Methods of Stabilizing the Clock Frequency of Microcontrollers
一种微控制器、时钟频率的技术,应用在输出稳定、功率的自动控制、具有存储的校准系数的设备等方向,达到减小电压依赖性、提高通信质量、减小温度依赖性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
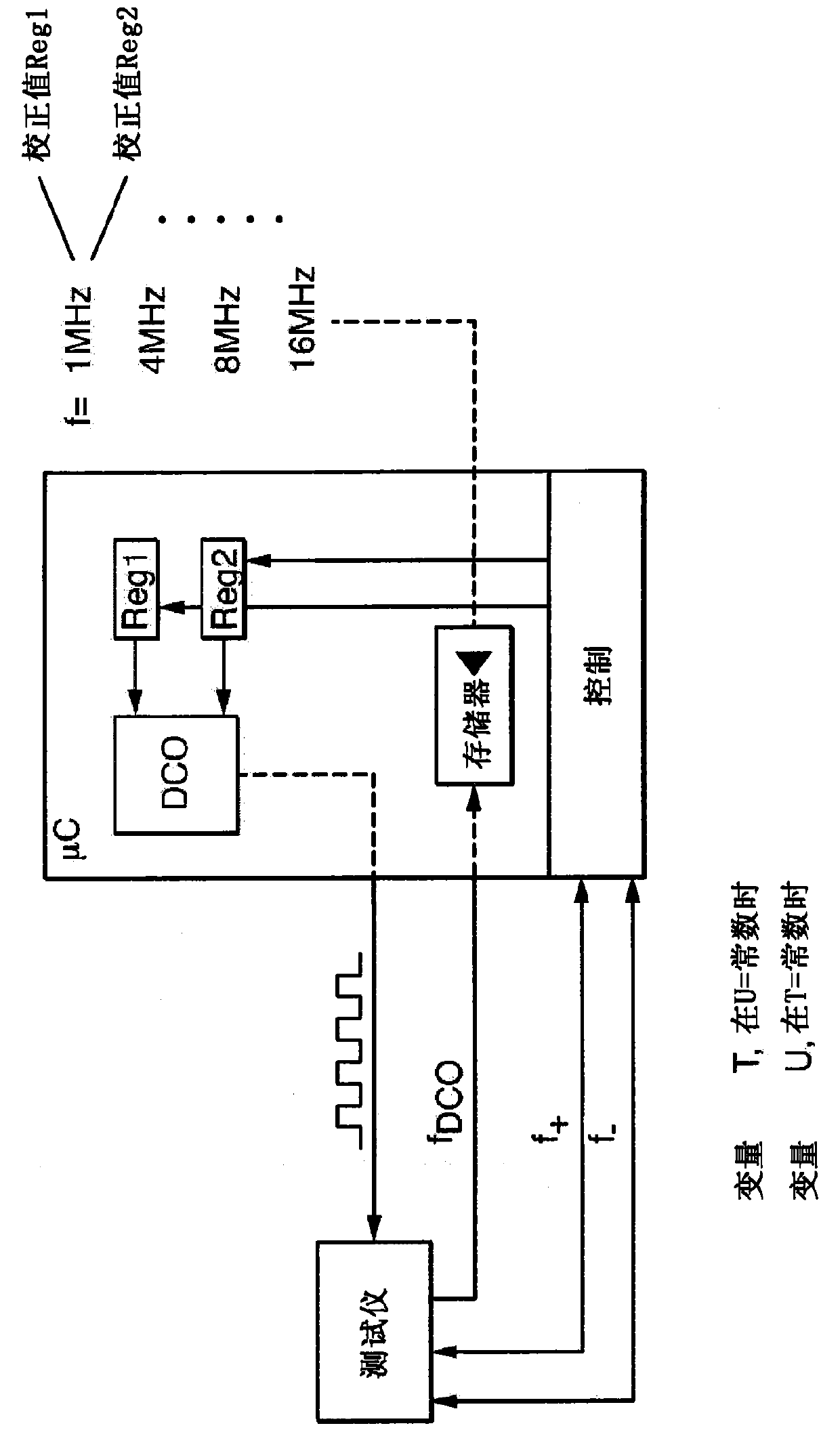
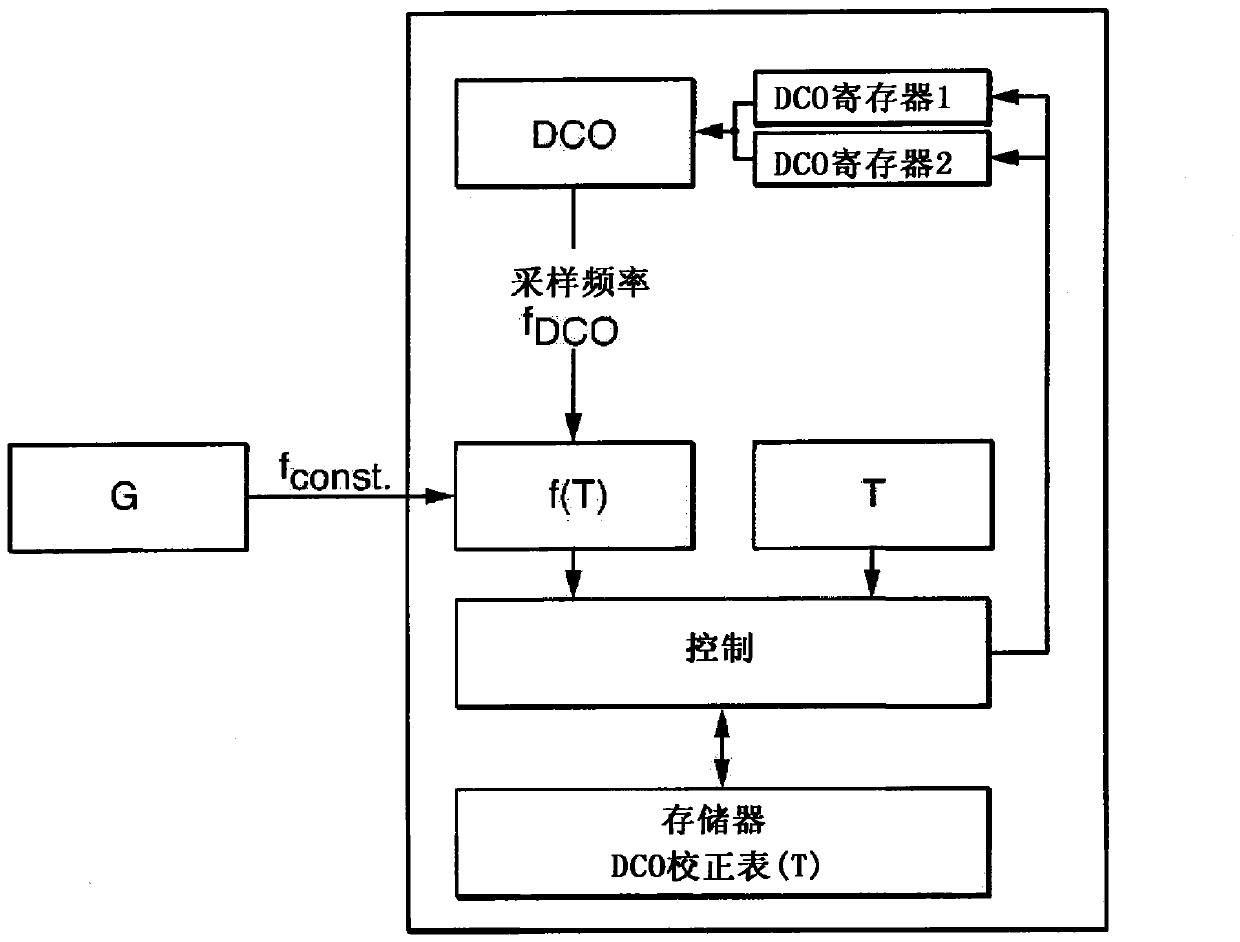
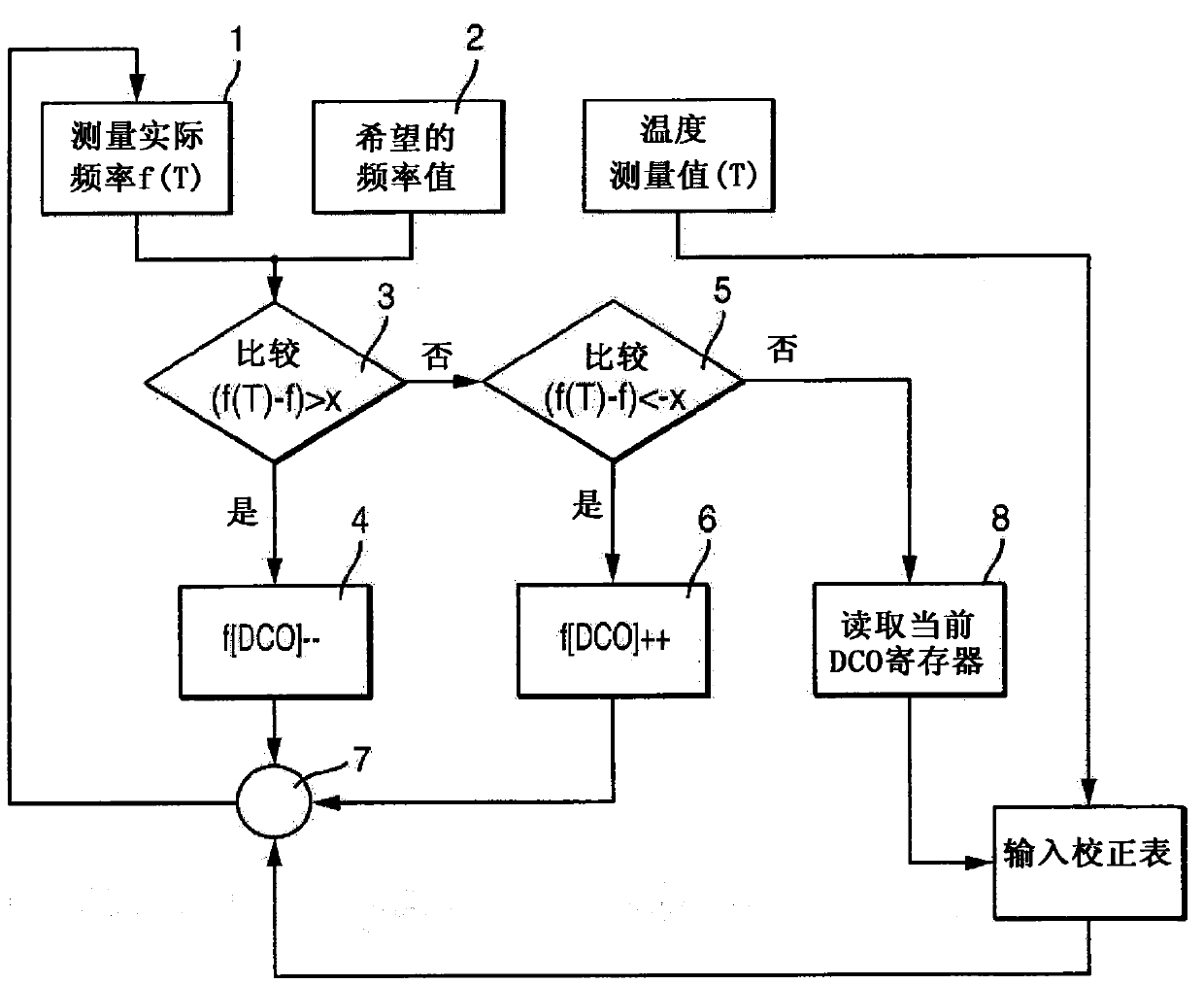
[0027] figure 1 A block diagram illustrating a first method for stabilizing the microcontroller μC clock frequency is shown. For this purpose, a defined clock frequency fDCO of the microcontroller μC is predetermined or determined at a defined temperature T1 of the microcontroller μC. In the illustrated case, the microcontroller μC is clocked via an adjustable oscillator DCO or an internal clock signal generator DCO, in particular a numerically controlled oscillator DCO. Via the adjustable oscillator DCO, different frequencies f can be set, here 1 MHz, 4 MHz, 8 MHz and 16 MHz.
[0028] A defined clock frequency fDCO (for example 1 MHz) of the microcontroller μC is supplied to a matching tester TESTER which is thermally insulated from the microcontroller μC. The microcontroller μC is then brought to a changed temperature T2 which deviates from the defined temperature T1 of the microcontroller μC. The change in the defined clock frequency fDCO caused by the temperature change...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com