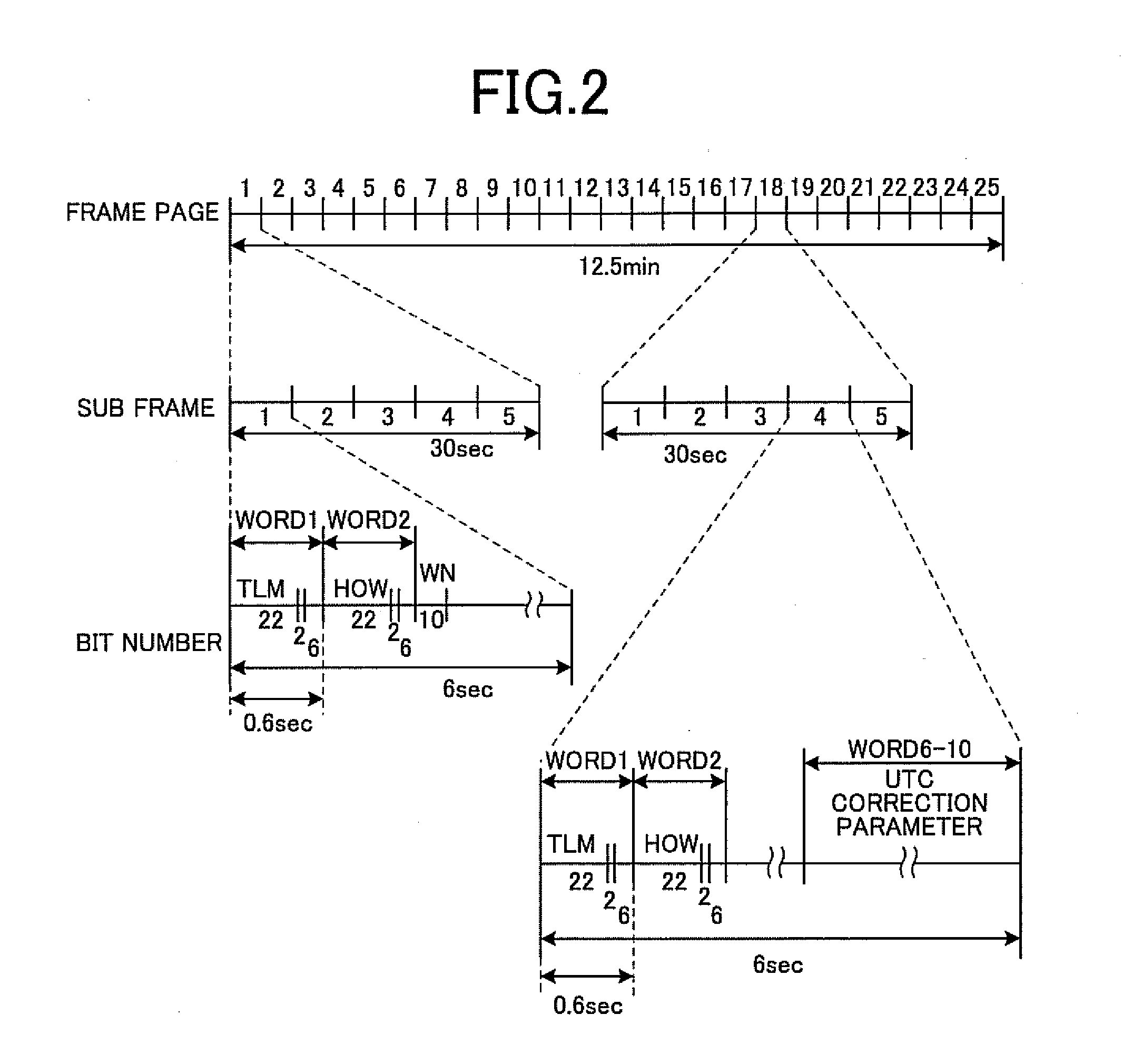
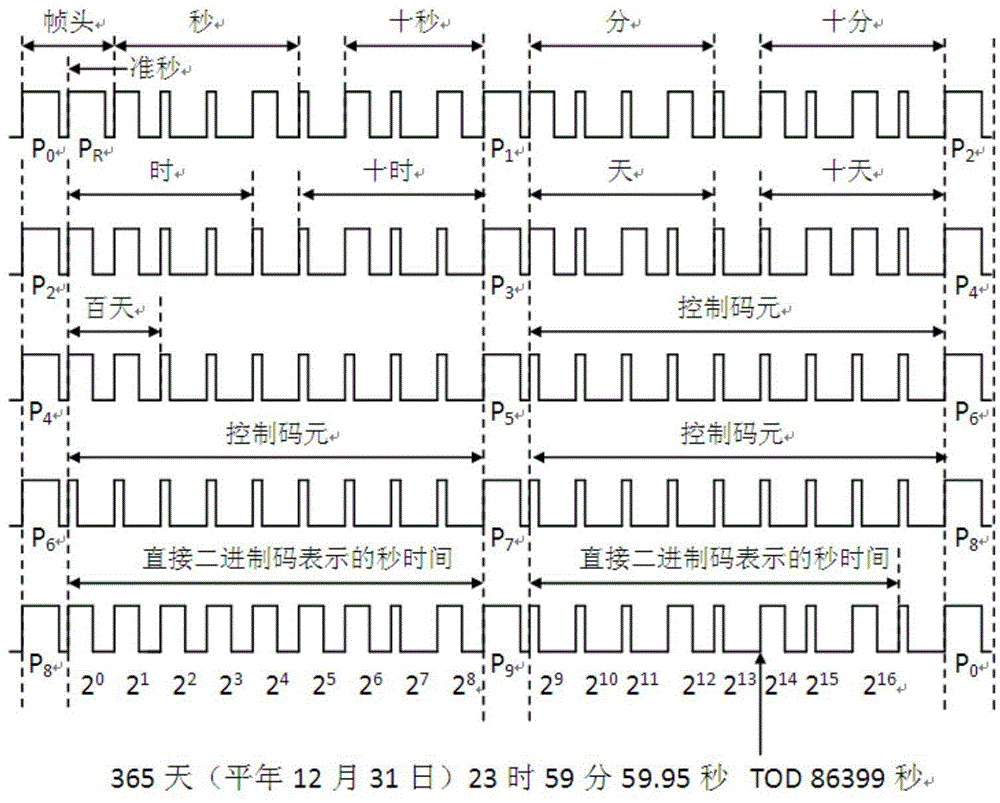
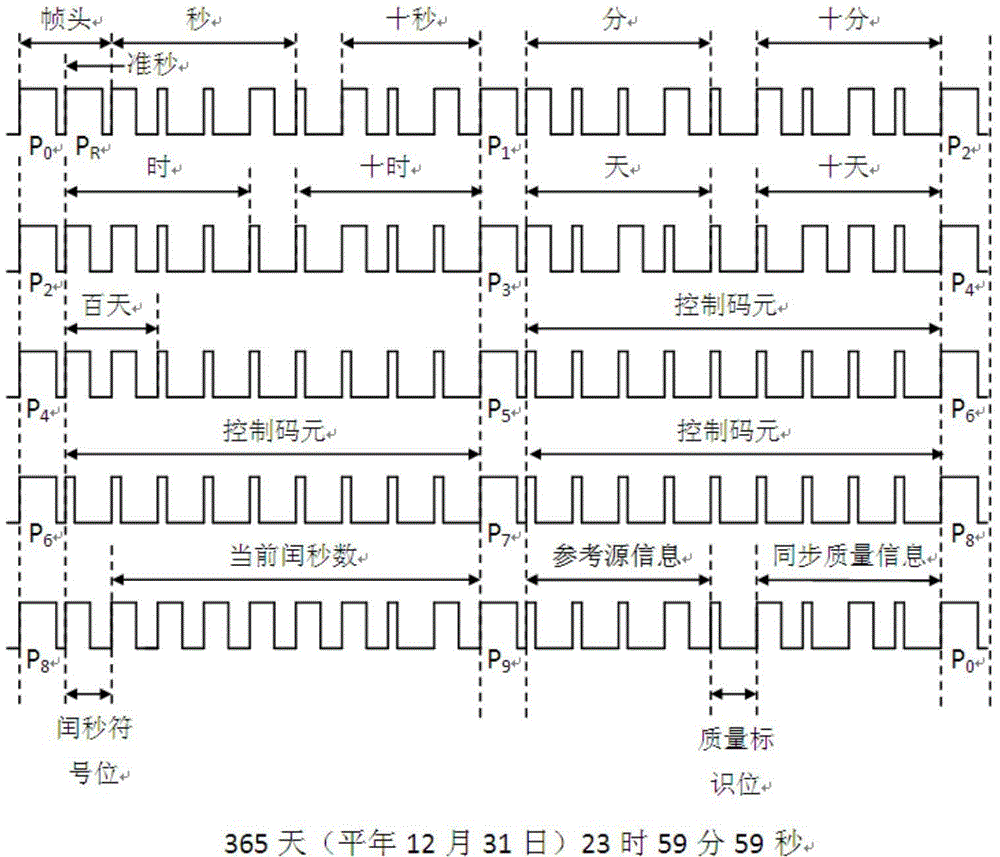
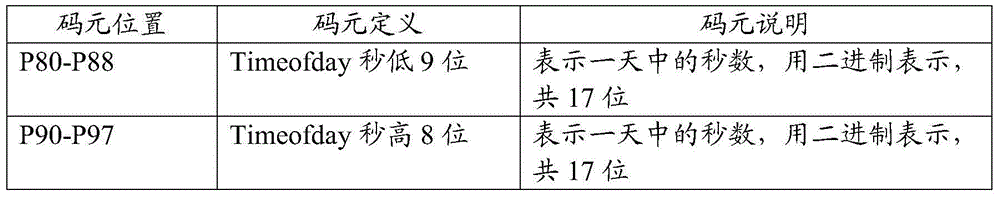
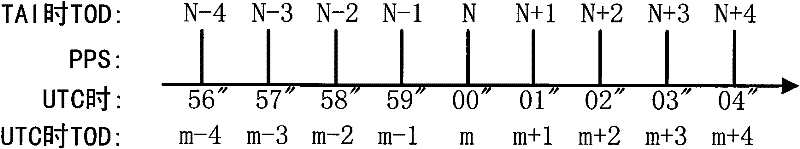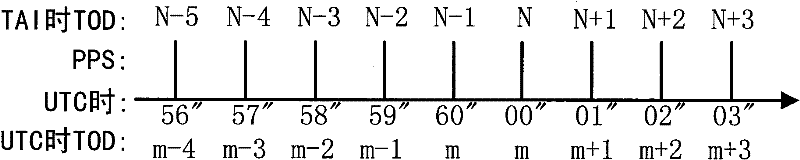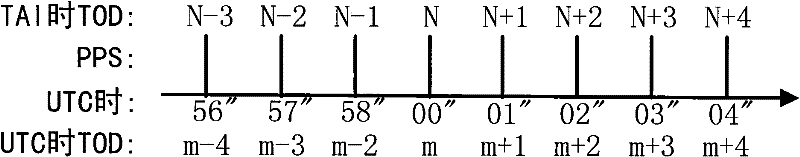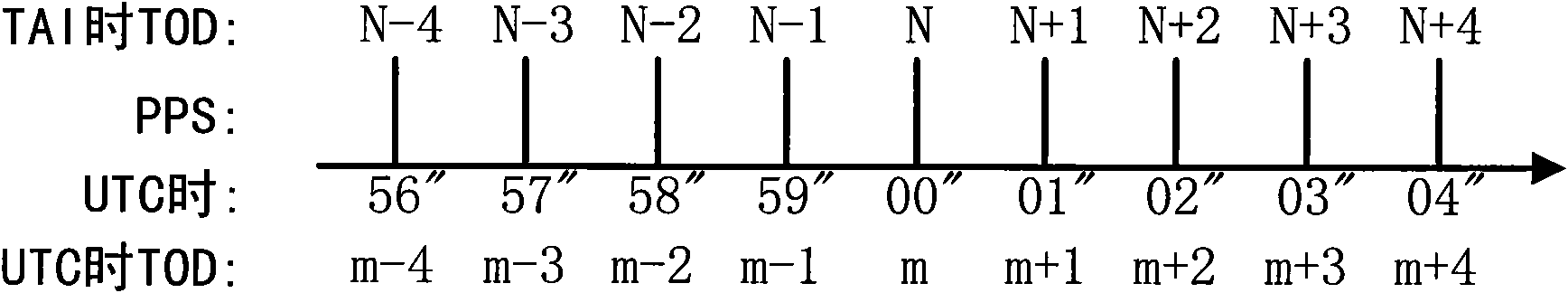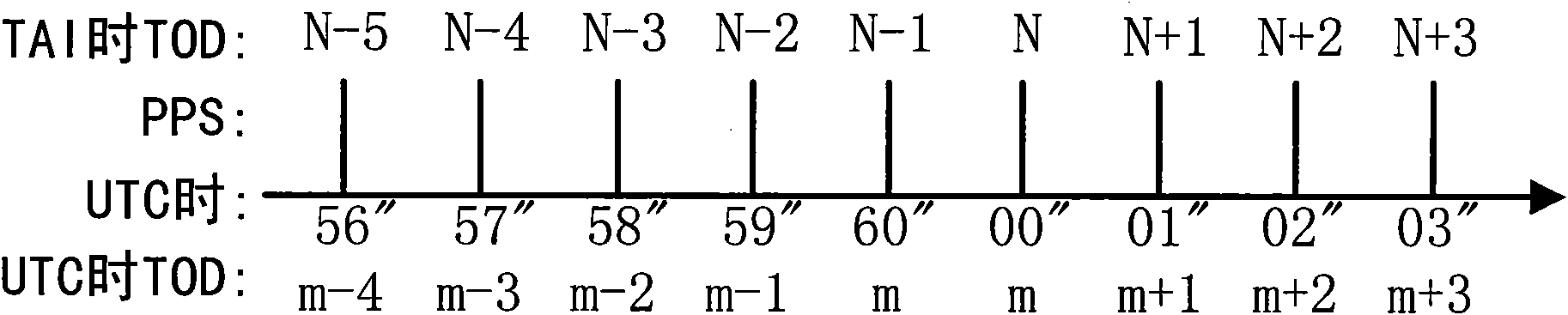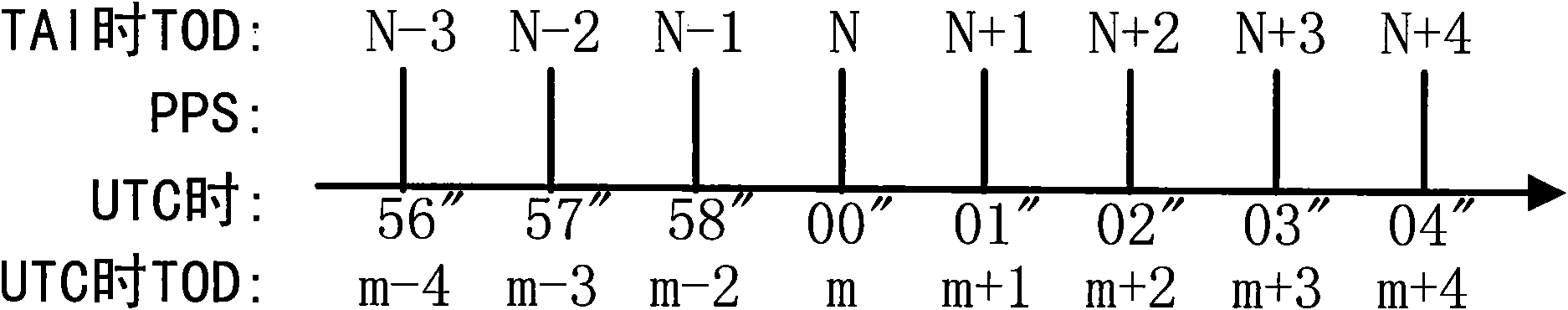Patents
Literature
44 results about "Leap second" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
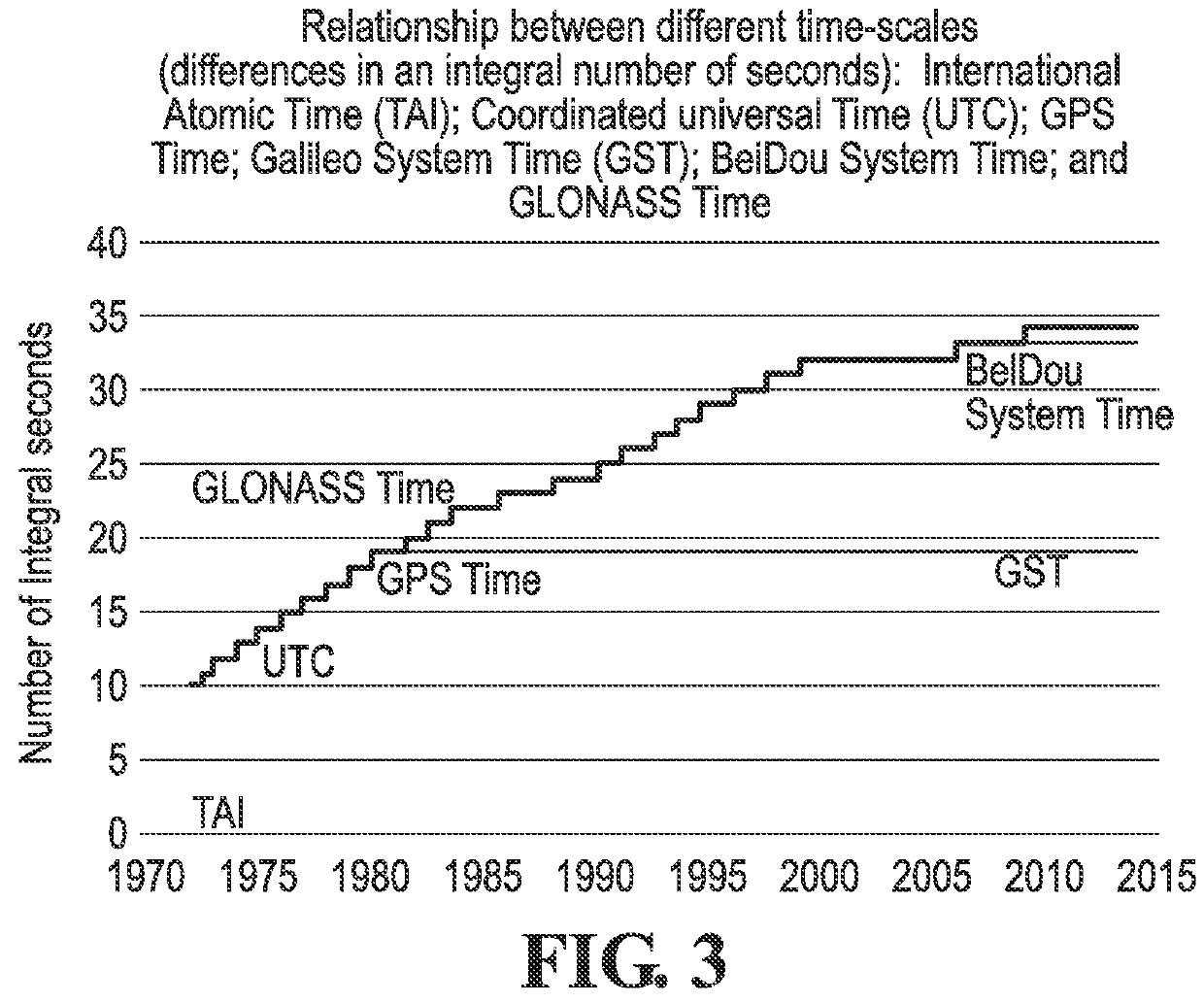
A leap second is a one-second adjustment that is occasionally applied to civil time to keep Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) close to the mean solar time at 0 Meridian, Greenwich, to accommodate irregularities and long-term slowdown in the Earth's rotation. UTC was introduced on January 1, 1972, initially with a 10-second lag behind International Atomic Time (TAI). Since that date, 27 leap seconds have been inserted, the most recent on December 31, 2016 at 23:59:60 UTC. In 2019, UTC lags behind TAI by 37 seconds.
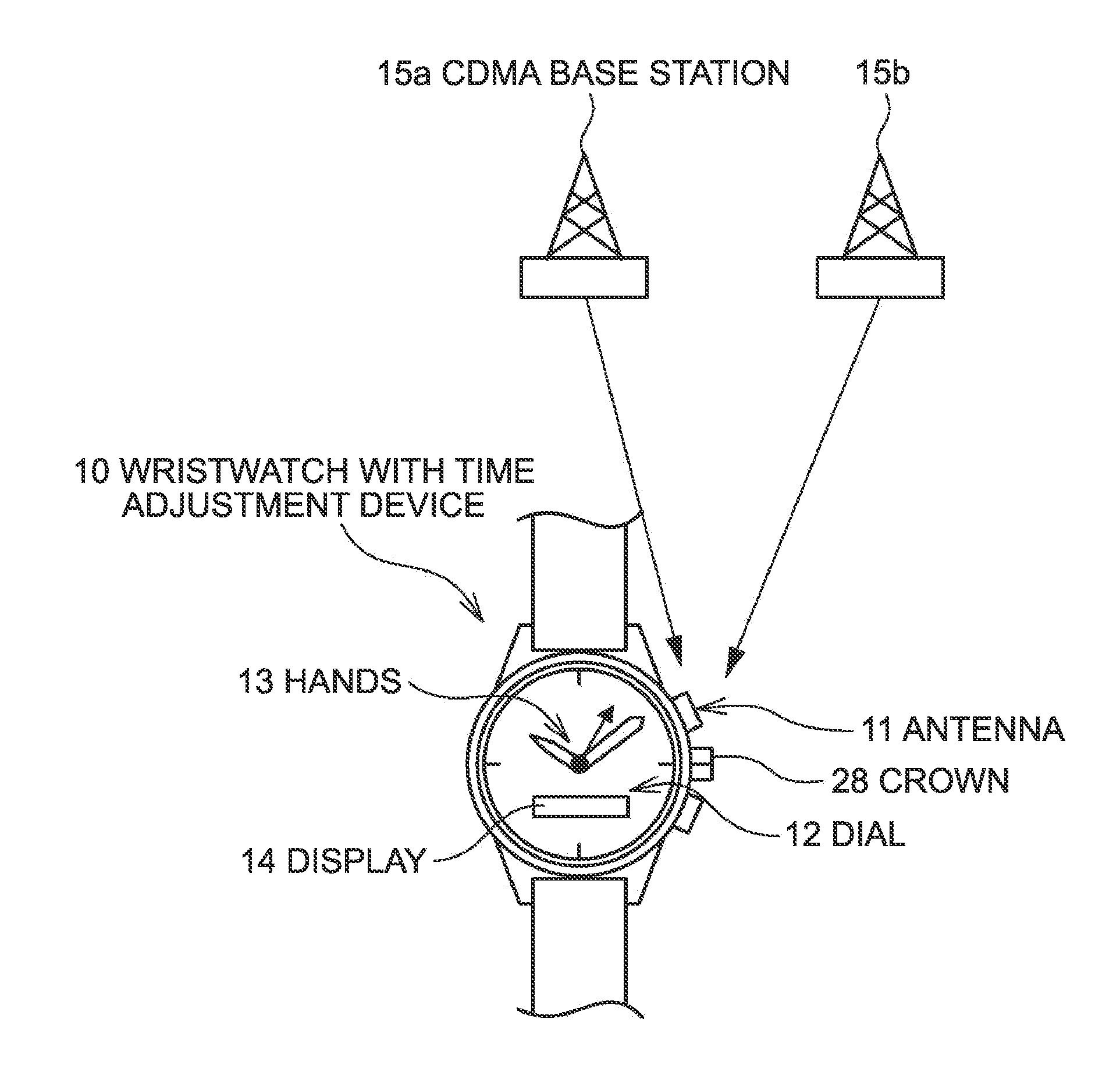
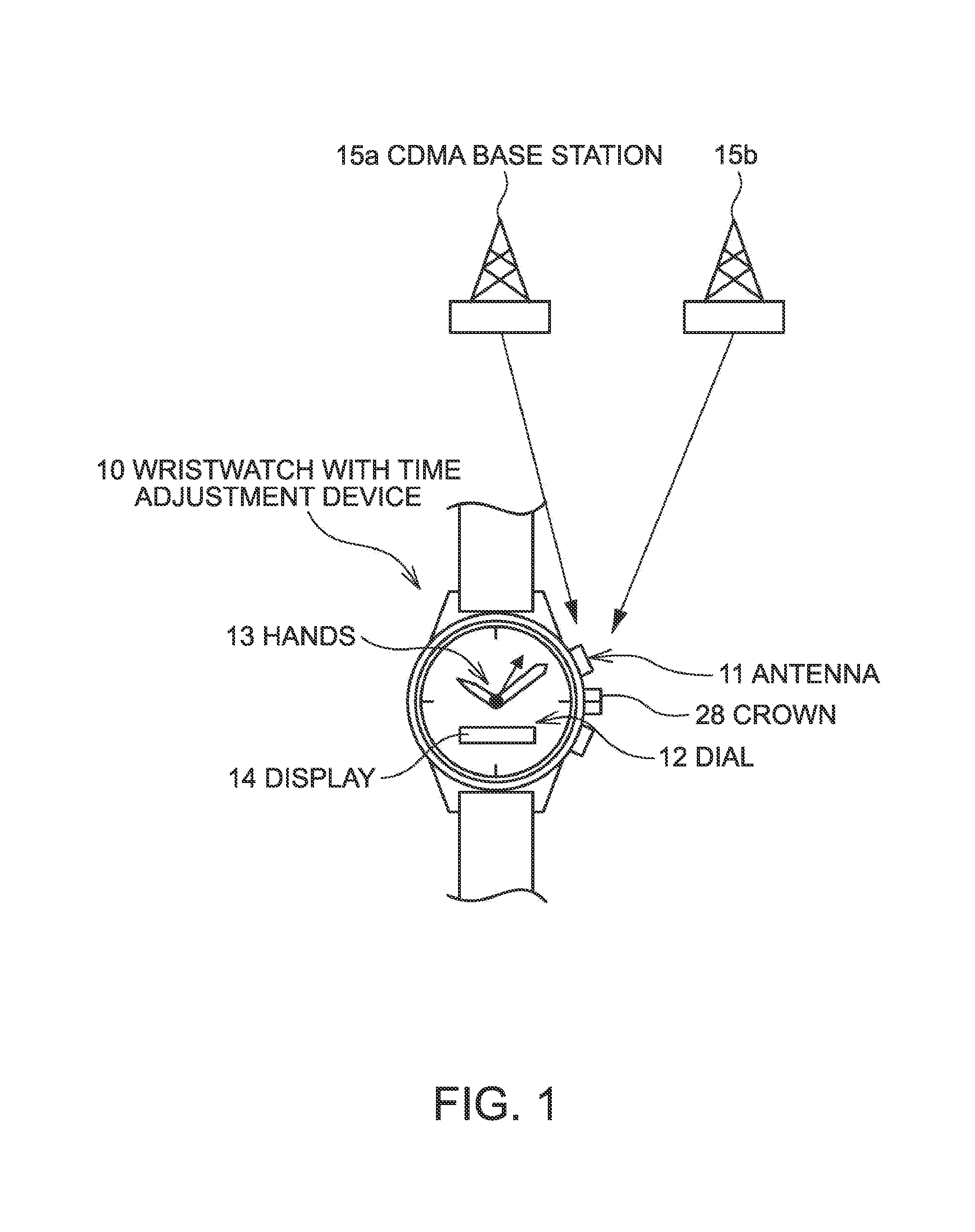
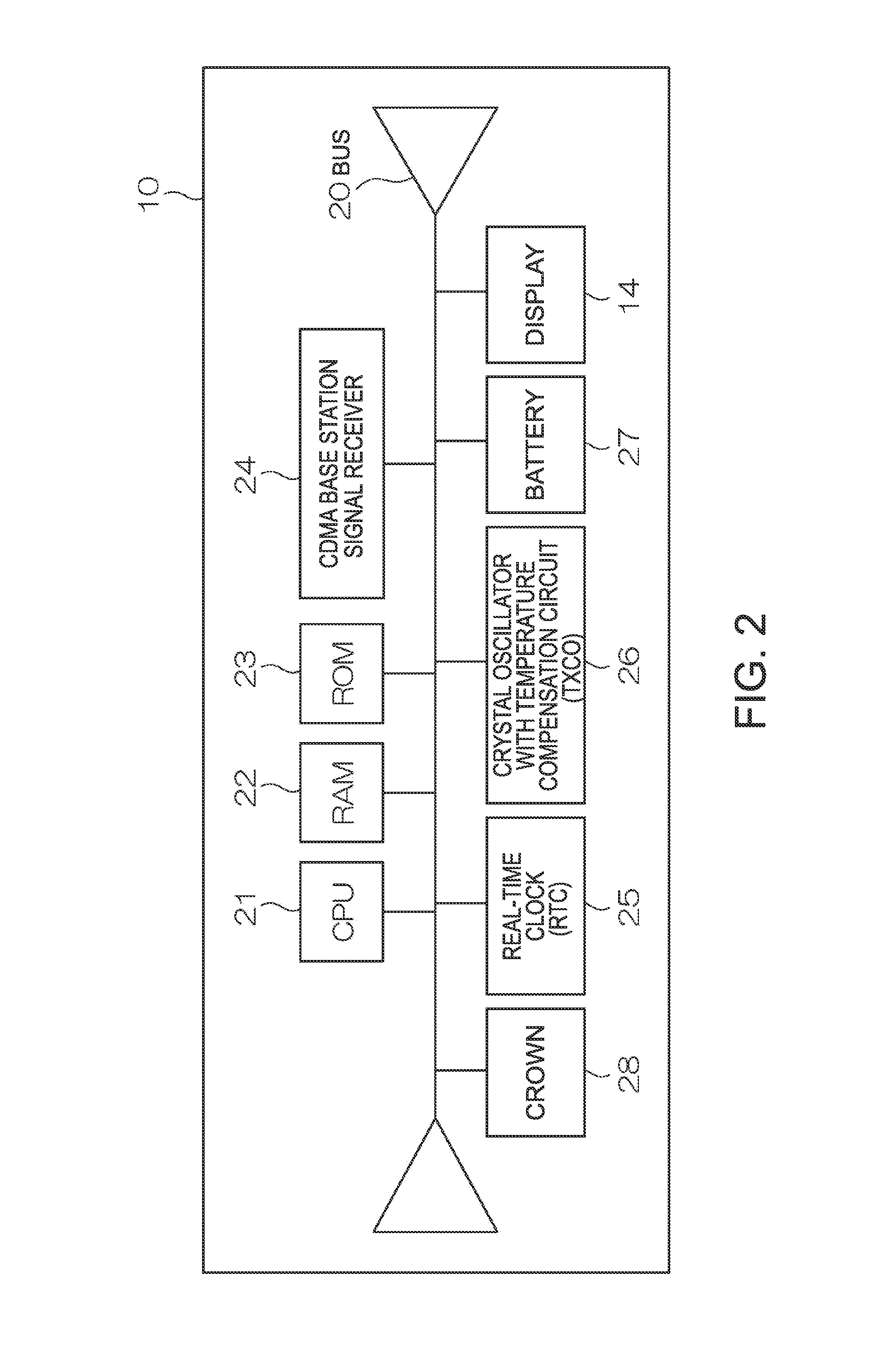
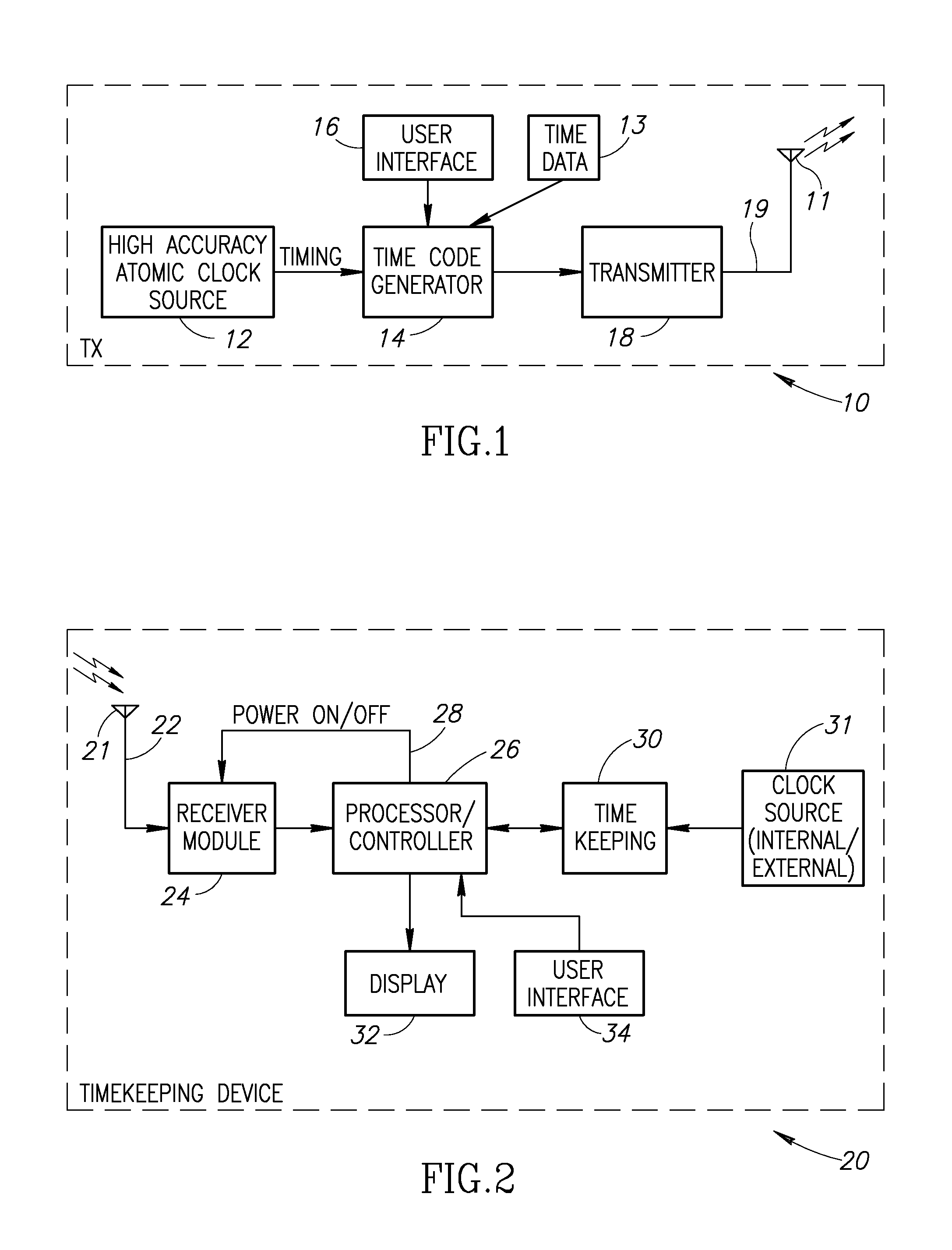
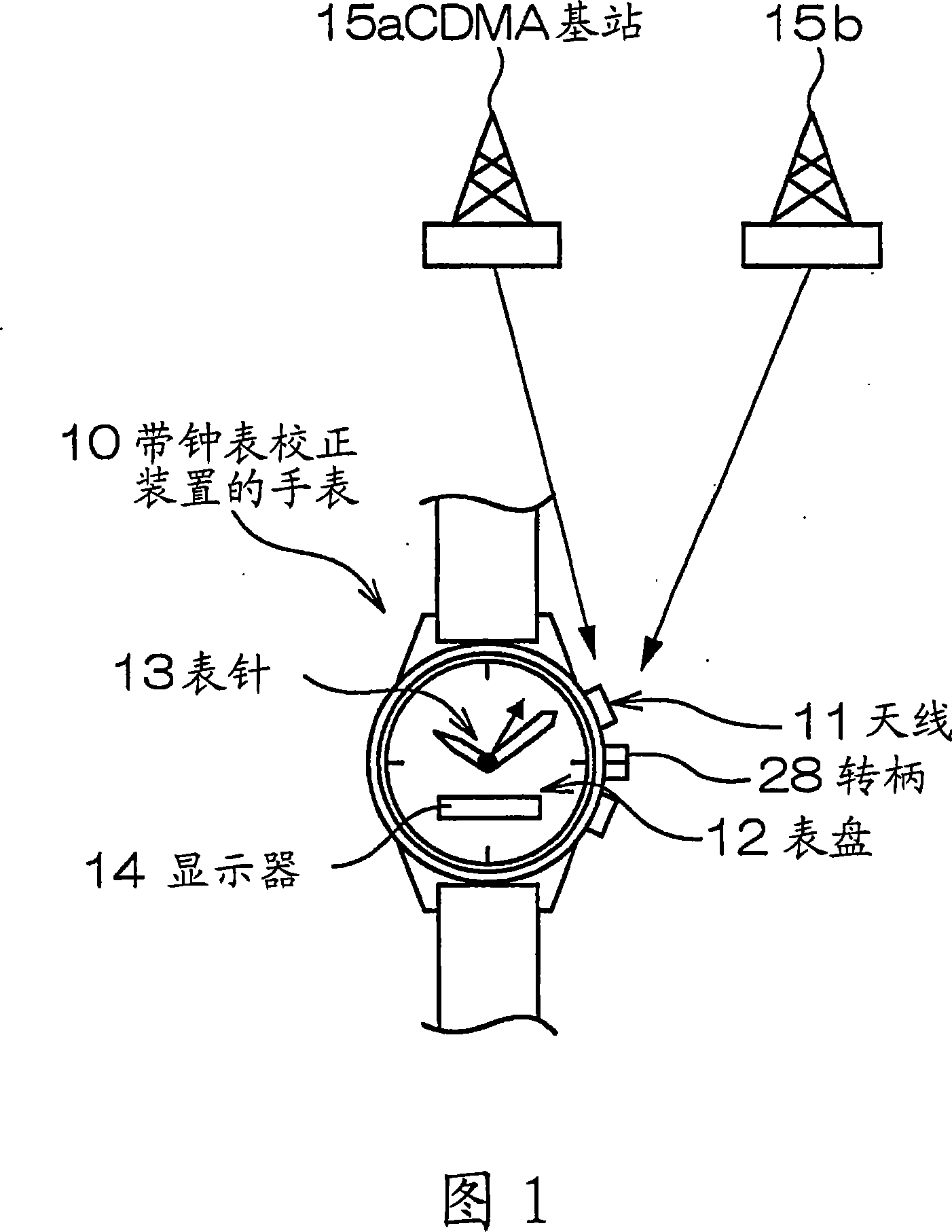
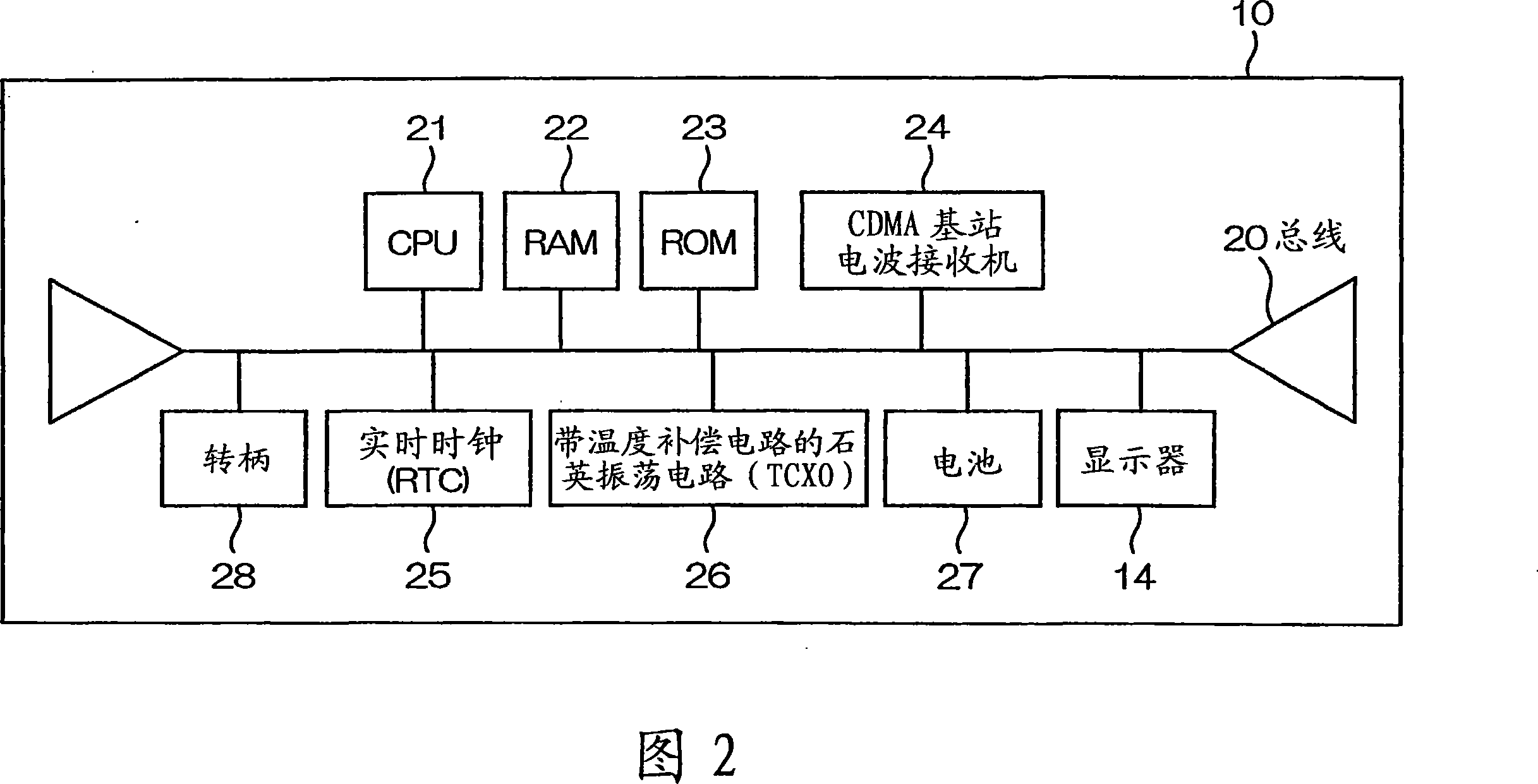
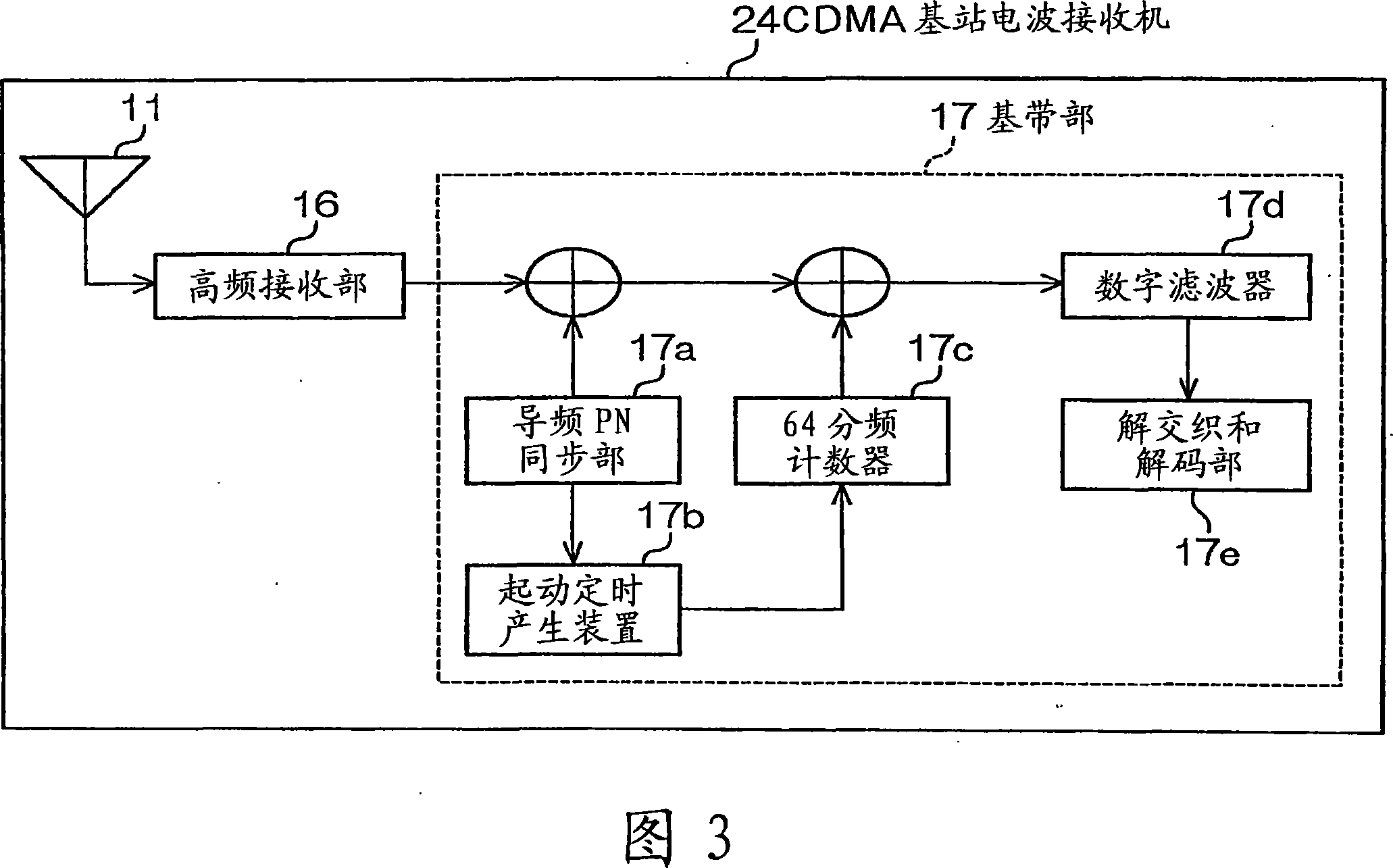
