Antibodies useful in passive influenza immunization
A technology of antibodies and monoclonal antibodies, applied in the direction of antibodies, immunoglobulins, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of low antibody efficacy, inferior efficacy, and high antibody
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
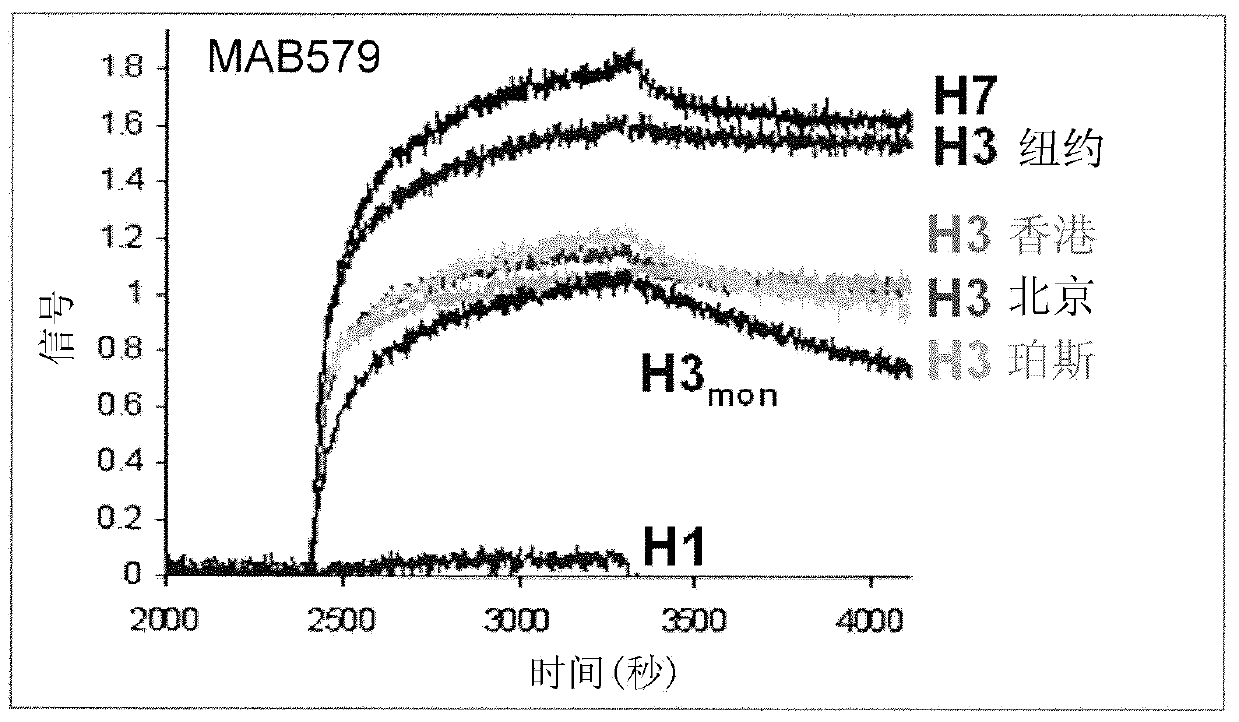
[0170] Affinity of MAB53 and MAB579
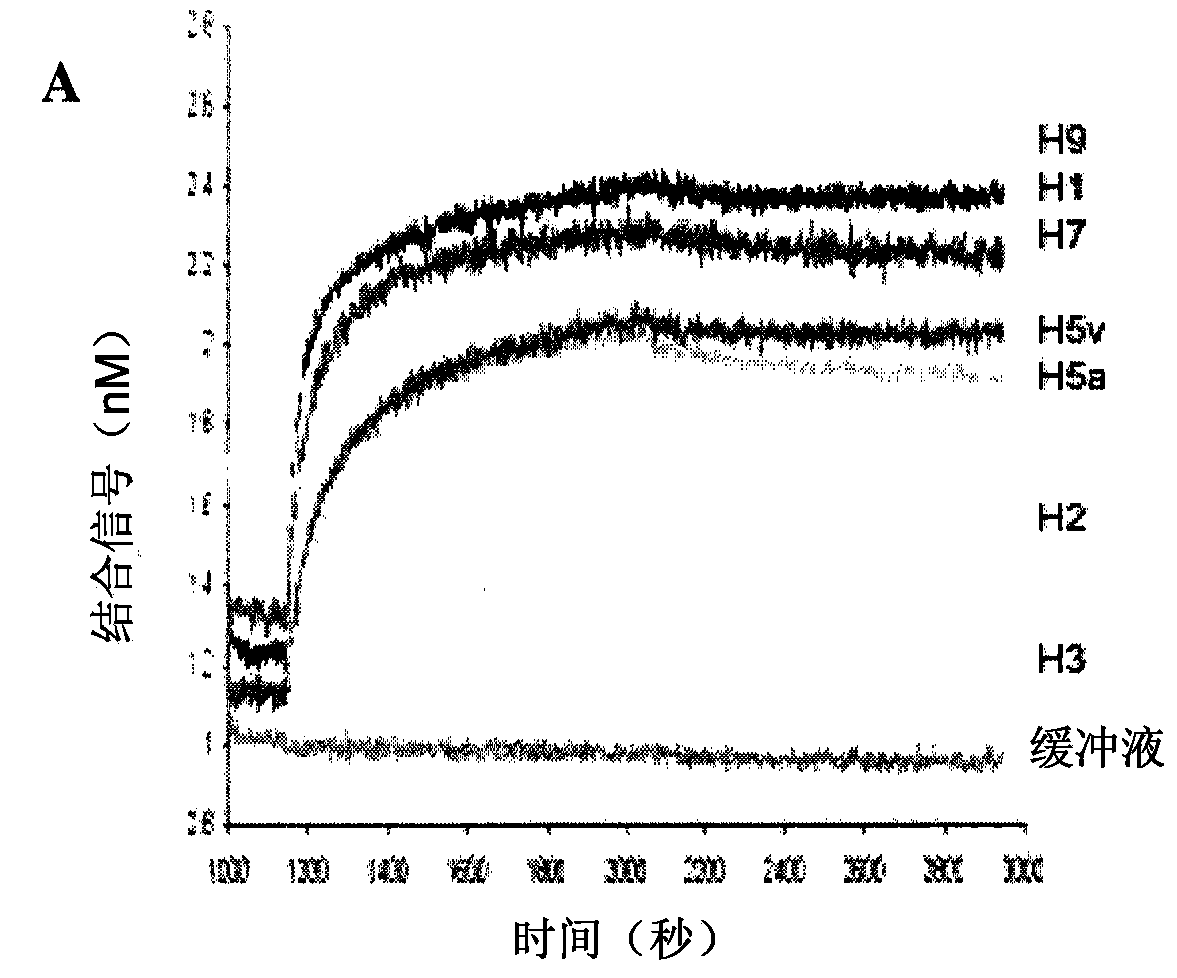
[0171] The affinity for MAB53 is reported in the PCT publication cited above. This antibody bound strongly to HA from clades H5, H7, H1 and H9, and with less affinity to H2 and H3. MAB579 binds HA with high affinity for H7 and H3. Figure 3A and 3B Shown using standard Ford bio TM Typical results were analyzed for each antibody.
example 2
[0173] Infection neutralized by MAB486 and MAB579
[0174] MAB486 and 579 were tested for inhibition of H1N1 and H3N2 (A / Perth / 16 / 2009) infection and plaque formation during the initial infection phase in the presence or absence of trypsin in MDCK cell monolayers. MAB486 and pAb xCP (rabbit polyclonal antibodies raised against the cleavage site consensus sequence) neutralize H1N1 only in the absence of trypsin (A / California / 04 / 2009), as Figure 4A As shown in , and if the virus is first activated with trypsin, infection and plaque formation cannot be inhibited. This demonstrates that antibodies against fusion regions with epitopes dependent on the intact fusion peptide (ie, protease susceptible) are not effective in controlling viral infection. Such as Figure 4B It was shown that MAB579 inhibits infection both in the presence and absence of trypsin.
