Optical module
A technology of optical modules and optical components, applied in the field of optical modules, can solve problems such as glass substrate damage, lower positioning accuracy, and deformation of positioning pins, and achieve the effect of suppressing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0044]
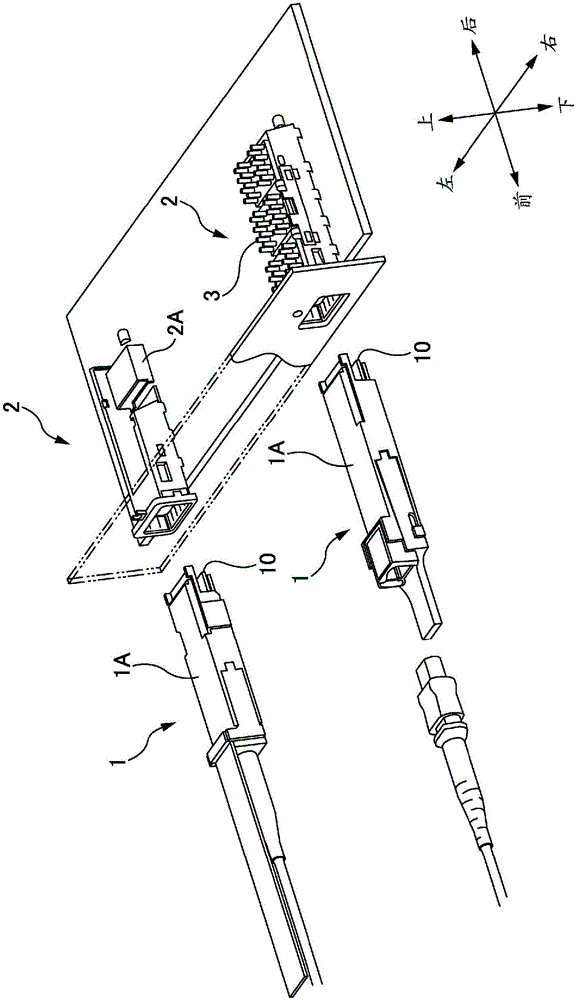
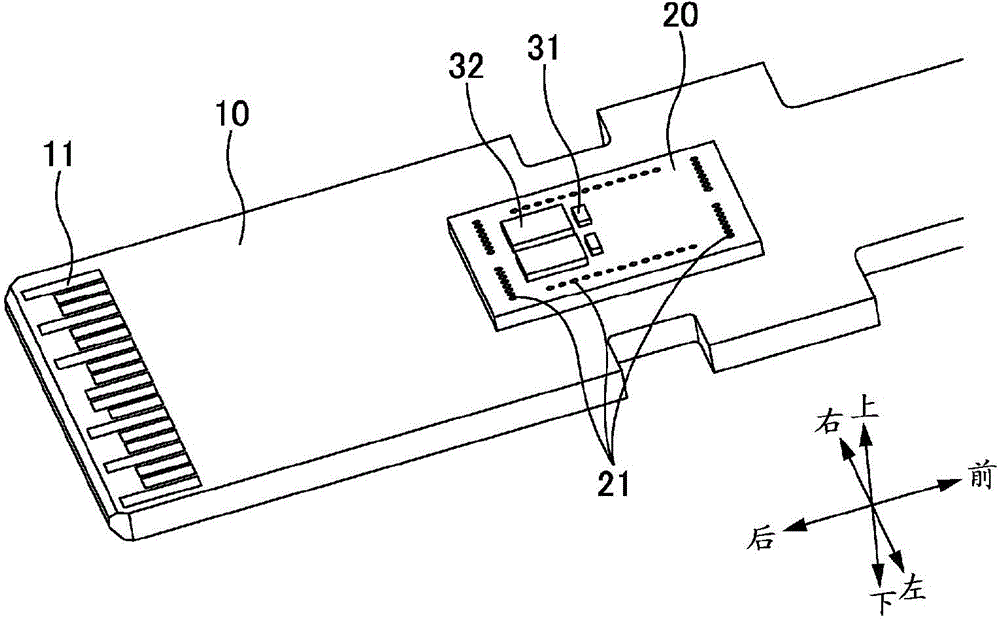
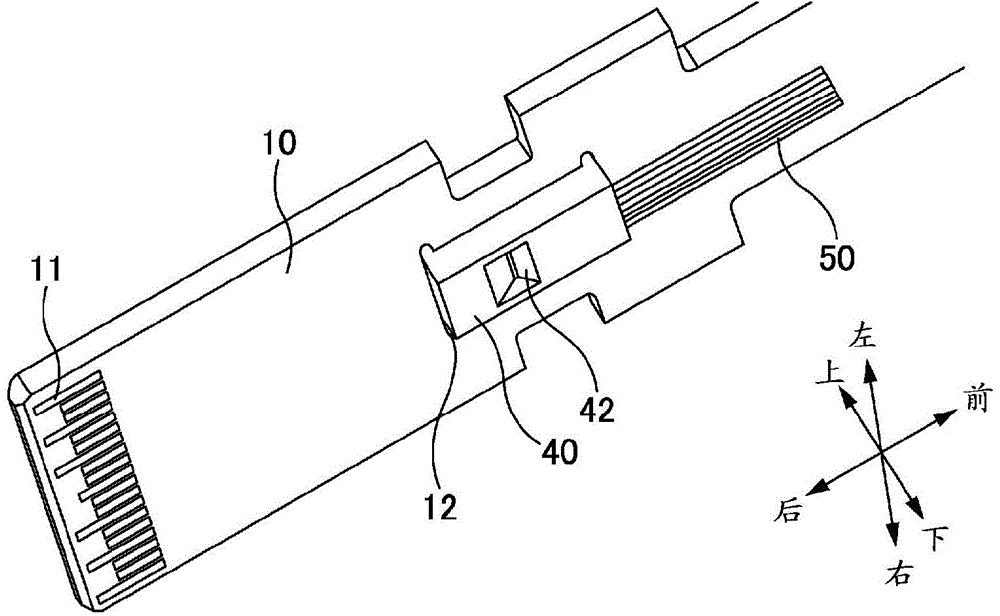
[0045] figure 1 It is an explanatory diagram of a pluggable optical transceiver. In addition, although a device including both an optical transmitter and an optical receiver is sometimes referred to as an optical transceiver, a device including only one of them is also referred to as an optical transceiver here. The pluggable optical transceiver in the figure is a QSFP type (QSFP: Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable) device specified by MSA (Multi Source Agreement). The pluggable optical transceiver has an optical module 1 and a cover 2 .
[0046] Two kinds of light modules 1 are depicted in the figure. As shown in the figure, optical fibers (including cords) may be fixed to the optical module 1 , or may be detachable from the optical module 1 . One of the two covers 2 in the figure is drawn by removing the heat sink 3 and cutting a part so that it can be observed.
[0047] In the description below, if figure 1Front and rear, top and bottom, and left and right are...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0110] Figure 11 It is explanatory drawing of 2nd Embodiment.