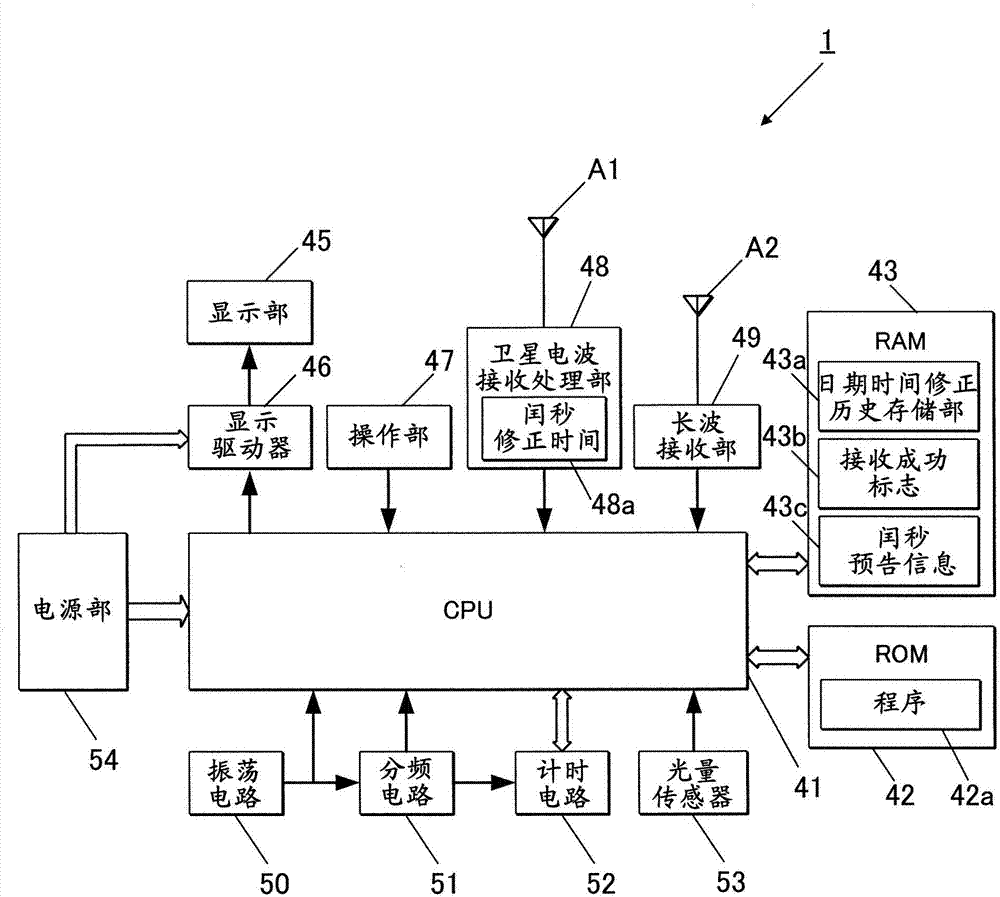
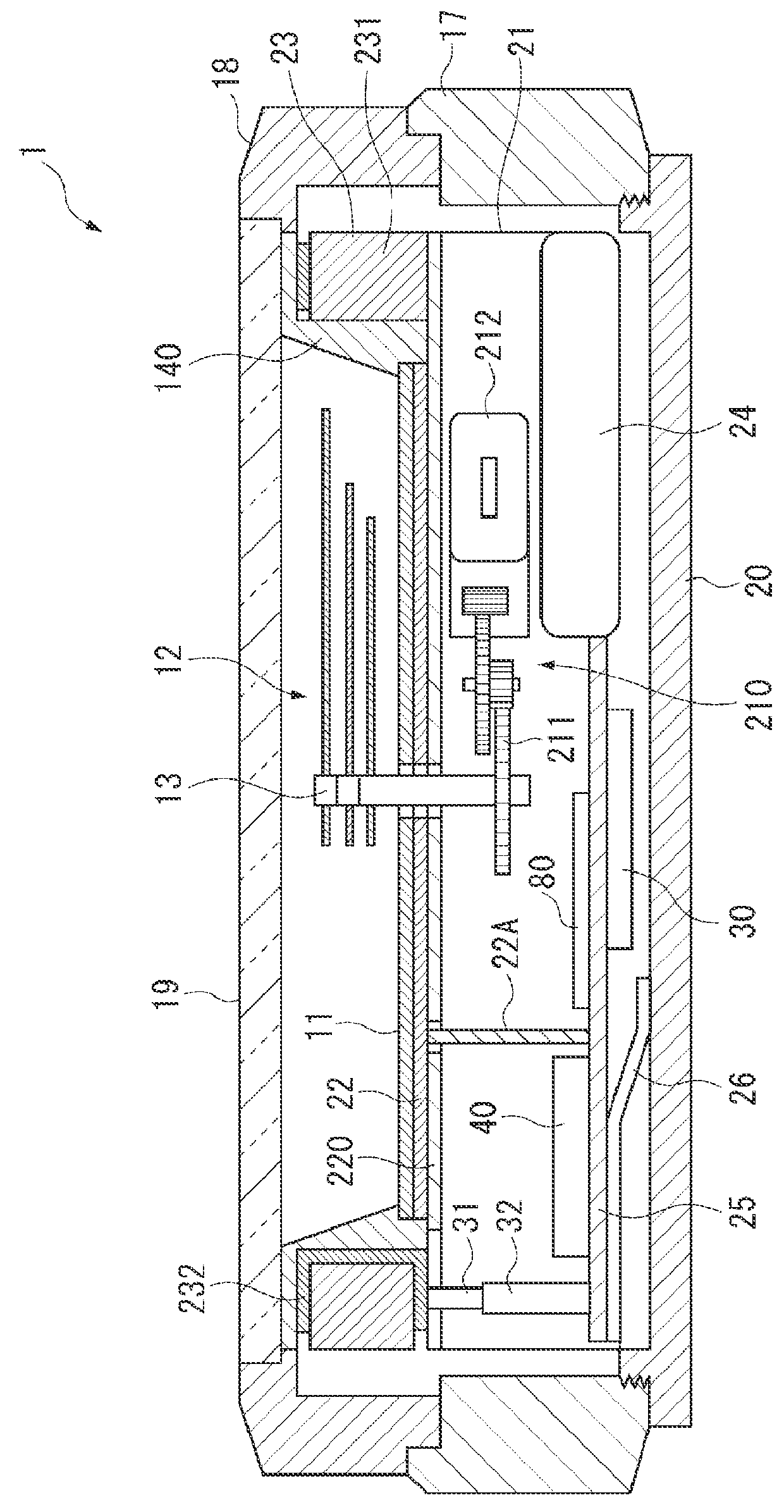
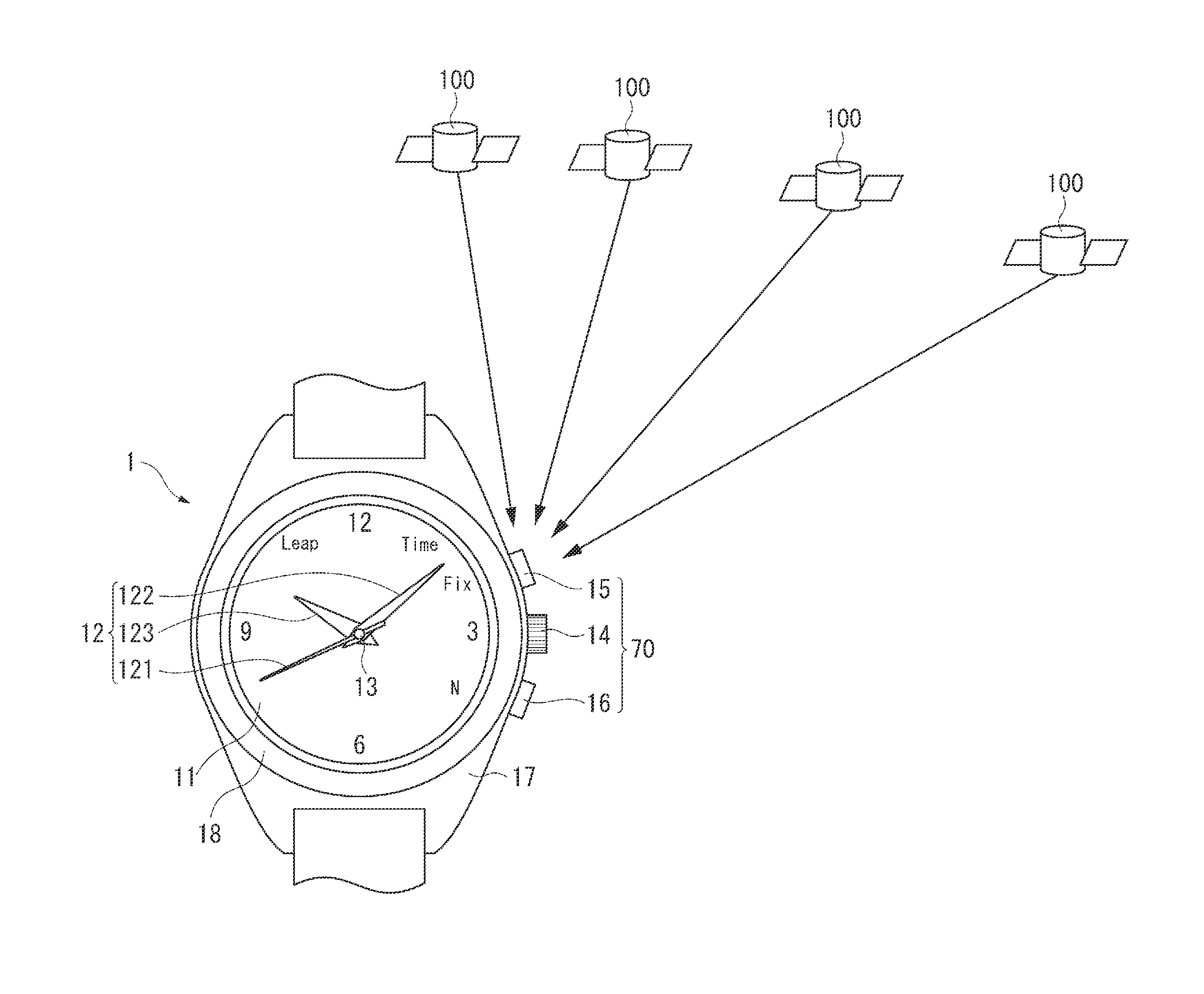
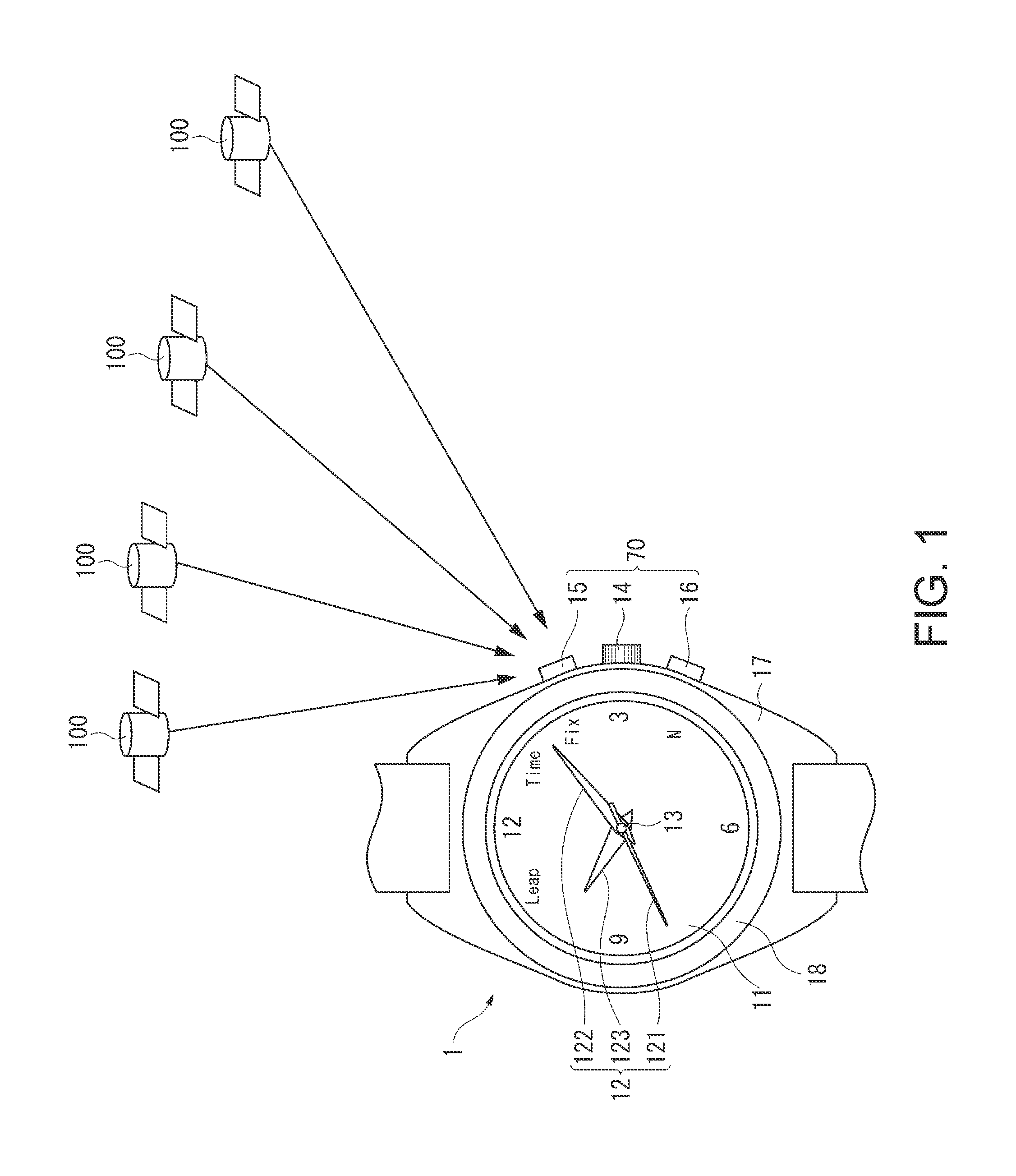
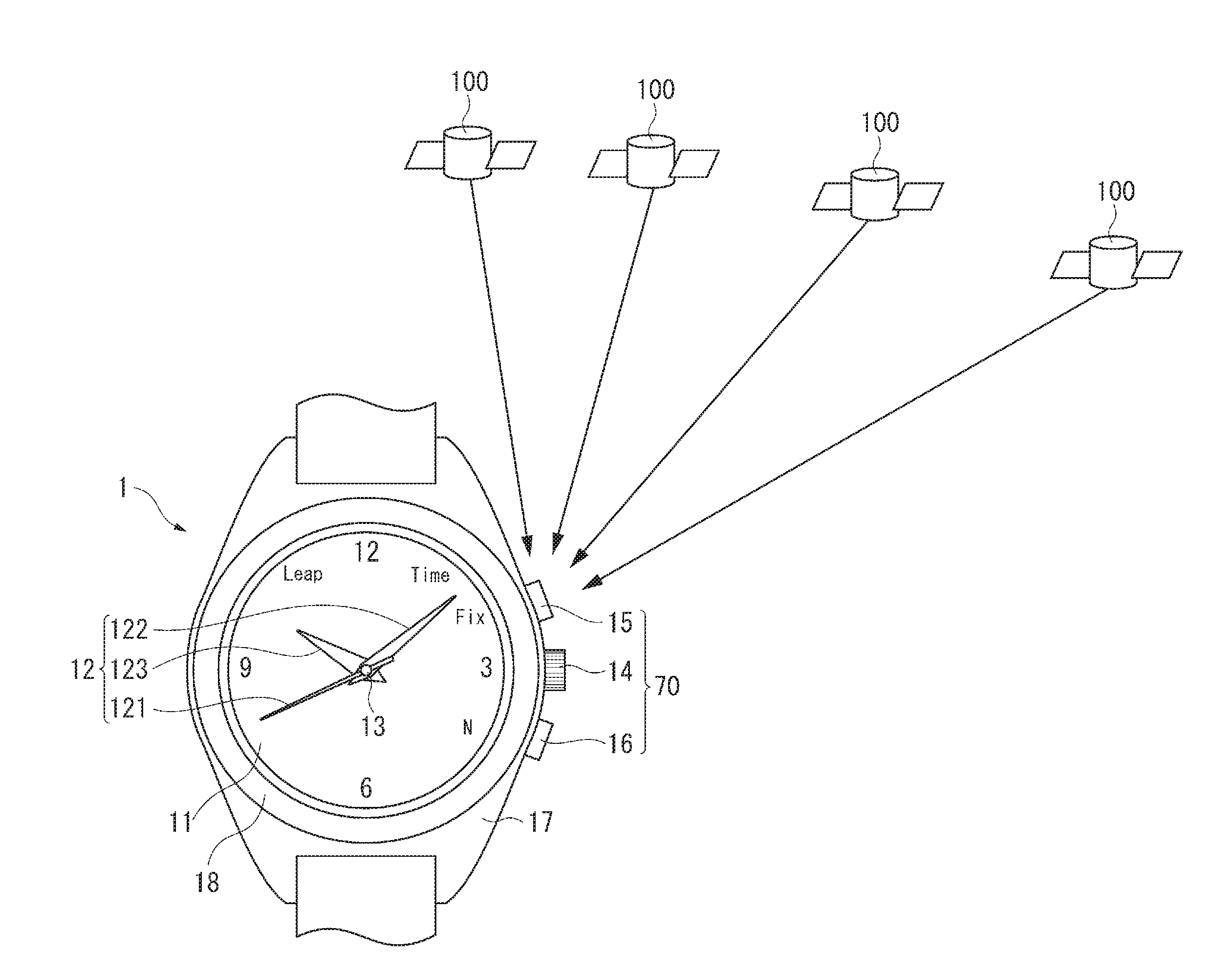
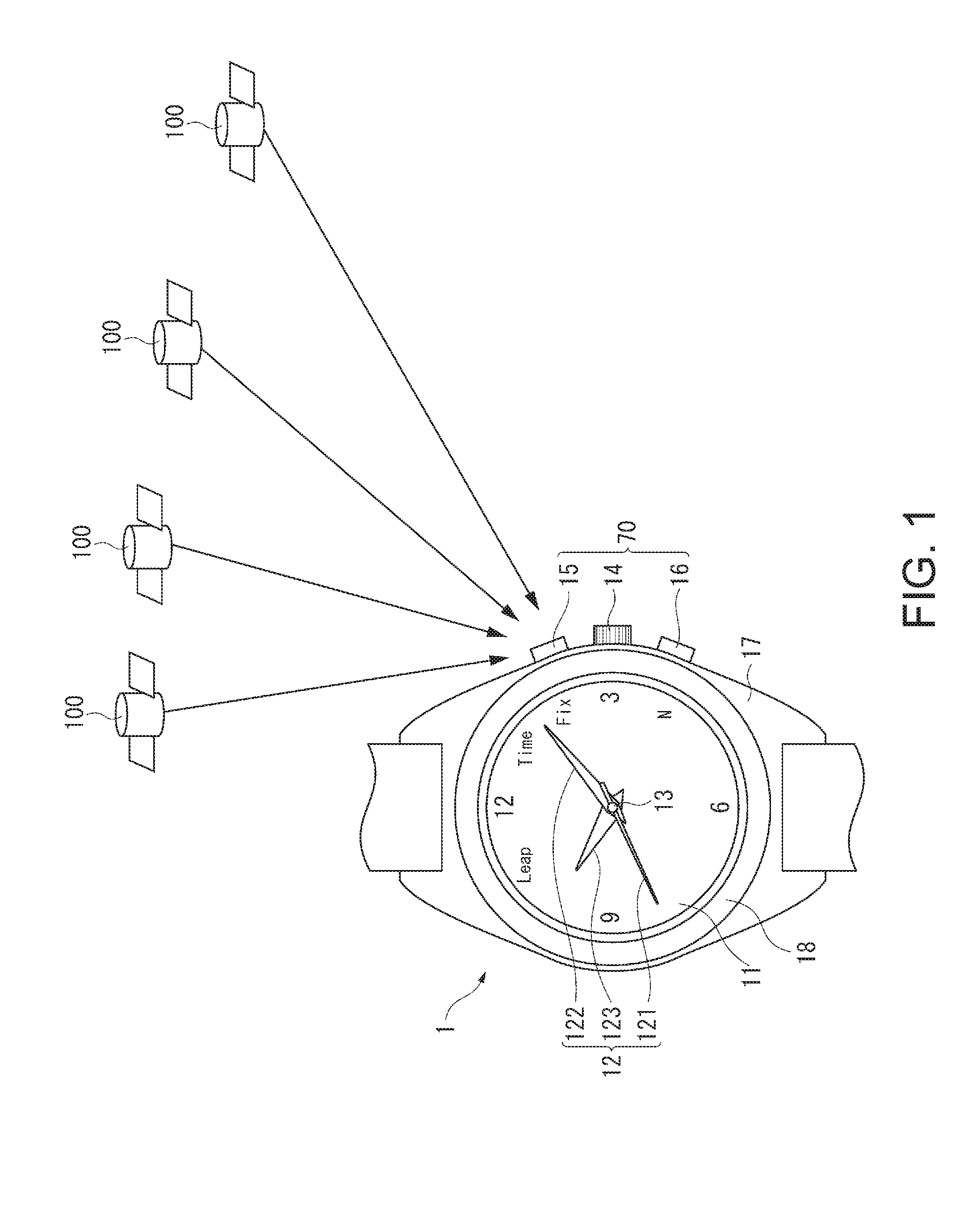
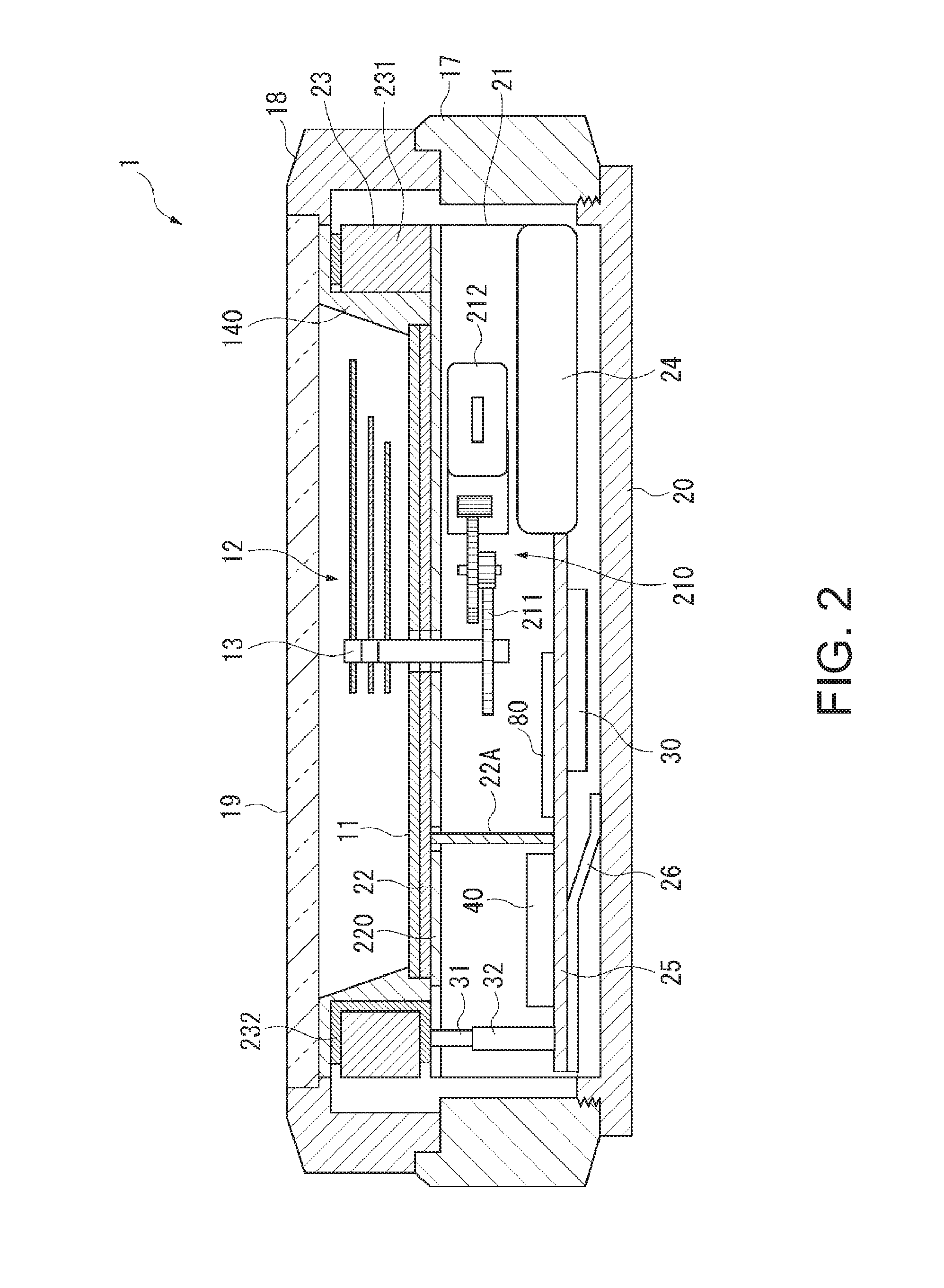
Time Adjustment Device, Timepiece with a Time Adjustment Device, and Time Adjustment Method
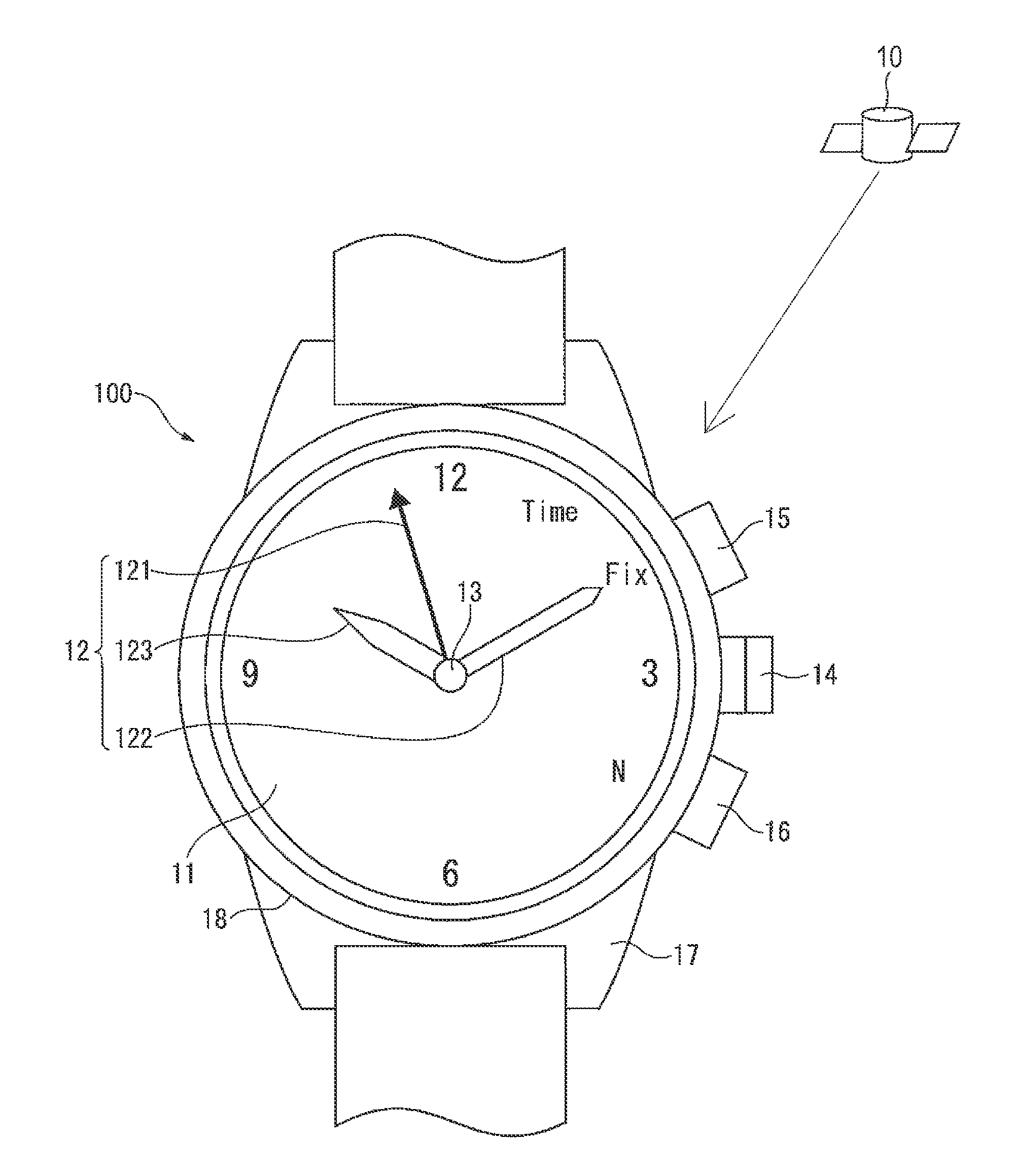
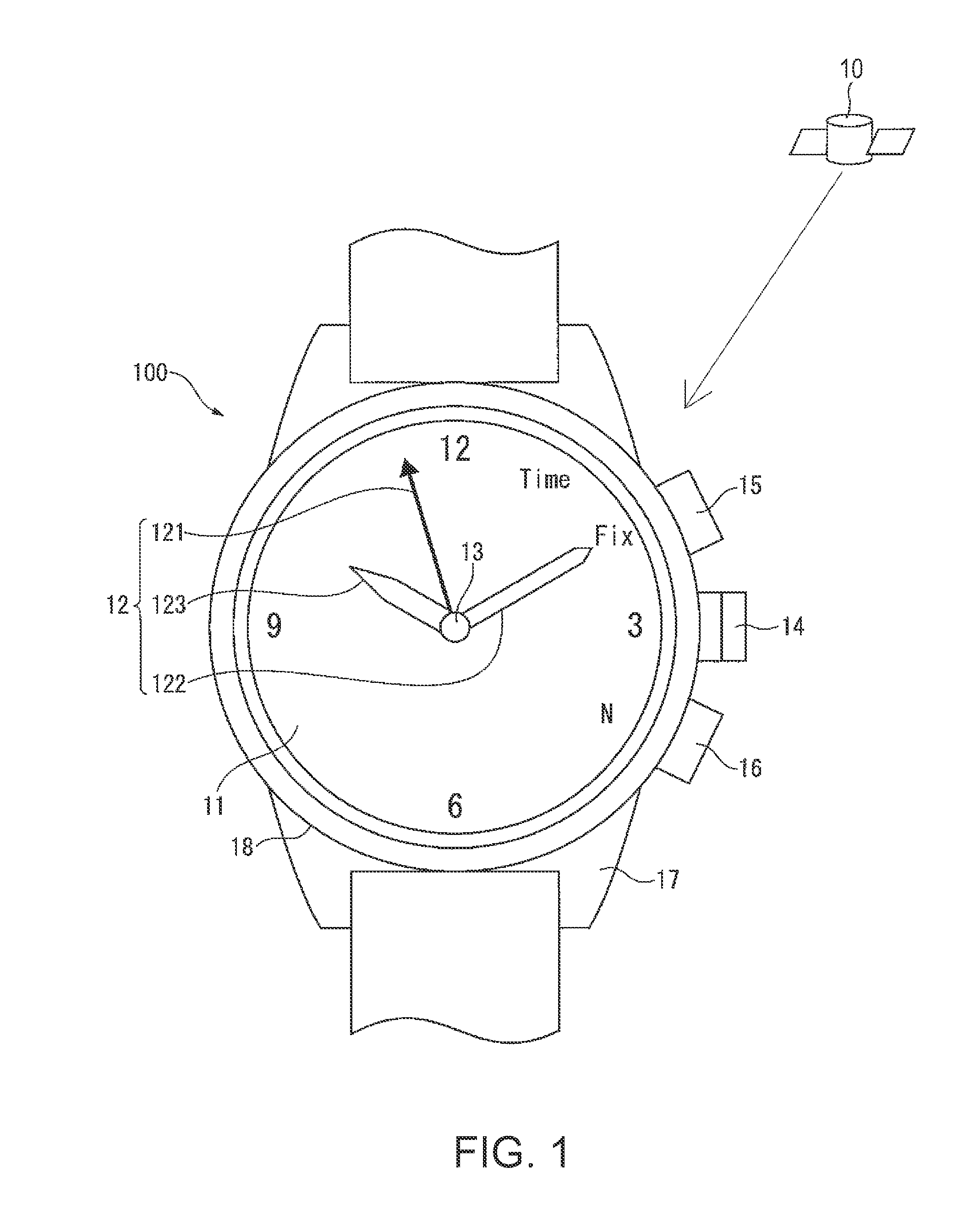
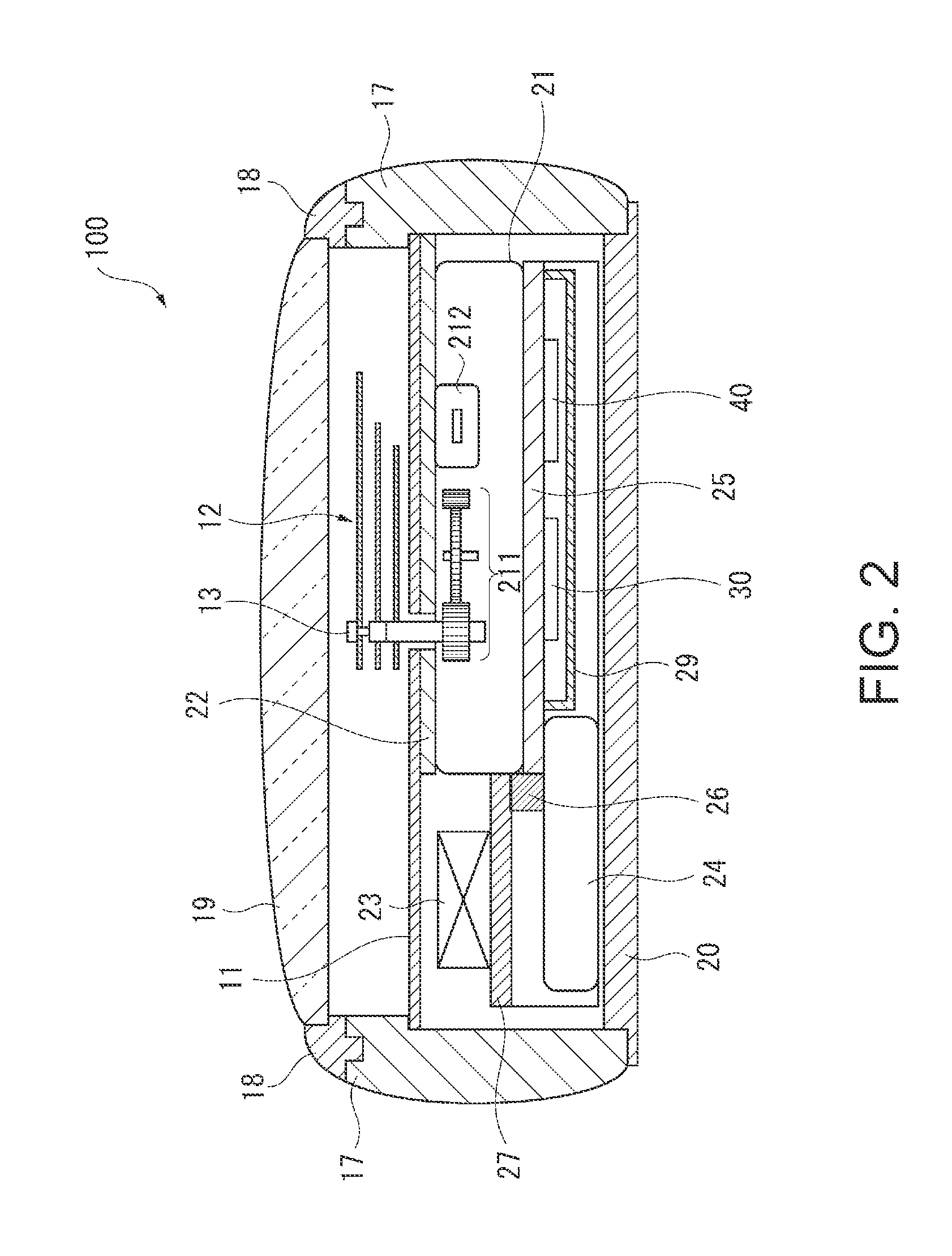
InactiveUS20080165628A1Accurately reflectPrecise managementSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingTime informationApplication time
A reception unit that receives a prescribed signal containing time information transmitted by a base station, a display time information adjustment unit that adjusts the time information displayed by a time information display unit based on the time information, a leap seconds information storage unit for storing leap seconds information that is time adjustment information based on rotation of the Earth and is contained in the time information, and a leap seconds application time information storage unit that stores leap seconds application time information for adjusting the displayed time information based on the leap seconds information. The display time information adjustment unit corrects the displayed time information based on the leap seconds information and the leap seconds application time information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