[0175] The ability of MAB53 to neutralize infection has been previously reported, but the affinity and EC for neutralizat...
example 3
[0179] Example 3 Determination of epitopes
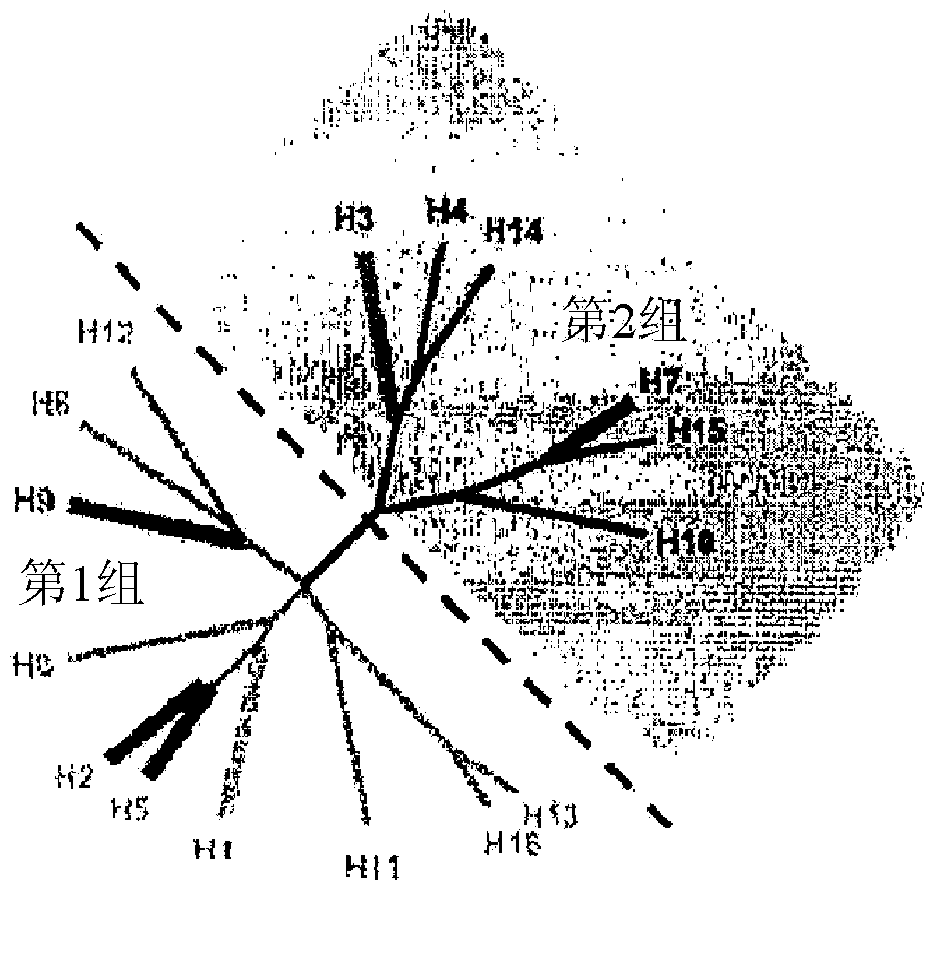
[0180] Using Pepscan CLIPS TM techniques to map the binding sites of MAB53 and MAB579. About 6,000 unique peptides were synthesized for H1 and H3 with different lengths and with linkers of different lengths to constrain the ends of each peptide in order to mimic the native structure. Binding of MAB53 and MAB579 to the stem region was confirmed by using rabbit serum as a competitor to the globular head or stem and by binding directly to peptides from the stem region. As noted above, MAB486 binds both Group 1 and Group 2, but only in HA 0 Protease cleavage to disulfide-linked HA 1 and HA 2 Binding in the previously preactivated state. It was deduced that the epitope used for cross-clade binding was spanning native trimeric HA 0 Discontinuous epitopes of two monomers of .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com