An Equivalence Method of Power Grid Based on Phase Angle Difference of Tie Lines
A power grid equivalent and tie line technology, applied in the field of value, can solve the problem that the network equivalent simplification cannot be used, and achieve the effects of convenient related analysis and calculation, reduction of power grid scale, and good equivalent accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
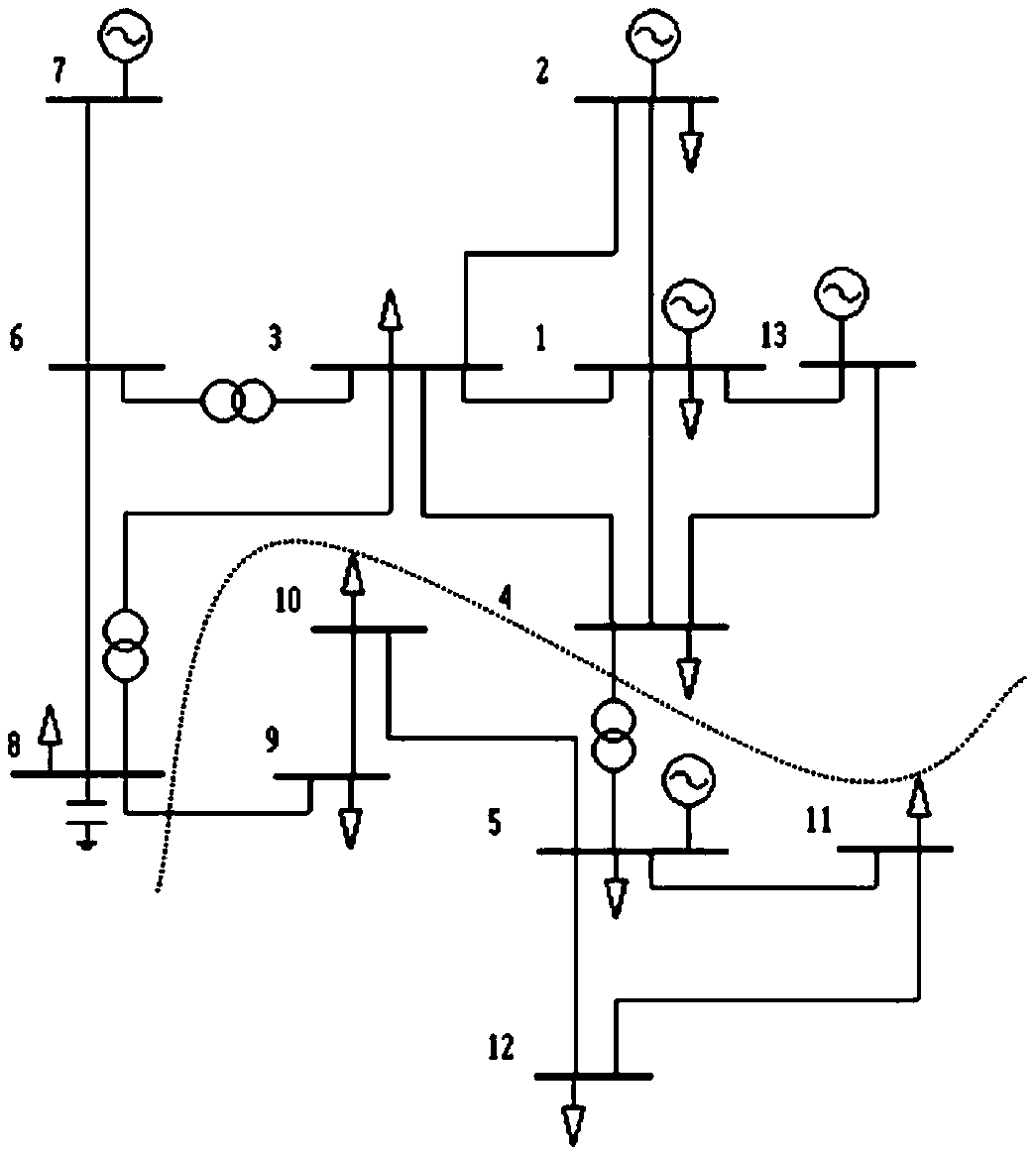
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the grid equivalent method based on the tie line phase angle difference, the method includes the following steps:
[0037] a) Divide the test grid into two sub-grids. Subgrid A is composed of nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 13, of which 4 and 8 are boundary nodes; subnet B is composed of nodes 5, 9, 10, 11, and 12, of which 5 and 9 is a boundary node; branch 4-5 and branch 8-9 are connection lines between subsystems;
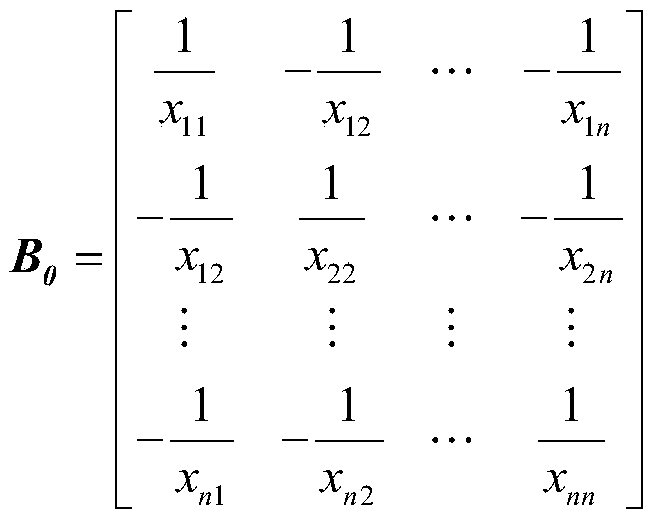
[0038] b) Assuming that the voltage amplitude of all nodes in the power grid is 1, the voltage phase angle θ of each node is obtained by using the DC power flow method i (i=1,2,...13);
[0039] c) According to the obtained DC power flow solution, calculate the line power on branch 4-5 and the line power on branch 8-9 Will As the equivalent injection power, connect to node 4 and node 8 respectively.
