Zero-mode and line-mode time difference radiation net fault location method achieved only through voltage without relying on two-terminal synchronization
A technology of fault location and radiation network, applied in fault location, measurement of electrical variables, measurement of electricity and other directions, can solve the problems of high operating cost of double-ended traveling wave method and difficulty in calibrating the arrival time of reflected wave head
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
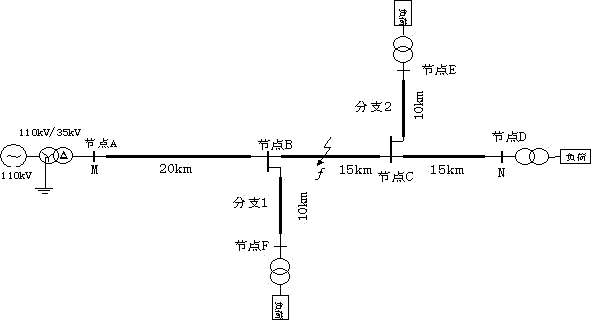
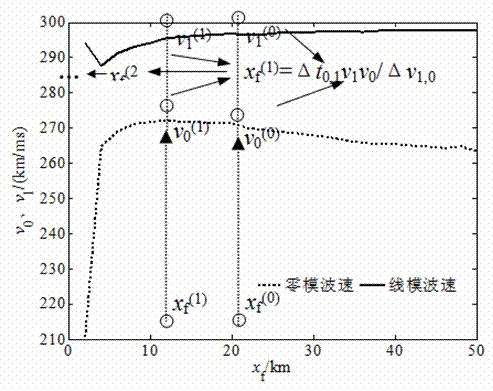
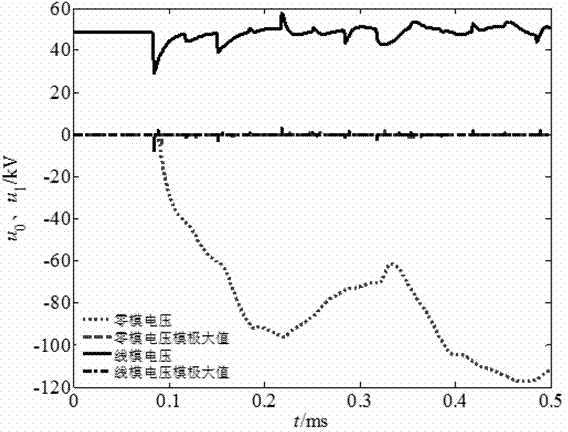
[0030] Example 1: Now assume that a single-phase grounded metal fault occurs on the trunk line 25km away from the M terminal, the initial phase angle of the fault is 90°, and the simulation sampling frequency is 10MHz, respectively use the wavelet modulus maximum value under the fifth scale to detect the measurement terminal Calibrate the time of the incoming line and zero-mode traveling wave components, and obtain the two measurement end lines of M and N, the zero-mode voltage traveling wave and its modulus maximum calibration as follows: image 3 shown. The arrival time difference of the M lateral line and zero-mode wave is △ t M = 0.0086ms, the time difference between N-side line and zero-mode wave is △ t N =0.0084ms, the wave velocity at the midpoint of the feeder is selected as the initial wave velocity iteration value, and the ranging formula is used Calculate the initial distance to fault x f (0) , the initial fault distance x f (0) Substituting the line and ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Assume that a single-phase grounded metal fault occurs on the branch 1 line 25km away from the M terminal, the initial phase angle of the fault is 50°, the fault transition resistance is 20Ω, and the simulation sampling frequency is 10MHz, respectively using the wavelet mode poles under the fifth scale The maximum value is time-calibrated for the line and zero-mode traveling wave components detected by the measuring end, and the two measuring end lines of M and N, the zero-mode voltage traveling wave and its modulus maximum value calibration are obtained. The arrival time difference between M side and N side line and zero-mode wave is △ t M and △ t N , select the wave velocity at the midpoint of the feeder as the initial wave velocity iterative value, and use the ranging formula Calculate the initial distance to fault x f (0) , the initial fault distance x f (0) Substituting the line and zero-mode interpolation curve for iteration, when the linear-m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com