FPGA based spliced image speckle noise eliminating method and device
A technology for splicing images and speckle noise, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as insufficient real-time performance, high cost, and reduced image resolution, and achieve high real-time transmission processing speed and cost-saving effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
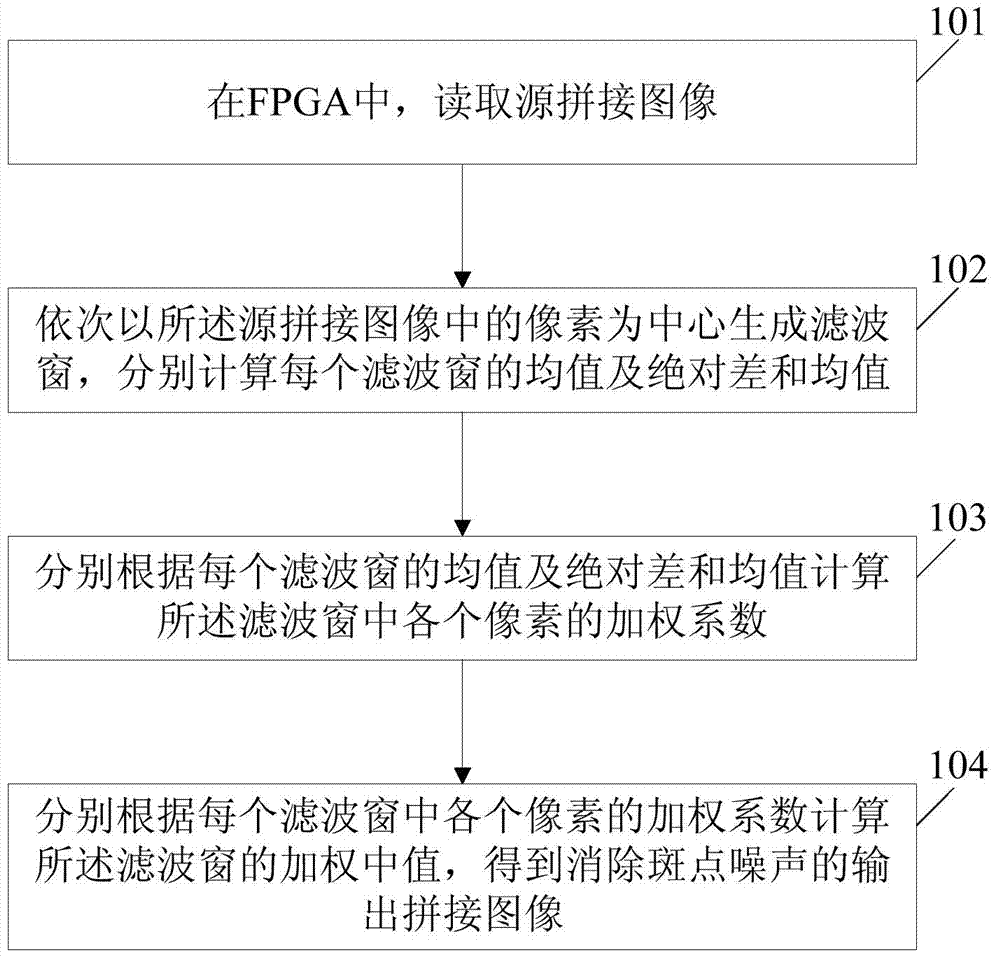
[0051] See figure 1 , is the flow chart of the first embodiment of the method for eliminating speckle noise in spliced images based on FPGA provided by the present invention, and the method includes:
[0052] S101. In the FPGA, read the source mosaic image. For example, if the source mosaic image has N horizontal sampling points and M vertical sampling points, the image can be stitched for each source in DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) of the FPGA Apply for an array Data[M][N] with a size of M*N respectively, which is used to cache the read pixel S(i,j) in the mosaic image of the road source, where i=0, 1,..., M-1, j=0, 1, ..., N-1, M, N are all natural numbers greater than zero.
[0053] S102. Generate filter windows centered on the pixels in the source stitched image in sequence, and calculate the mean value, absolute difference and mean value of each filter window respectively. The filter window can be square or rectangular, but in...