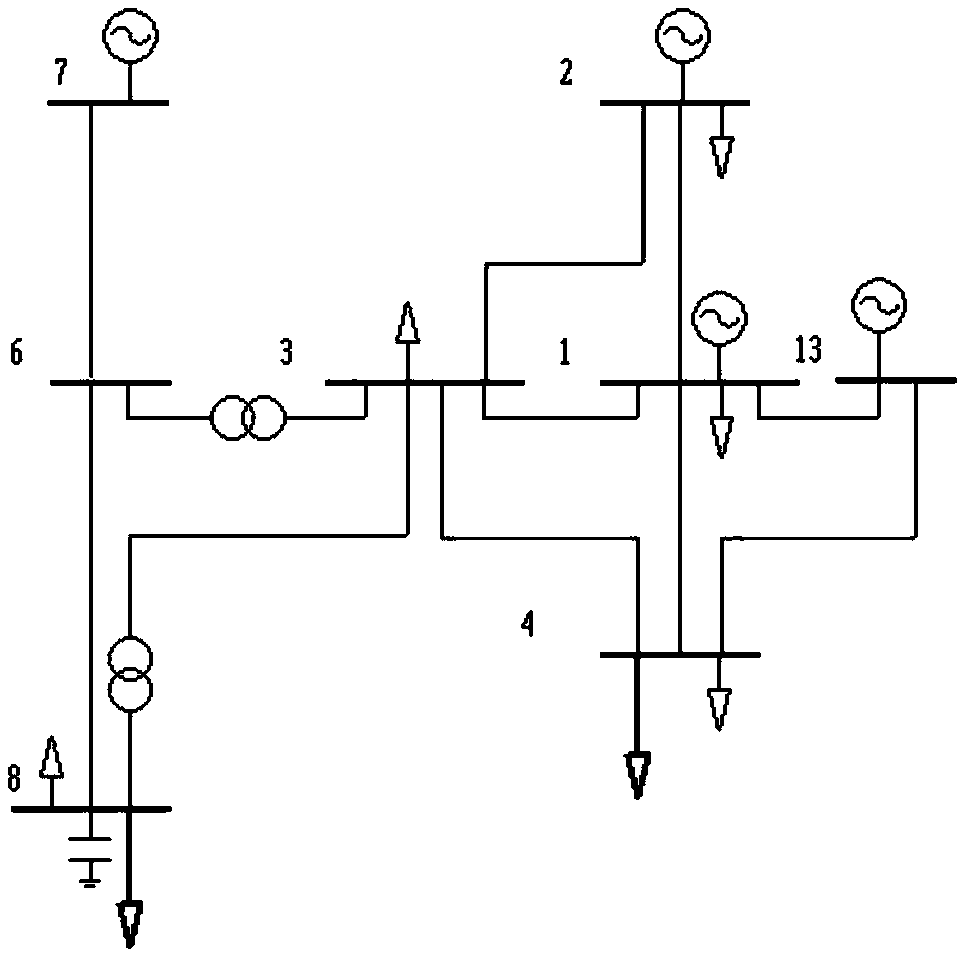
[0040] d) Obtain the grid equivalent network including only the equivalent injected power of sub-grid A and sub-grid B, suc...
Embodiment 2
[0047] On the basis of Example 1, the system load level is gradually increased from 1.0 times to 3.0 times, the power flow calculation is performed on the power grid after the equivalent value, and the approximate power flow result at this time is compared with the accurate power flow result before the equivalent value, and the table is obtained 2.
[0048] It can be seen from the results in the table that with the increase of the load level, the voltage amplitude and phase angle errors of all nodes are within 4%, which shows that the proposed equivalent model and method have good equivalence under different load levels. value precision.
[0049] Table 2 Comparison of power flow results of each node in sub-grid A under different load levels
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] The above calculation and analysis results show that the proposed equivalence model and calculation method can approximate the local power grid when the exact power flow solution of the power grid is unknow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com