Neutralizing gp41 antibodies and their use
A technology of antibodies and monoclonal antibodies, applied in the direction of antibodies, applications, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of cross-reactivity or limited potency of antibody strains, and the inability to provide therapeutic interventions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0409]Several embodiments include methods for producing monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to a target antigen, wherein the method comprises: (a) isolating a population of memory B cells from a subject that has been exposed to the target antigen, wherein the memory B cells are CD19+IgA-IgD-IgM-B cells; (b) contacting the isolated memory B cell population with an effective amount of IL-21, IL-2 and CD40; (c) from the isolated memory B cell isolating a nucleic acid molecule from a cell population; (d) amplifying nucleic acid encoding a variable heavy chain and a variable light chain from said nucleic acid; (e) expressing a variable heavy chain and a variable light chain from said nucleic acid to obtain from said nucleic acid The variable heavy and variable light chains generate antibody molecules; and (f) selecting monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to the target antigen.
[0410] Certain embodiments include methods for isolating a repertoire of B cells speci...
Embodiment 1
[0418] Isolation and characterization of broadly neutralizing MPER-specific monoclonal antibodies
[0419] This example illustrates the isolation and characterization of HIV-1 gp41-specific binding antibodies from HIV-1 infected subjects.
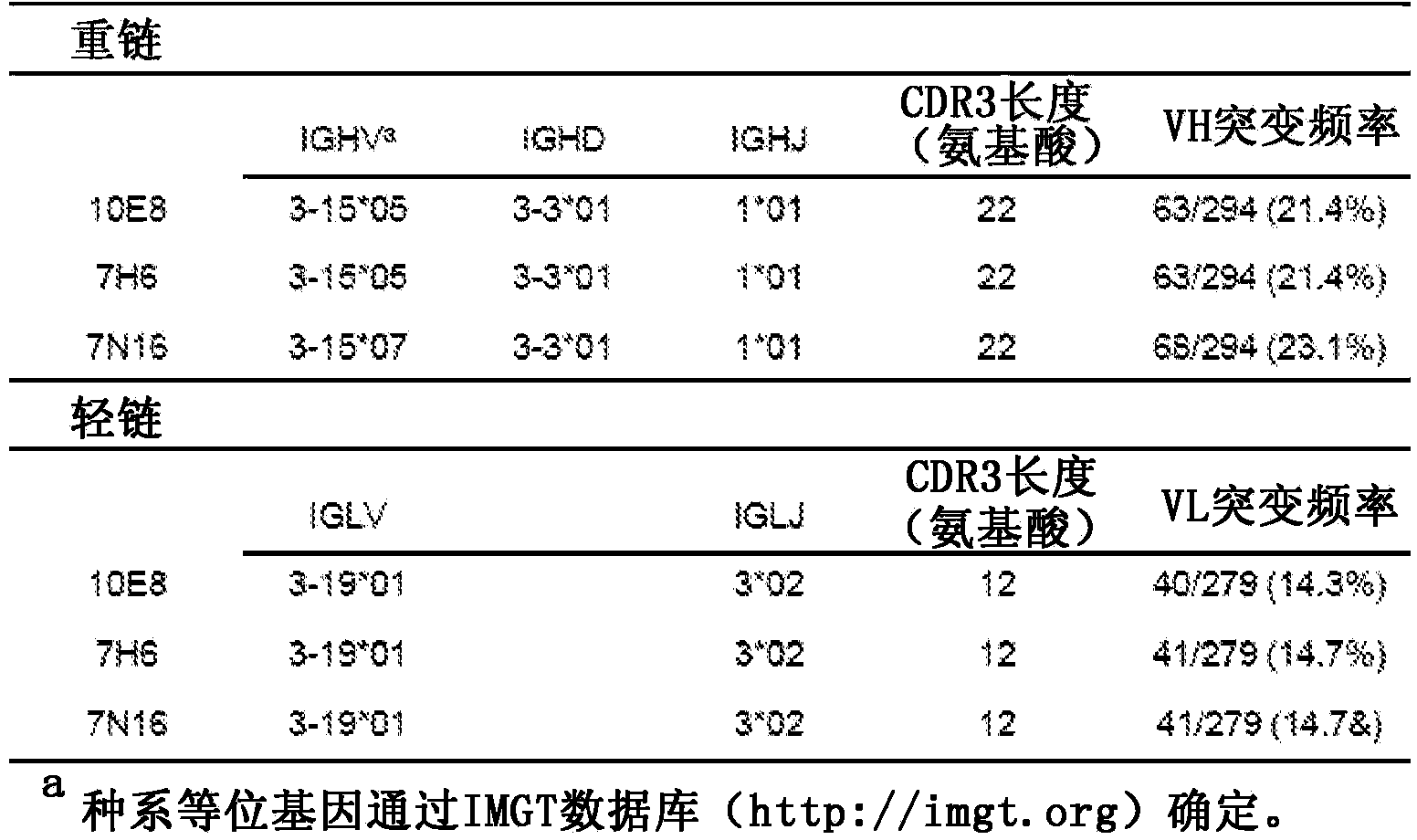
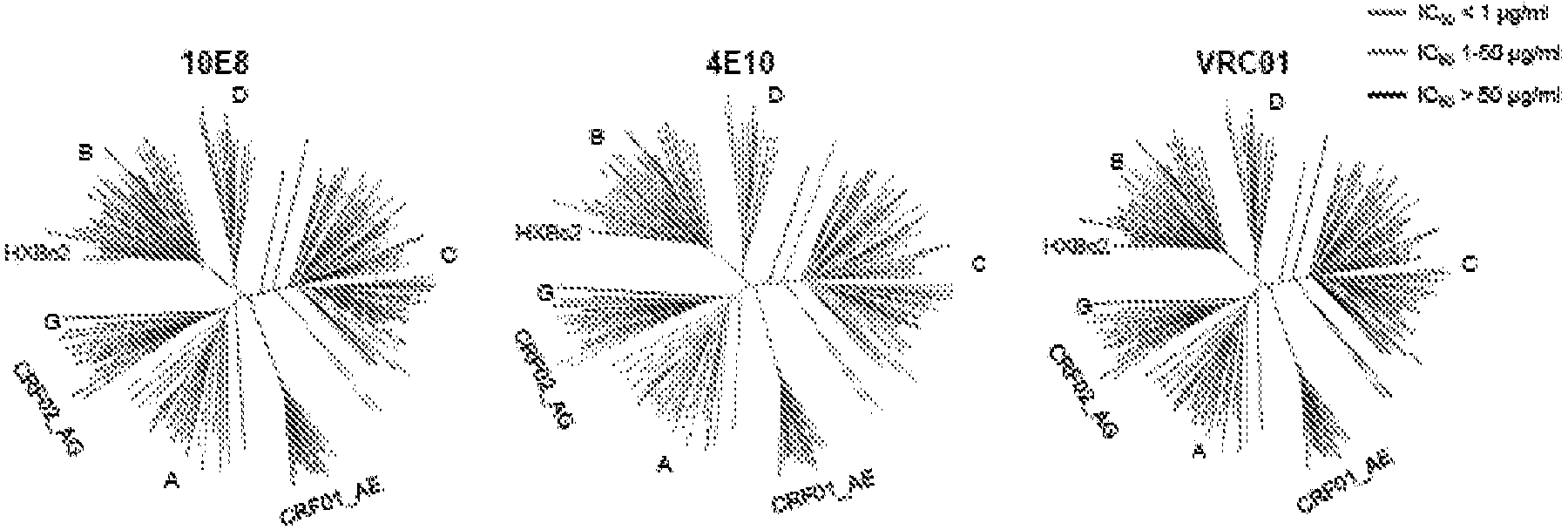
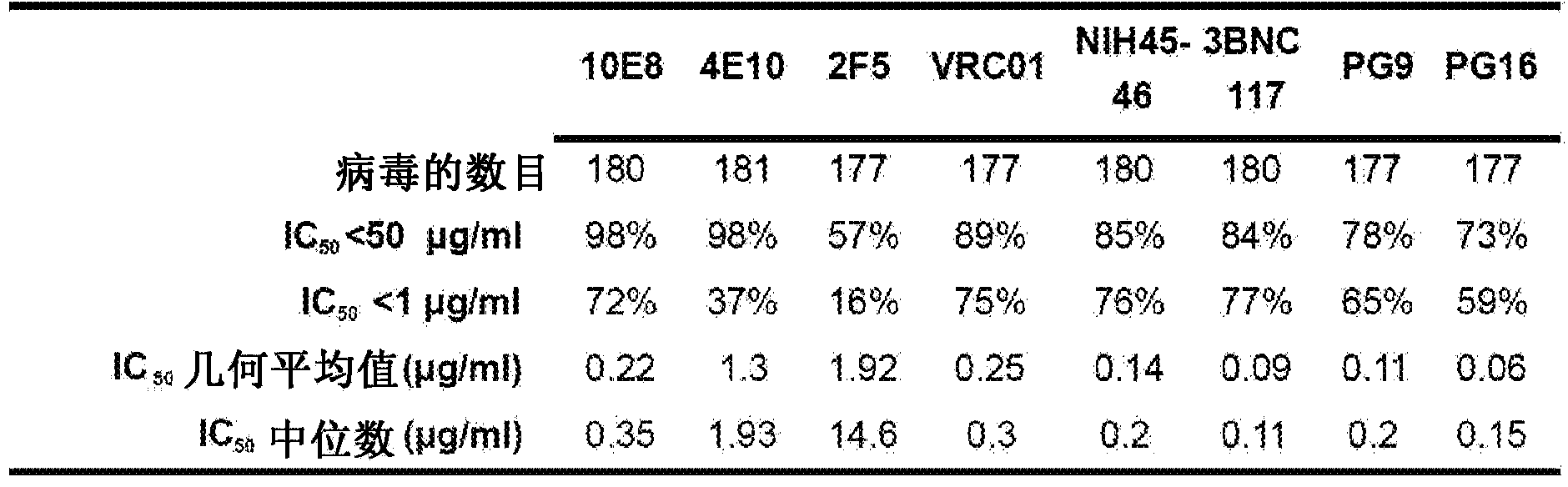
[0420] Summary. Characterization of human monoclonal antibodies has provided considerable insight into the mechanisms of broad HIV-1 neutralization. This example describes the isolation of an HIV-1 gp41 membrane proximal outer region (MPER) specific antibody designated 10E8, which neutralized -98% of the virus tested. Analysis of sera from 78 healthy HIV-1 infected donors demonstrated that 27% contained MPER-specific antibodies and 8% contained 10E8-like specificity. In contrast to other neutralizing MPER antibodies, 10E8 does not bind phospholipids, is not autoreactive, and binds to cell surface envelopes. The structure of 10E8 in complex with the intact MPER revealed a susceptibility site comprising a narrow stretch of highly conserved...
Embodiment 2
[0464] neutralization assay
[0465] This example describes the methods used to test the neutralization breadth and potency of the antibodies disclosed herein.
[0466] Neutralization of monoclonal antibodies was measured using a single round of infection of HIV-1 Env-pseudovirus and TZM-bl target cells. HIV-1 Env-pseudoviruses were generated by co-transfecting 293T cells with a pSG3ΔEnv backbone containing a luciferase reporter gene and a second plasmid expressing HIV-1 Env. At 72 hours after transfection, the pseudovirus-containing supernatant was harvested and frozen at -80°C until further use. Anti-gp41 membrane proximal outer region (MPER) specific activity of patient sera and antibodies was measured using HIV-2 / HIV-1 MPER chimeras. Wild-type HIV-27312A was used as a control. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated as the antibody / inhibitor concentration that caused a 50% reduction in infection. For competition assays, a fixed concentration of peptide w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com