Field dibbling and mulching method for stevia
A stevia and field technology, which is applied in planting methods, intermittent quantitative sowing machinery, excavation/covering of trenches, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving high yield, insufficient labor, and small root system, and achieve lower production costs. artificial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
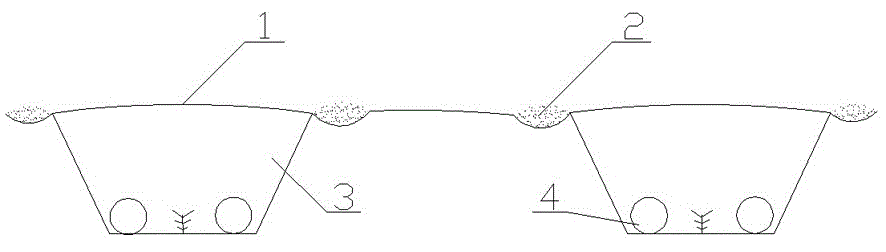
[0013] A method for film-covering stevia on-demand in field, digging trapezoidal grooves with upper opening width 8-10 cm, lower opening width 4-6 cm, and depth 5-7 cm in the field, and trapezoidal groove bottom according to hole spacing 16-18 cm Stevia seeds are sown on-demand by centimeters. The stevia seeds fall to the bottom of the tank, and the top of the seeds is not covered with soil, instead of the traditional method of ditching and dropping seeds. Cover the rows with soil, and timely drip irrigation to adjust the water humidity under the film. When the seedling height reaches the top of the film, the film is broken and the seedlings are released. According to the emergence situation, the seedlings are thinned and the seedlings are replenished to keep the number of seedlings from 11,000 to 12,000 plants / mu.
[0014] According to the climatic conditions of the planting area, one or two drip irrigation belts are laid in each trapezoidal groove.
[0015] During mechanized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com