A method for extracting polyphenylene sulfide from non-woven fabric
A technology of polyphenylene sulfide and non-woven fabrics, which is applied in the field of extraction, can solve problems such as the tight supply and demand of polyphenylene sulfide, and achieve the effect of alleviating the tight supply and demand and reducing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
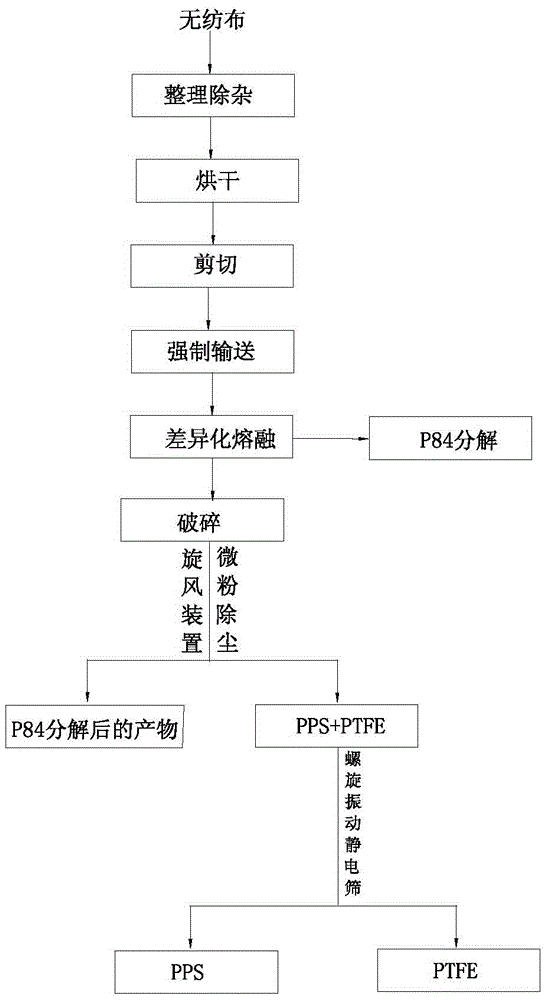
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for extracting polyphenylene sulfide from a non-woven fabric provided in this embodiment, the non-woven fabric includes polyphenylene sulfide, polytetrafluoroethylene and polyimide fibers, the method may further comprise the steps:
[0027] The first step, pre-treatment: collect and arrange the non-woven fabric, and remove the impurity particles on its surface; then put the finished non-woven fabric in an oven with a temperature of 85°C, and dry the non-woven fabric to reduce its moisture content. It is less than 1wt.%; and then the non-woven fabric is divided by a shearing device to form a square piece of cloth with a side length of 2cm to 3cm.
[0028] The second step is differential melting; the divided non-woven fabric is fed through a forced feeder and transported to an air-filled melting device. The melting device includes three temperature zones, and the temperature of the upstream temperature zone is 200°C, the temperature in...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for extracting polyphenylene sulfide from a non-woven fabric provided in this embodiment, the non-woven fabric includes polyphenylene sulfide, polytetrafluoroethylene and polyimide fibers, the method may further comprise the steps:
[0033]The first step, pre-treatment: collect and arrange the non-woven fabric, and remove the impurity particles on its surface; then put the finished non-woven fabric in an oven with a temperature of 80°C, and dry the non-woven fabric to reduce its moisture content. It is less than 1wt.%; the non-woven fabric is divided by a shearing device to form a rectangular piece of cloth with a length of 3cm-4cm and a width of 2cm-3cm.
[0034] The second step is differential melting; the divided non-woven fabric is fed through a forced feeder and transported to an air-filled melting device. The melting device includes three temperature zones, and the temperature of the upstream temperature zone is The temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for extracting polyphenylene sulfide from a non-woven fabric provided in this embodiment, the non-woven fabric includes polyphenylene sulfide, polytetrafluoroethylene and polyimide fibers, the method may further comprise the steps:
[0039] The first step, pre-treatment: collect and arrange the non-woven fabric, and remove the impurity particles on its surface; then put the finished non-woven fabric in an oven with a temperature of 90°C, and dry the non-woven fabric to reduce its moisture content. It is less than 1wt.%; and then the non-woven fabric is divided by a shearing device to form a circular cloth piece with a diameter of 2-3cm.
[0040] The second step is differential melting; the divided non-woven fabric is fed through a forced feeder and transported to an air-filled melting device. The melting device includes two temperature zones, and the temperature of the upstream temperature zone is The temperature in the downstream te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com