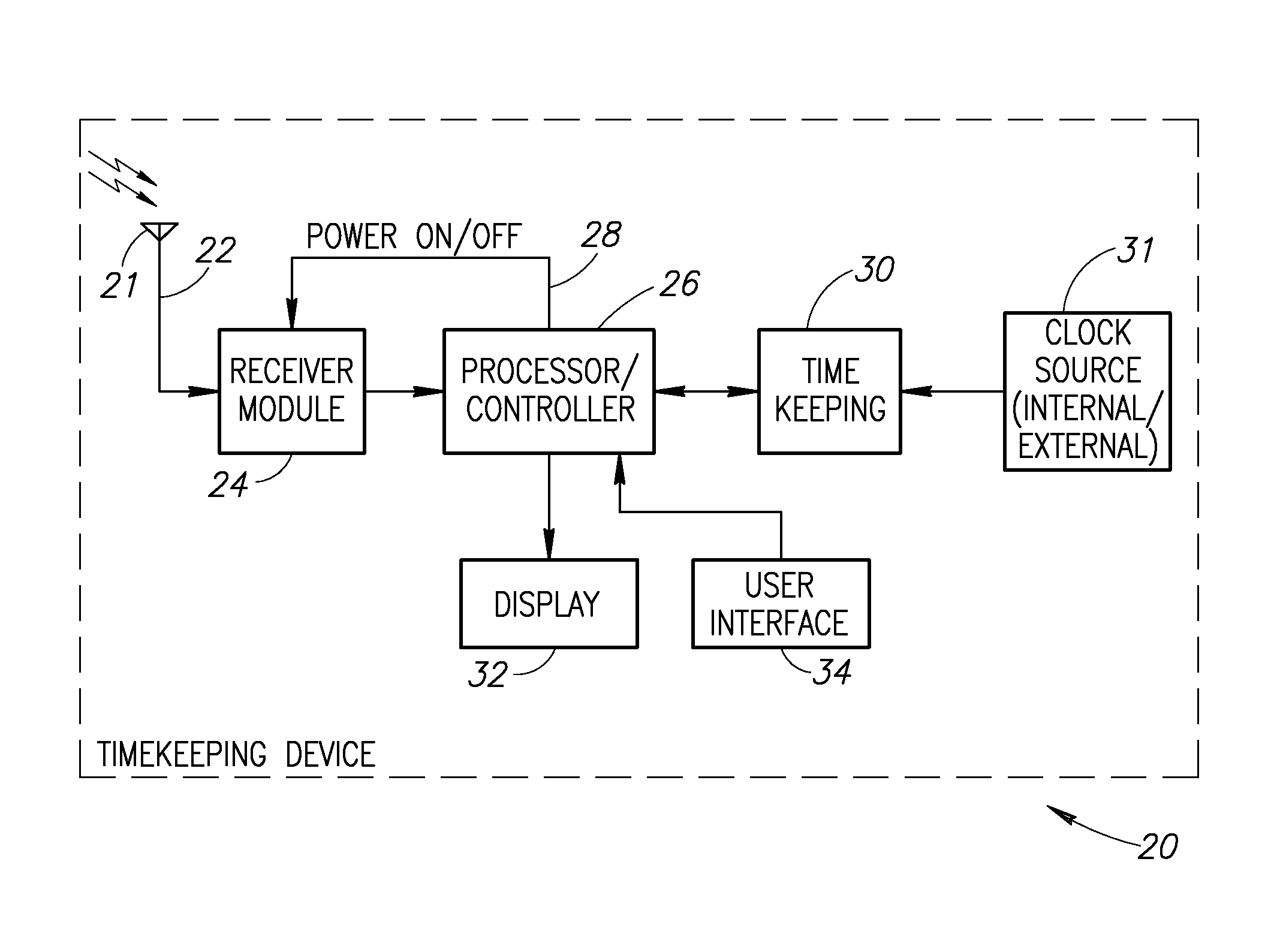
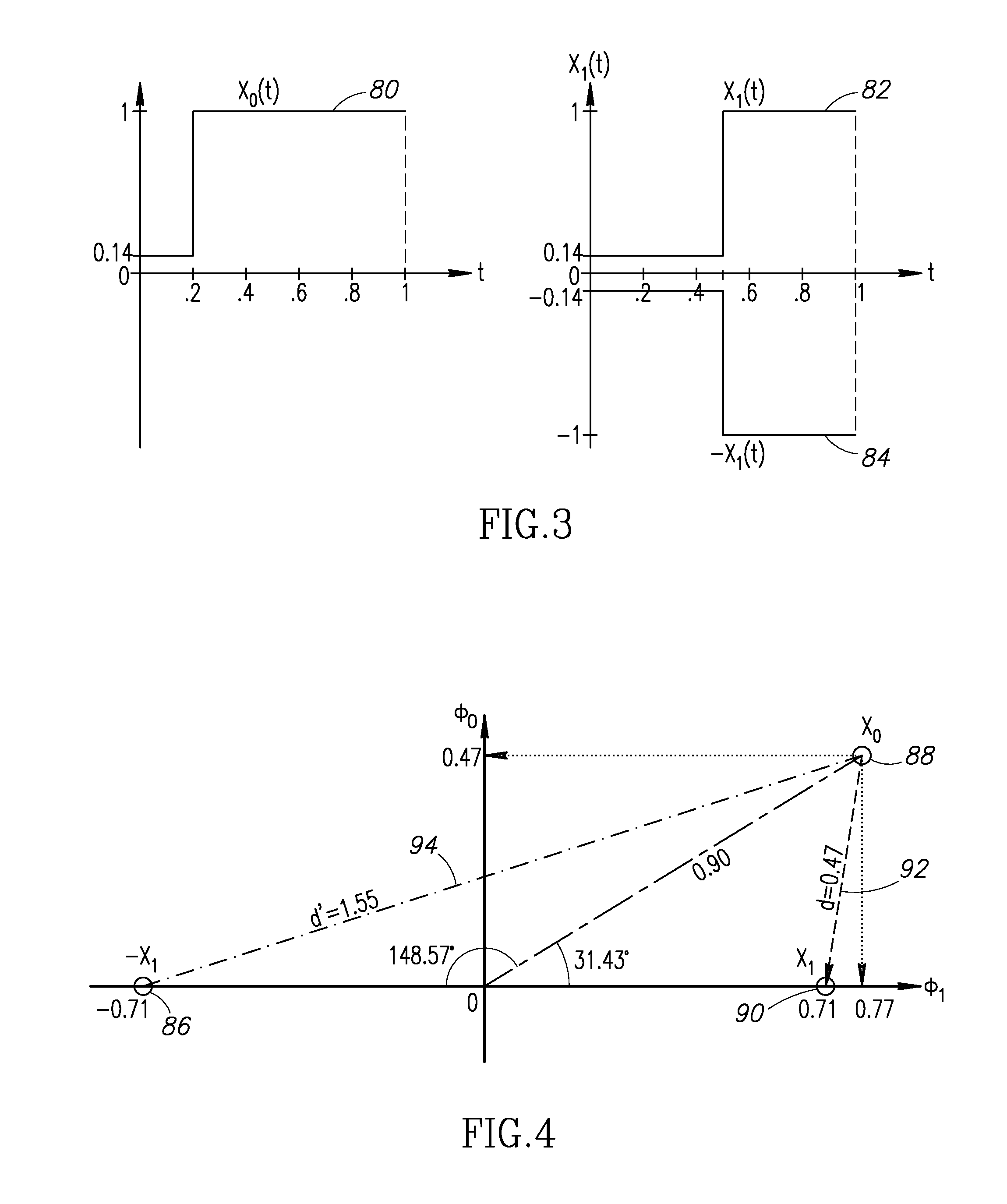
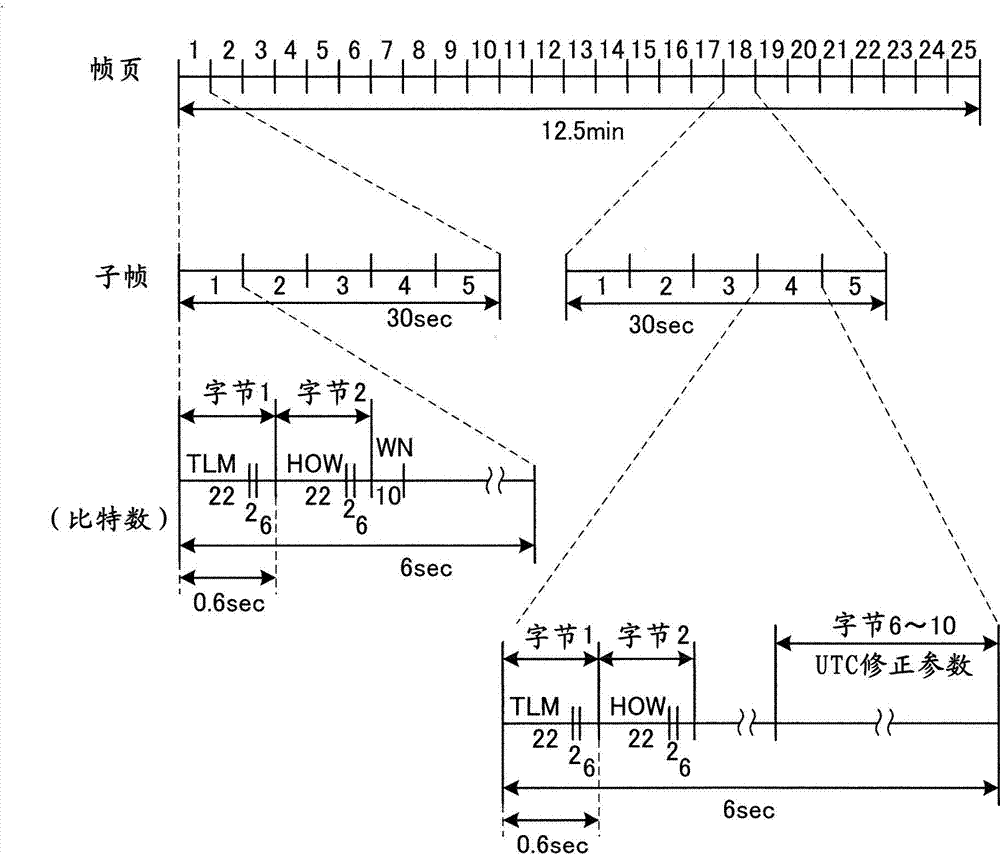
Timing and time information extraction in a radio controlled clock receiver
InactiveUS8300687B1Duration/width modulated pulse demodulationRadio-controlled time-piecesTime scheduleTime information
A novel and useful system and method for extracting timing, time and additional information from a broadcast received in a radio controlled clock (RCC) receiver. The RCC receiver extracts timing information represented by a known synchronization sequence that is used for acquisition and tracking purposes. The RCC receiver extracts time information as a merged 26-bit time information word linearly coded into 31 bits comprising the number of minutes (or hours) since the turn of the current century. A minute counter representing the 26 bits is converted into the date, hour, and minute. The RCC extracts additional information including the schedule for the next daylight saving time transition and for an imminent leap second. The communications protocol optionally employs error correcting codes to provide protection for data fields in the frame, which the RCC may use to enhance reception reliability in the presence of noise and interference.