no. 2 example
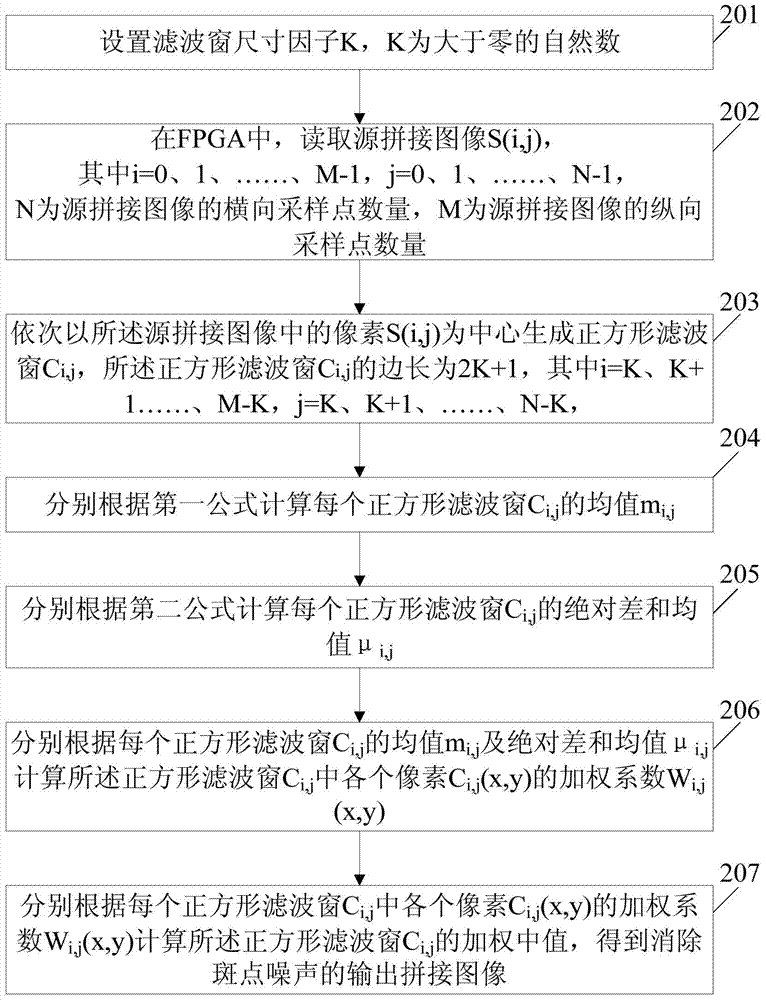
[0057] See figure 2 , is the flowchart of the second embodiment of the FPGA-based mosaic image speckle noise elimination method provided by the present invention, the method comprising:
[0058] S201. Set a filter window size factor K, where K is a natural number greater than zero.
[0059] S202. In the FPGA, read the pixel S(i,j) of the source mosaic image. For example, if the source mosaic image has N horizontal sampling points and M vertical sampling points, M and N are both natural numbers greater than zero, you can apply for a size of M*N for each source mosaic image in the FPGA's DDR SDRAM. Array Data[M][N] to store the read pixel S(i,j) in the mosaic image of the road source. Wherein i=0, 1,..., M-1, j=0, 1,..., N-1, M and N are both natural numbers greater than zero.
[0060] S203. Generating a square filter window C centered on the pixels in the source stitched image in sequence i,j , the side length of the square filter window is 2K+1. For example, for pixel S(...
no. 3 example
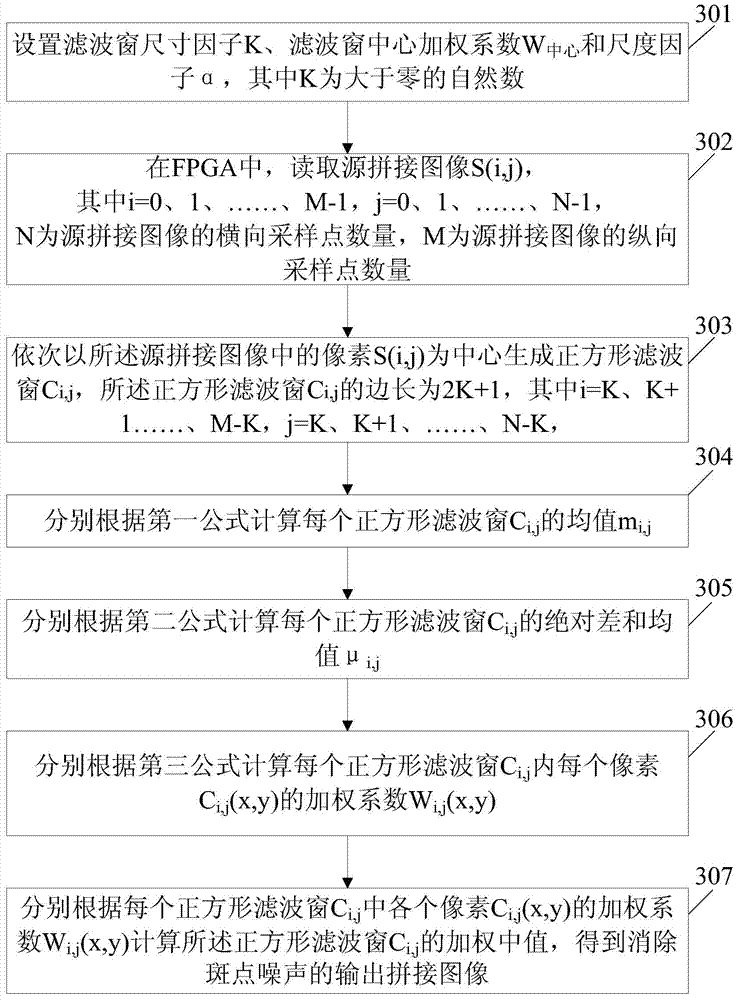
[0065] See image 3 , is the flowchart of the third embodiment of the method for eliminating speckle noise in spliced images based on FPGA provided by the present invention, and the method includes:
[0066] S301. Set the filter window size factor K and the filter window center weight coefficient W 中心 and scale factor α, where K is a natural number greater than zero.
[0067]S302. In the FPGA, read the pixel S(i, j) of the source mosaic image. For example, if the source mosaic image has N horizontal sampling points and M vertical sampling points, and both M and N are natural numbers greater than zero, you can apply for each source mosaic image in the FPGA's DDR SDRAM with a size of M*N. The array Data[M][N] is used to store the read pixel S(i,j) in the mosaic image of the road source. Wherein i=0, 1,..., M-1, j=0, 1,..., N-1, M and N are both natural numbers greater than zero.
[0068] S303. Generate a square filter window C centered on the pixels in the source stitched ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com