Vacuum smelting quick-setting equipment, permanent magnet quick-setting alloy and manufacturing method of permanent magnet
A technology of vacuum smelting and manufacturing methods, which is applied in vacuum smelting quick-setting equipment, the manufacture of rare earth permanent magnet quick-setting alloys, and the manufacture of permanent magnets. It can achieve the effects of saving heavy rare earth resources, fine grain boundary phase, and low product cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
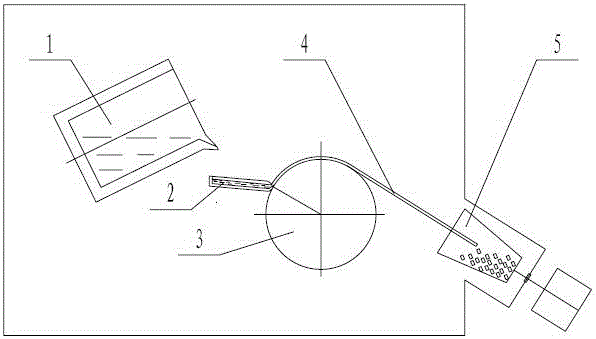
[0042] use Figure 4 A manufacturing method of NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet quick-setting alloy for equipment. First, 600Kg of NdFeB raw material is added to the melting crucible. The heating temperature of the melting crucible is 1430 ° C. After refining, it is cast into the tundish and passes through the gap of the tundish. , the alloy liquid is cast to the first rotating roller smoothly, the first rotating roller rotates at a speed of 1.2m / s, the diameter of the first rotating roller is 610mm, the alloy sheet rotates with the rotating roller, and the rotation angle of the alloy sheet on the first rotating roller is 140° , then falls on the second rotating roller, the free surface contacts with the second rotating roller to form an alloy sheet, the second rotating roller speed is 1.6m / s, the second rotating roller diameter is 610mm, the rotation of the alloy sheet on the second rotating roller The angle is 58°, the temperature at which the alloy flakes leave the second ...
Embodiment 2
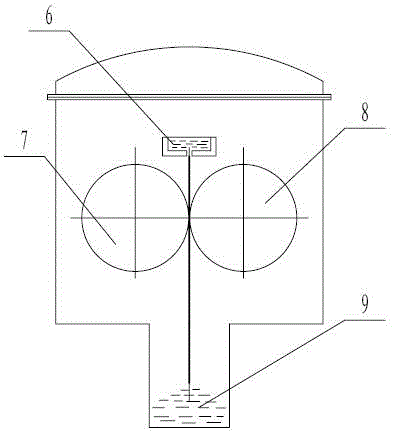
[0046] a use Figure 5The double-alloy rare earth permanent magnet quick-setting alloy method of the double-door vacuum quick-setting equipment shown, firstly, the NdFeB quick-setting alloy raw material containing Pr and Nd is loaded into the crucible of the first side-opening induction heater, Close the side-opening furnace door, start heating after vacuuming, heat up to 800°C, and then fill in argon to continue heating to melt the NdFeB raw material into an alloy and refine it. The refining temperature is 1440°C. After refining, pass the molten alloy liquid through The tundish is cast onto the first rotating roll with water cooling to form alloy flakes, and then the alloy flakes fall onto the second rotating roll to continue cooling to form alloy flakes. The temperature at which the alloy flakes leave the first rotating roll is in the range of 820°C. The rotating speed of the first rotating roller is 1m / s, the diameter of the first rotating roller is 810mm, and the rotation ...
Embodiment 3
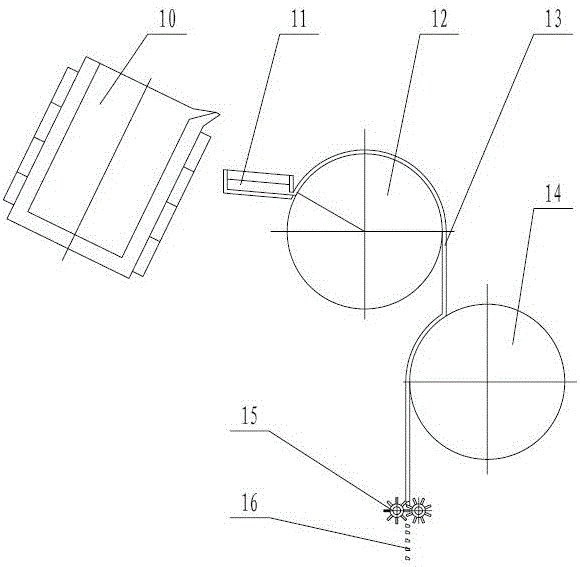
[0050] First, the raw materials containing the ingredients in Table 3 are batched separately according to the serial number. The raw materials sold in the market are praseodymium neodymium alloy, metal lanthanum, metal cerium, metal neodymium, metal terbium, gadolinium iron, holmium iron, dysprosium iron, pure iron, boron iron, niobium Iron, metal gallium, metal zirconium, metal cobalt, metal aluminum, metal copper are selected, and the pure iron, boron iron, metal cobalt, and metal copper in the NdFeB raw material are heated to a temperature range of 300-1500 ° C under vacuum conditions. Control the vacuum degree 5×10 3 Pa to 5×10 -2 Pa range, after 10-240 minutes, fill with argon and add the remaining NdFeB raw material, then heat until the raw material melts into a molten alloy, and cast into a double-sided cooling quick-setting alloy sheet through a tundish in a molten state; Put the alloy flakes into the hydrogen crushing furnace, feed hydrogen gas to let the alloy flak...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com