Wireless sensor network route method based on artificial potential field
A wireless sensor and artificial potential field technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of complex calculation methods, a large amount of routing overhead, and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
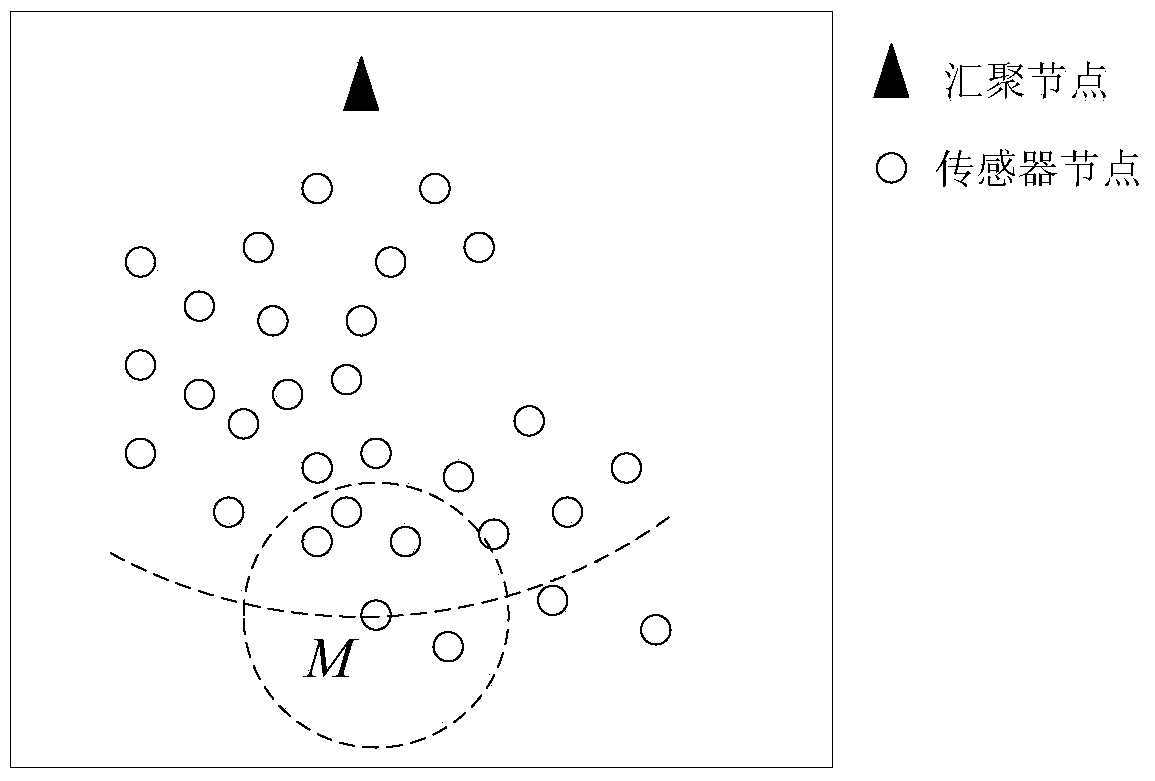
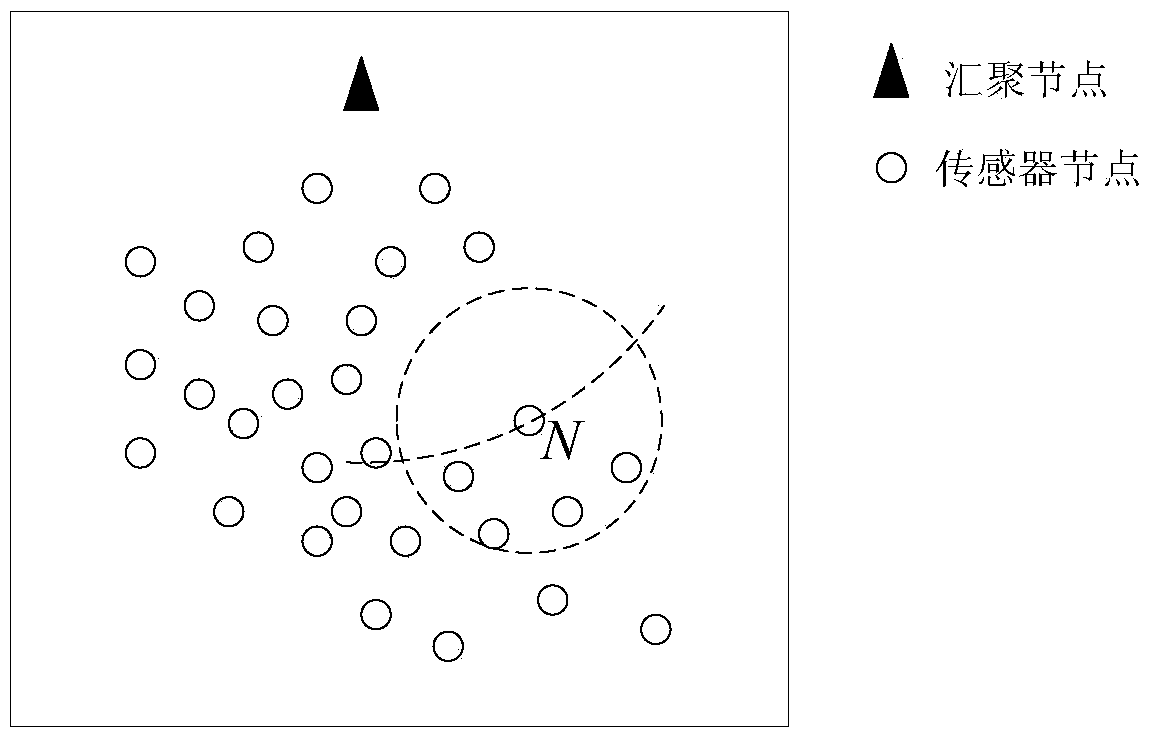
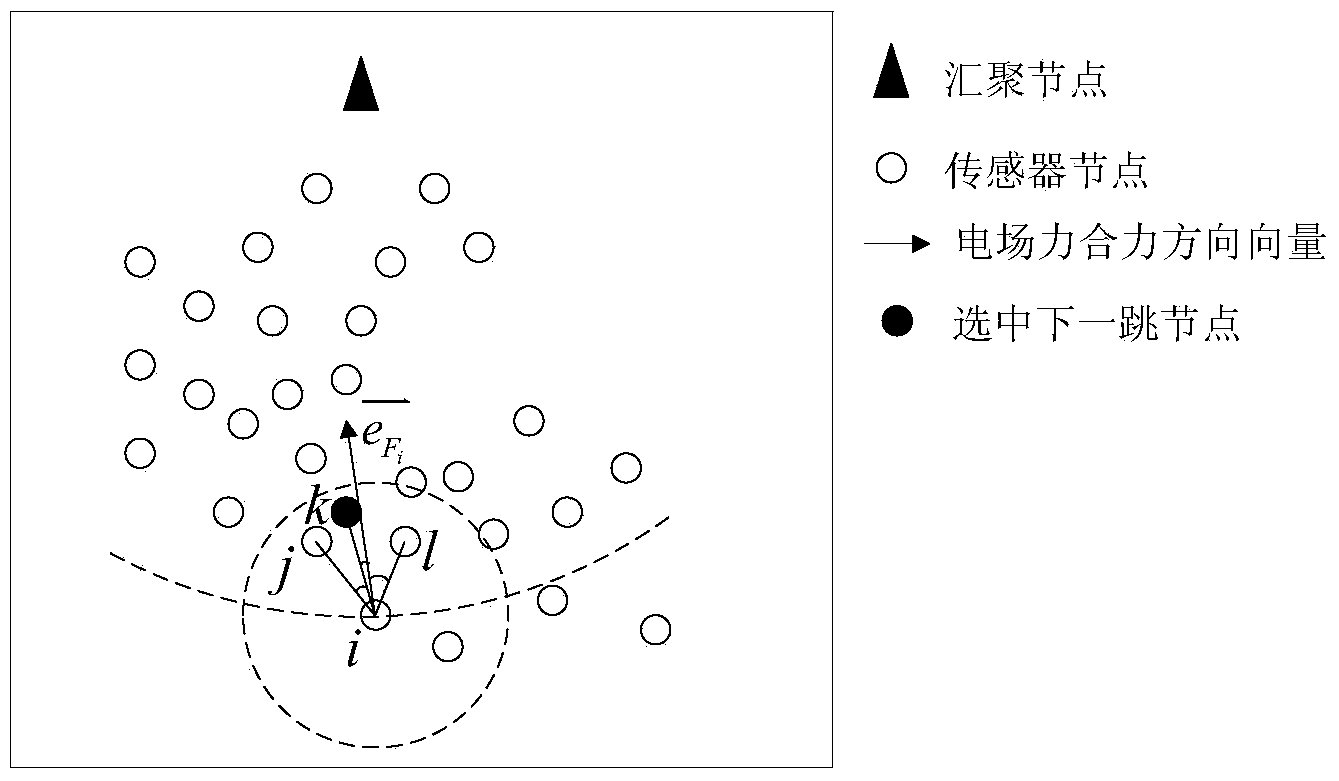
[0054] figure 1 is a typical network topology, where the dotted circle centered on node M represents the wireless communication radius of node M. The center of the arc passing through node M is the sink node, and the radius is the distance from M to the sink node. Follow the steps below to initialize:
[0055] a) Encode the sink nodes in the network and set their ID equal to 1; encode the sensor nodes in the network so that their IDs are different from each other and not equal to 1, and then all sensor nodes initialize their empty flags is "false";
[0056] b) The sensor node obtains its own position coordinates P through the positioning device i (x i ,y i ), where x i 、y i The horizontal and vertical coordinate values of their location points respectively; the sensor node reads its own remaining power V through the power management module i ;
[0057...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com