Stirling engine
A Stirling engine, linear motion technology, applied in the direction of machine/engine, hot gas variable capacity engine device, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of thermal cylinder parameter design limitation, high cost, overall complexity, etc., to achieve overall aesthetics The effect of raising and lowering the overall height and facilitating reasonable arrangement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
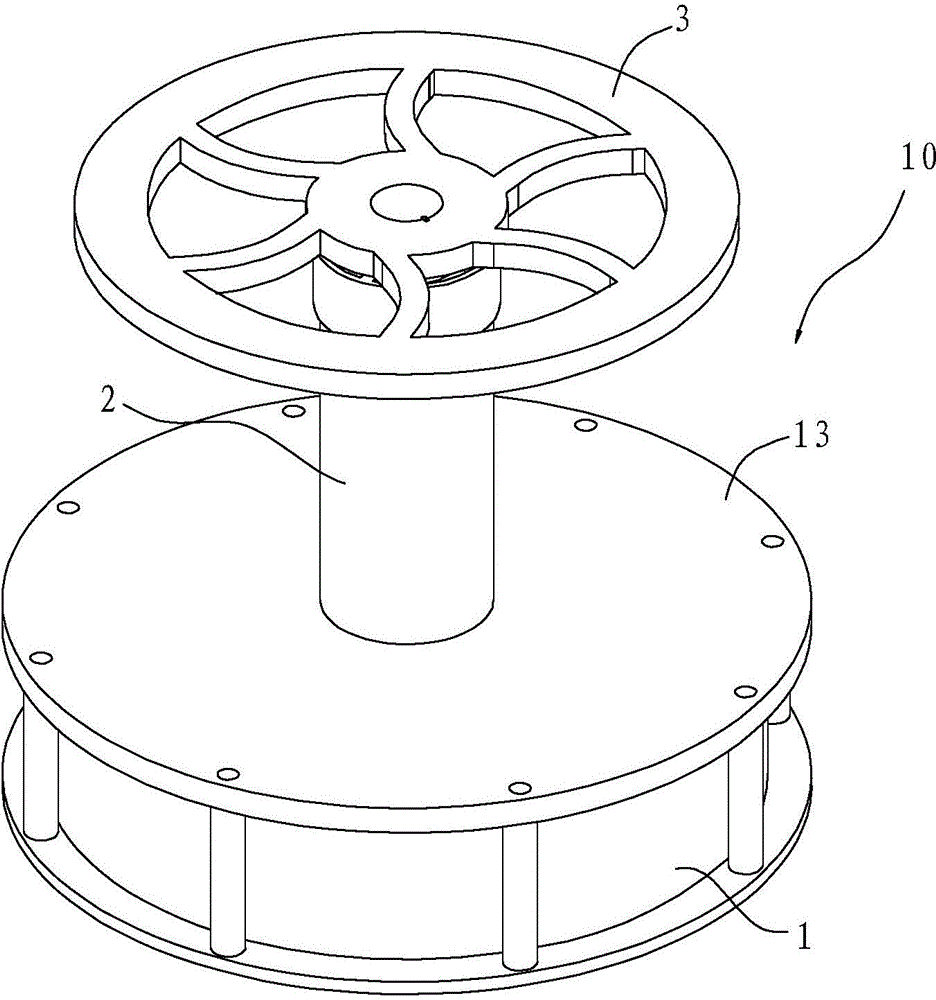
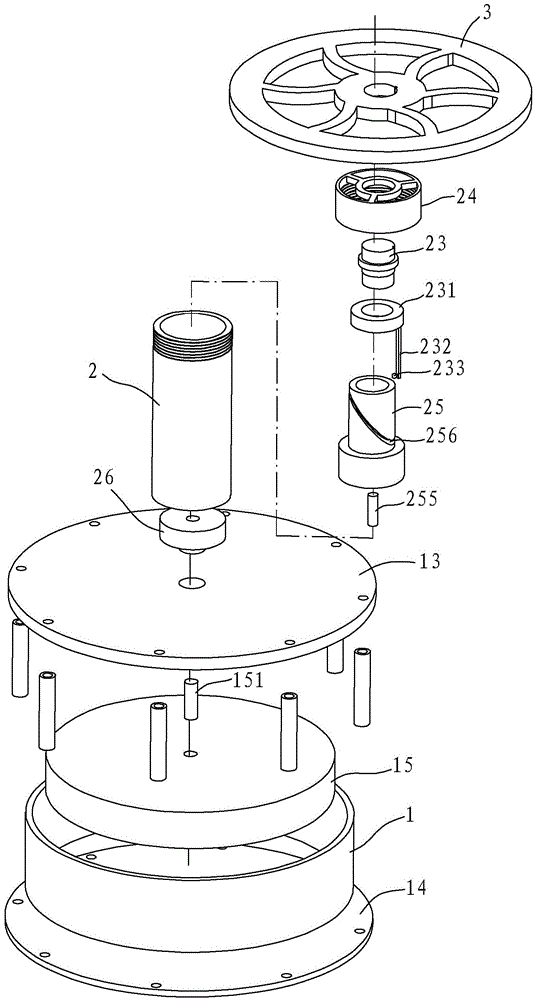
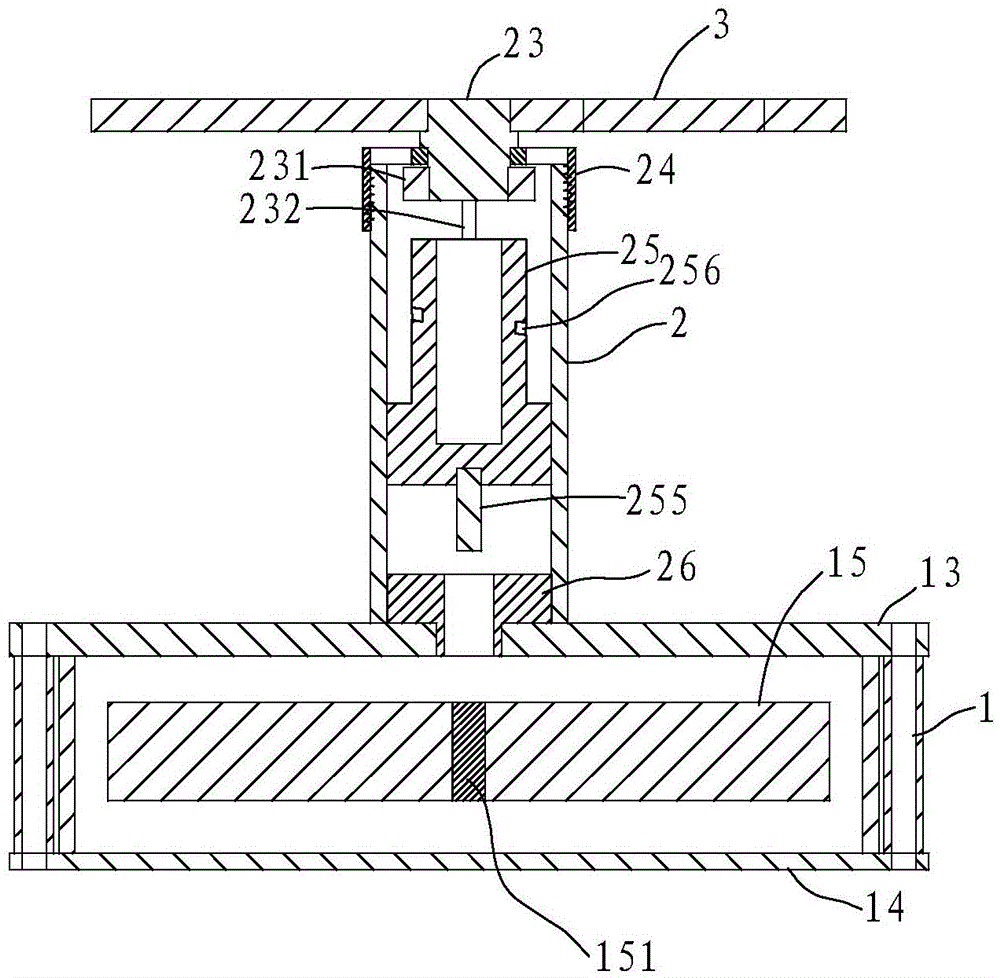
[0033] like Figure 1~4 As shown, the Stirling engine 10 includes a first cylinder 1, a second cylinder 2, a first piston 15 (displacement piston) and a second piston 25 (power piston), and the first cylinder 1 has a heat dissipation surface 13 and a heat absorption surface 14. The Stirling engine 10 is a low-temperature differential Stirling engine, and the heat-absorbing surface 14 absorbs energy so that the volume of the first cylinder 1 expands and pushes the first piston 15 .
[0034] The bottom end of the second piston 25 of the Stirling engine 10 is provided with a magnet 255 , and a guide groove 256 is obliquely formed on the outer periphery of the second piston 25 . Or, alternatively, the middle part of the second piston 25 can also be formed hollow, and the guide groove 256 can be formed on the inner wall. However, it is preferred to form the guide groove 256 on the outer periphery.
[0035] The first piston 15 is provided with a driving block 151 which cooperates...
Embodiment 2
[0045] like Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the way to prevent the rotation of the second piston 25 is that the cross section of the second cylinder 2 is square, correspondingly, the first The cross section of the two pistons 25 is also square. The square design can limit the rotation of the second piston 25 to ensure that the second piston 25 can move up and down.
Embodiment 3
[0047] like Figure 6 ~ Figure 8 , in this embodiment, the difference from the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is that in the second cylinder 2, a rotating block 29 is arranged above the second piston 25 and below the cover 24, and the rotating shaft 23 runs through the rear end of the cover 24 It is connected with the rotating block 29 and rotates synchronously. On the second piston 25, the first magnet unit 251 and the second magnet unit 252 are arranged at intervals such as the upper end surface, and on the rotating block 29, the third magnet unit 291 and the fourth magnet unit 292 are arranged at intervals on the lower end surface, in each magnet unit A plurality of magnets with the same magnetic poles may be included, the first magnet unit 251 and the second magnet unit 252 have opposite magnetic poles, and the third magnet unit 291 and the fourth magnet unit 292 have opposite magnetic poles.
[0048] After an initial power is given to the flywheel 3, the first magnet unit ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com