Aircraft radar target detection method based on GCV (generalized cross validation)
An airborne radar and target detection technology, which is applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of real-time noise power, difficulty in accurate measurement, low computational complexity, and performance degradation of rank reduction processing methods, etc., to improve target detection performance and good parameter estimation performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
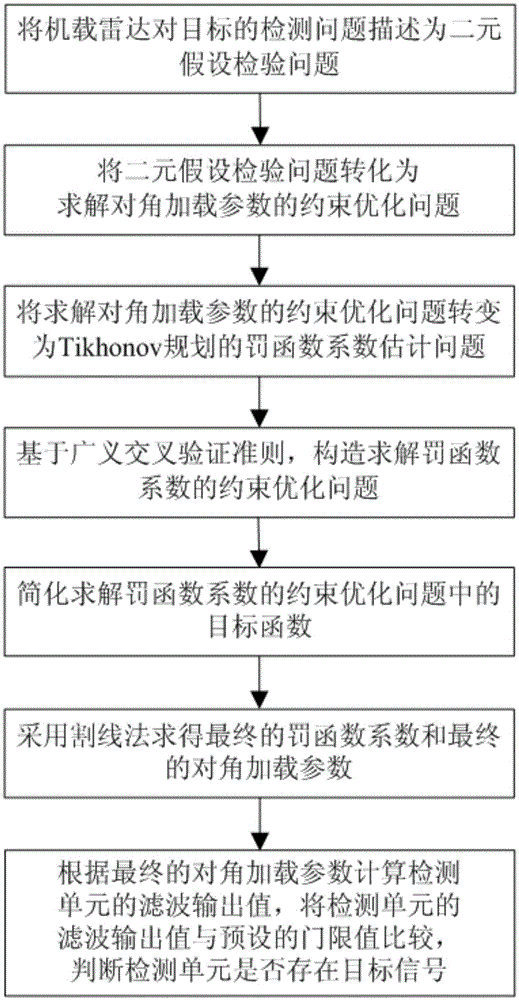
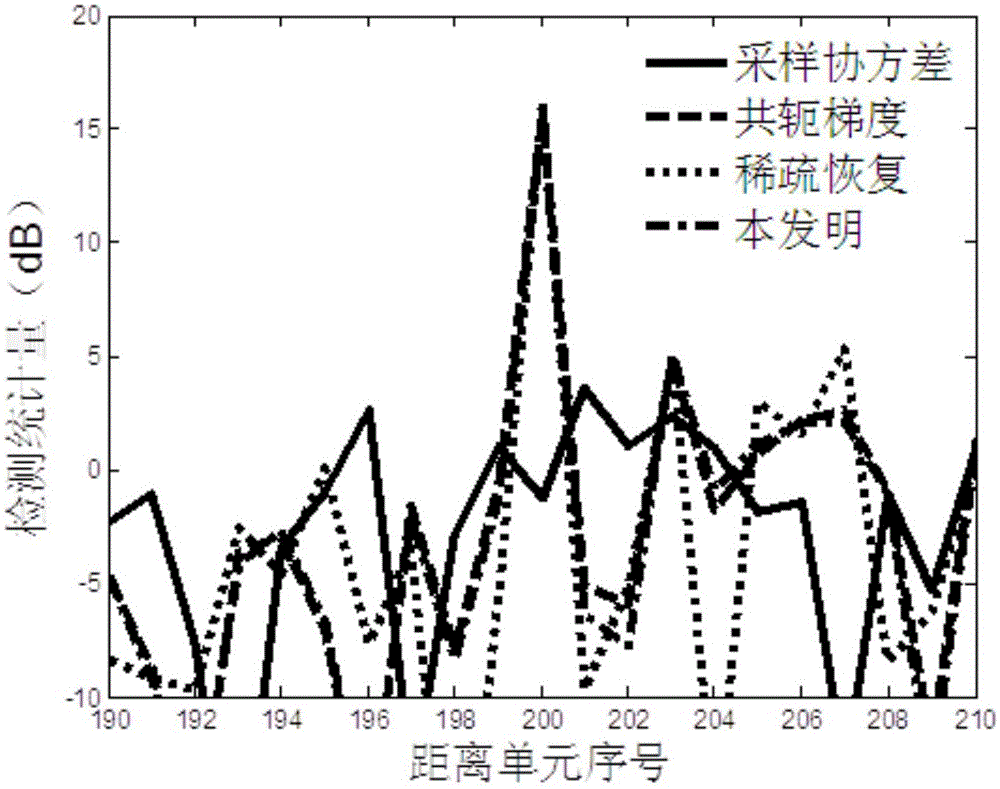
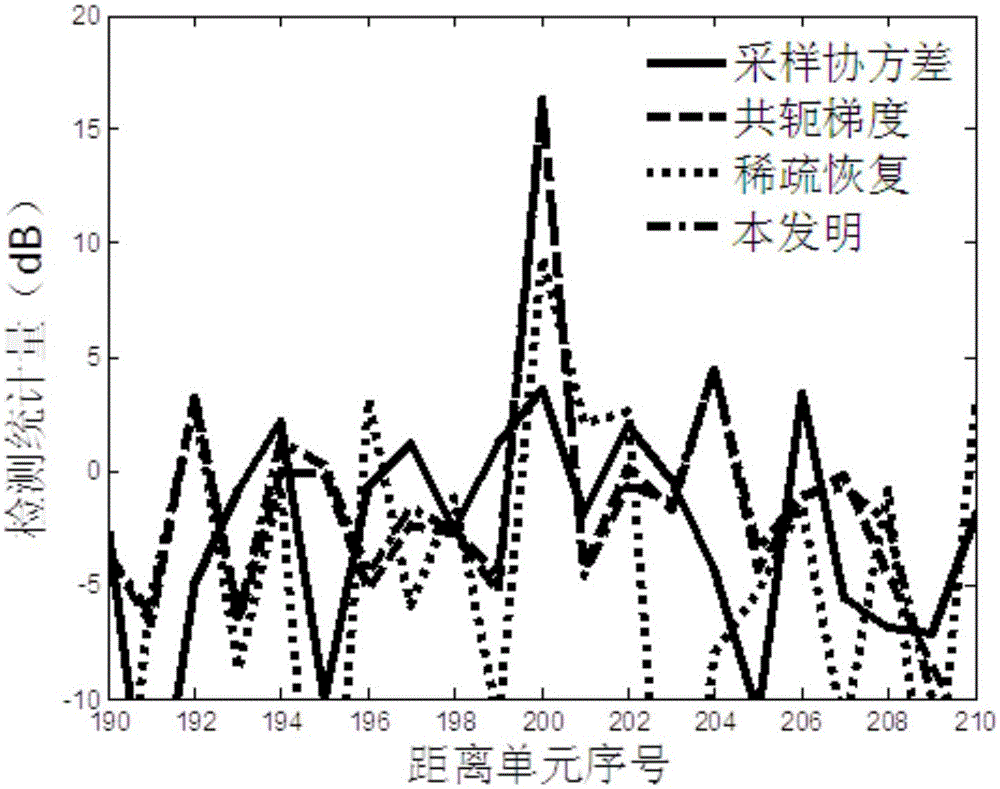
[0026] refer to figure 1 , a kind of GCV-based airborne radar target detection method of the present invention comprises the following specific steps:
[0027] Step 1, set the airborne radar to work in the pulse Doppler system, set x as the data vector of the detection unit; describe the detection problem of the airborne radar to the target as a binary hypothesis testing problem, and judge whether there is a target in the detection unit signal; the binary hypothesis testing problem is converted into a constrained optimization problem for solving diagonally loaded parameters; the binary hypothesis testing problem includes H 0 Hypothesis and H 1 Suppose, if H 0 If the assumption is true, it is considered that there is no target signal in the detection unit; if H 1 If the assumption is true, it is considered that there is a target signal in the detection unit.
[0028] The specific sub-steps of step 1 are:
[0029] 1.1 Set the airborne radar array as a uniform linear array, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com