Owner:GRINDSTONE CAPITAL
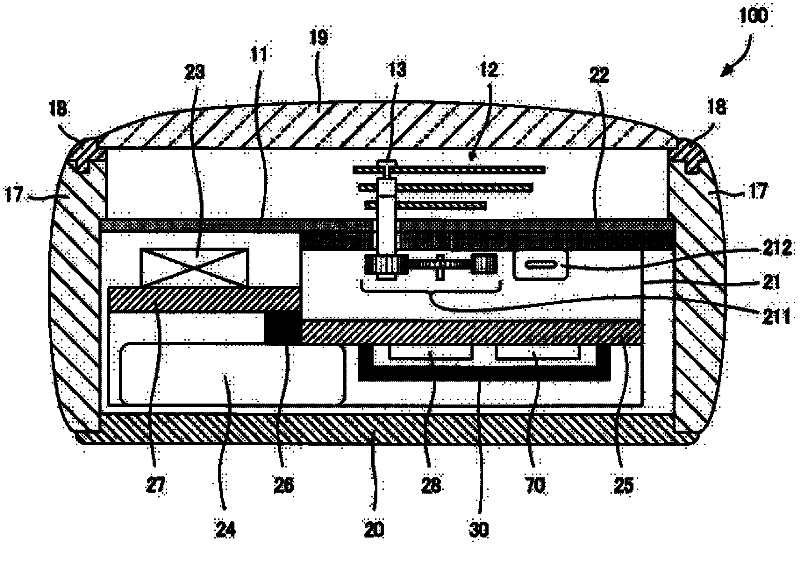
Electronic Timepiece and Reception Control Method for an Electronic Timepiece
ActiveUS20120201101A1Reduce processor loadEasy to getSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationData miningLeap second
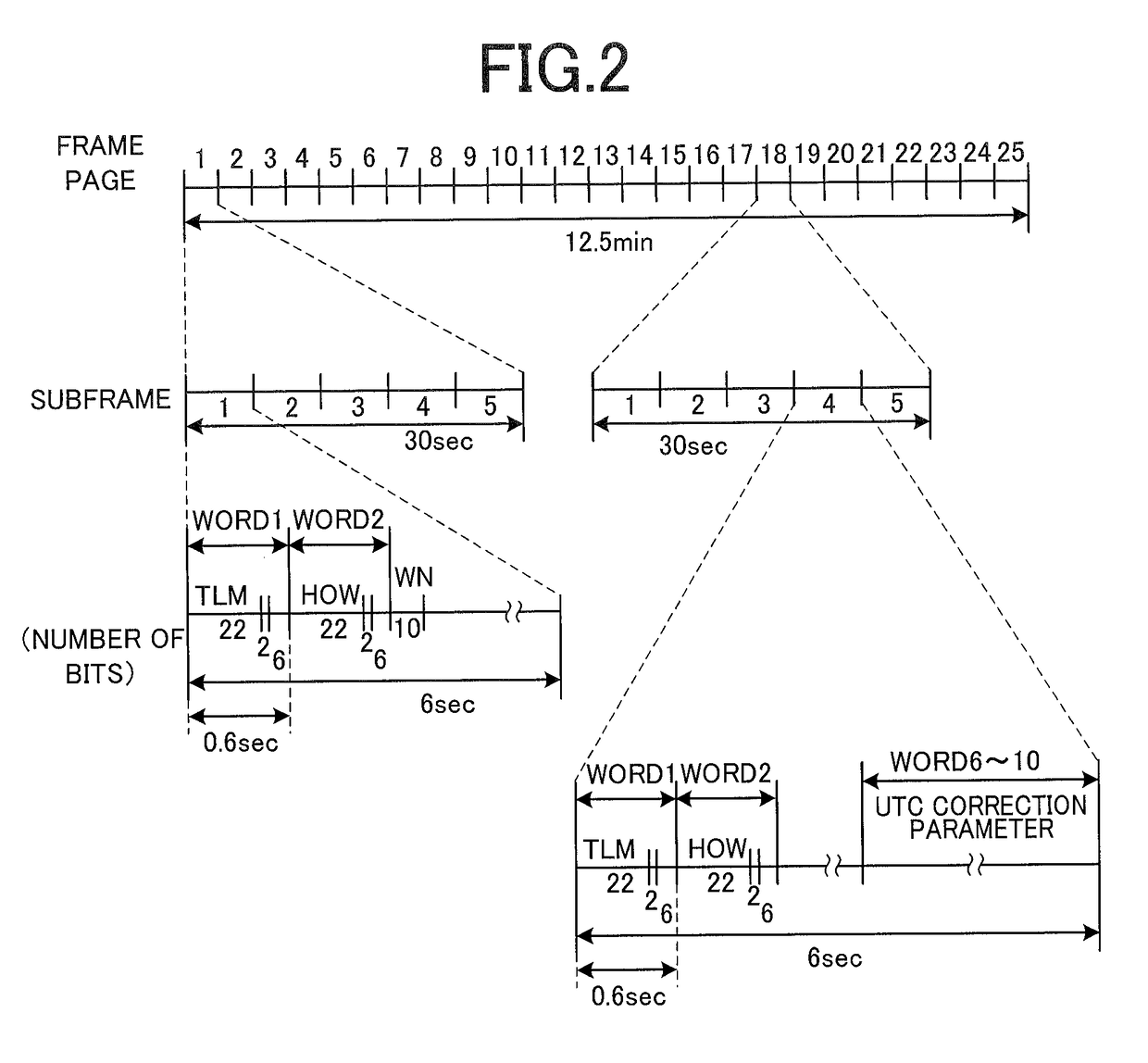
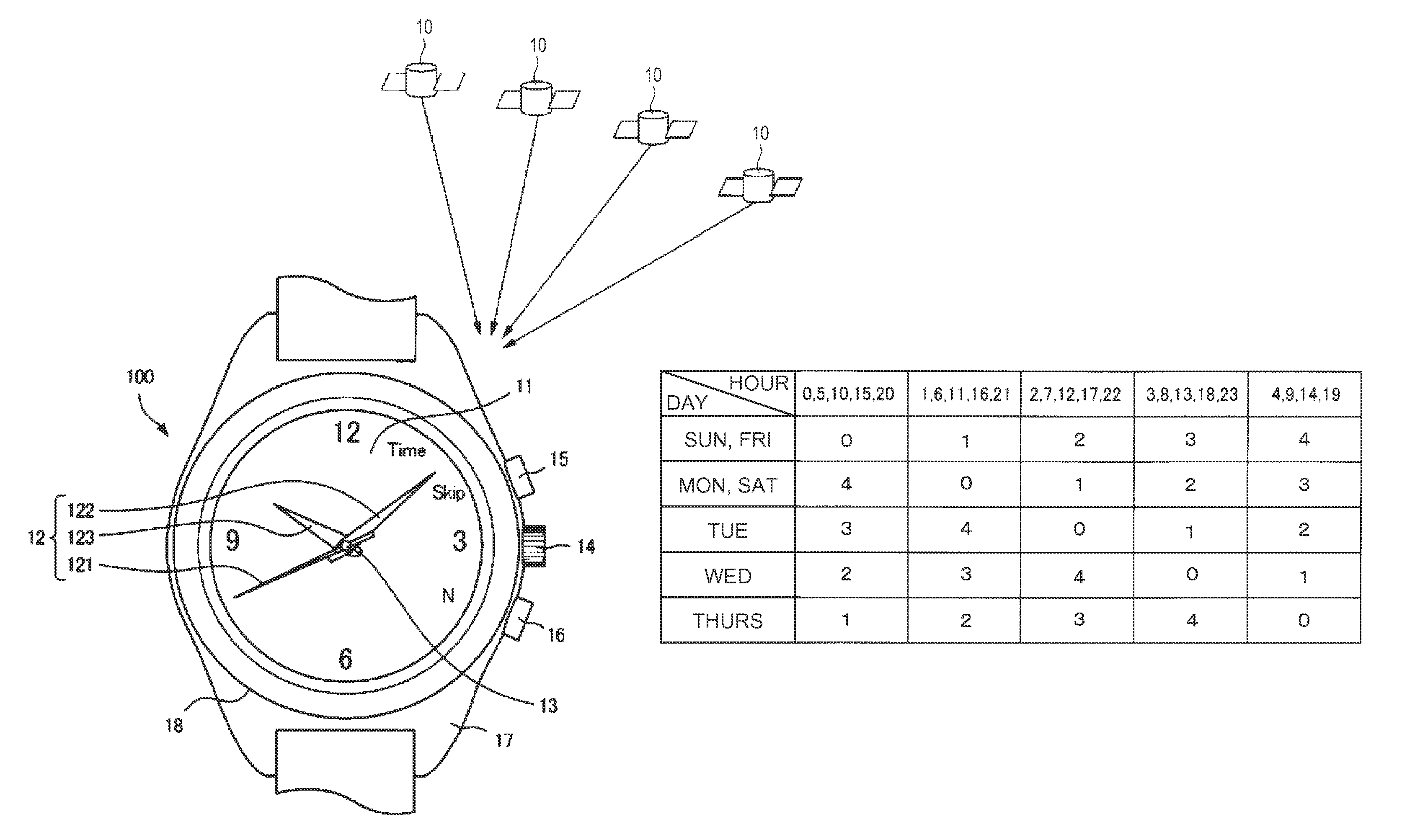
An electronic timepiece can easily acquire a leap second information reception time with minimal processor load. A first table groups leap second information reception times expressed by hour, minute, second, and day values into plural minute-second patterns of minute-second combinations that are common to plural hours, and relates numbers identifying these minute-second patterns to the day and hour values. The minute-second combinations are grouped by number in a second table. The number corresponding to the day and hour of the internal time is found from the first table (S1). A minute-second combination that is later than the internal time is found from the minute-second combinations corresponding to the acquired number (S2). And leap second reception time is calculated. If the resulting leap second reception time matches the internal time is determined (S9). If the times match, the leap second information is received (S10, S11).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
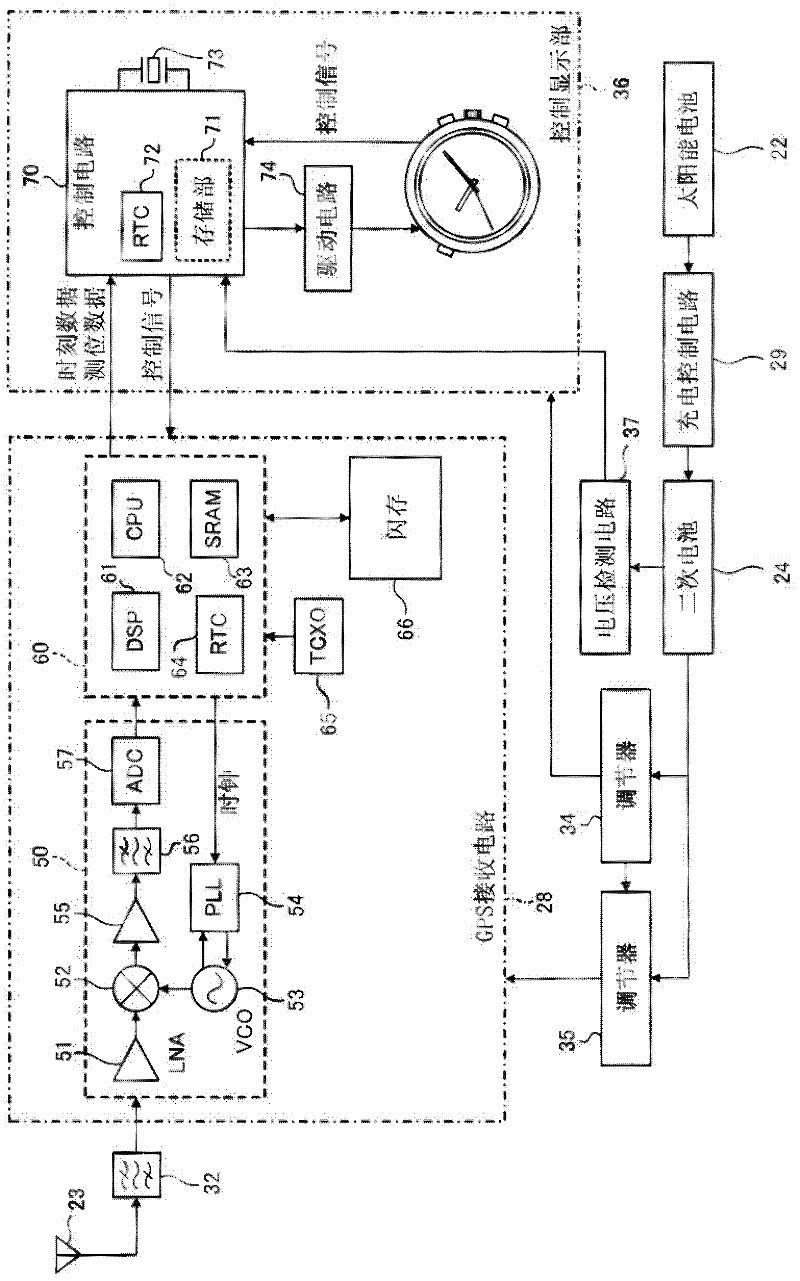
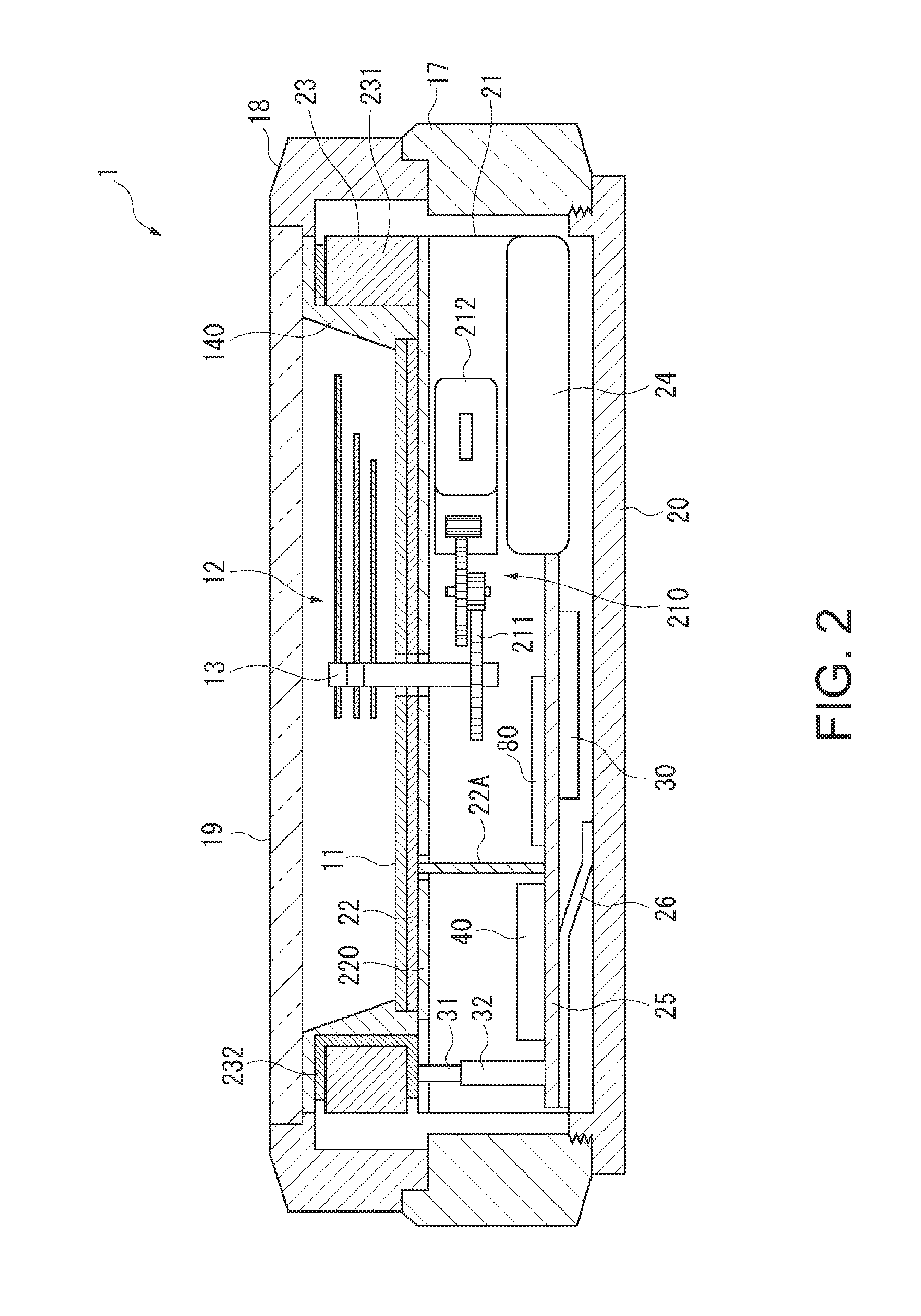
Electronic Timepiece and Control Method Therefor
InactiveUS20120243383A1Efficient collectionReduce power consumptionSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingTemporal informationElectrical battery
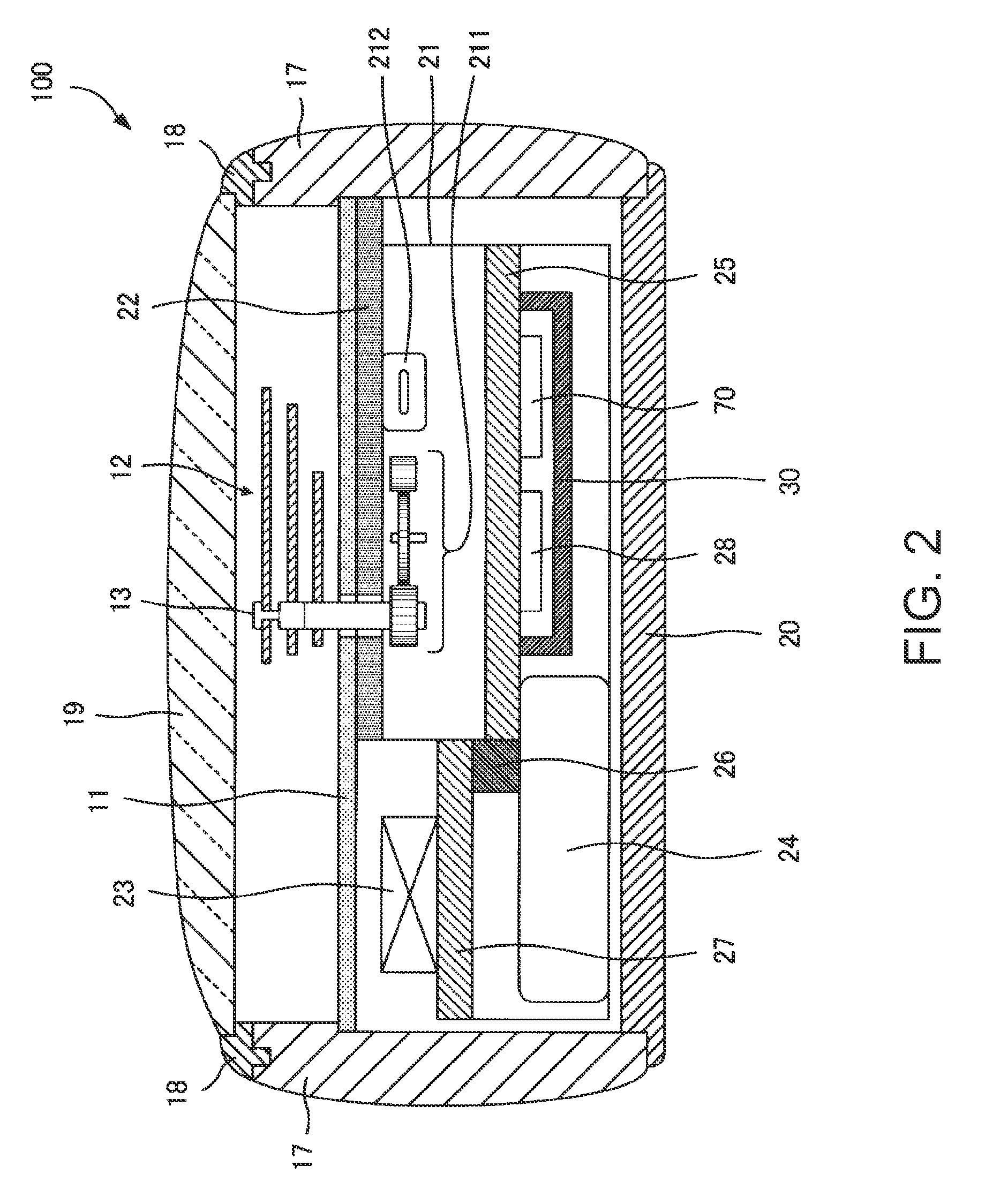
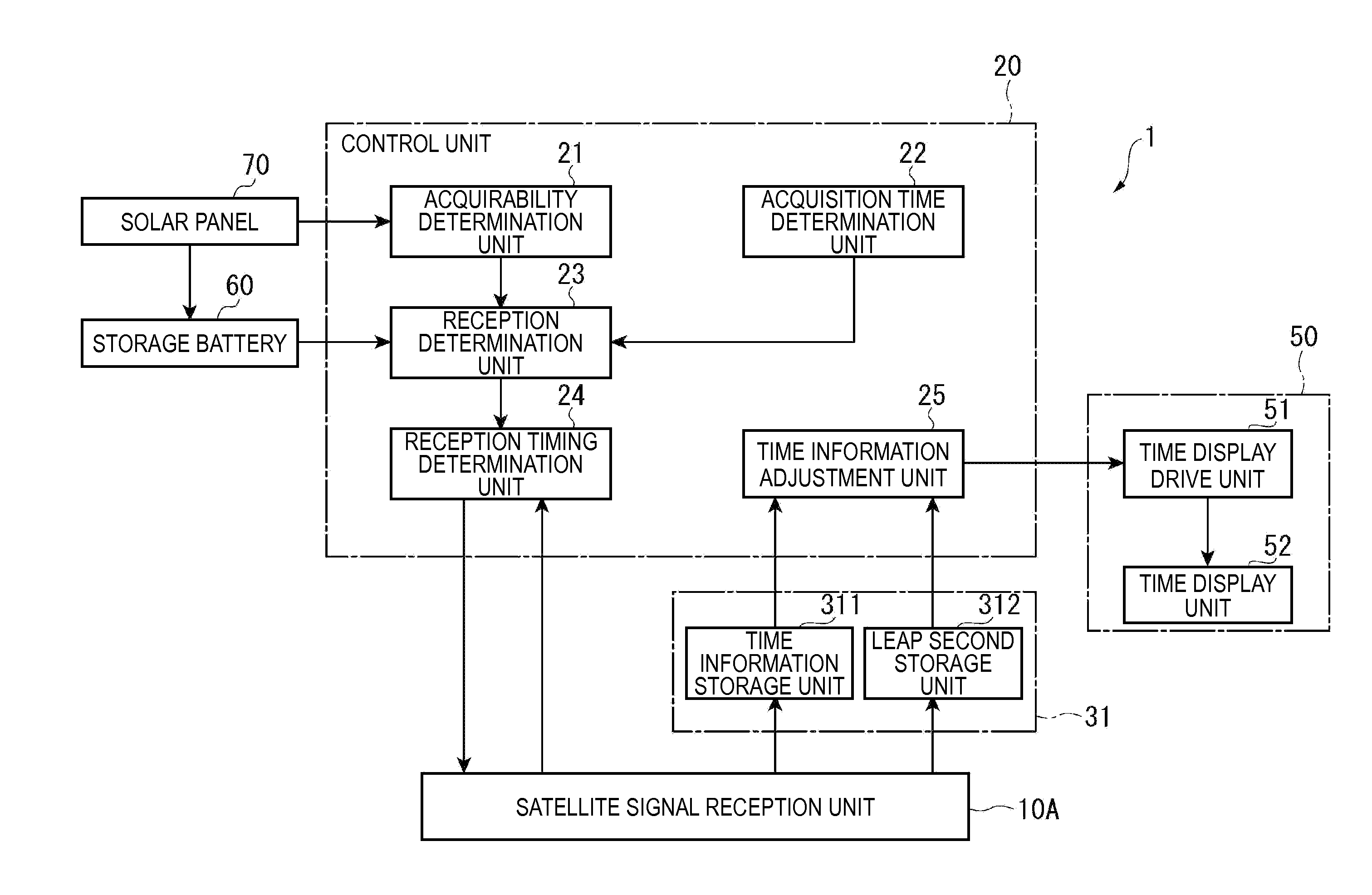
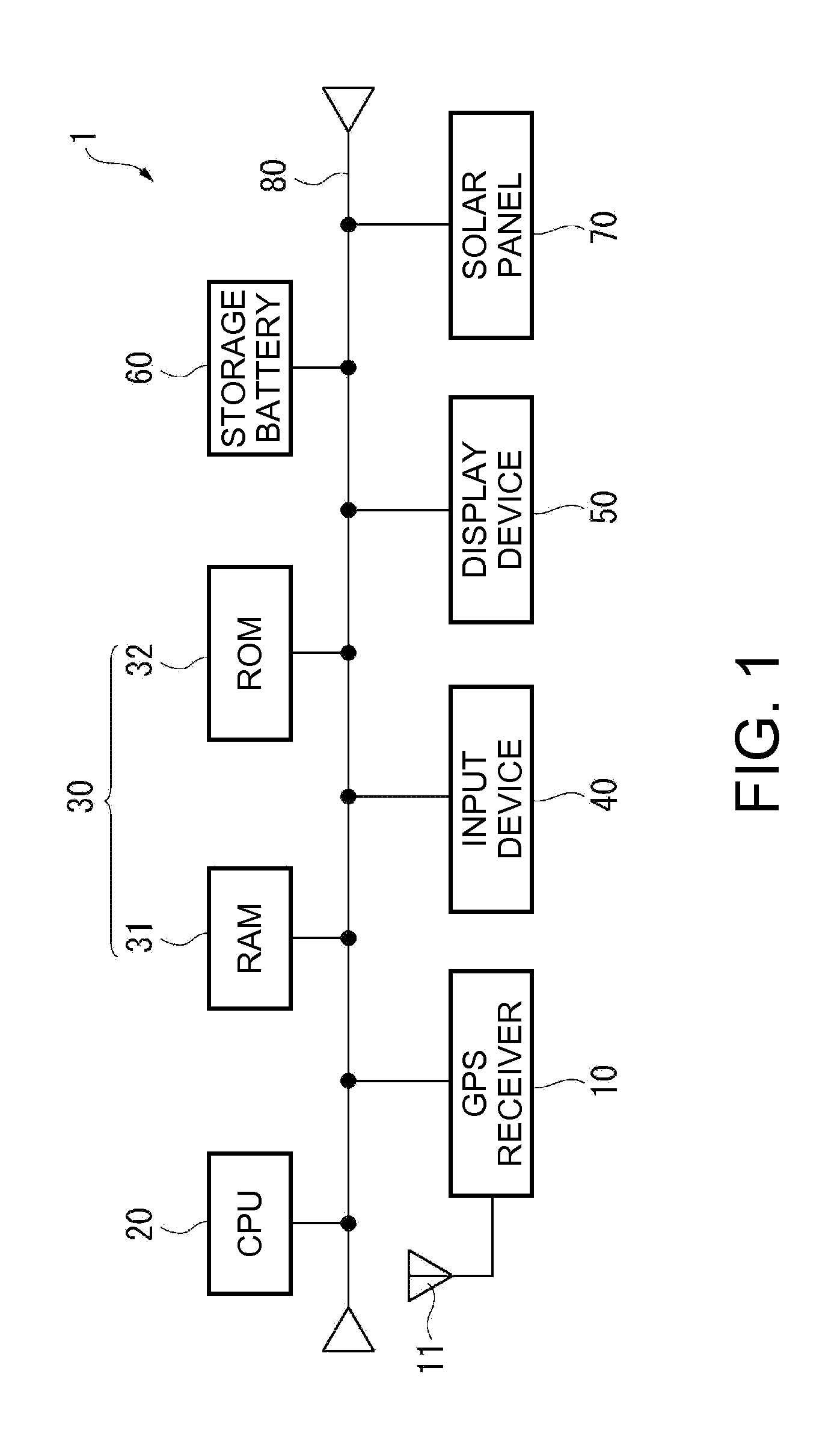
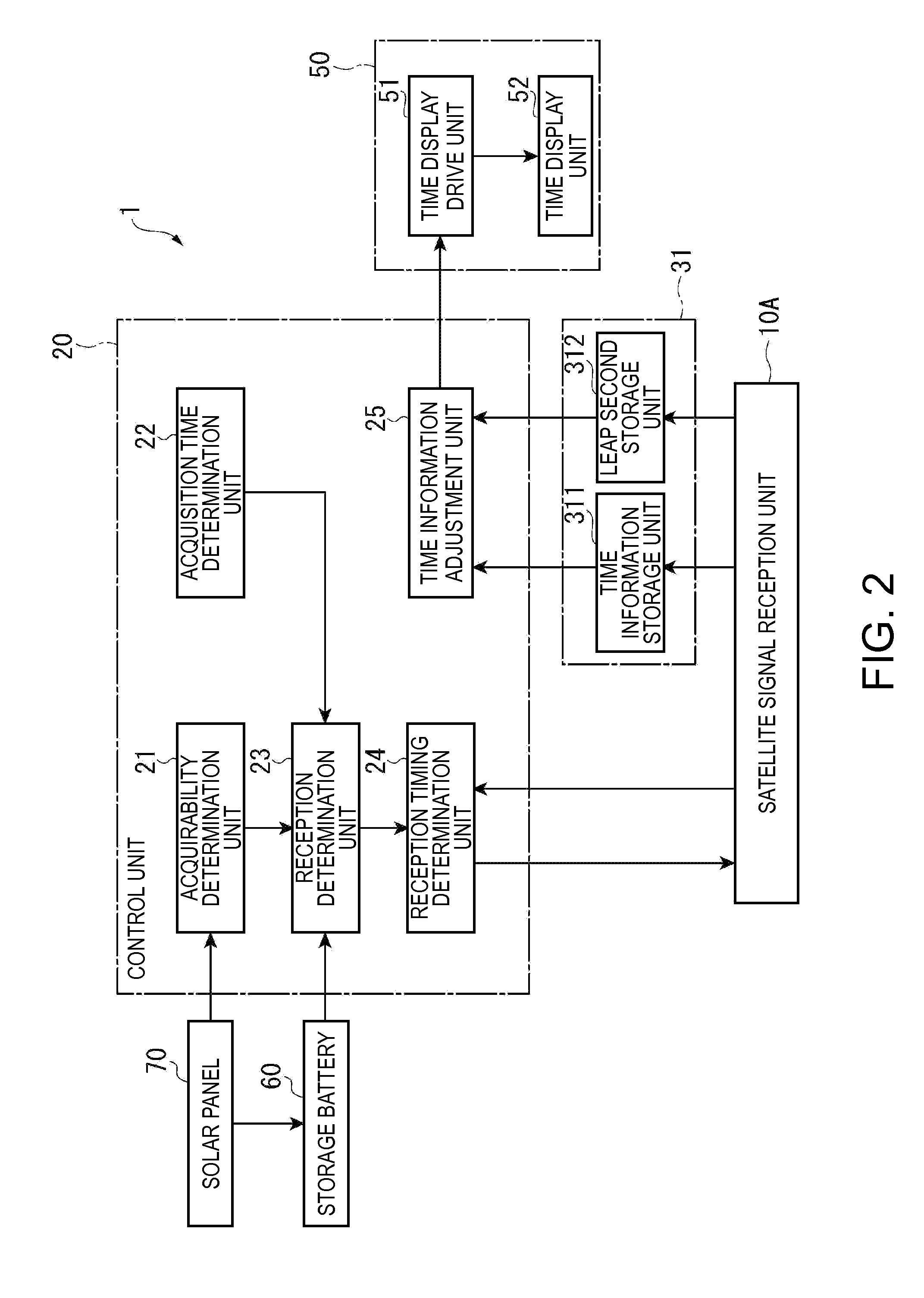
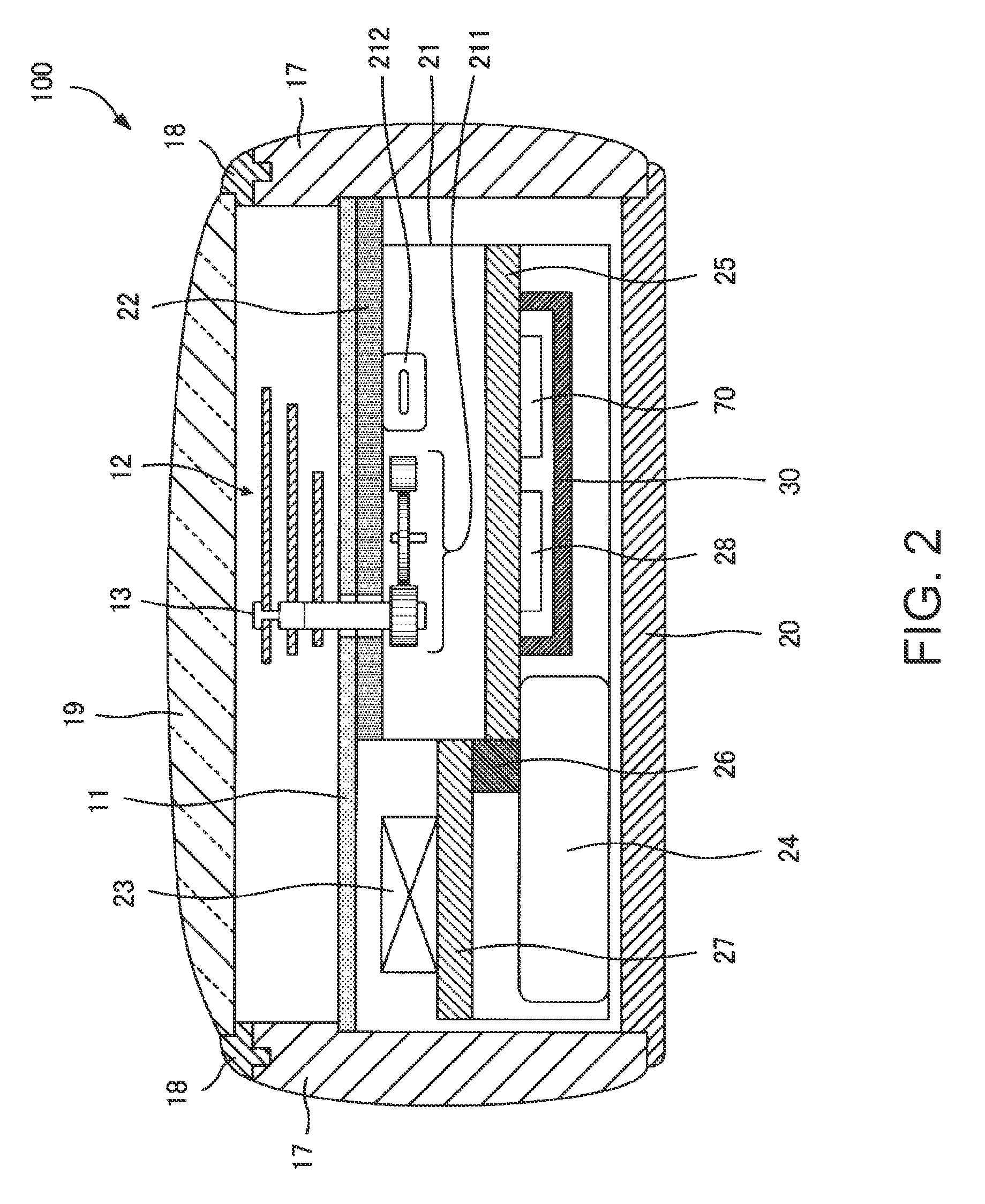
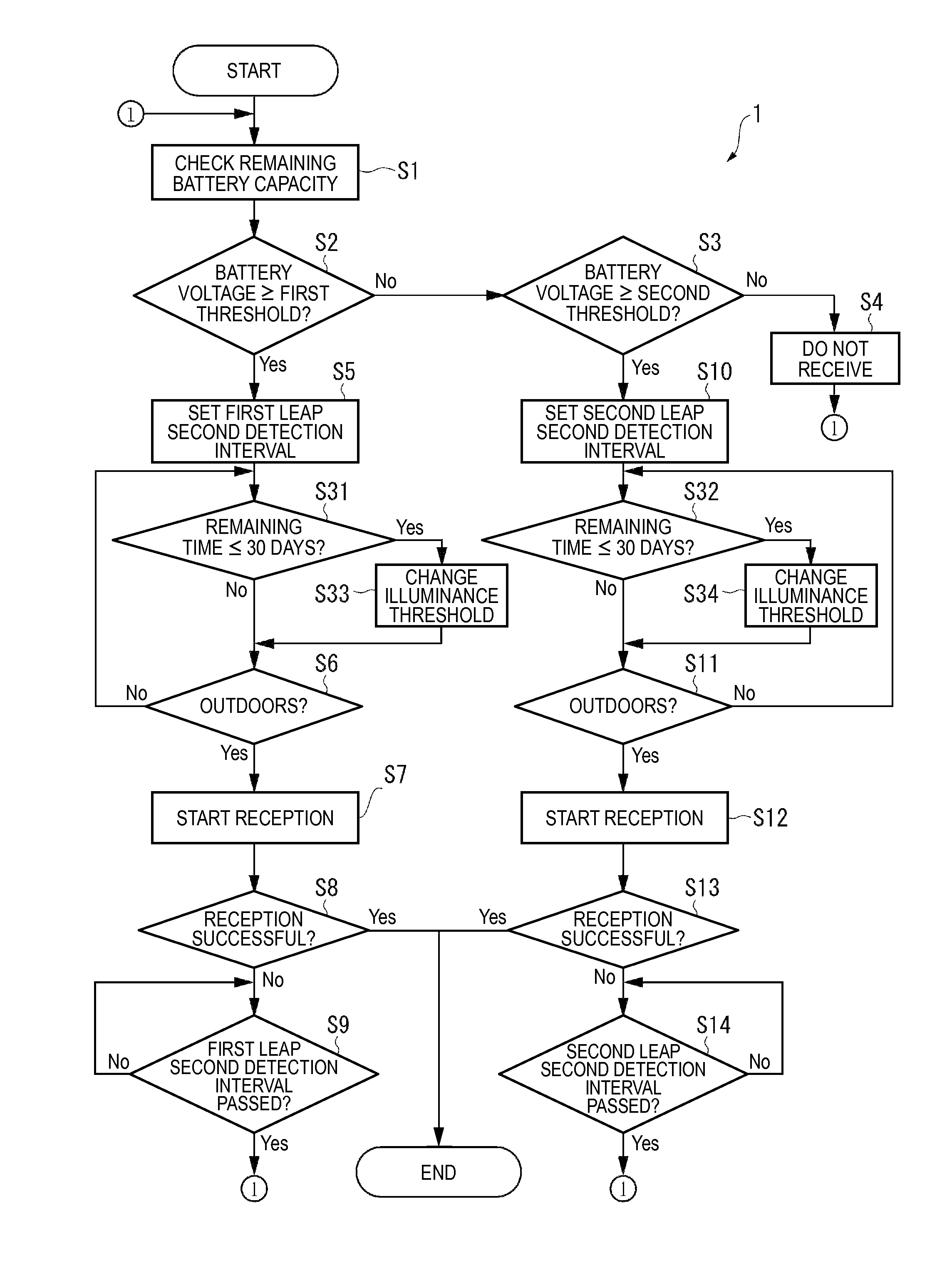
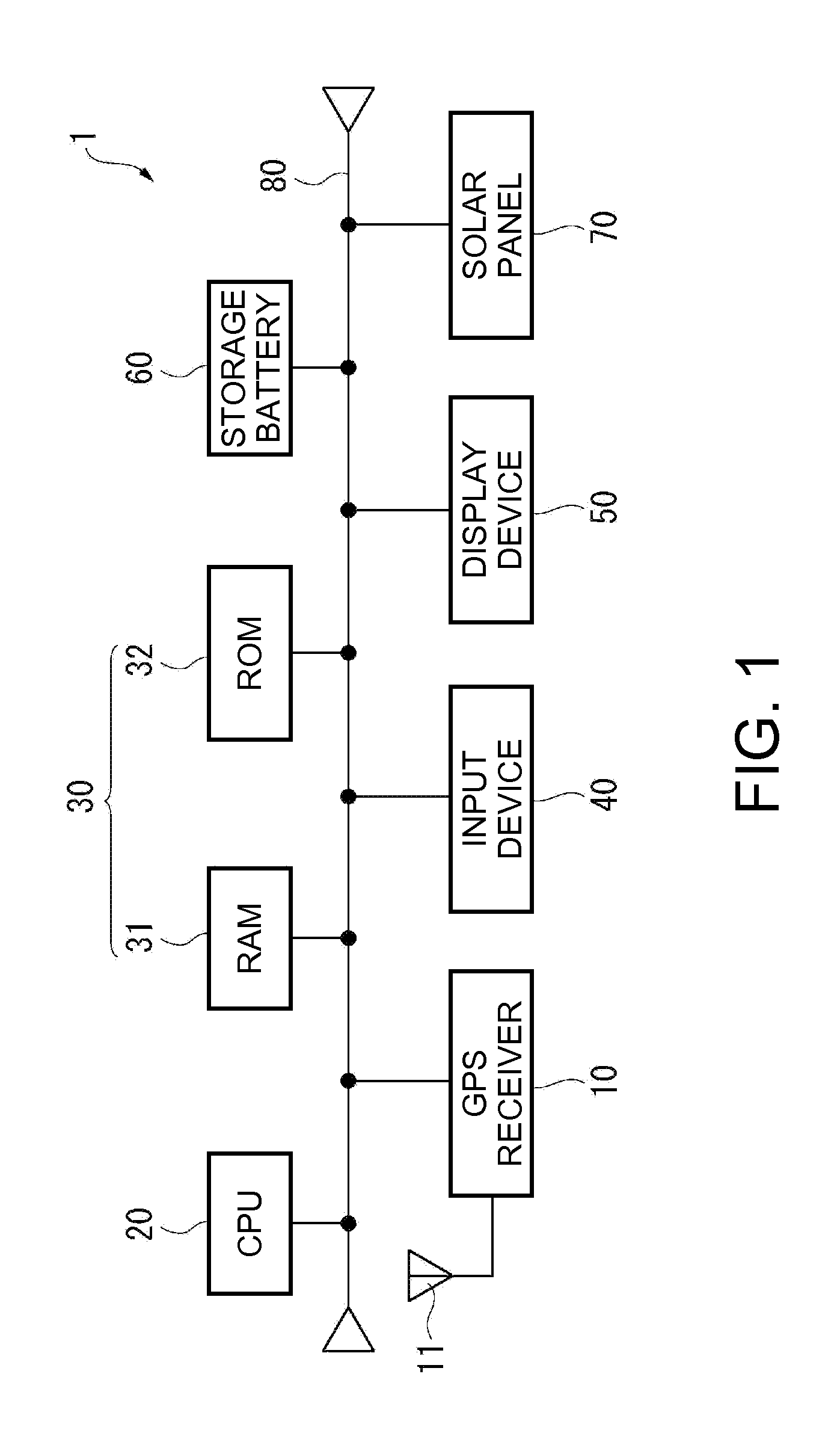
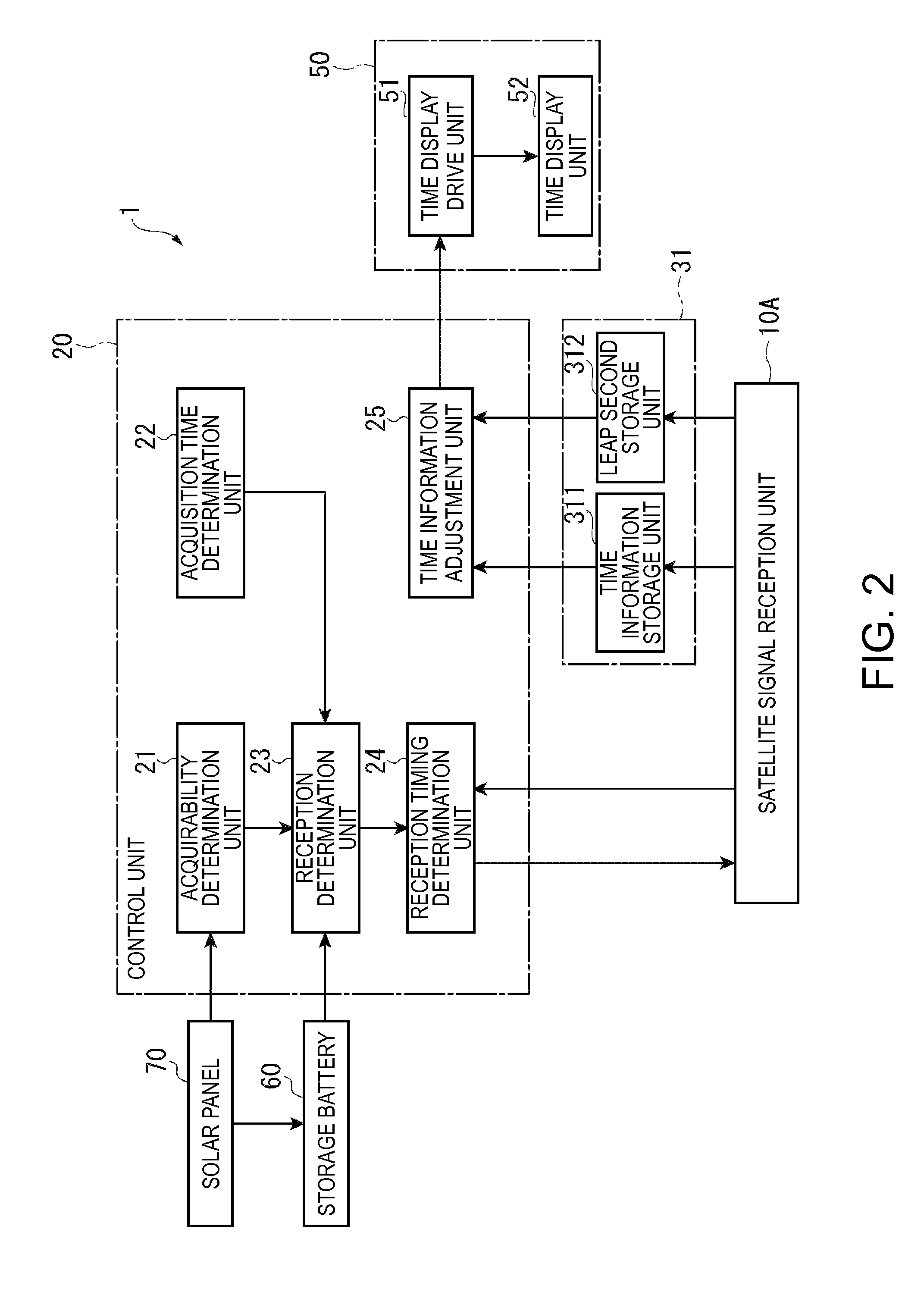
An electronic timepiece efficiently acquires leap second information, reduces power consumption, and enables displaying the correct time. A GPS wristwatch 1 has a satellite signal reception unit 10A that receives satellite signals, a power supply including a solar panel 70 and storage battery 60, a time information adjustment unit 25 that keeps time, a reception timing determination unit 24 that operates the satellite signal reception unit 10A, receives a satellite signal, and acquires leap second information contained in the satellite signal, and a reception determination unit 23 that detects the remaining capacity of the storage battery 60. When the remaining battery capacity measured by the reception determination unit 23 is greater than or equal to a specific value, the reception timing determination unit 24 sets the reception frequency for receiving a satellite signal higher than when the remaining battery capacity is less than the specific value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Time Adjustment Device, Timekeeping Device With A Time Adjustment Device, And Time Adjustment Method
ActiveUS20120188854A1Reduce power consumptionShort acquisition timeSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingTime informationEngineering
A time adjustment device can acquire time information in a short time, reduce power consumption, and display the correct time. A GPS wristwatch has a reception unit that receives satellite signals; a time information generating unit that generates internal time information; a reception control unit that controls the reception unit; and a time information adjustment unit that adjusts the internal time information. The time information adjustment unit has a first information time adjustment means that receives first information containing year, month, day, hour, minute, second, and satellite health information, and adjusts the internal time information; a second information time adjustment means that receives second information including leap second information, and adjusts the internal time information; a third information time adjustment means that receives third information of hour, minute, second information, and adjusts the internal time information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Timing time leap second processing method
ActiveCN102281114AGuaranteed to workTo avoid the impact of time synchronizationTime-division multiplexSystem timeComputer science
