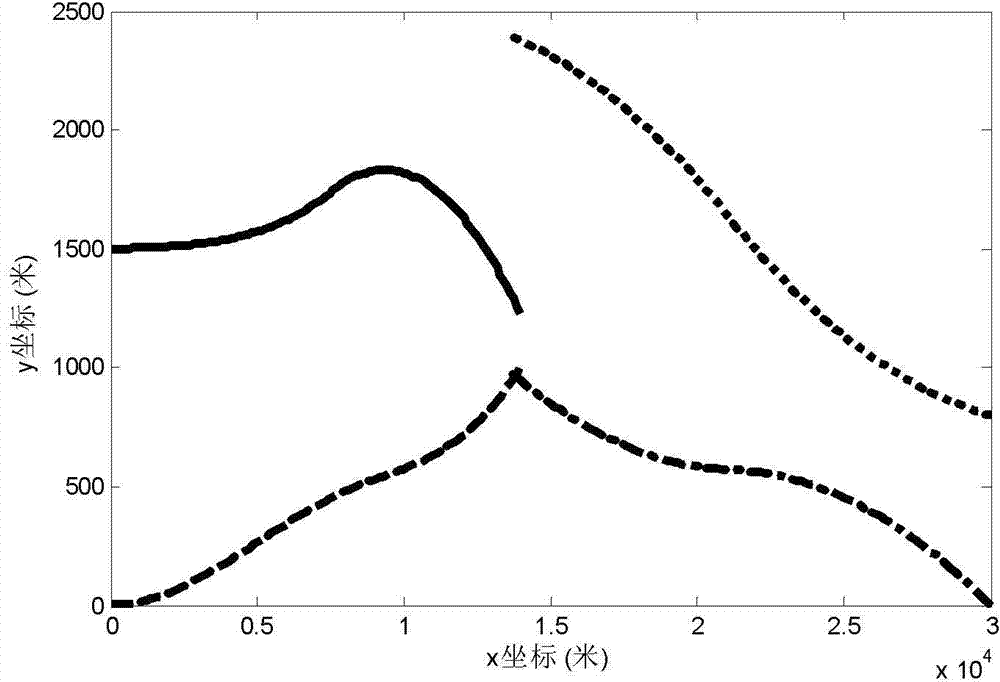
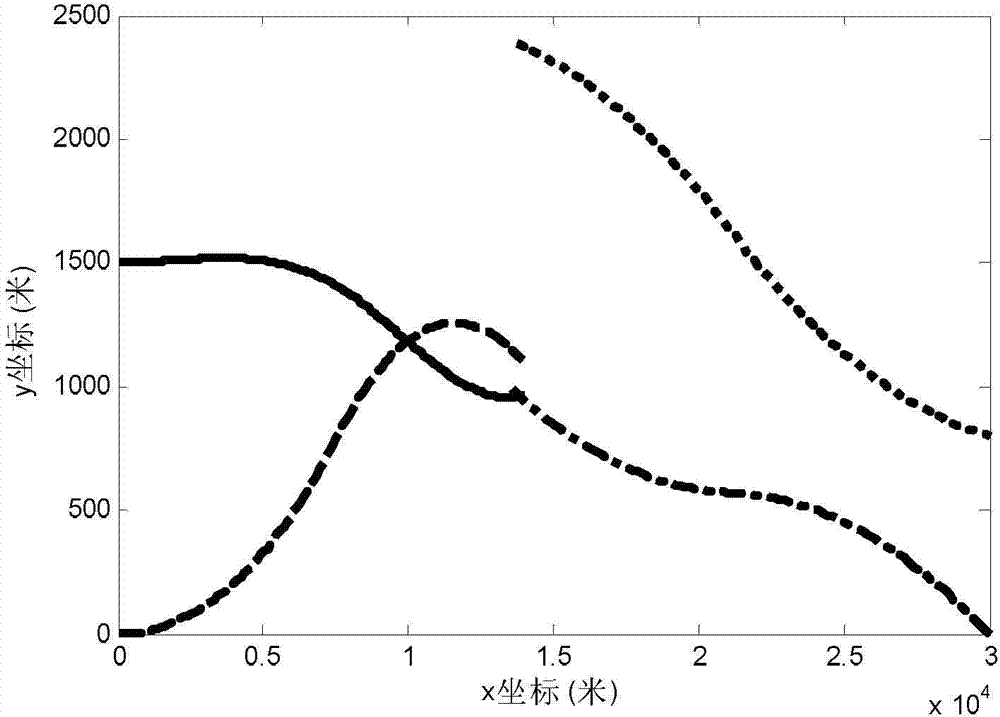
[0026] Step 3, constructing the integral of the probability density function of the target position at the terminal moment in the reachable set of multiple interceptors as the cooperative guidance cost functi...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the relative motion measurement information is:
[0029] Since only the line-of-sight angle q between the interceptor and the target can be measured, assuming that the measurement noise of the line-of-sight angle is v, then
[0030] y M i d = r ( t ) sin ( q + v ) = r ( t ) sin ( ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the specific process of applying the Kalman filter described in step 2 (1) to obtain the estimated value of the target state at the current moment is:
[0034] The relative motion equation between the interceptor and the target is established as
[0035] X · = AX + B 1 u + B 2 w - - - ( 4 )
[0036] Among them, u represents the control input, w represents the acceleration command form of the target, and the system state is
[0037] X = [ y y a T · ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com