Rotor of a rotating electrical machine
A technology for a rotating electrical machine and a rotor is applied in the field of the rotor of the rotating electrical machine, which can solve the problems such as the decrease of the anti-skid toughness of the rotating shaft 224, and achieve the effect of suppressing the pressing stress.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
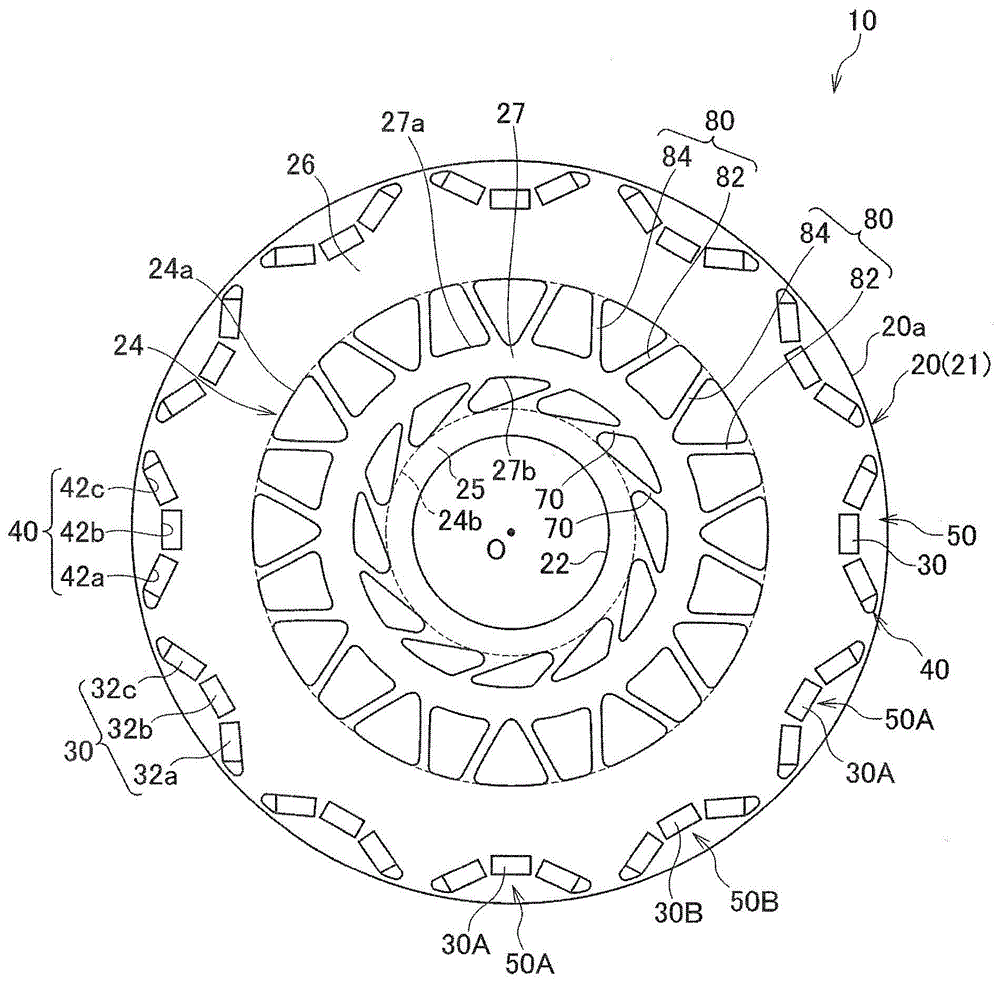
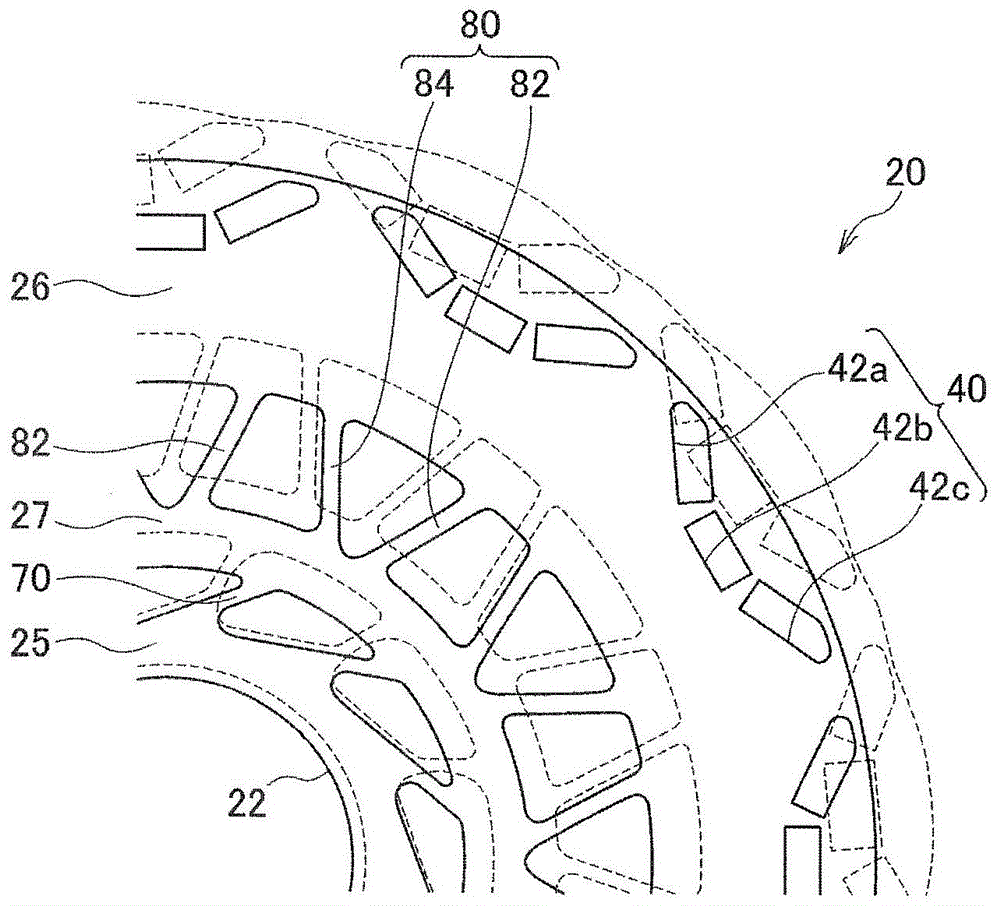
[0104] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the rotor 10 of the rotating electrical machine according to the first embodiment includes a substantially annular rotor core 20 and a rotating shaft (not shown), and is disposed on the inner peripheral side of a stator (not shown). The rotor core 20 has A plurality of magnetic pole portions 50 formed at predetermined intervals along the circumferential direction are press-fitted into the shaft hole 22 formed in the center portion of the rotor core 20 with the rotating shaft. It should be noted, figure 1 , the symbol O is the center of the rotor 10 .
[0105] The rotor core 20 is formed by laminating a plurality of annular electromagnetic steel sheets having substantially the same shape, for example, silicon steel sheets 21 , and has a plurality of magnet insertion holes 40 formed at predetermined intervals along the circumferential direction.
[0106] The magnetic pole portion 50 is configured by inserting the permanent mag...