The invention discloses a time service time leap second processing method, which includes two processes: the input is atomic time and leap second forecast, the output is coordinated universal time, and the input is coordinated universal time and leap second forecast, and the output is atomic time. The present invention adopting the above-mentioned technical scheme provides the conversion from UTC to atomic time, and the conversion from atomic time to UTC. The two time system conversion methods ensure that the systems using UTC and atomic time can be synchronized and unified at the time when the leap second occurs. Avoid the impact of leap seconds on time synchronization and ensure the normal operation of the time synchronization system.
Owner:郑州威科姆科技股份有限公司
Time adjustment device, timepiece with a time adjustment device, and time adjustment method
A reception unit that receives a prescribed signal containing time information transmitted by a base station, a display time information adjustment unit that adjusts the time information displayed by a time information display unit based on the time information, a leap seconds information storage unit for storing leap seconds information that is time adjustment information based on rotation of the Earth and is contained in the time information, and a leap seconds application time information storage unit that stores leap seconds application time information for adjusting the displayed time information based on the leap seconds information. The display time information adjustment unit corrects the displayed time information based on the leap seconds information and the leap seconds application time information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electronic timepiece and reception control method for an electronic timepiece
ActiveCN102636985AEasy and small load to obtainReduce power consumptionSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationData miningLeap second
An electronic timepiece can easily acquire a leap second information reception time with minimal processor load. A first table groups leap second information reception times expressed by hour, minute, second, and day values into plural minute-second patterns of minute-second combinations that are common to plural hours, and relates numbers identifying these minute-second patterns to the day and hour values. The minute-second combinations are grouped by number in a second table. The number corresponding to the day and hour of the internal time is found from the first table (S1). A minute-second combination that is later than the internal time is found from the minute-second combinations corresponding to the acquired number (S2). And leap second reception time is calculated. If the resulting leap second reception time matches the internal time is determined (S9) . If the times match, the leap second information is received (S10, S11).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transmission apparatus, transmission method, reception apparatus, and reception method
ActiveUS20180034571A1Influence on a reception side by occurrence of a leap second can be suppressedSpecial service provision for substationSynchronisation arrangementTime informationShift time
A time information generating unit generates absolute time information synchronized with absolute time information acquired from an external source. The time information generating unit generates time information by shifting, to shifted time, occurrence time of a leap second that can be represented by the absolute time information acquired from the external source. A transmission unit transmits a signal including transmission media and the absolute time information generated by the time information generating unit. Thereby, influence on a reception side by occurrence of a leap second is suppressed.
Owner:SONY CORP
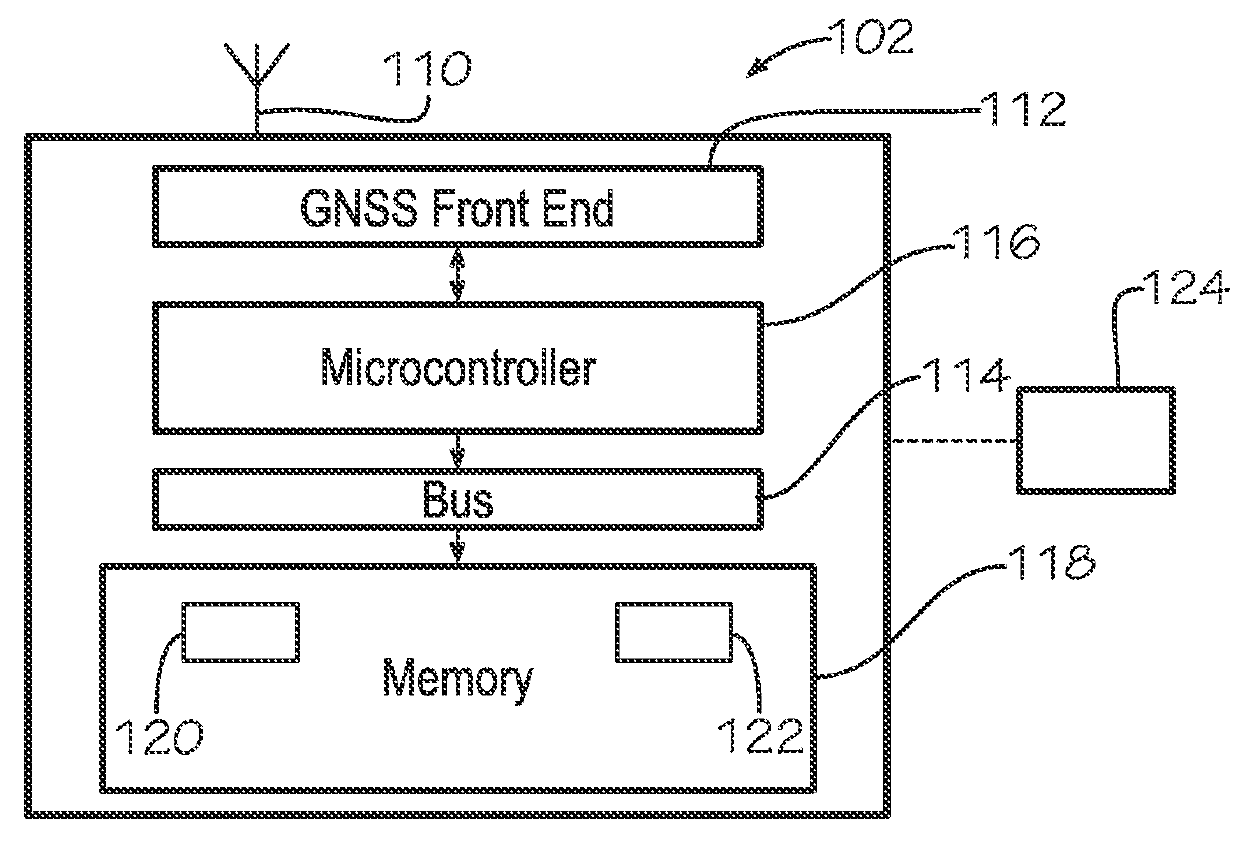
GNSS receiver
A method for use with a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver is provided. The method includes obtaining a first system time from a satellite of a first satellite navigation system, obtaining a second system time from a satellite of a second satellite navigation system, calculating a difference between the first system time and the second system time to obtain a number of leap seconds between Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the second satellite system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
