A coding format and coding method of time-frequency synchronization state information based on irig‑b
A technology of time-frequency synchronization and coding method, which is applied in the directions of synchronization devices, multiplexing communication, time-division multiplexing systems, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to transmit time synchronization status information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings:
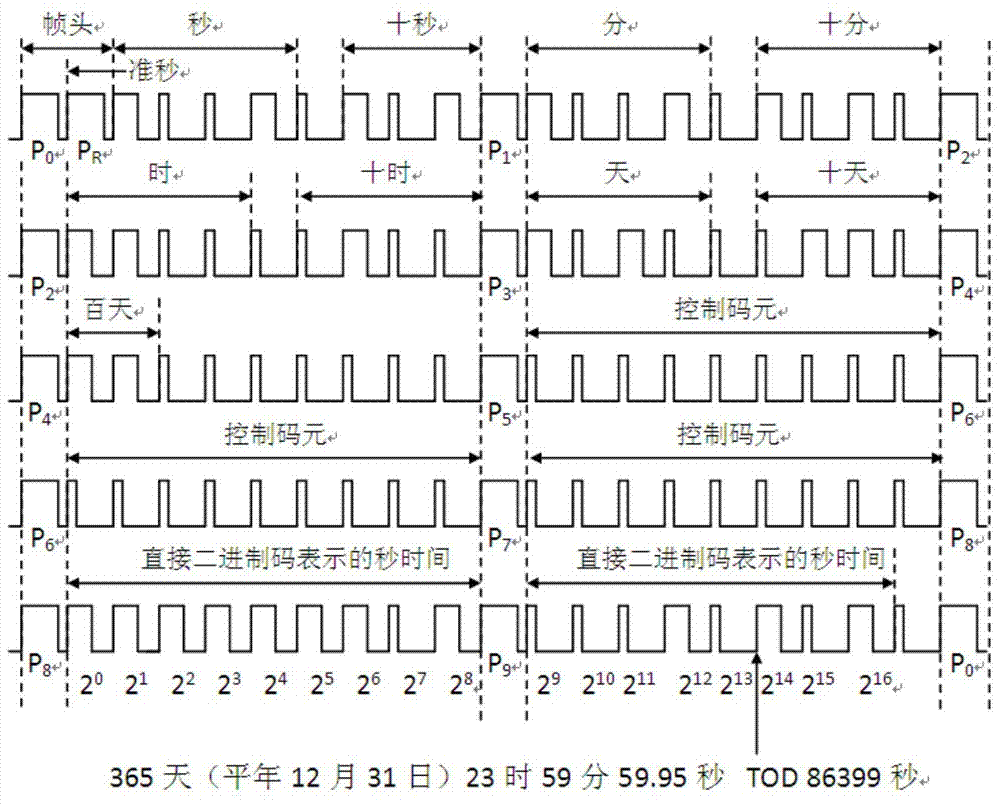
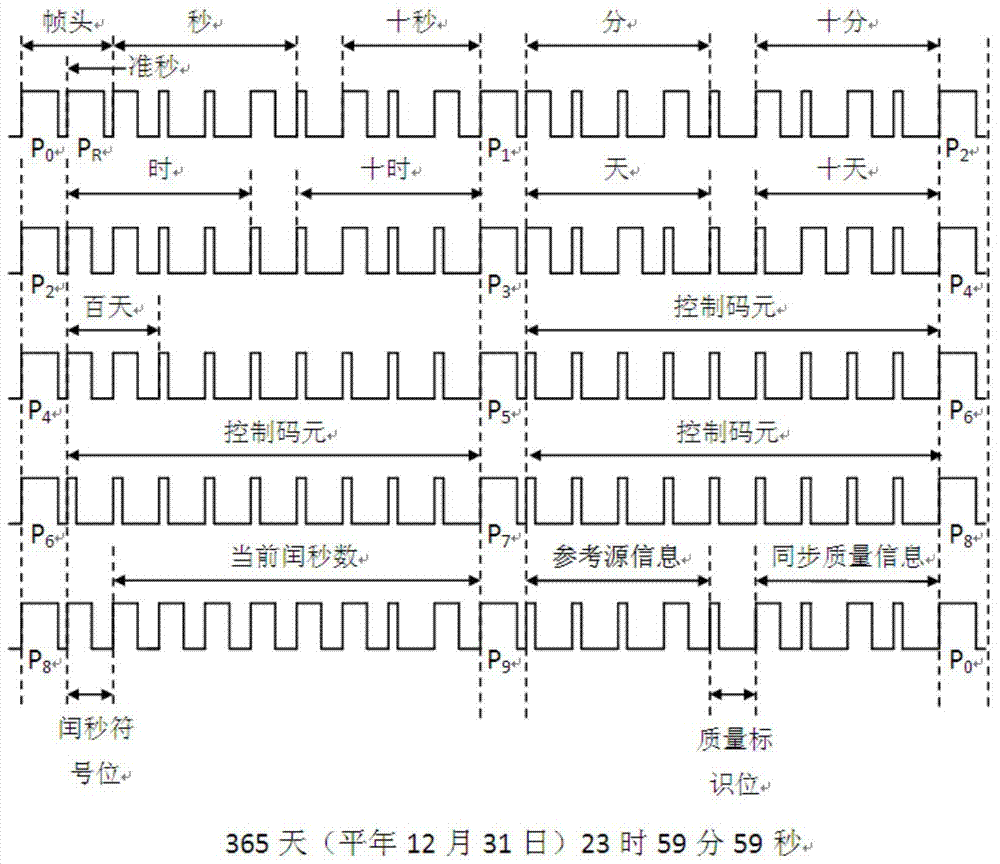
[0022] See figure 1 , The present invention re-encodes P80-P88 and P90-P98 in the IRIG-B code in the IEEESTD1344-1995 standard based on the IRIG-B time-frequency synchronization status information encoding format. The specific symbol definitions are as follows:
[0023] P80-P88: Represents the number of seconds in a day, expressed in binary, a total of 17 digits, the lower 9 digits;
[0024] P90-P97: Represents the number of seconds in a day, expressed in binary, a total of 17 digits, the upper 8 digits;
[0025] P80: Leap second sign bit, ‘1’ means positive leap second; ‘0’ means negative leap second; the range of leap second is 0~255.
[0026] P81-P88: The number of leap seconds between the current international atomic time and UTC time, expressed in binary, with P81 being the lowest bit and P88 being the highest bit;
[0027] P90-P93: Current time-frequency synchronization device...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com