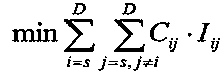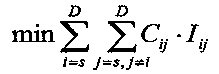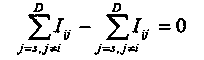Method for solving optimal path of wireless sensor network by using differential evolution
A wireless sensor and optimal path technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc., can solve problems such as long search time, stagnant local optimal solution, sensitive search speed and precision, etc., to achieve good performance and good convergence sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The present invention proposes a method for solving the optimal path of wireless sensor networks by using differential evolution. According to the knowledge of graph theory, an undirected graph G=(V, E) is used to describe the path problem of wireless sensor networks, and to study the optimal path of wireless sensor networks. Nodes and information transmission, in the undirected graph G=(V, E), V represents the collection of all nodes in the network, E is the collection of all communication routes, V=V head , V 1 ,...,V k ,...,V n ;E=E 1 ,...,E k ,...,E n ;E 1 is the connection link of the first node, E k is the connecting link of the kth node; suppose that V head is the target node in the cluster, that is, the cluster head node; the kth node is the source node, and the path optimization model is established, and then the differential evolution algorithm is used as a search tool to obtain the minimum energy consumption required to transfer from the source node to...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The method of using differential evolution to solve the optimal path of the wireless sensor network in this embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that further: V i , V j is a node in the undirected graph G=(V, E), node V i and V j The energy consumed by transferring links between is C ij , the energy consumption matrix of the entire network is C=[C ij ], the matrix is a symmetric matrix L of n*n, namely C ij =C ji ; node V i and V j The connection between is I ij , if node V i to V j There is a link between them, then I ij =1, otherwise I ij =0;
[0034] Transform the optimal path in the wireless sensor network into a minimization problem, and obtain the optimization objective function
[0035]
[0036] In the formula, i and j are node numbers, which are natural numbers; s is the source node, and D is the target node; the optimal transmission path is obtained by obtaining the minimum energy consumption required for transmission from the source n...
Embodiment 3
[0038] The method of using differential evolution to solve the optimal path of the wireless sensor network in this embodiment is different from that in Embodiment 2 in that: a path-based variable-length decimal chromosome coding method is used to code and design chromosomes, and randomly generate initialization chromosomes Population, chromosomes are composed of integer queues, and the integers of each gene are different. These integers are the node numbers in the wireless sensor network. The first and last genes of all chromosomes are the source node and the target node respectively;
[0039] After the population is initialized, the mutation operation is first performed, and the set-based DE / rand / 1 mutation is adopted, and the chromosome r2 and r3 are subtracted to obtain c, which is equivalent to r2-r3 in the classic differential mutation, and then the chromosome r1 and c are merged. Set operation, similar to r1+(r2-r3) in classic mutation, because it is a set processing, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com