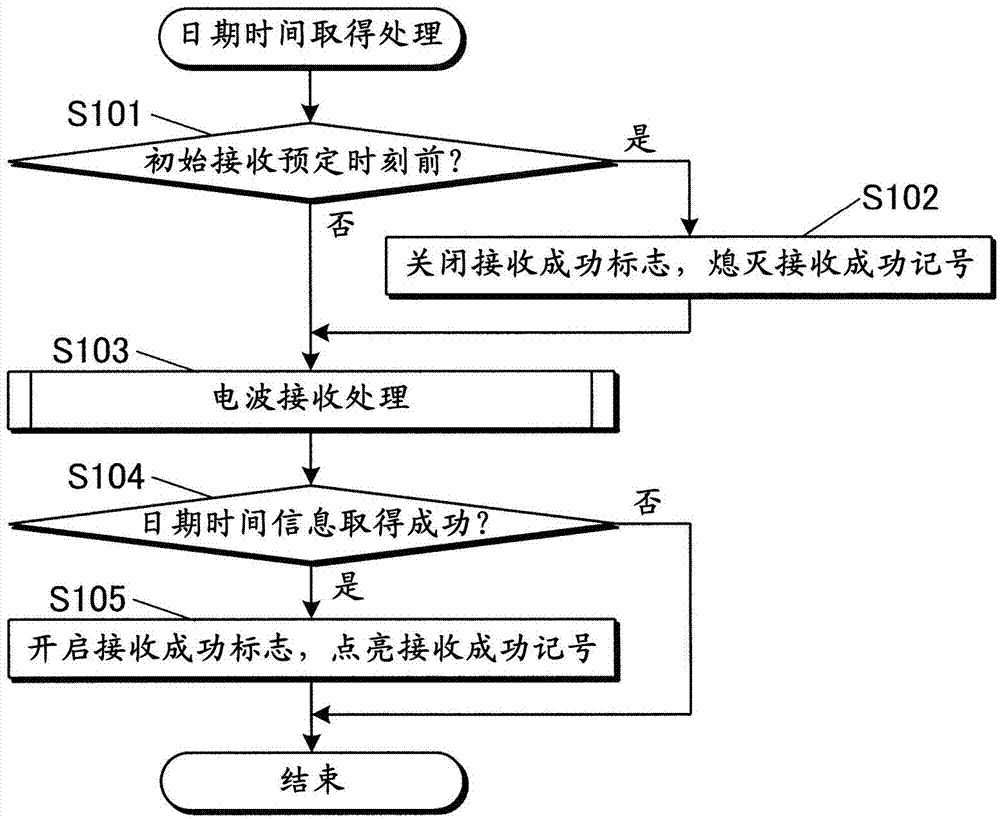
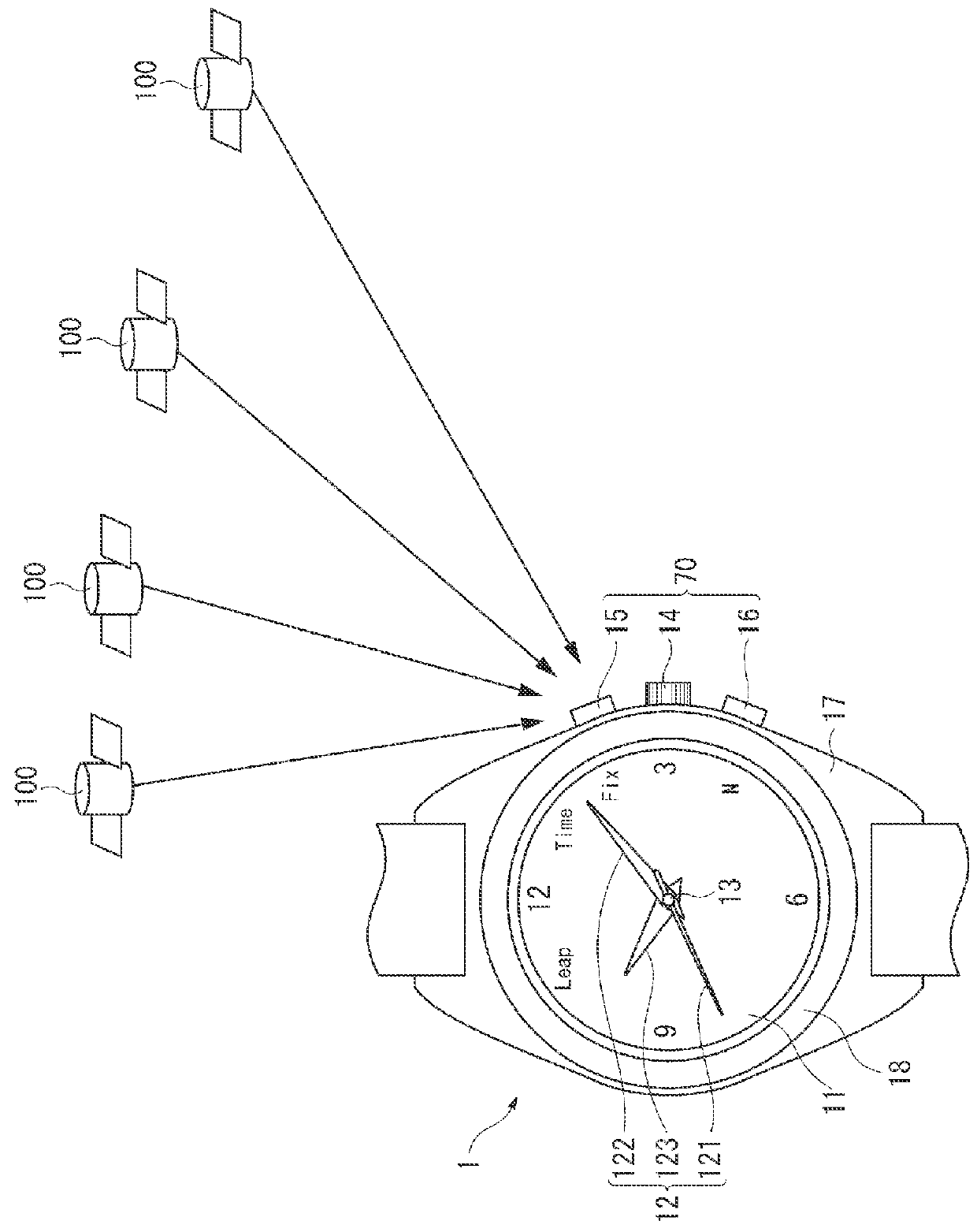
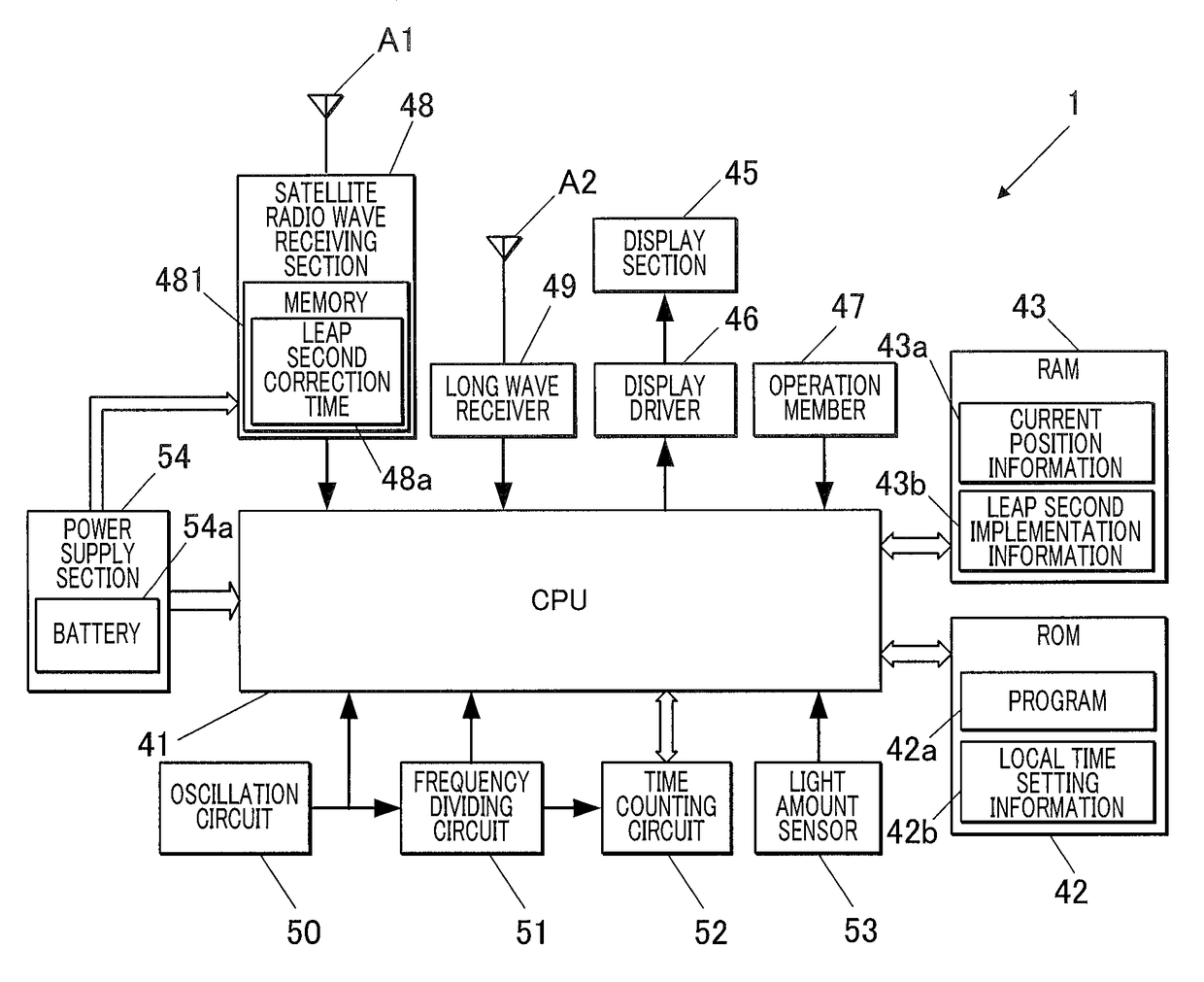
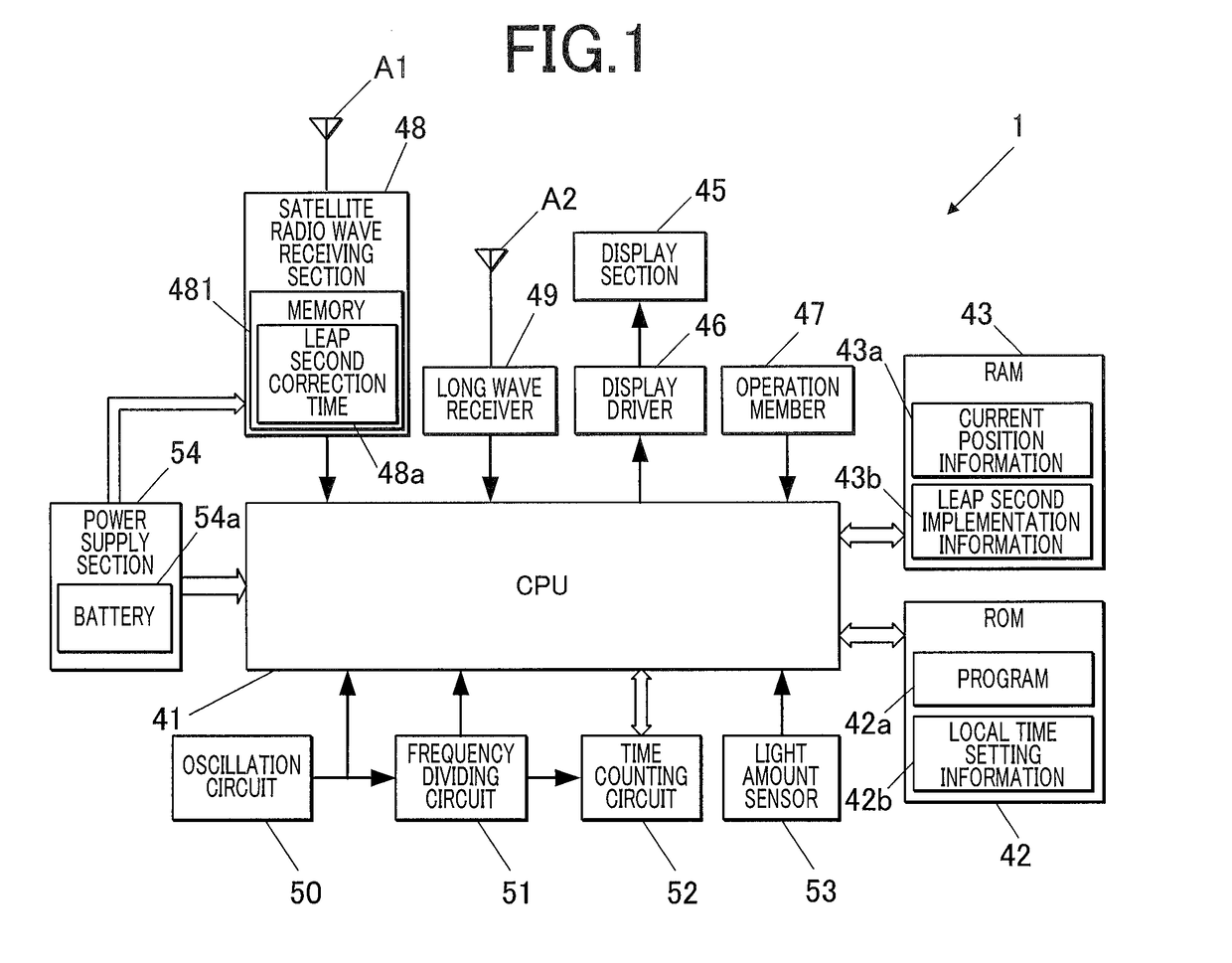
Radio-Controlled Timepiece
ActiveUS20150198928A1Suppressing increaseGrowth inhibitionMechanical clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesTime informationEngineering
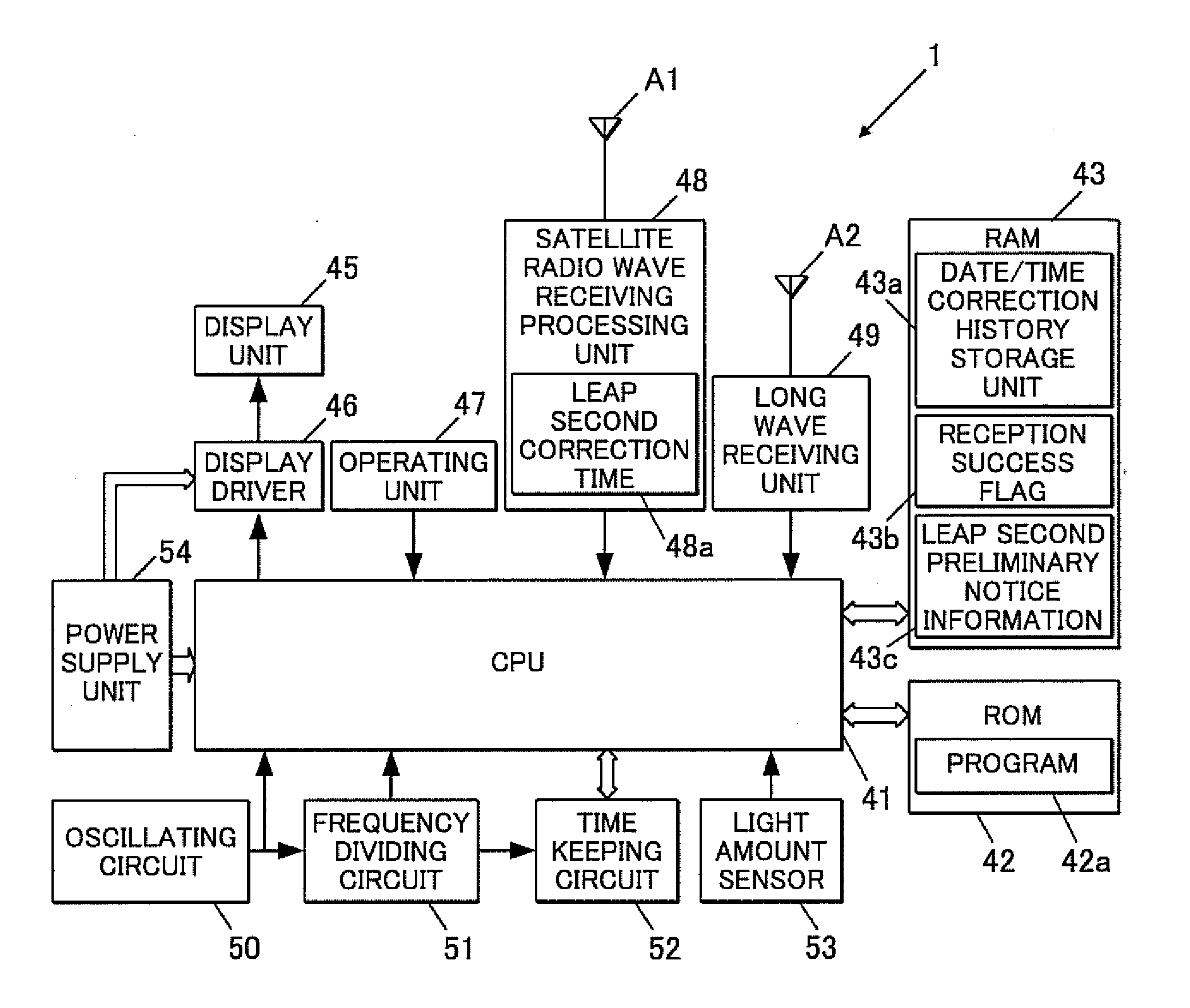
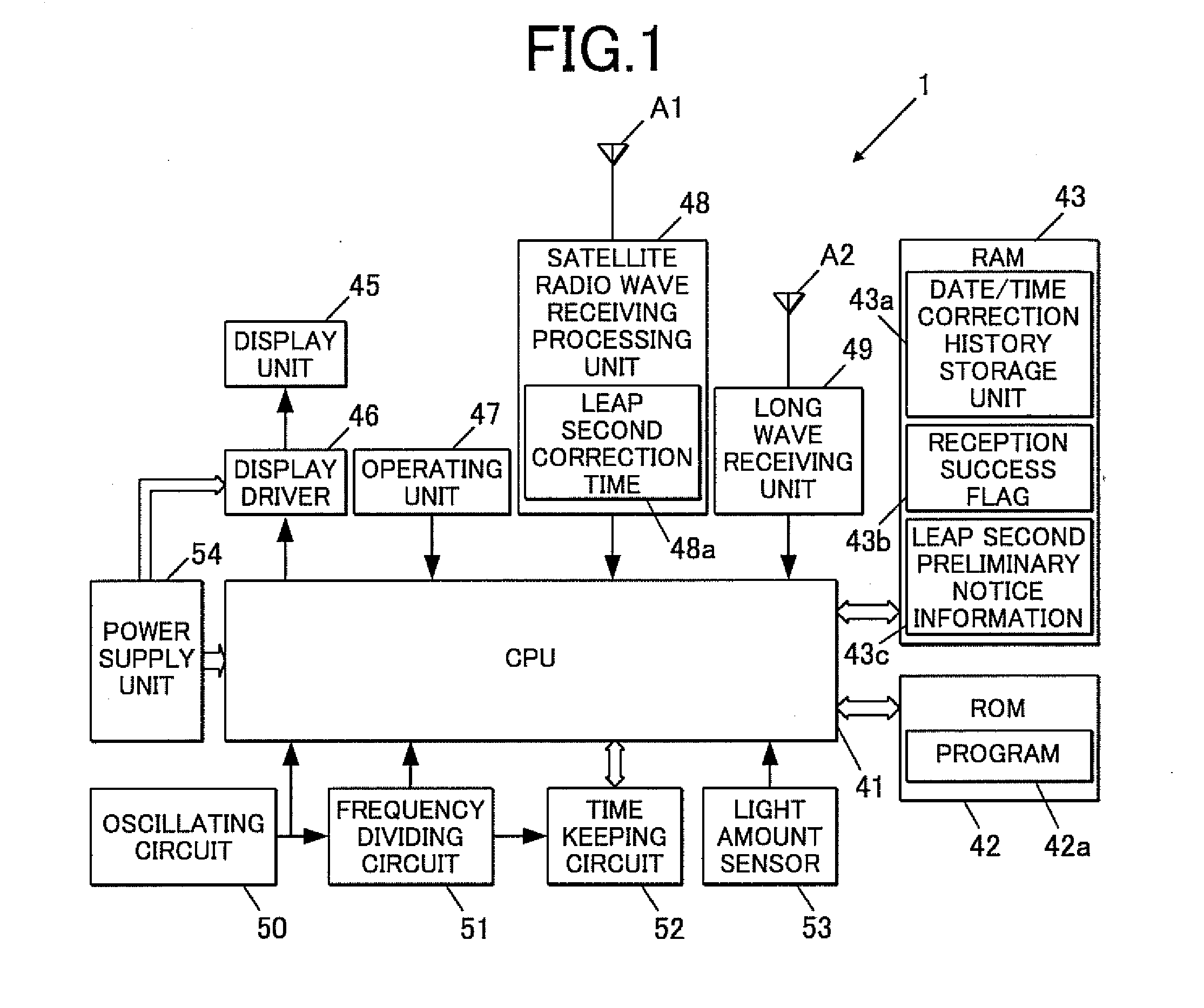
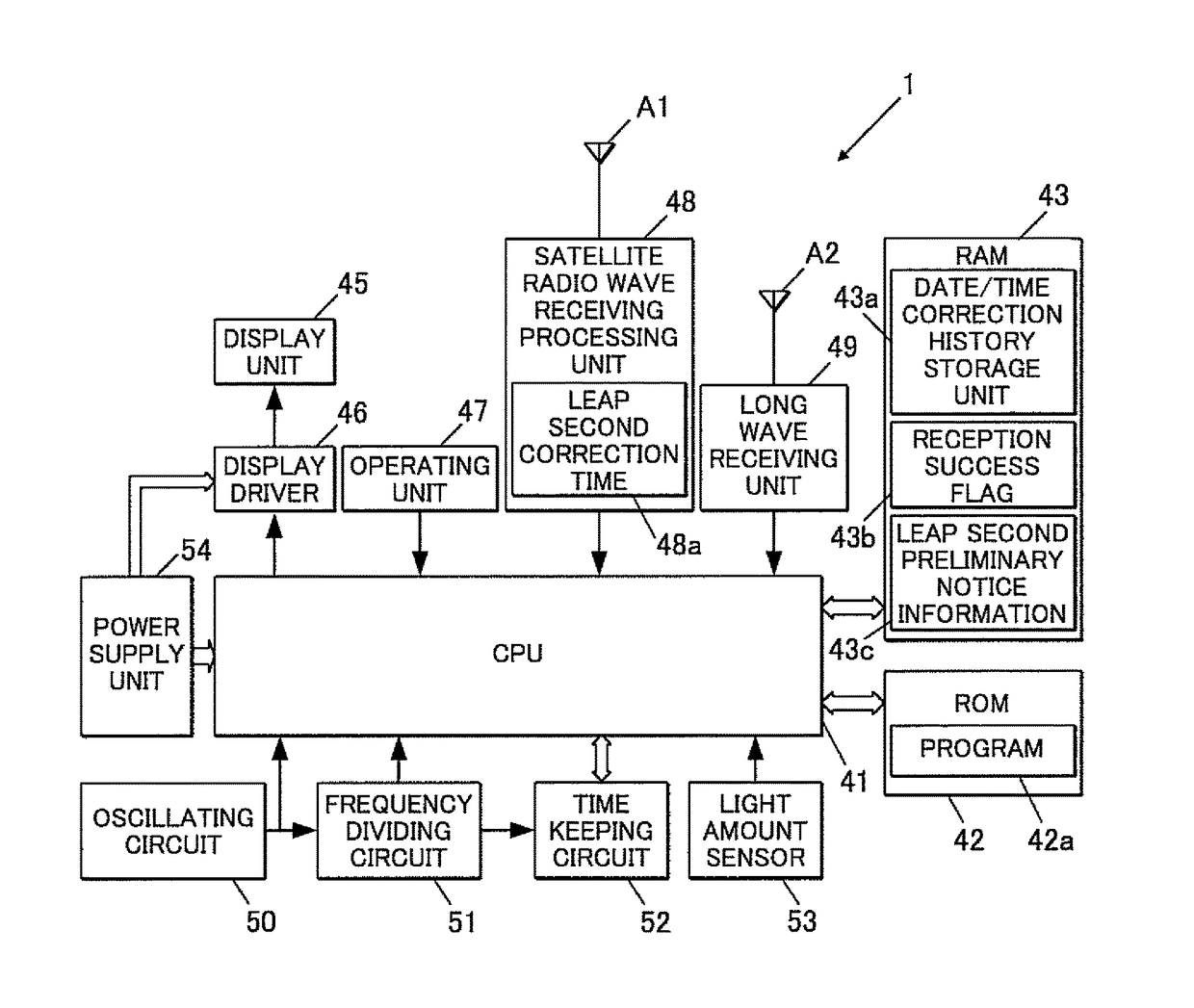
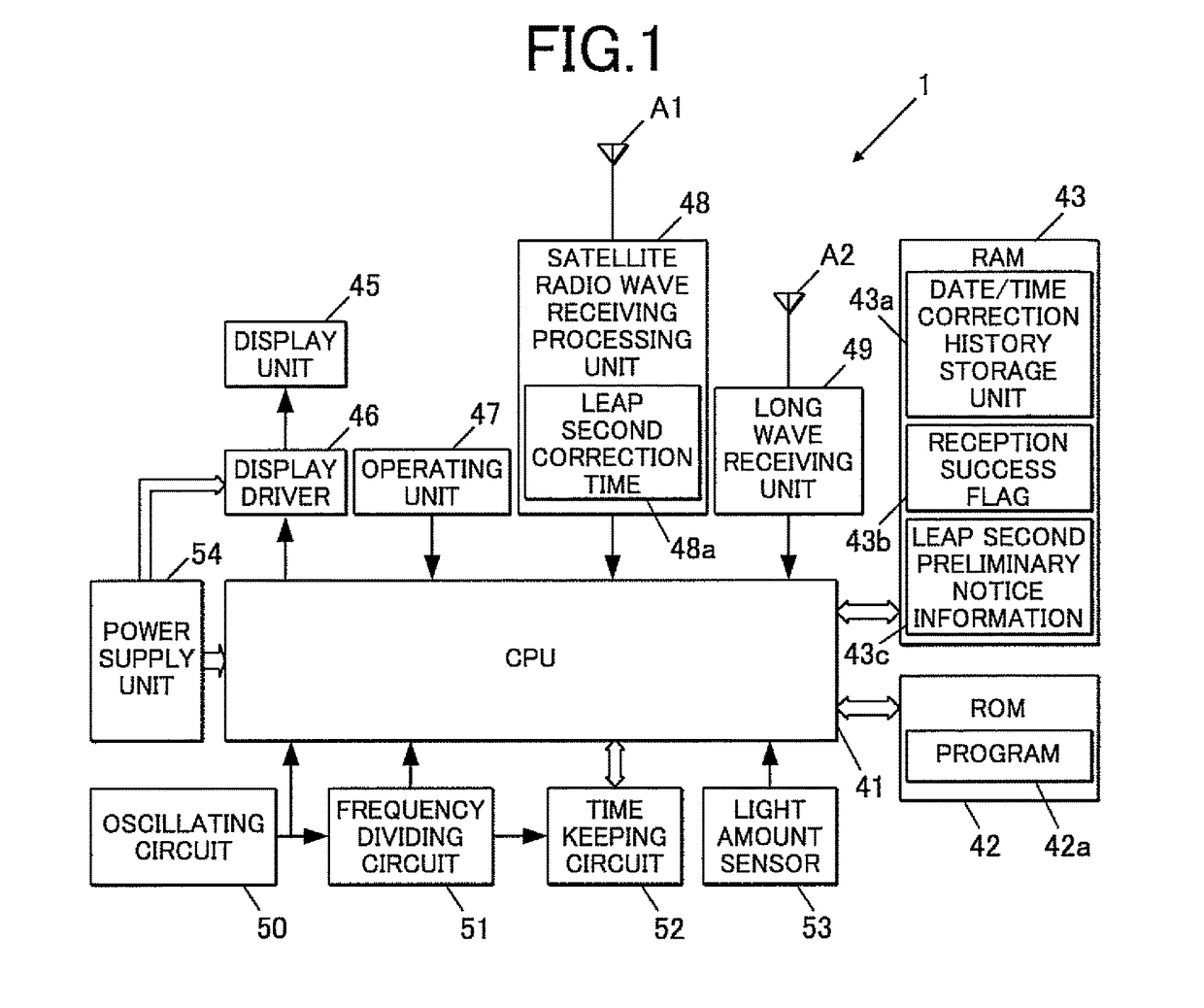
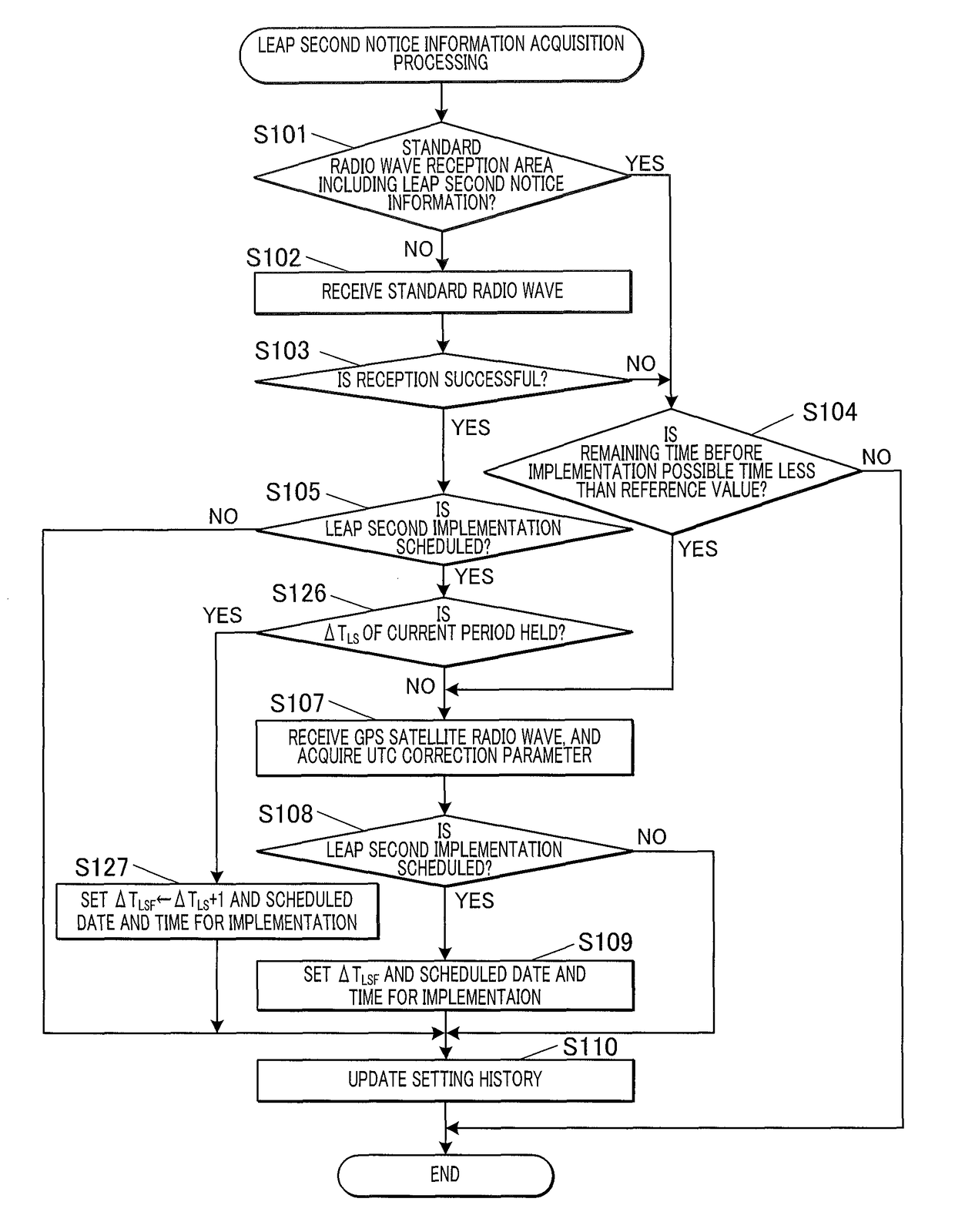
A radio-controlled timepiece is shown including the following. A timekeeping unit keeps date and time. A date / time obtaining unit obtains date / time information from outside to correct the date and time of the timekeeping unit. A preliminary notice information obtaining unit obtains from outside preliminary notice information regarding whether leap second adjustment in which a leap second is inserted or deleted is executed. A date / time obtaining necessity setting unit sets whether the date / time information needs to be obtained based on history of obtaining the date / time information. The date / time obtaining necessity setting unit sets that the date / time information needs to be obtained when the preliminary notice information is not obtained by the adjustment possible date / time or the leap second adjustment is executed at the adjustment possible date / time, and does not change setting when the preliminary notice information is obtained and the leap second adjustment is not executed.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
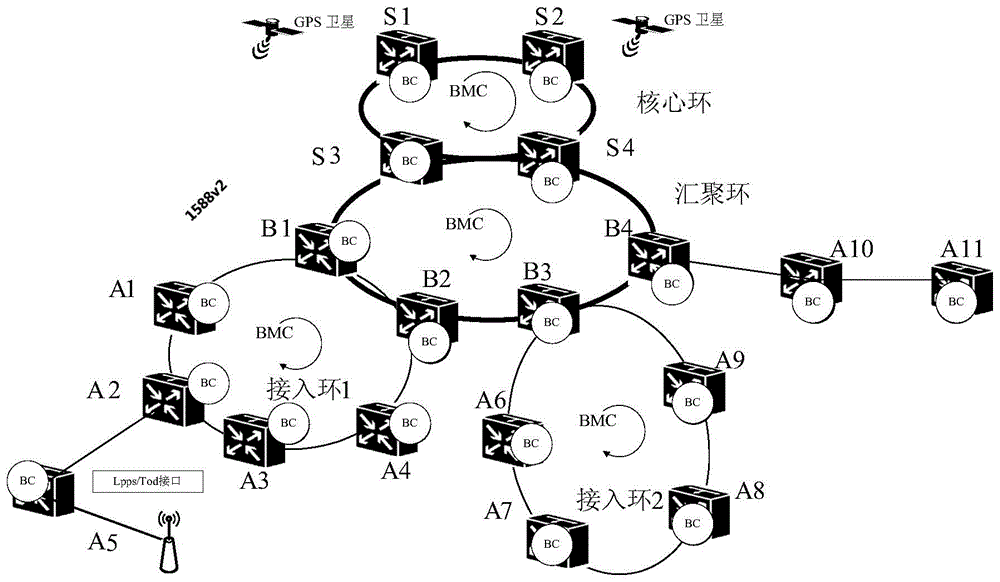
IRIG-B-based time and frequency synchronization state information coding format and coding method
ActiveCN104601268ATroubleshoot delivery issuesSolve the problem that some key time synchronization status information cannot be transmittedTime-division multiplexInformation transmissionCoded element
The invention discloses an IRIG-B-based time and frequency synchronization state information coding format and coding method. Through regulating and improving an IRIG-B coding method and redefining partial bytes of an IRIG-B code element, the time synchronization state information transmission can be realized, the problem that an existing IRIG-B coding method cannot transmit some key time synchronization state information is solved, and accordingly each node in a time synchronization network can monitor leap seconds, time service sources, time quality and frequency quality.
Owner:DATANG TELECOM TECH CO LTD
Radio-controlled timepiece
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
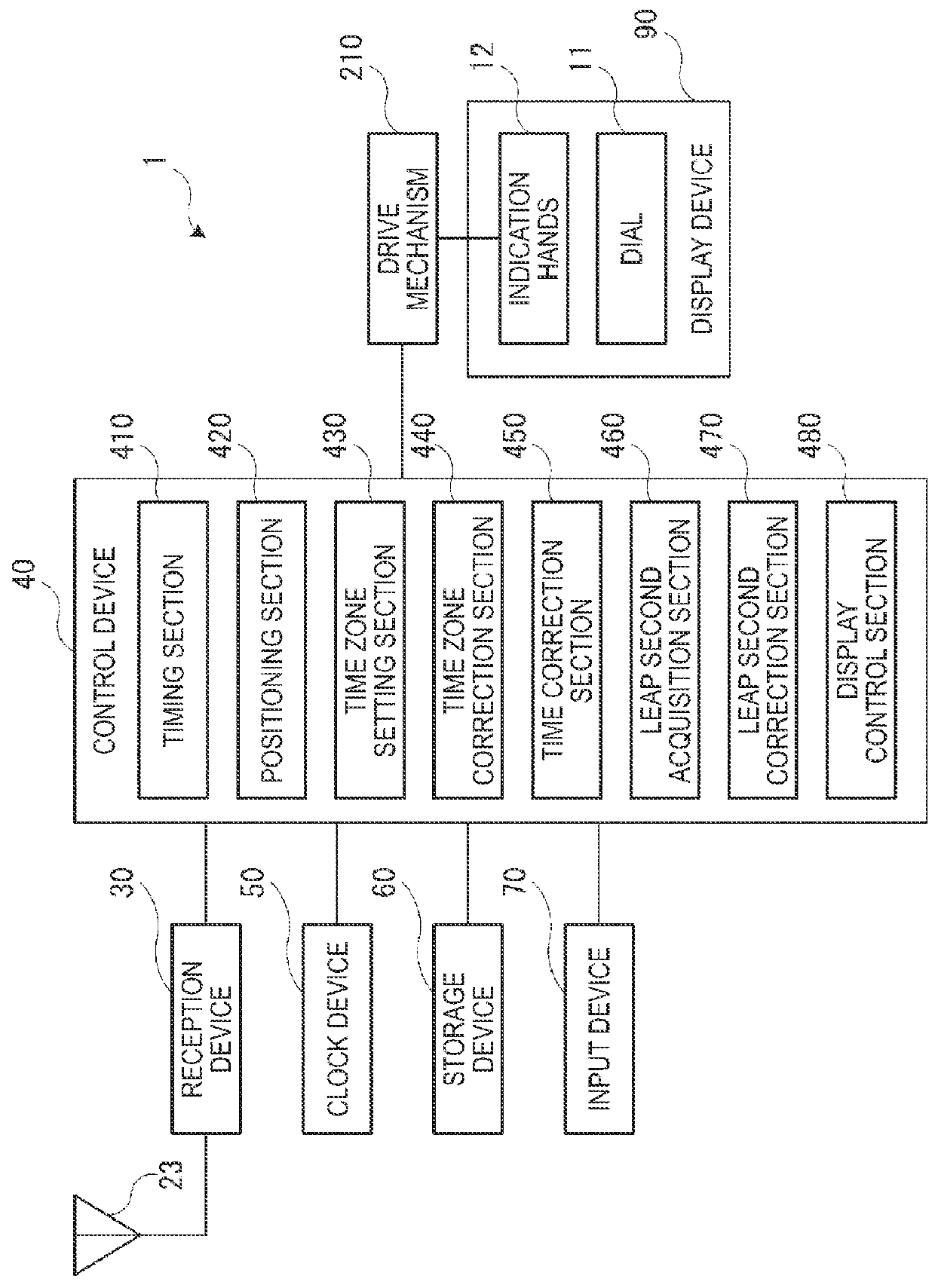
Electronic timepiece and method for controlling display operation of electronic timepiece
An electronic timepiece includes a display section, a display control section, a reception section, a clock section, a timing section, a leap second acquisition section, a time correction section that corrects internal time information by using time information acquired by the timing section, and a leap second correction section that corrects the internal time information by using leap second information acquired by the leap second acquisition section. In a case where the operation of the timing section is followed by the operation of the leap second acquisition section, the time correction section corrects the internal time information by using the time information acquired by the timing section, and the display control section causes the display section to display, before the leap second acquisition section acquires the leap second information, time based on the internal time information corrected by the time correction section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Radio timepiece, method for acquiring leap second correction information and recording medium
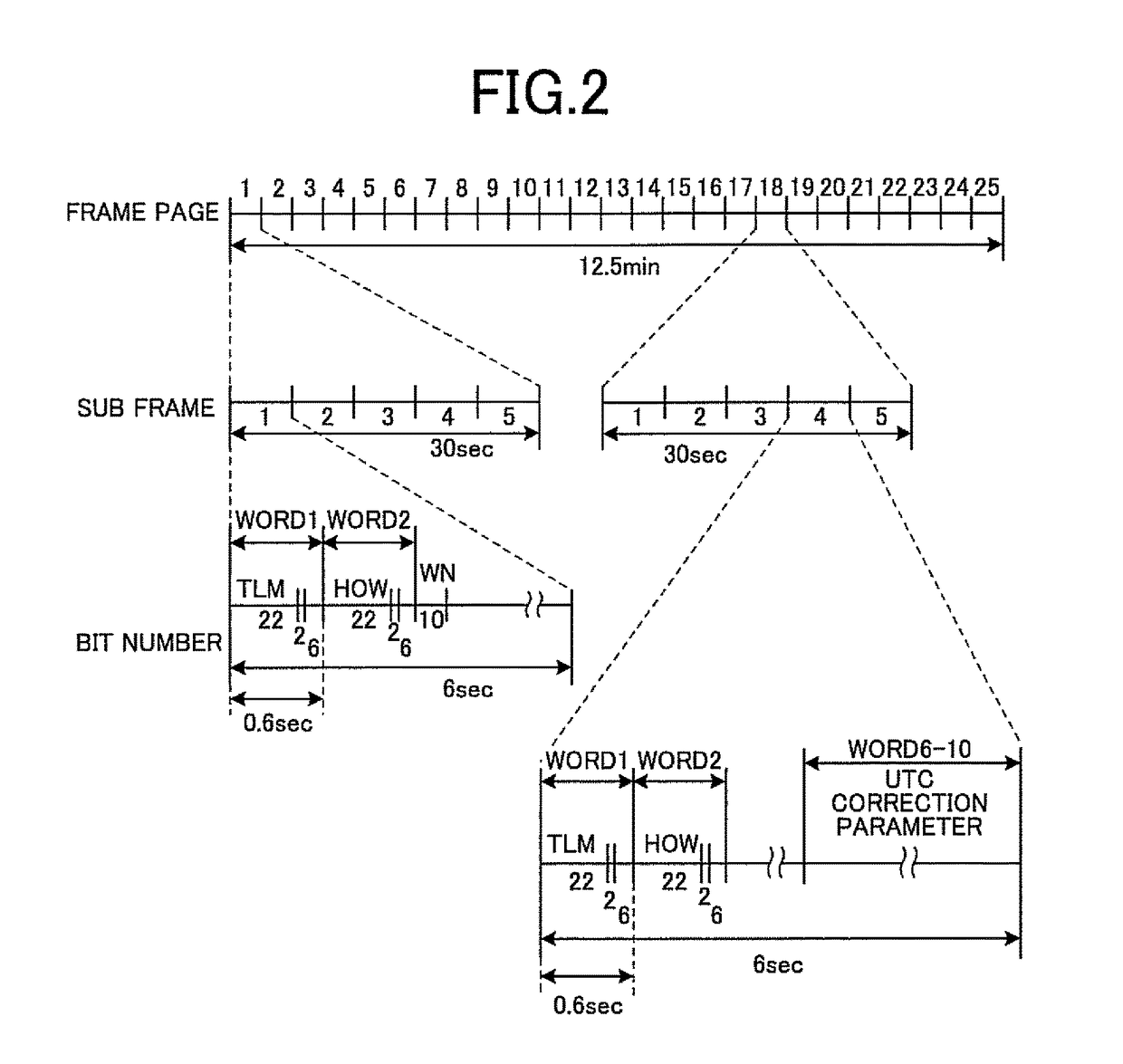
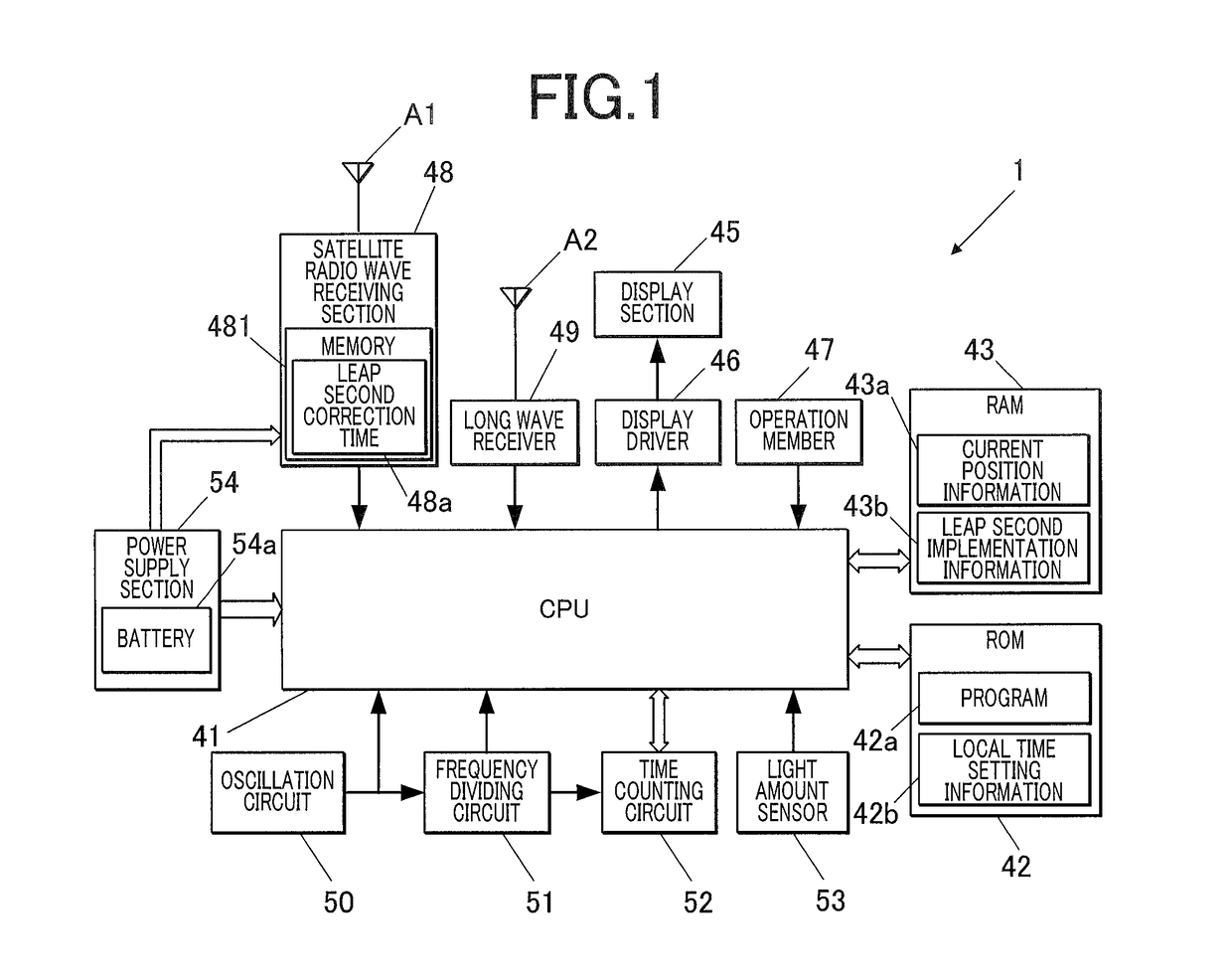
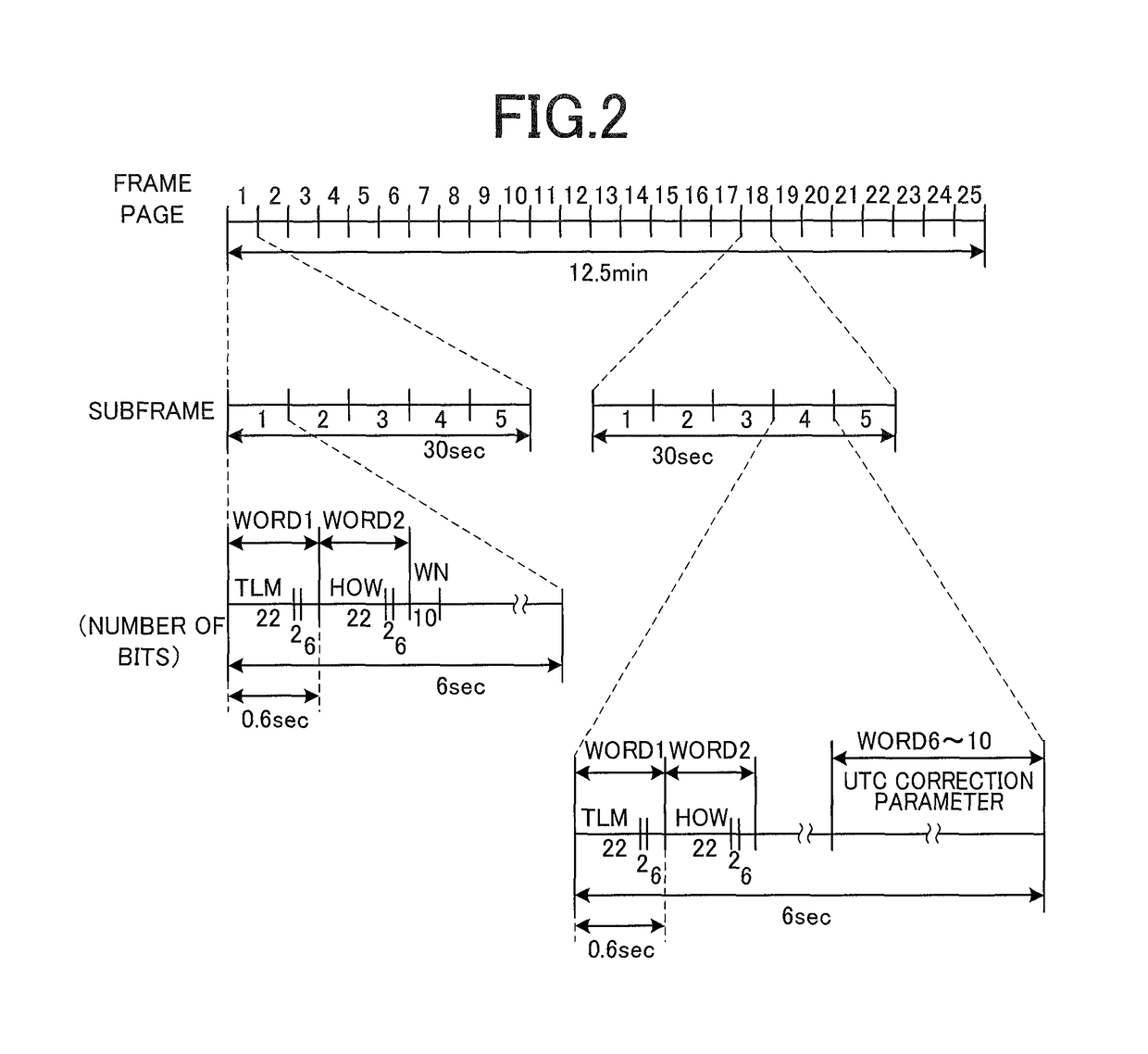
ActiveUS20170277141A1Efficient implementationCount moreSynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesSatellite radioProgram planning