[0111] In the aforementioned first embodiment, the protective film 24 is formed along the edge of the positioning hole 23 , and the protective film 24 is not formed at the bottom of the positioning hole 23 . In contrast, in the second embodiment, the protective film 24 is formed on the inner surface of the positioning hole 23 , and the protective film 24 is also formed on the bottom of the positioning hole 23 .
[0112] Since the damaged layer when forming the positioning hole 23 is not only formed on the edge of the positioning hole 23, but also largely formed on the inner surface of the positioning hole 23, by forming the protective film 24 on the inner surface of the positioning hole 23, it is possible to further suppress the damage of the glass substrate. 20 for breakage.
[0113] However, in the second embodiment, since the protective film 24 is also formed on the bottom of the positioning hole 23, it is n...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0115] Figure 12 It is explanatory drawing of 3rd Embodiment.
[0116] In the aforementioned first embodiment, the protective film 24 is formed together with the passivation film 25 . Therefore, the protective film 24 has the same material as the passivation film 25 and the same thickness as the passivation film 25 . On the other hand, the protective film 26 of the third embodiment has a material different from that of the passivation film 25 .
[0117] According to the third embodiment, since the protective film 26 can be formed independently of the passivation film 25, the material and film thickness can be freely set. Therefore, the material of the protective film 26 can be selected regardless of the adhesiveness with the glass substrate side electrode 22 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear expansion rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear expansion rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com