Method for Solidifying and Forming Precursor in Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene Dry Spinning Process
An ultra-high molecular weight, polyethylene spinning technology, applied in the direction of single-component polyolefin artificial filament, wet spinning, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of high moisture content in raw silk, lengthy and complicated process, etc., to achieve Effects of increasing crystal orientation, enhancing fiber strength, and improving tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
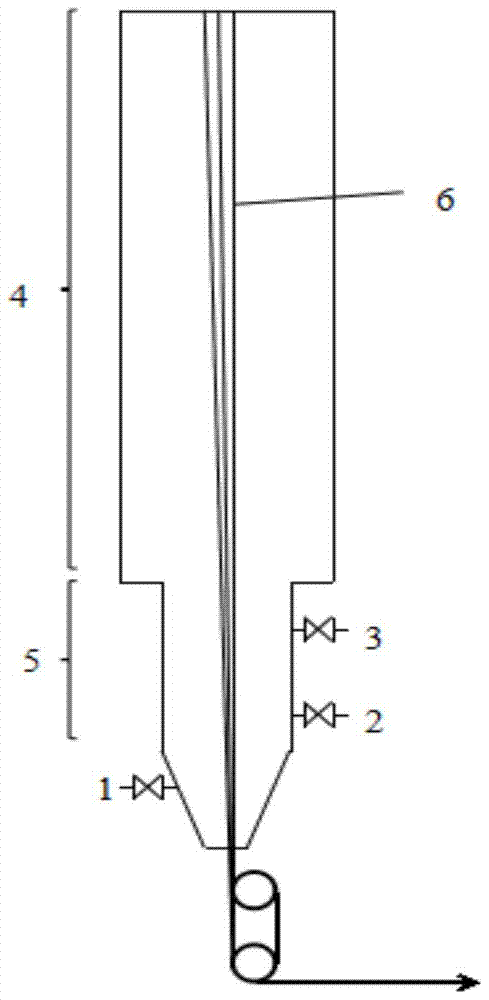
[0032] A method for solidifying and forming precursors in ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene dry spinning process, such as figure 1 As shown, the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene spinning solution is extruded from the spinneret and enters the tunnel in the form of tow 6 for solidification and molding. The tunnel includes a uniform heating zone 4 and a circulating blowing zone 5 arranged in sequence up and down, and the tow 6 passes through in sequence. After the uniform heating zone 4 and the circulating blowing zone 5, a precursor with a certain degree of crystal orientation is formed.
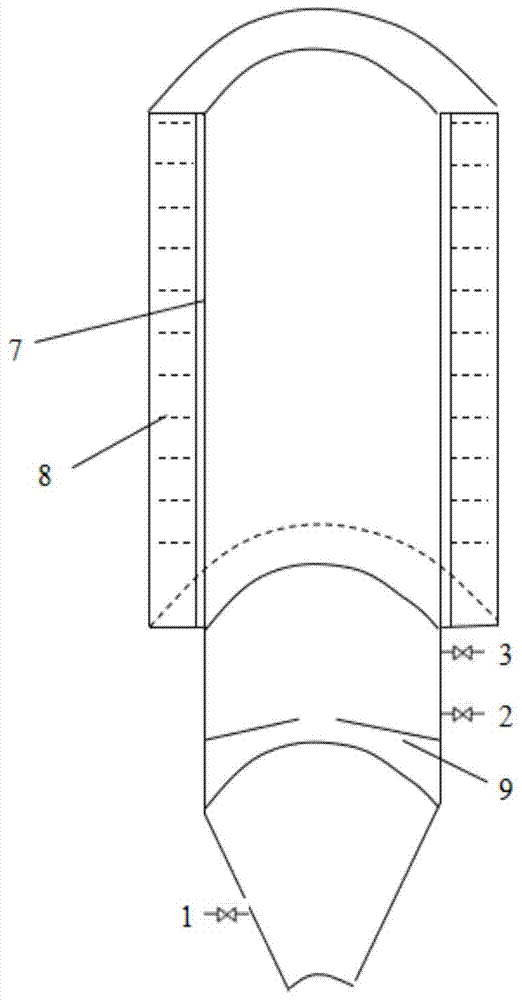
[0033] refer to figure 2 , the structure of the uniform heating zone 4 is a hollow cylindrical shell, the shell is divided into inner and outer layers, the inner layer is the heating layer 7, and the outer layer is the insulation layer 8; the uniform heating zone 4 can be set in one or more sections, and the heating method of the heating layer 7 Including heat conduction oil h...
Embodiment 2
[0040]Using the process of Example 1 and the tunnel described in Example 1 to solidify and form the precursor during the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene dry spinning process, decahydronaphthalene is a solvent, and the mass percent concentration is 8% ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene spinning solution After being extruded by the spinneret, it enters the tunnel device, the length of the tunnel is 8m, the temperature in the tunnel is 100°C, the residence time of the filaments in the tunnel is 30sec, the inert gas is nitrogen, the temperature is 20°C, and the flow rate is 50Nm 3 , a pair of symmetrical baffles, the angle between the baffle and the tunnel is 90°, the solvent residue in the obtained precursor is 0.7% by weight, and the strength of the precursor is 4.2cN / dtex.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Using the process of Example 1 and the tunnel described in Example 1 to solidify and form the precursor during the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene dry spinning process, decahydronaphthalene is a solvent, and the mass percent concentration is 8% ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene spinning solution After being extruded by the spinneret, it enters the tunnel device, the length of the tunnel is 6m, the temperature in the tunnel is 100°C, the residence time of the filaments in the tunnel is 25sec, the inert gas is nitrogen, the temperature is 25°C, and the flow rate is 40Nm 3 , a pair of asymmetrical baffles, the angle between the baffles and the tunnel is 90°, the solvent residue in the obtained precursor is 0.9% by weight, and the strength of the precursor is 4.0cN / dtex.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com