A radio timepiece, including: a satellite radio wave receiver; a ground wave receiver; a memory; and a controller, wherein the controller performs area determination operation of determining whether a current position is located within a geographical range where the ground wave receiver is capable of acquiring notice information regarding implementation / non-implementation of the leap second adjustment, when the controller determines that the current position is located within the geographical range, the controller controls the ground wave receiver to acquire the notice information, the controller determines, with the notice information, whether the leap second adjustment is scheduled to be implemented at an implementation candidate timing of the leap second adjustment, and when the controller determines that the leap second adjustment is scheduled to be implemented, the controller changes the leap second correction information at or after the implementation candidate timing.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Electronic timepiece and reception control method for an electronic timepiece
ActiveUS8514667B2Reduce processor loadEasy to getSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationData miningLeap second
An electronic timepiece can easily acquire a leap second information reception time with minimal processor load. A first table groups leap second information reception times expressed by hour, minute, second, and day values into plural minute-second patterns of minute-second combinations that are common to plural hours, and relates numbers identifying these minute-second patterns to the day and hour values. The minute-second combinations are grouped by number in a second table. The number corresponding to the day and hour of the internal time is found from the first table (S1). A minute-second combination that is later than the internal time is found from the minute-second combinations corresponding to the acquired number (S2). And leap second reception time is calculated. If the resulting leap second reception time matches the internal time is determined (S9). If the times match, the leap second information is received (S10, S11).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
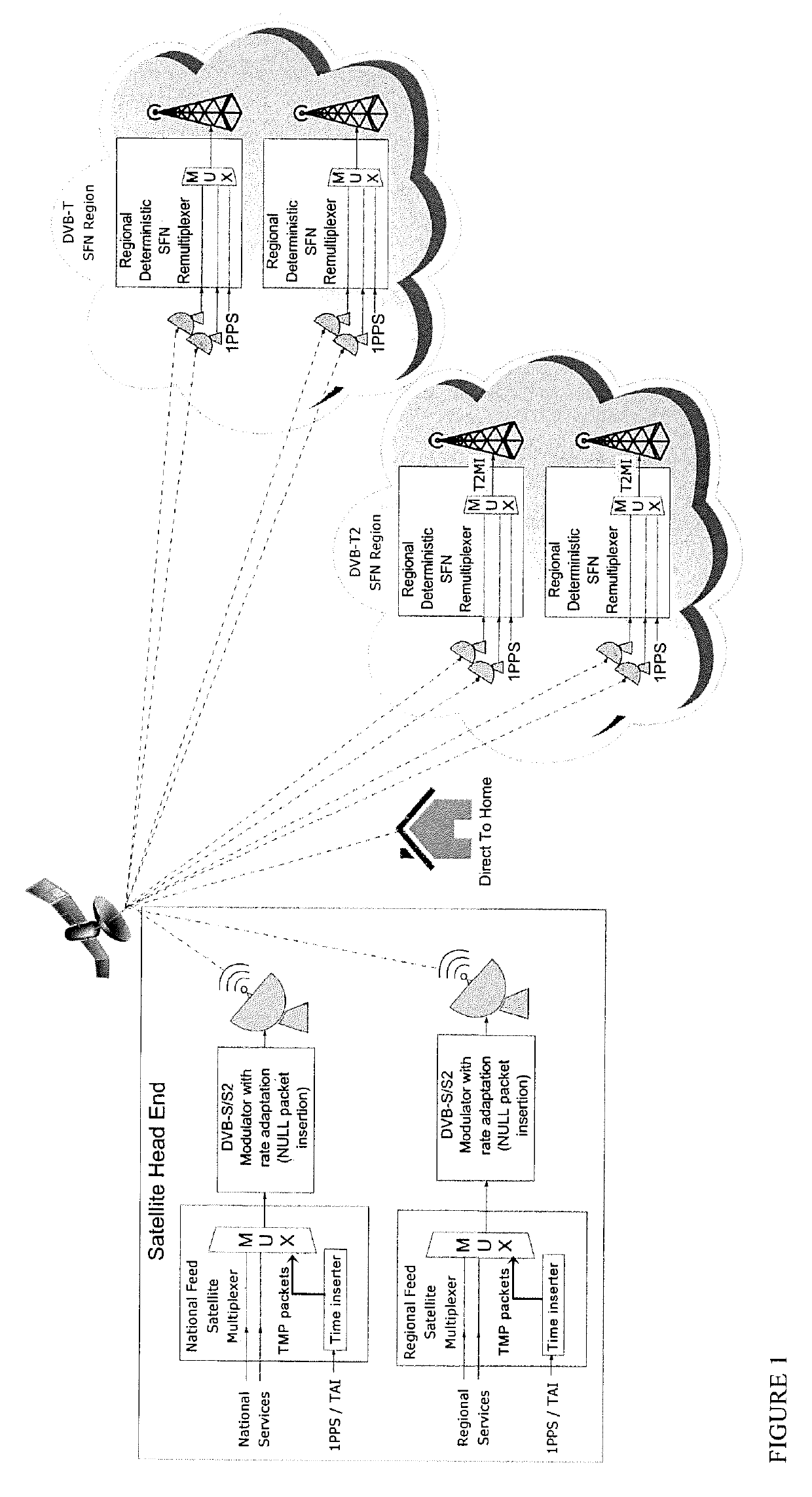
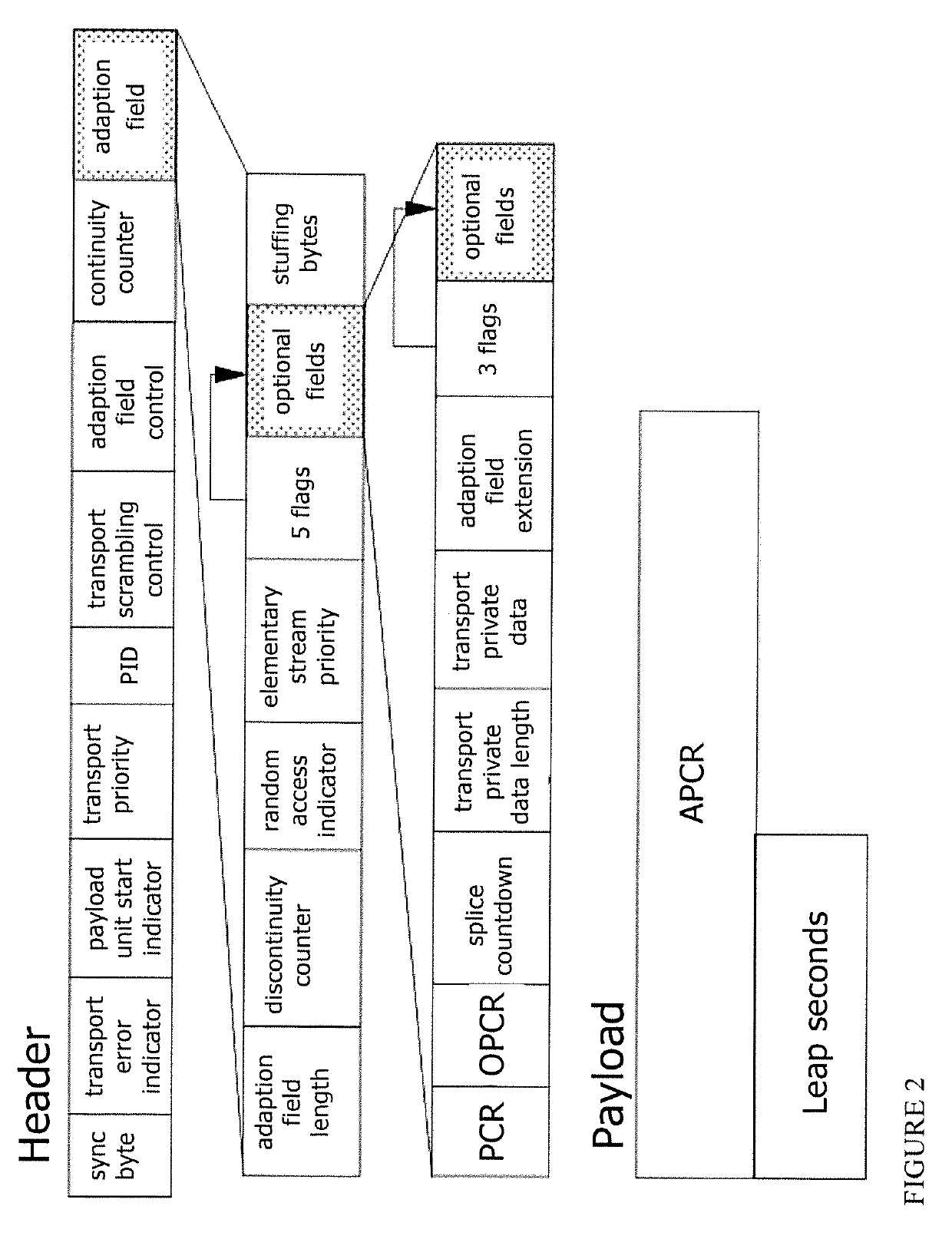
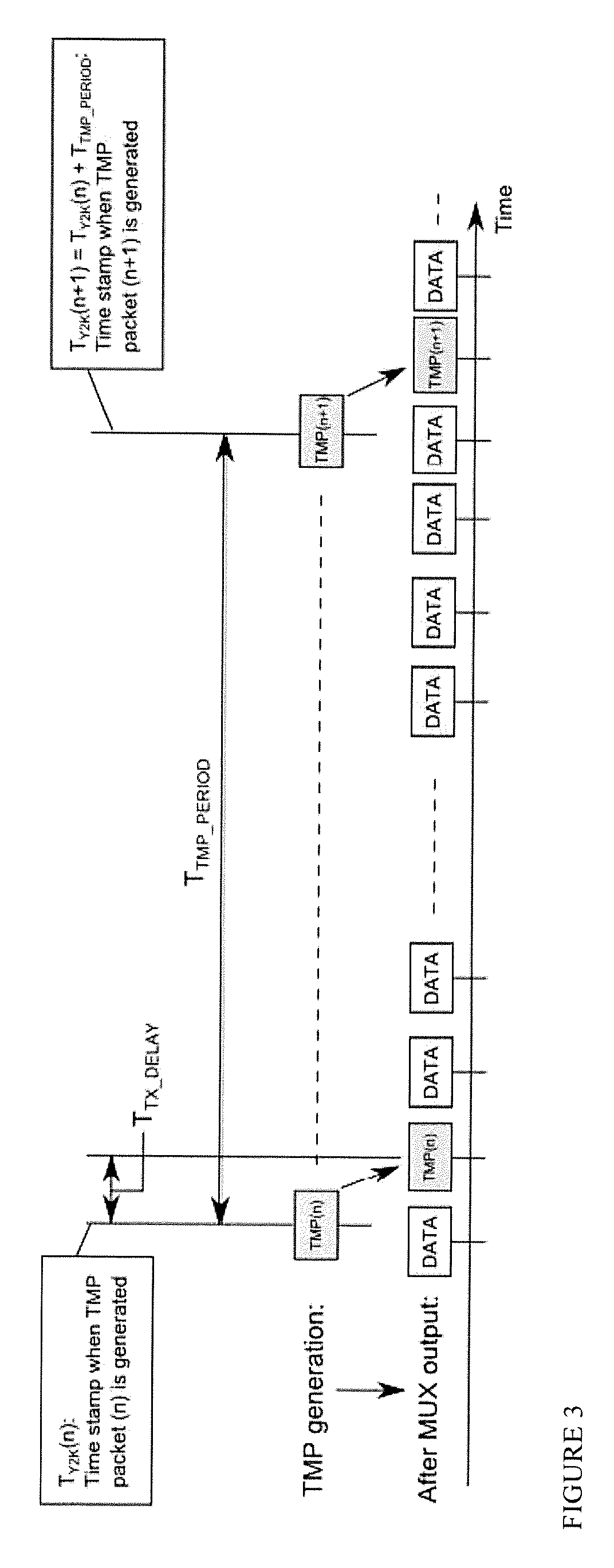
Deterministic re-multiplexing for dvb sfn networks
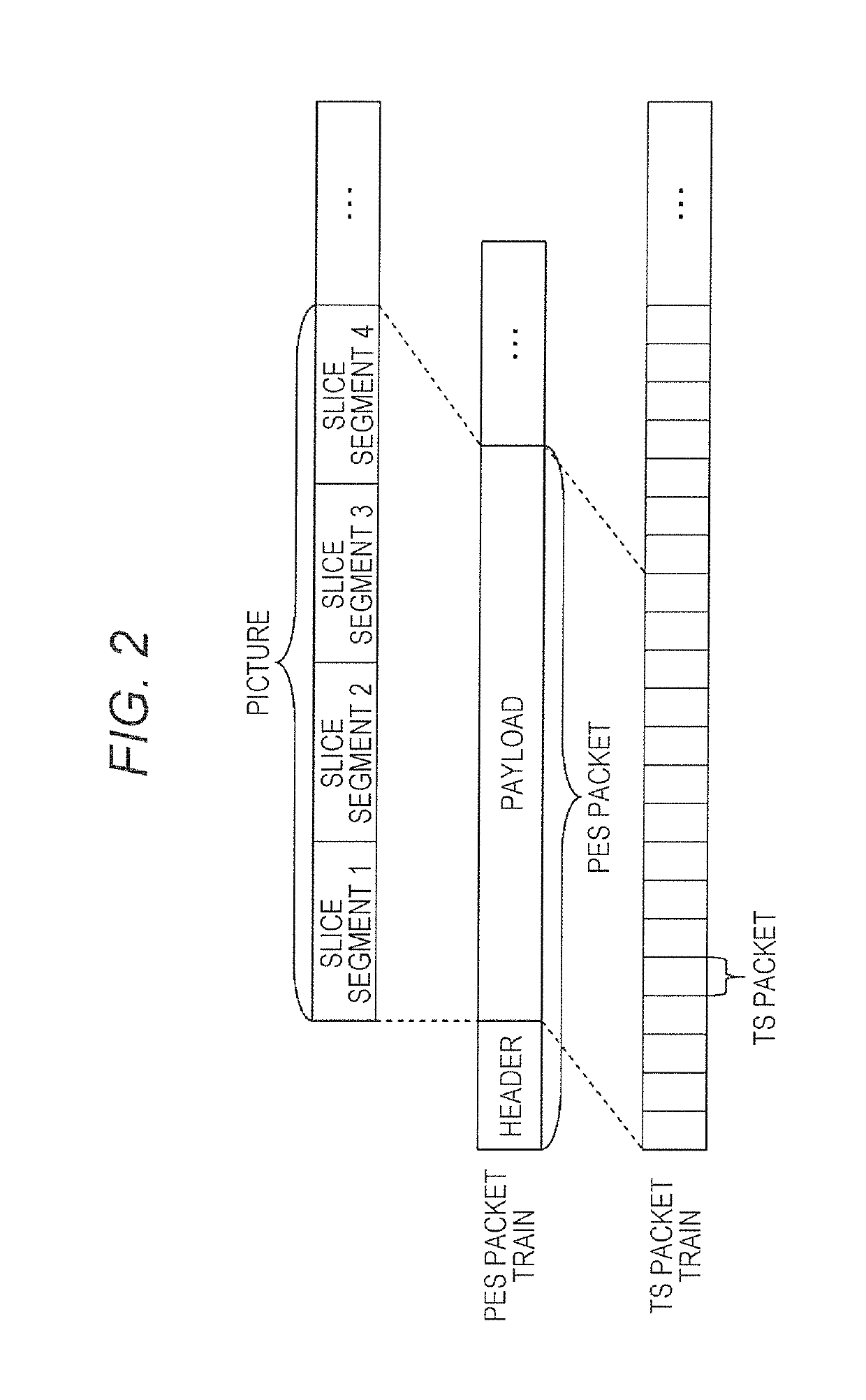
ActiveUS20190327008A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast-related systemsProgram clock referenceMultiplexing
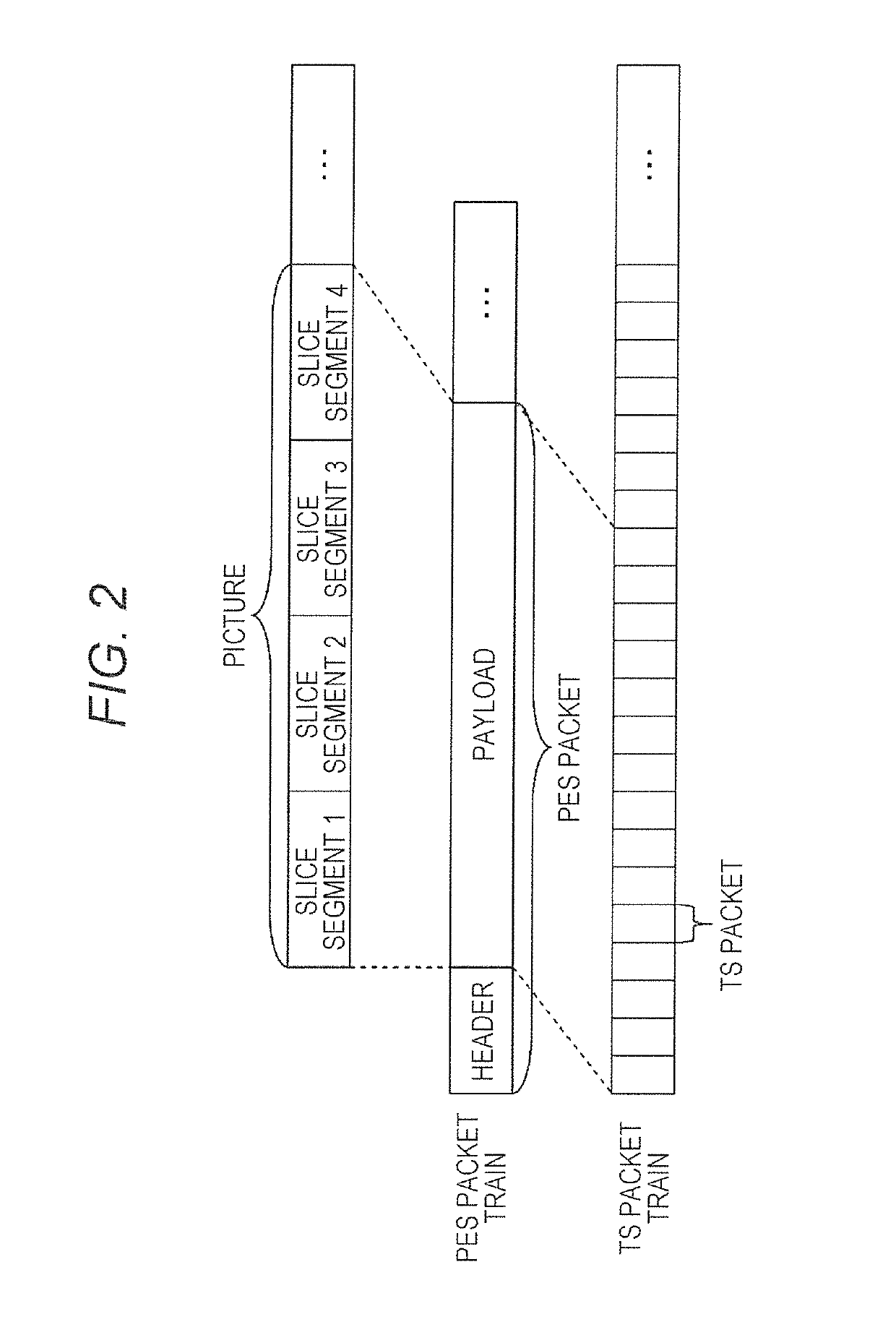
A method for adding Time Marker Packets, TMPs, comprising Metadata to an MPEG-2 transport stream transmitted via a broadcast network for providing a deterministic transport stream, comprising providing feeds of data from at least one source, where the feeds comprise payload packets being referenced by a common 1 PPS reference, and where the feeds are input to at least one multiplexer, MUX; providing Time Marker Packets, TMPs, as input to each multiplexer, where each TMP comprises a plurality of time stamps per second measured relative to said 1 PPS reference, and each TMP has a value representing an Absolute Program Clock Reference, APCR, at the time of transmission, where the APCR is based on the Epoch time, and where the TMP packet further comprises PCR, OPCR locked to said 1 PPS and UTC leap seconds. The invention is further defined by a device for executing said method, as well as a method for coding a deterministic transport stream in a Single Frequency Network, SFN, and a device for executing this method.
Owner:NEVION AS
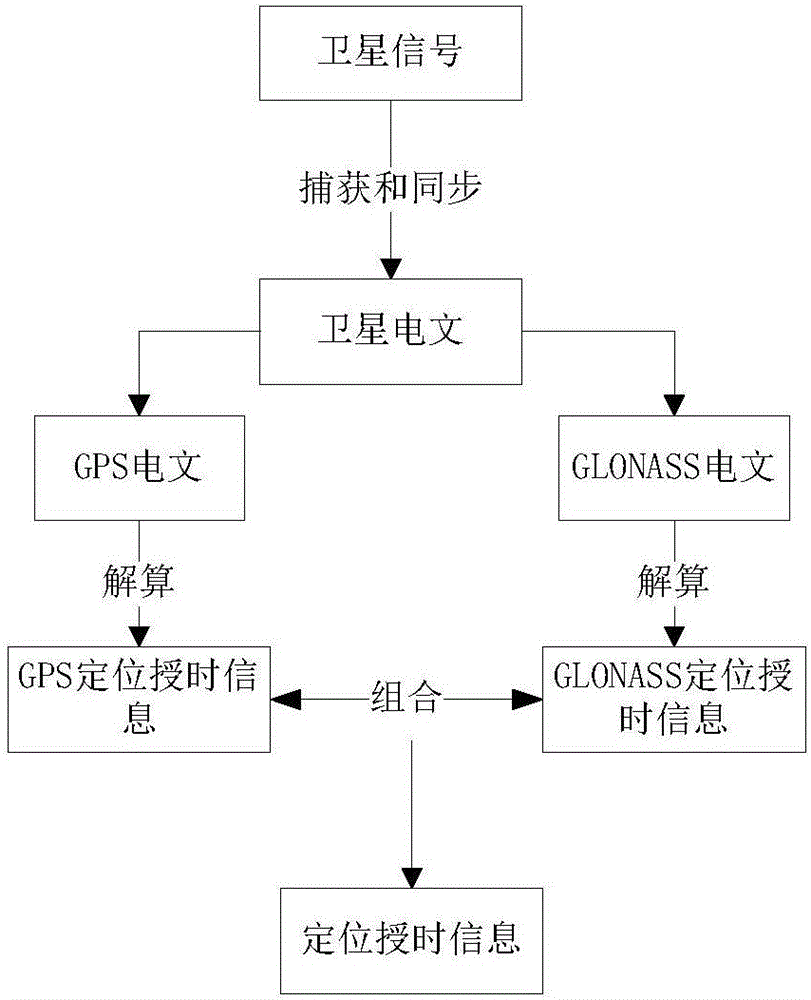
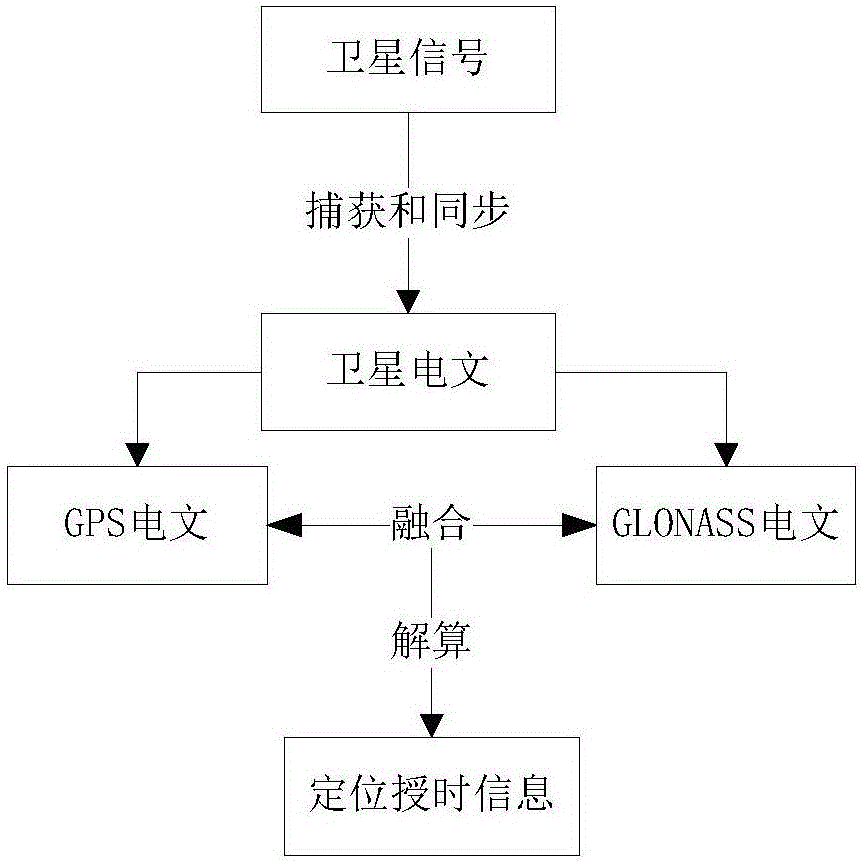
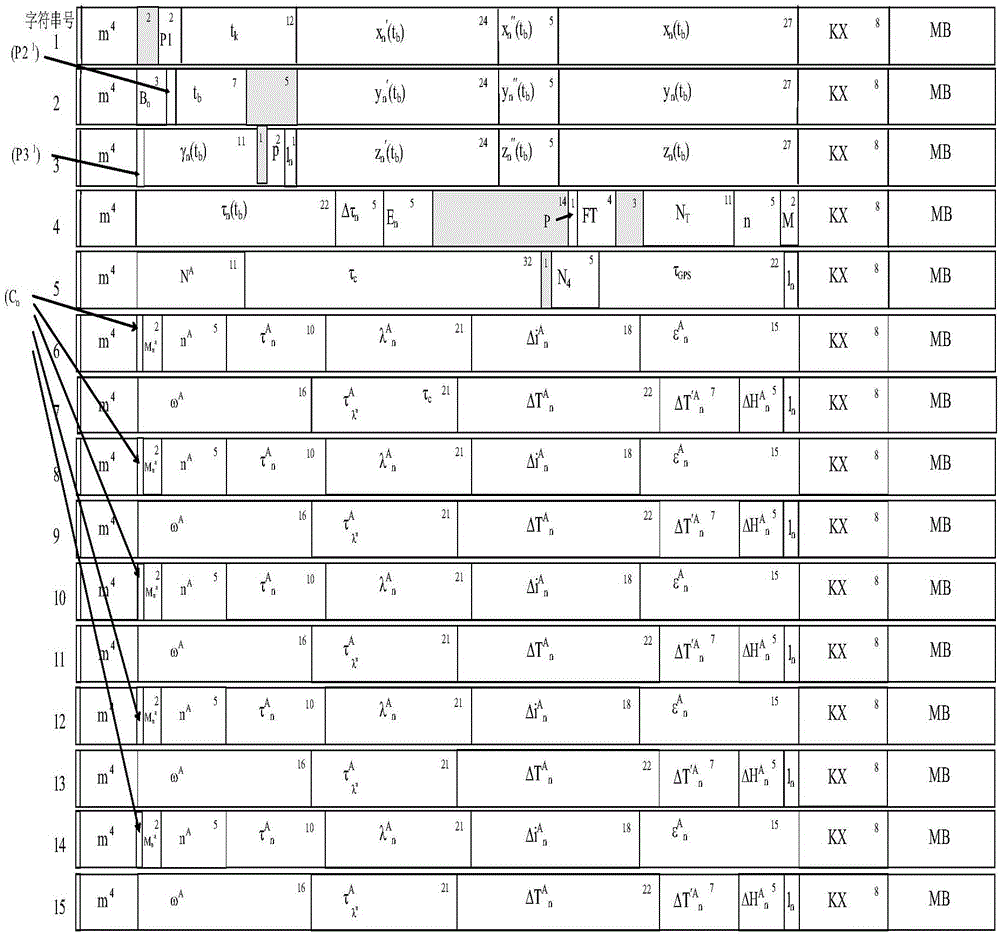
Integrated GPS and GLONAS positioning time service method
InactiveCN106405588AImprove performanceHigh time accuracySatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixLeap second
The invention discloses an integrated GPS and GLONAS positioning time service method. The method comprises steps of S1 present hour, minute and second determination; S2, leap second correction; and S3, previous circle overturning. Through the method, after a satellite of two systems is captured, in a resolution process, difference of a GPS and GLONASS system in a navigation message is utilized to realize mutual complementation, depth fusion is carried out, a mode of first resolution and then combination in the prior art is changed, performance of an integrated GPS and GLONAS receiver in the prior art is effectively improved, including reducing the first positioning time, improving time service precision and effectively processing special conditions such as leap second correction and thousand-circle overturning.
