Light-emitting diode drive circuit
A technology of light-emitting diodes and driving circuits, which is applied to the layout of electric lamp circuits, light sources, electric light sources, etc., can solve the problem that the current error is not enough to meet the high-quality display, and achieve the effect of reducing the bias error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The following is an introduction to the preferred embodiments of the present invention. Each embodiment is used to illustrate the principle of the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. The scope of the invention should be determined by the appended claims.
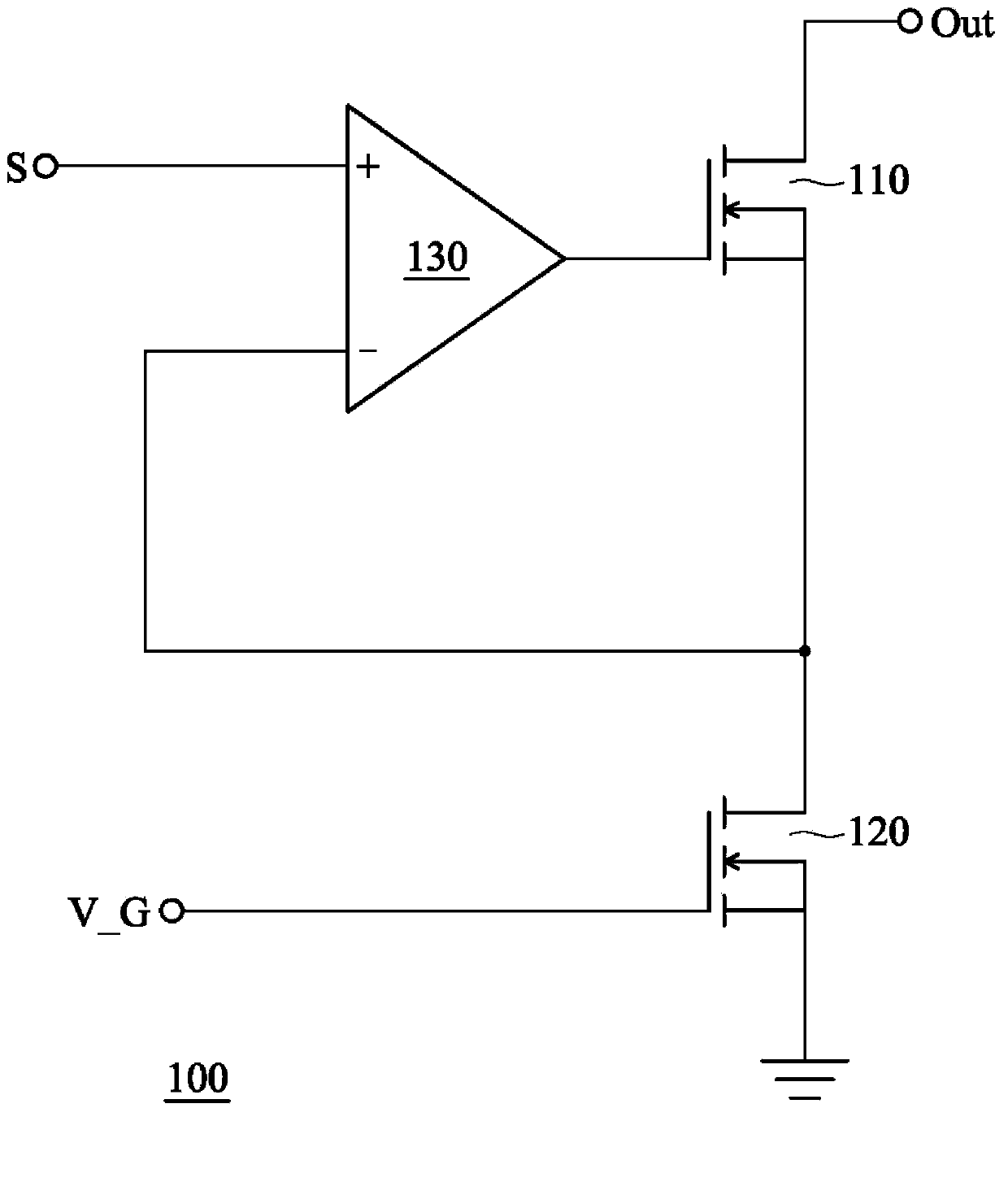
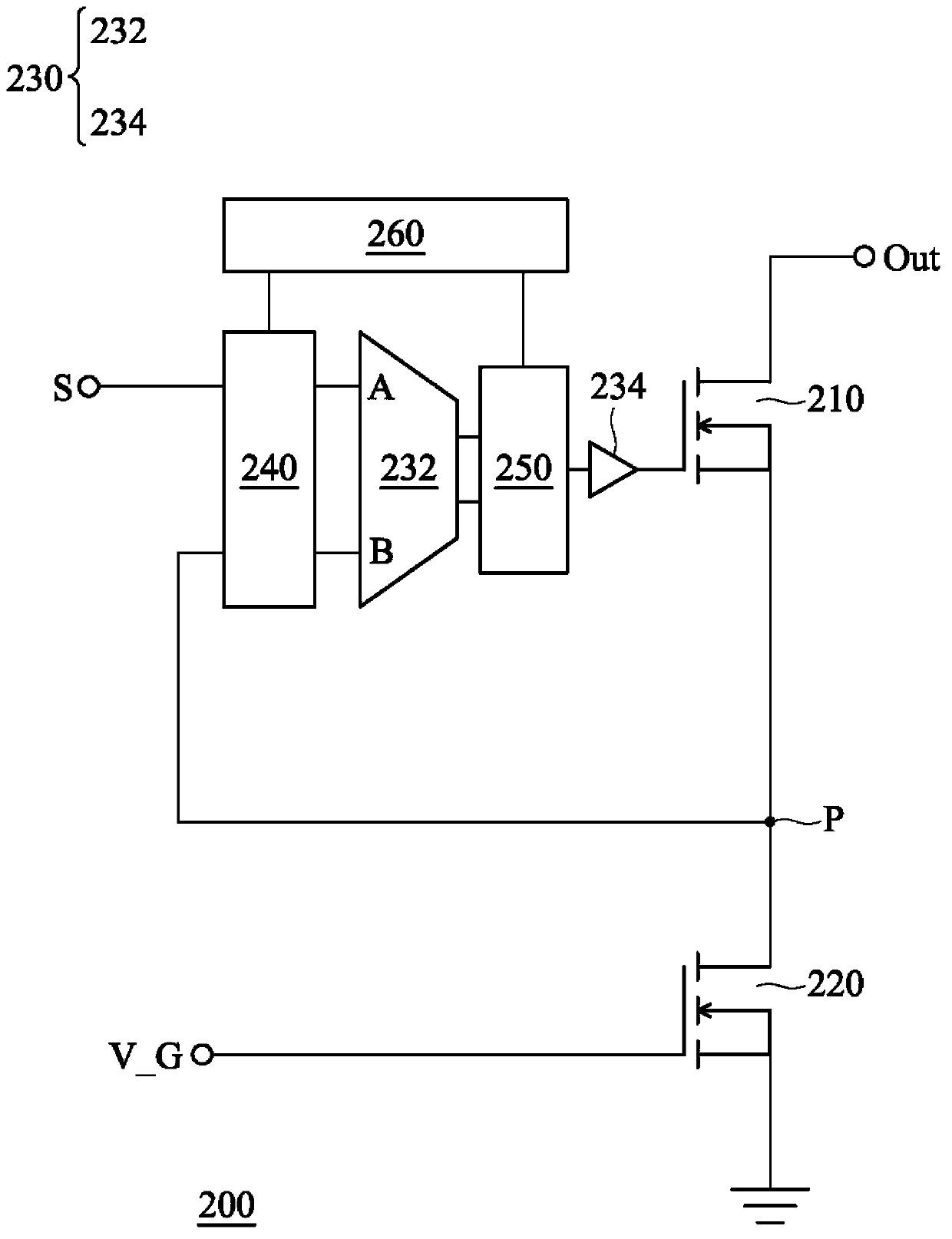
[0016] figure 1 It is a circuit structure diagram of a driving circuit of a light emitting diode (LED). In this figure, the LED driving circuit 100 includes an output NMOS (N channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, NMOS) transistor 110 , a grounded NMOS transistor 120 , and an operational amplifier 130 . The output NMOS transistor 110 has a drain connected to the output terminal Out and a source connected to the drain of the grounded NMOS transistor 120 in series, wherein the output terminal Out is further connected to an LED (not shown). The grounded NMOS transistor 120 receives the bias voltage V_G with a gate and grounded with a source. The operational amplifier 130 can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com