An Elmd Algorithm for Optimal Noise Parameter Selection for Bearing Fault Diagnosis
A technology for fault diagnosis and noise parameters, applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the optimal noise coefficient selection, etc., to suppress the modal aliasing phenomenon and accurately process the analysis. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
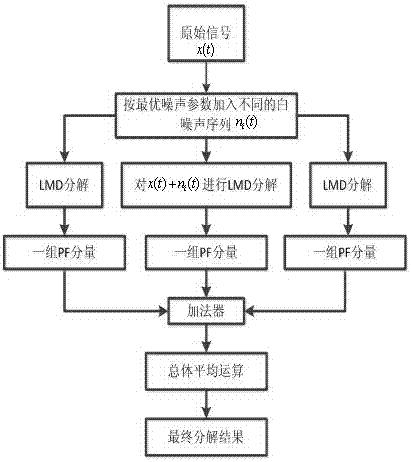
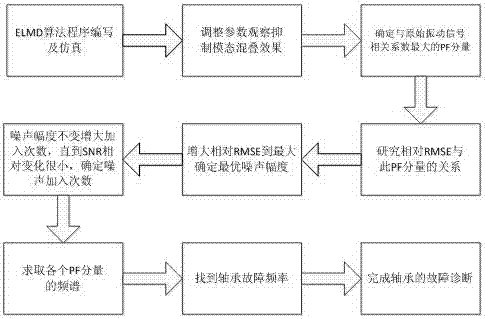
[0029] see figure 1 , figure 2 .
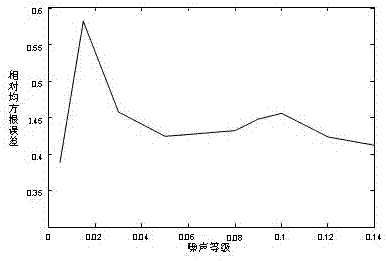
[0030] There are two important parameters to consider in the ELMD algorithm: the magnitude of the white noise and the number of times white noise is added . The relative root mean square error criterion (Relative-RSME) is used to judge the decomposition performance of ELMD under different noise amplitudes; the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is used to measure the residual noise in the decomposition results after adding different noise times.
[0031] The relative root mean square error is defined as follows:
[0032] (1)
[0033] (2)
[0034] in, is the original vibration signal; for the original vibration signal the PF component with the highest correlation; is the number of sampling points of the original vibration signal.
[0035] When the relative root mean square error criterion (Relative-RSME) is very small, close to zero, it means infinitely close to ,Right now contains the same components as the original sig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com