no. 2 approach
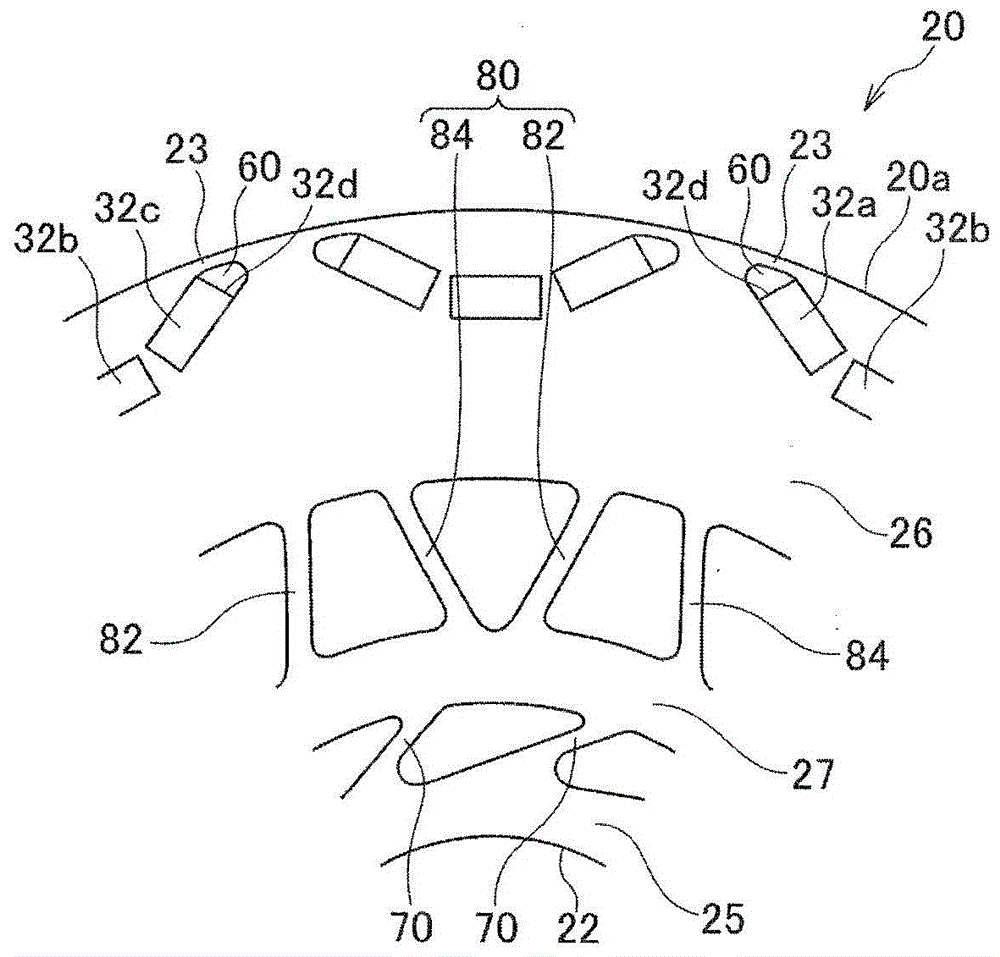
[0132] Next, the rotor of the rotating electrical machine according to the second embodiment will be described. The rotor 10A of the rotating electrical machine of this embodiment is the same as the first embodiment in basic structure, and differs in the structure of the inner peripheral side rib 70 and the outer peripheral side rib 80 , so the same parts are omitted or simplified by attaching the same reference numerals. illustrate.
[0133] Such as Figure 7 and Figure 8 As shown, in the rotor 10A of the rotating electric machine according to this embodiment, the inner peripheral rib 70 includes: Figure 7 The first inner peripheral side rib 72 extending clockwise in the center; the other side in the circumferential direction ( Figure 7 The middle is the second inner peripheral side rib 74 extending counterclockwise.
[0134] The outer peripheral end portion of the first inner peripheral side rib 72 is connected to the outer peripheral side end portion of the second in...
no. 3 approach
[0143] Next, the rotor of the rotating electric machine according to the third embodiment will be described. The rotor 10B of the rotating electrical machine of this embodiment is the same as the second embodiment in basic structure, and differs in the structure of the inner peripheral side rib 70 and the outer peripheral side rib 80 , so the same parts are omitted or simplified by attaching the same reference numerals. illustrate.
[0144] Such as Figure 10 and Figure 11 As shown, in this embodiment, as in the second embodiment, the included angle α formed by the first inner peripheral rib 72 and the second inner peripheral rib 74 is set to be larger than that between the first outer peripheral rib 82 and the second inner peripheral rib 82 . The angle β formed by the two peripheral side ribs 84 is large (α>β).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com