Structure fatigue life calculation method based on non-linear cumulative damage theory
A technology of cumulative damage and fatigue life, applied in the testing, measuring devices, instruments, etc. of machine/structural components, which can solve problems such as poor engineering applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments.
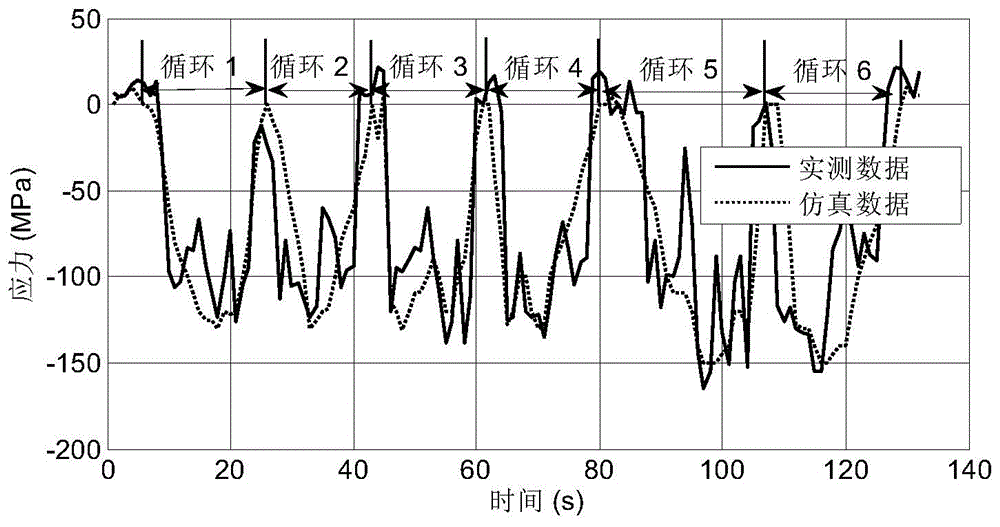
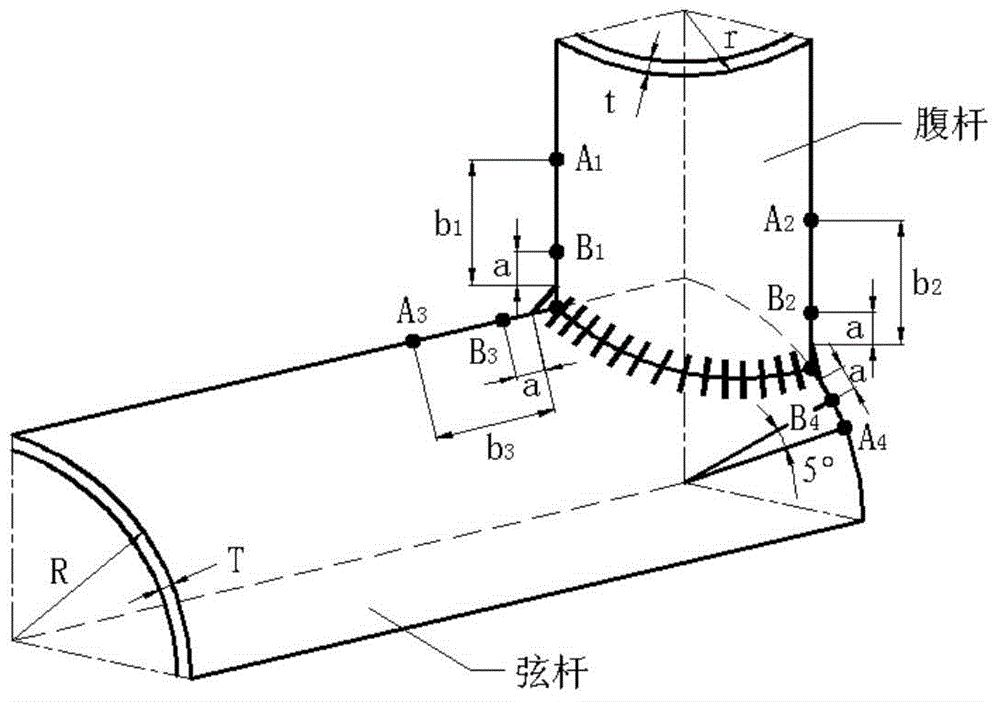
[0058] Case selected Figure 5 The welded structure shown is taken from a dangerous section of the truss boom of a rubber-tyred crane. The material parameters are: when the material is Q345B, the elastic modulus E = 200741MPa, the fatigue strength index b = -0.0943, the fatigue ductility index c = -0.5395, the fatigue strength coefficient σ f '=947.1MPa, fatigue ductility coefficient ε f '=0.4644, with cycle hardening characteristics.
[0059] Determine its fatigue life by calculating its complete cumulative damage. Specific steps are as follows:
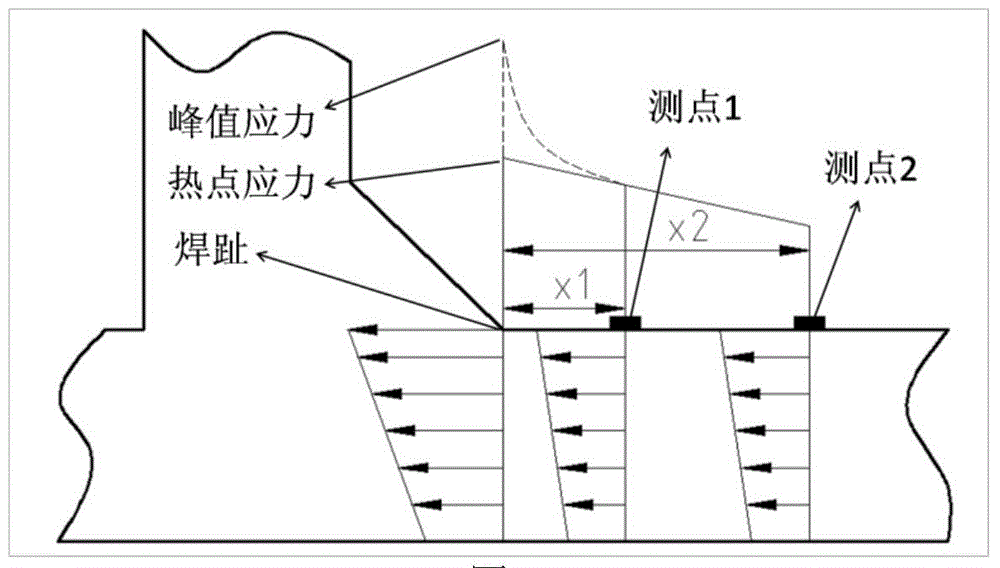
[0060] Step 1: Determine the fatigue risk area of the component through the finite element analysis software. By right Figure 5 Establish a finite element model, analyze two typical working conditions in Ansys, and obtain multiple points with larger stress values. Two typical working conditions are shown in Table...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com