Owner:重庆九洲星熠导航设备有限公司
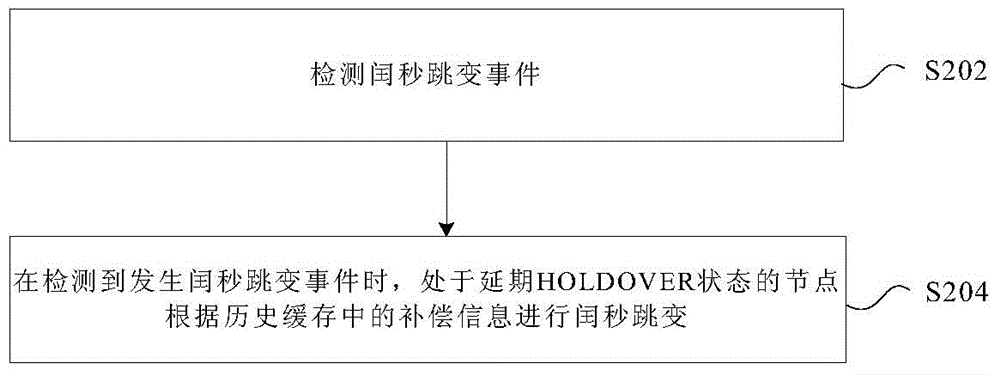
Leap second jumping processing method and device
InactiveCN106160909AHigh precisionSolve the problem that the accuracy of time synchronization of the entire network cannot be improvedTime-division multiplexRadio-controlled time-piecesLeap secondOperations research
The invention provides a leap second jumping processing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: detecting a leap second jumping event; and when the leap second jumping event is detected, carrying out leap second jumping by a node in a delayed HOLDOVER state according to the compensation information in a historical buffer. By adopting the leap second jumping processing method and device provided by the invention, the problem in the prior art that the accuracy of the time synchronization of an overall network cannot be improved is solved, and thus an effect of improving the accuracy of the time synchronization of the overall network is achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Electronic Timepiece And Method For Controlling Display Operation Of Electronic Timepiece
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Intelligent test system and method used for IRIG (Inter-range Instrumentation Group)-B code fault-tolerant function of time synchronizer
ActiveCN102591194AImprove the level of intelligenceConvenient and objective evaluationSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationTest efficiencyTest performance
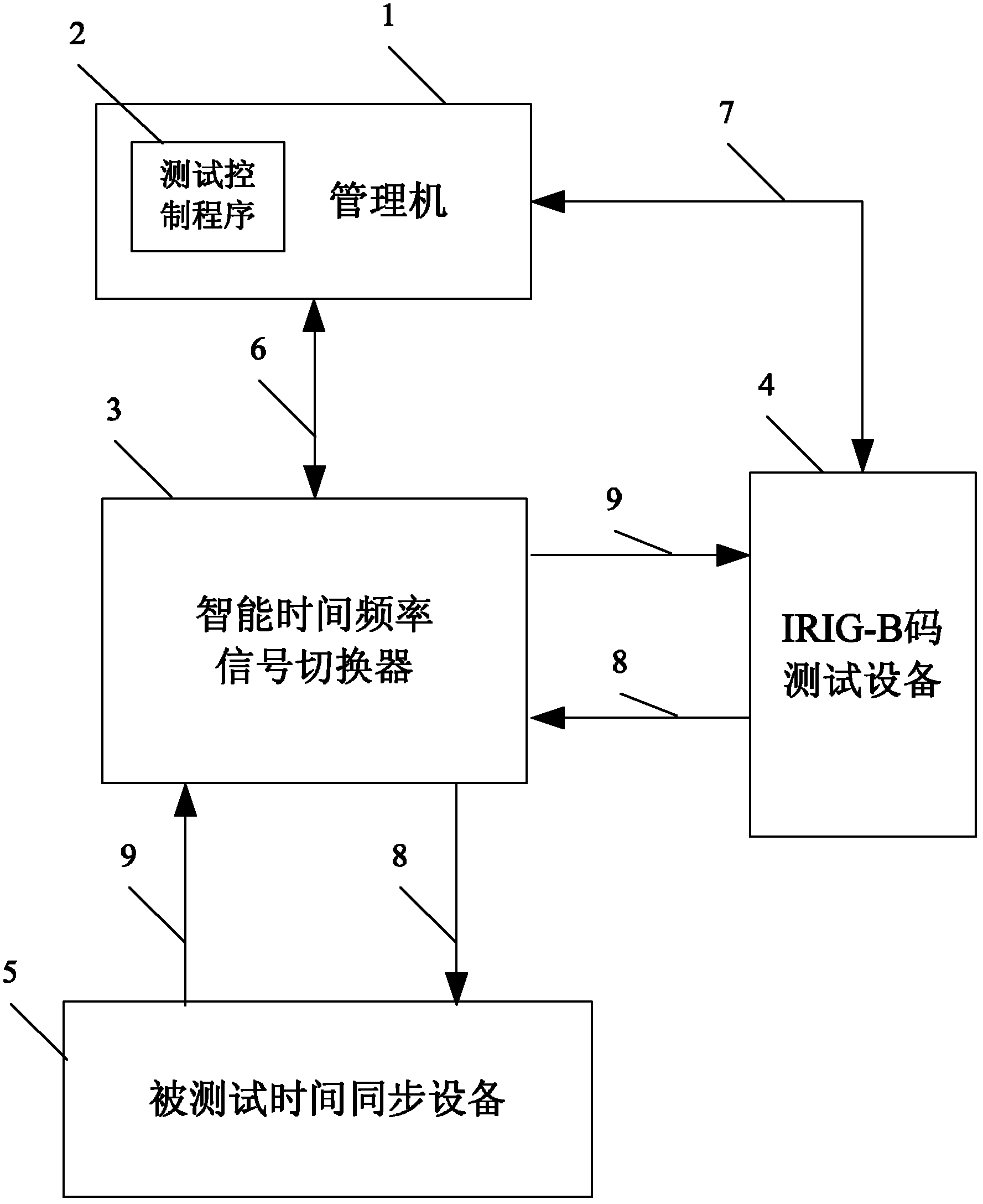
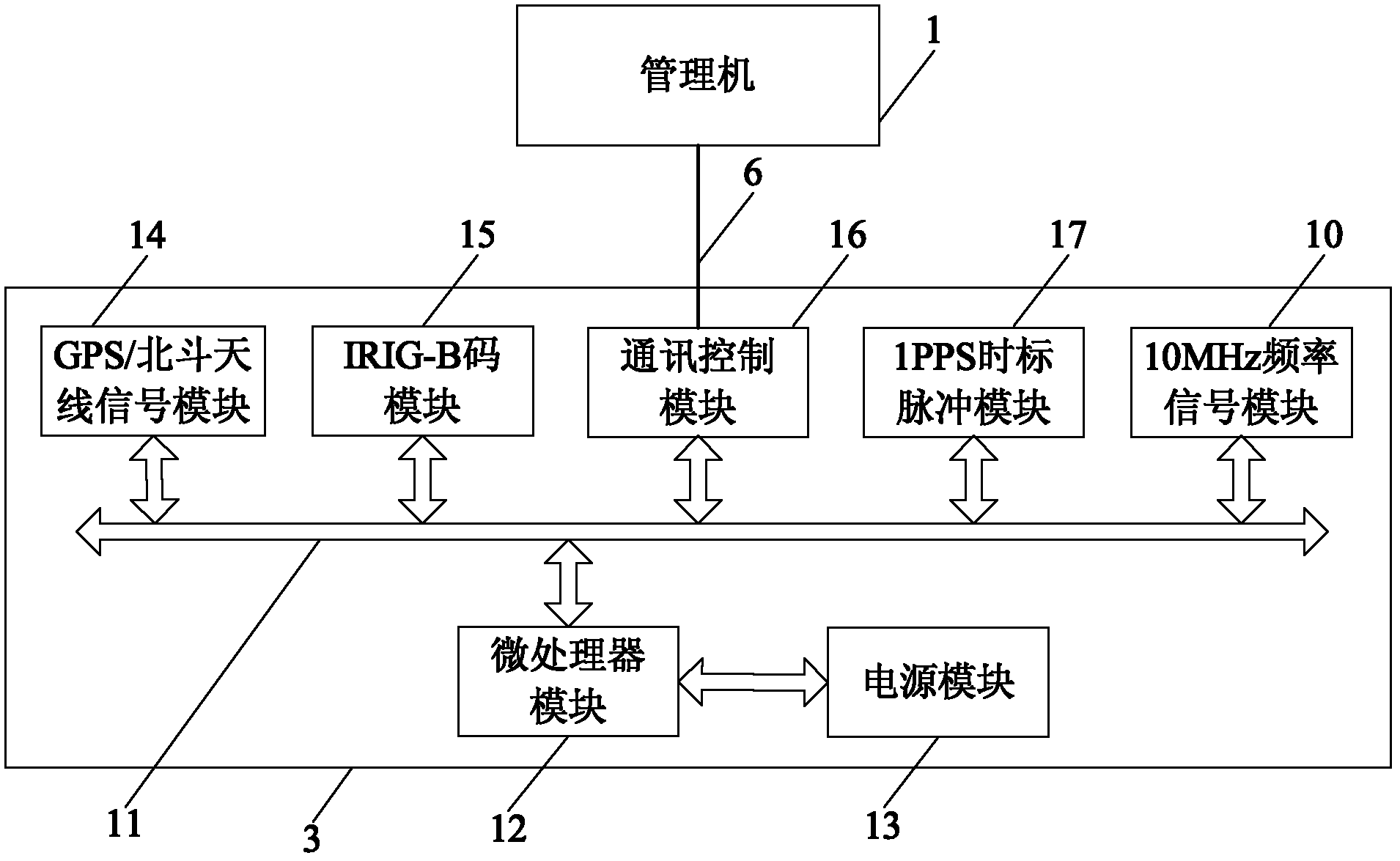
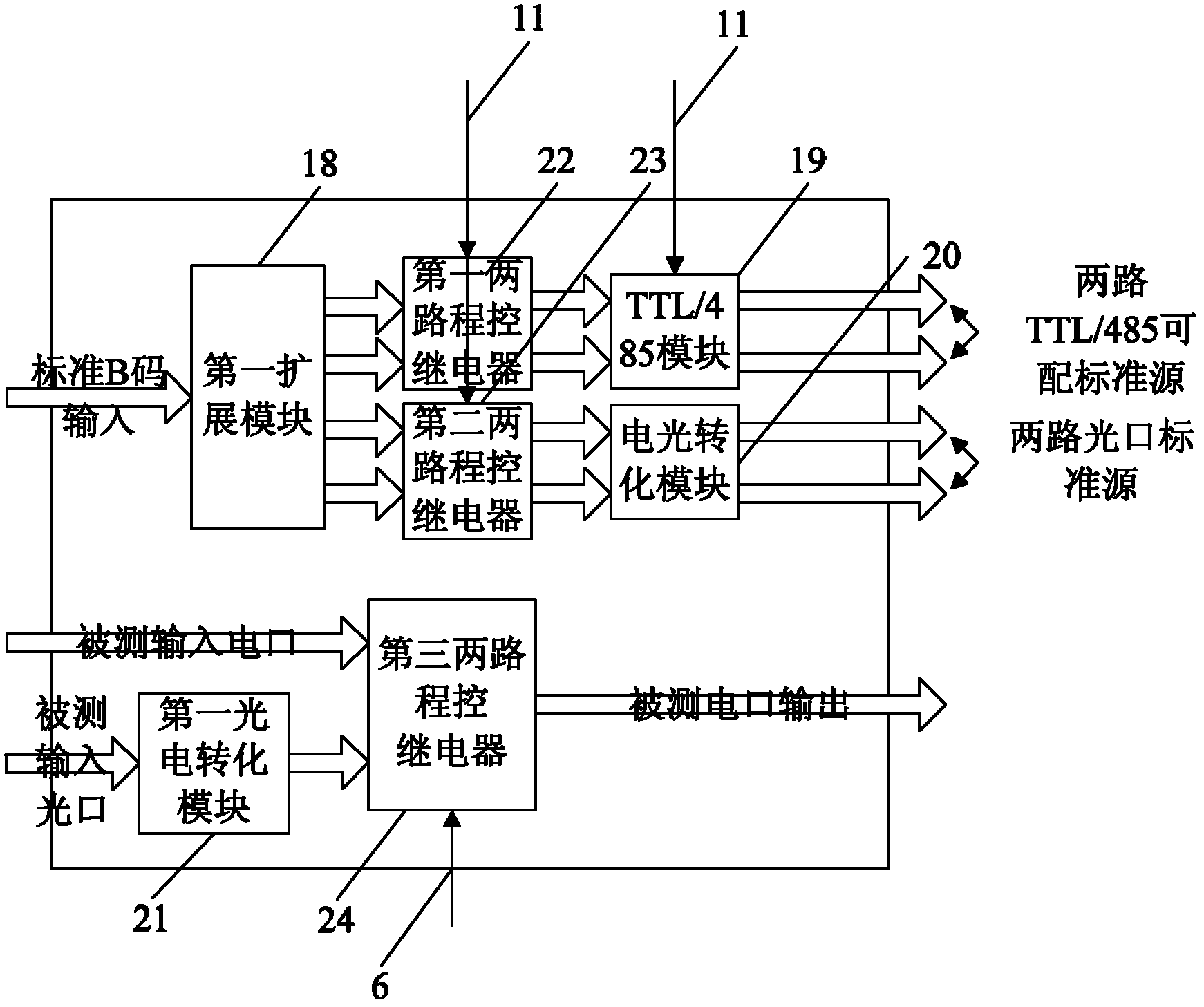
The invention relates of an intelligent test system and a method used for IRIG (Inter-range Instrumentation Group)-B code fault-tolerant functions of a time synchronizer. The intelligent test system comprises a management machine and an IRIG-B code test device, wherein the managing machine is used for running test, analysis and management programs, and the IRIG-B code test device is connected with the management machine by a communication link to realize program control. The intelligent test system is characterized by being provided with an intelligent time frequency signal switcher, the program control of the management machine is realized by the test, analysis and management programs in the management machine, and the switching of the program control is carried out by the intelligent time frequency signal switcher. The intelligent test system is used for testing an IRIG-B code precision recognizing function, an IRIG-B code leap second processing function, and a IRIG-B code leap yearprocessing function. Under the condition of no manual intervention, the intelligent test system and the test method can easily and effectively carry out an intelligent test on the IRIG-B code fault-tolerant function and performance of the time synchronizer, and actually enhance the intelligent level of testing the complex functions and the performance of the time synchronizer. The test performance is accurate, the test efficiency is high, and the test time is greatly shortened.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Transmitting method, receiving method, transmitting device, and receiving device
ActiveUS20190281328A1Broadcast-related systemsTime-division multiplexTime informationComputer science
A transmitting method of storing data configuring an application into a predetermined data unit and transmitting the stored data in the predetermined data unit, which includes: generating time specification information indicating an operation time of the application, based on reference time information received from an external source; and transmitting (i) the predetermined data unit and (ii) control information indicating the generated time specification information, wherein the control information includes the generated time specification information and identification information indicating whether or not the time specification information is time information indicating a time that is before a leap second adjustment.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Time Service Time Leap Second Processing Method
ActiveCN102281114BGuaranteed to workTo avoid the impact of time synchronizationTime-division multiplexSystem timeImpact time
The invention discloses a time service time leap second processing method, which includes two processes: the input is atomic time and leap second forecast, the output is coordinated universal time, and the input is coordinated universal time and leap second forecast, and the output is atomic time. The present invention adopting the above-mentioned technical scheme provides the conversion from UTC to atomic time, and the conversion from atomic time to UTC. The two time system conversion methods ensure that the systems using UTC and atomic time can be synchronized and unified at the time when the leap second occurs. Avoid the impact of leap seconds on time synchronization and ensure the normal operation of the time synchronization system.
Owner:郑州威科姆科技股份有限公司
Electronic timepiece and control method therefor
InactiveUS9098071B2Efficient collectionReduce power consumptionSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingTime informationEngineering
An electronic timepiece efficiently acquires leap second information, reduces power consumption, and enables displaying the correct time. A GPS wristwatch 1 has a satellite signal reception unit 10A that receives satellite signals, a power supply including a solar panel 70 and storage battery 60, a time information adjustment unit 25 that keeps time, a reception timing determination unit 24 that operates the satellite signal reception unit 10A, receives a satellite signal, and acquires leap second information contained in the satellite signal, and a reception determination unit 23 that detects the remaining capacity of the storage battery 60. When the remaining battery capacity measured by the reception determination unit 23 is greater than or equal to a specific value, the reception timing determination unit 24 sets the reception frequency for receiving a satellite signal higher than when the remaining battery capacity is less than the specific value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Application compatible leap second support
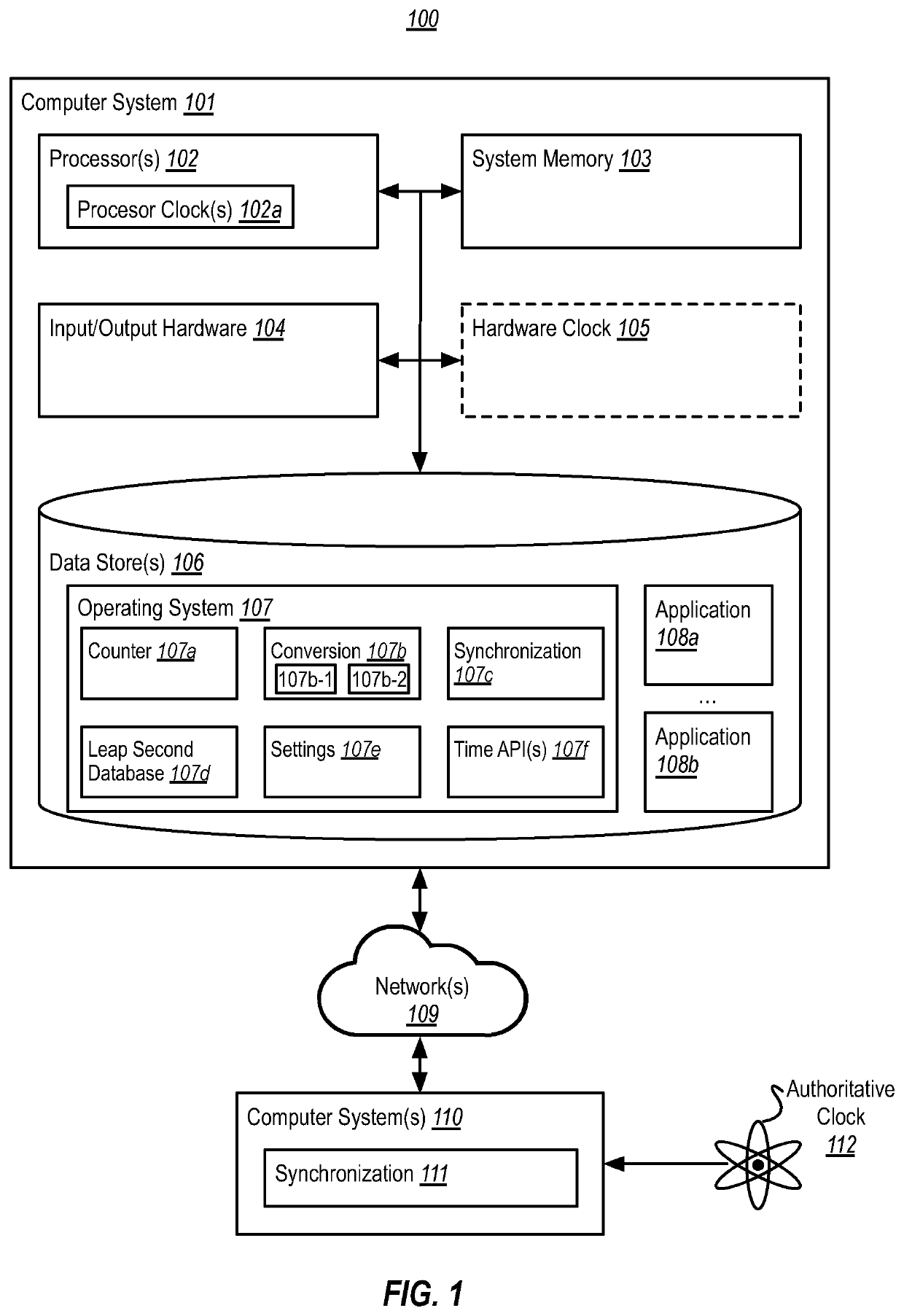
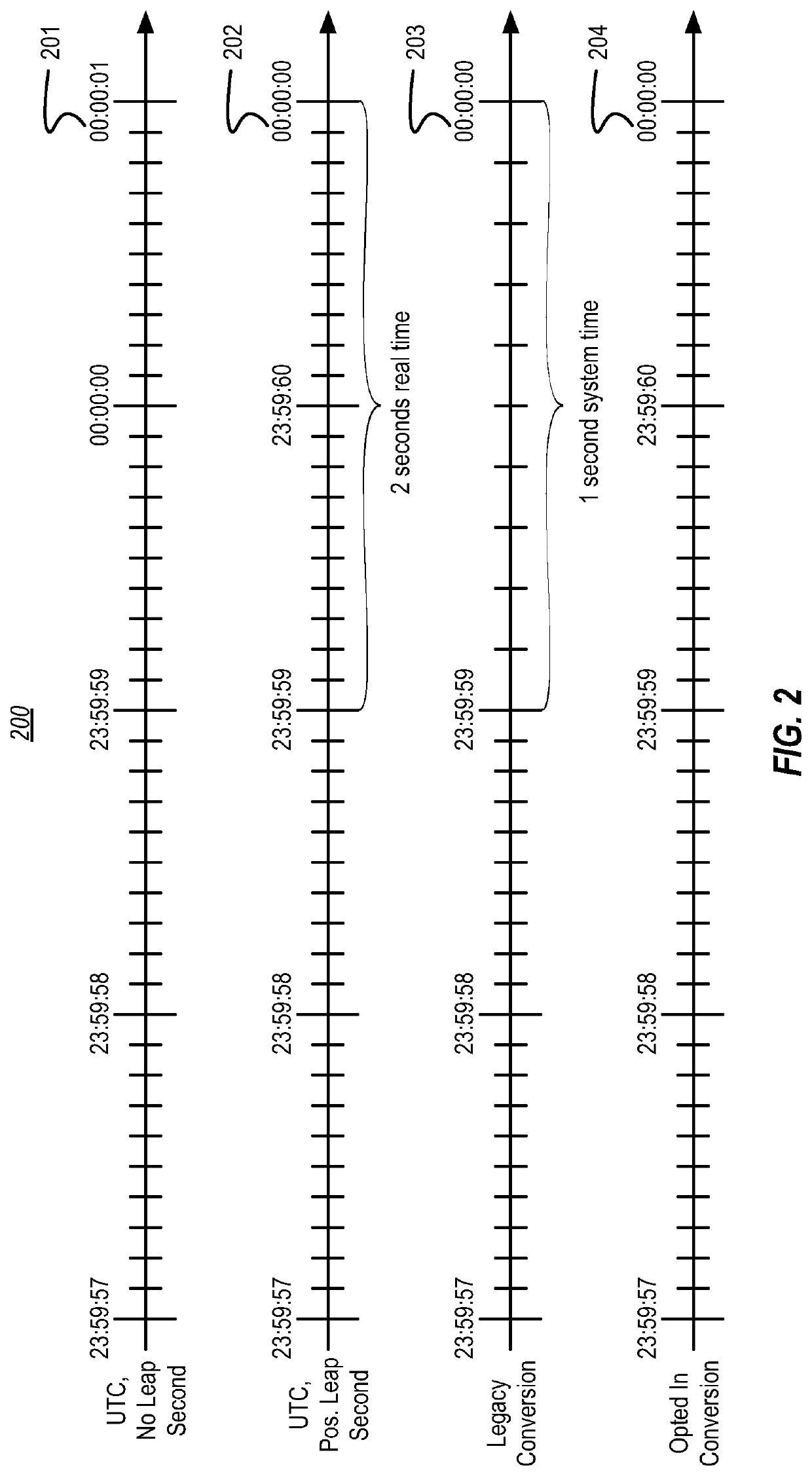
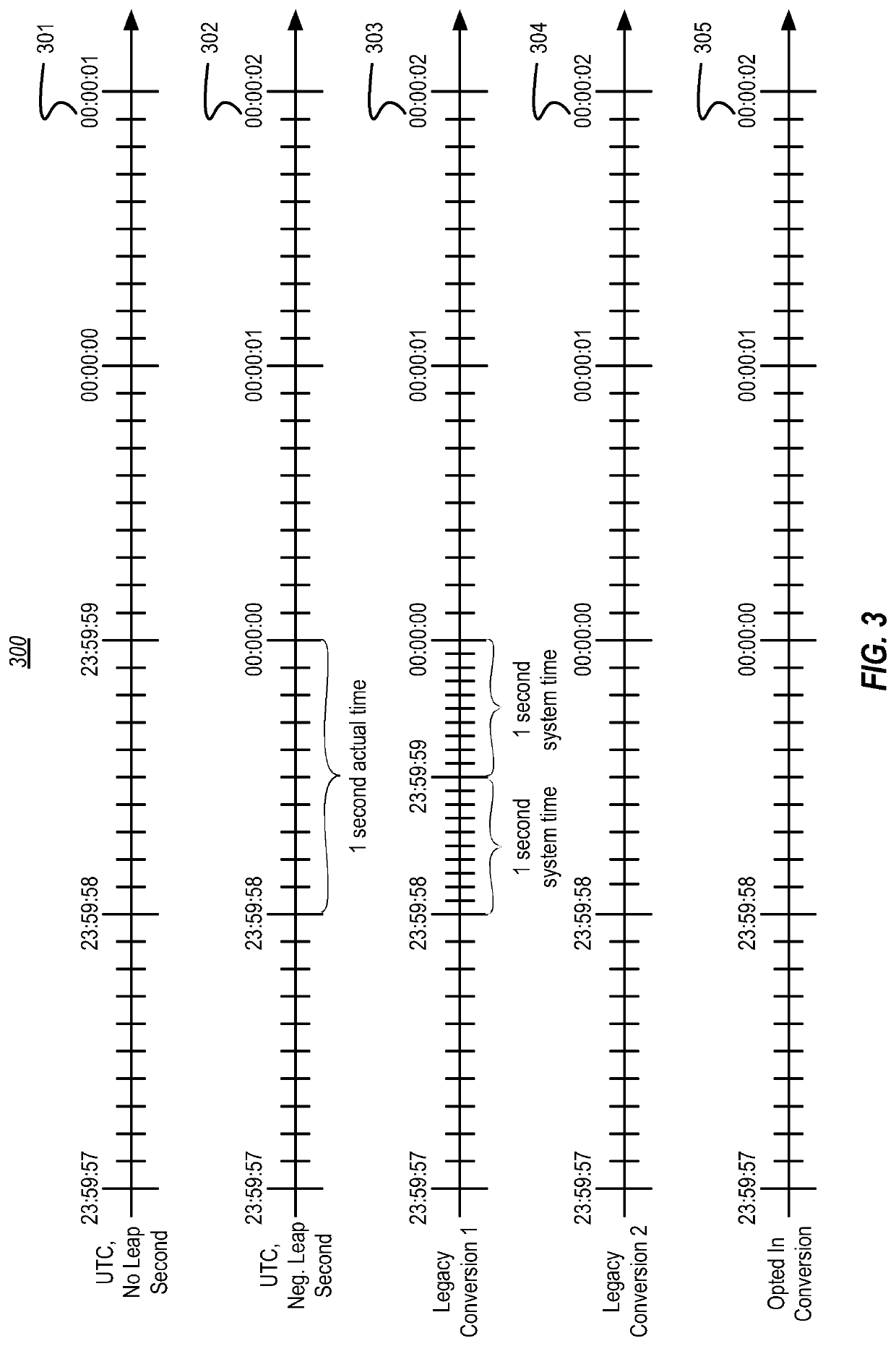
ActiveUS10809759B2Generating/distributing signalsSelective content distributionSystem timeMultiple applications
Exposing a leap second to a plurality of applications includes identifying a system setting enabling leap second support and that a positive leap second should be added to the end of a chosen date. Based on the system setting enabling leap second support and based on the occurrence of the positive leap second, a first conversion component is exposed to a first application. The first conversion component presents, over a period of two seconds of actual time, a last second of the chosen date as if it is one second of system time. Based on the system setting enabling leap second support, based on the occurrence of the positive leap second, and based on a second application opting in to leap seconds, a second conversion component is exposed to the second application. The second conversion component presents an extra 61st second of system time at the end of a last minute of the chosen date.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Transmitting method, receiving method, transmitting device, and receiving device
A transmitting method of storing data that configures an application in a predetermined data unit and transmitting the predetermined data unit. The predetermined data unit includes generating time specification information indicating an operation time of the application, based on reference time information received from an external source. The transmitting method includes transmitting (i) the predetermined data unit and (ii) control information indicating the generated time specification information. The control information includes the generated time specification information and identification information indicating whether the time specification information is time information indicating a time that is before a leap second adjustment.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Radio-controlled timepiece
A radio-controlled timepiece is shown including the following. A timekeeping unit keeps date and time. A date / time obtaining unit obtains date / time information from outside to correct the date and time of the timekeeping unit. A preliminary notice information obtaining unit obtains from outside preliminary notice information regarding whether leap second adjustment in which a leap second is inserted or deleted is executed. A date / time obtaining necessity setting unit sets whether the date / time information needs to be obtained based on history of obtaining the date / time information. The date / time obtaining necessity setting unit sets that the date / time information needs to be obtained when the preliminary notice information is not obtained by the adjustment possible date / time or the leap second adjustment is executed at the adjustment possible date / time, and does not change setting when the preliminary notice information is obtained and the leap second adjustment is not executed.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
No-leap second timer
The invention provides a no-leap second timer, namely an O.A. clock which is a 24-solar-term accurate constant value designed according to the present astronomical theory, and therefore, the O.A. clock can synchronize international time. The O.A. clock leads all global standard systems to finally have accurate time evidences, thoroughly avoids the trouble of leap second supplement in all former calendars and can accurately run for one hundred and eight thousand years under an energy holding state. The O.A. clock can be produced by adopting the traditional mechanical-clock technology or adopting a design procedure of an electronic clock, and the O.A. clock can not be replaced by any clocks in the past in aviation, navigation, space operation, international information networks, global scientific researches, and the like, thereby a clock which is manufactured now not only has a timing function of the conventional clock, but also has a special function of recording calendars.
Owner:孙嘉林 +1
Radio timepiece, method for acquiring leap second correction information and recording medium
ActiveUS9952561B2Count moreMany timesSynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesSatellite radioEngineering
A radio timepiece, including: a satellite radio wave receiver; a ground wave receiver; a memory; and a controller, wherein the controller performs area determination operation of determining whether a current position is located within a geographical range where the ground wave receiver is capable of acquiring notice information regarding implementation / non-implementation of the leap second adjustment, when the controller determines that the current position is located within the geographical range, the controller controls the ground wave receiver to acquire the notice information, the controller determines, with the notice information, whether the leap second adjustment is scheduled to be implemented at an implementation candidate timing of the leap second adjustment, and when the controller determines that the leap second adjustment is scheduled to be implemented, the controller changes the leap second correction information at or after the implementation candidate timing.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Electronic Timepiece and Method for Controlling Display Operation of Electronic Timepiece
ActiveUS20160216697A1Quick checkVisual indicationElectric power supply circuitsTime informationControl electronics
An electronic timepiece includes a display section, a display control section, a reception section, a clock section, a timing section, a leap second acquisition section, a time correction section that corrects internal time information by using time information acquired by the timing section, and a leap second correction section that corrects the internal time information by using leap second information acquired by the leap second acquisition section. Ina case where the operation of the timing section is followed by the operation of the leap second acquisition section, the time correction section corrects the internal time information by using the time information acquired by the timing section, and the display control section causes the display section to display, before the leap second acquisition section acquires the leap second information, time based on the internal time information corrected by the time correction section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com