Finite time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking space non-cooperative target
A non-cooperative target, fault-tolerant control technology, applied in the field of limited-time fault-tolerant control, which can solve the problems of large tracking control error and low tracking monitoring accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
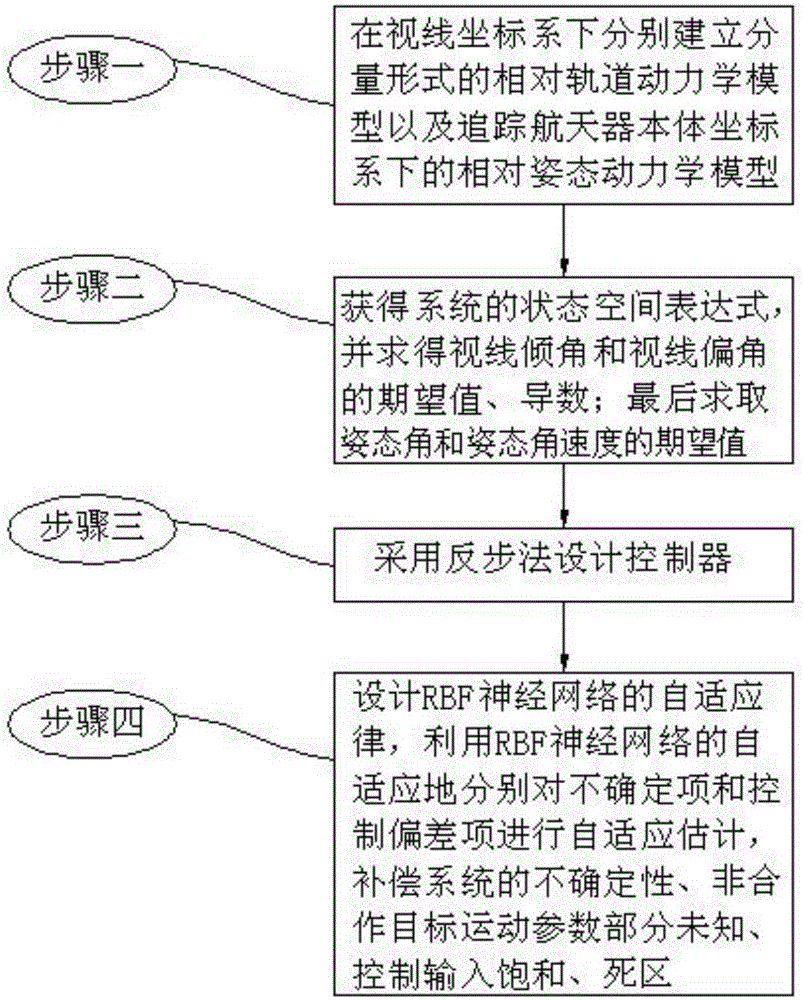
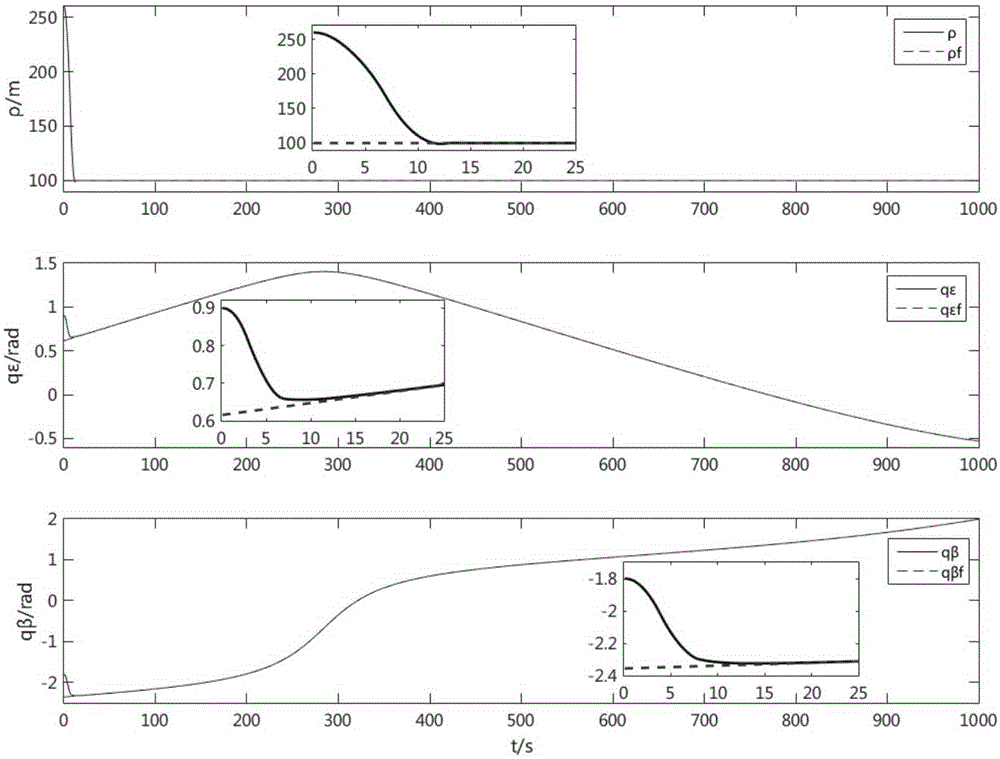
[0035] The finite-time fault-tolerant control method of approaching and tracking space non-cooperative targets in this embodiment, such as figure 1 Shown flow chart, described method is realized through the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. Establish the relative orbital dynamics model in component form under the line-of-sight coordinate system: ρ ·· - ρ ( q · ϵ 2 + q · β 2 cos ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
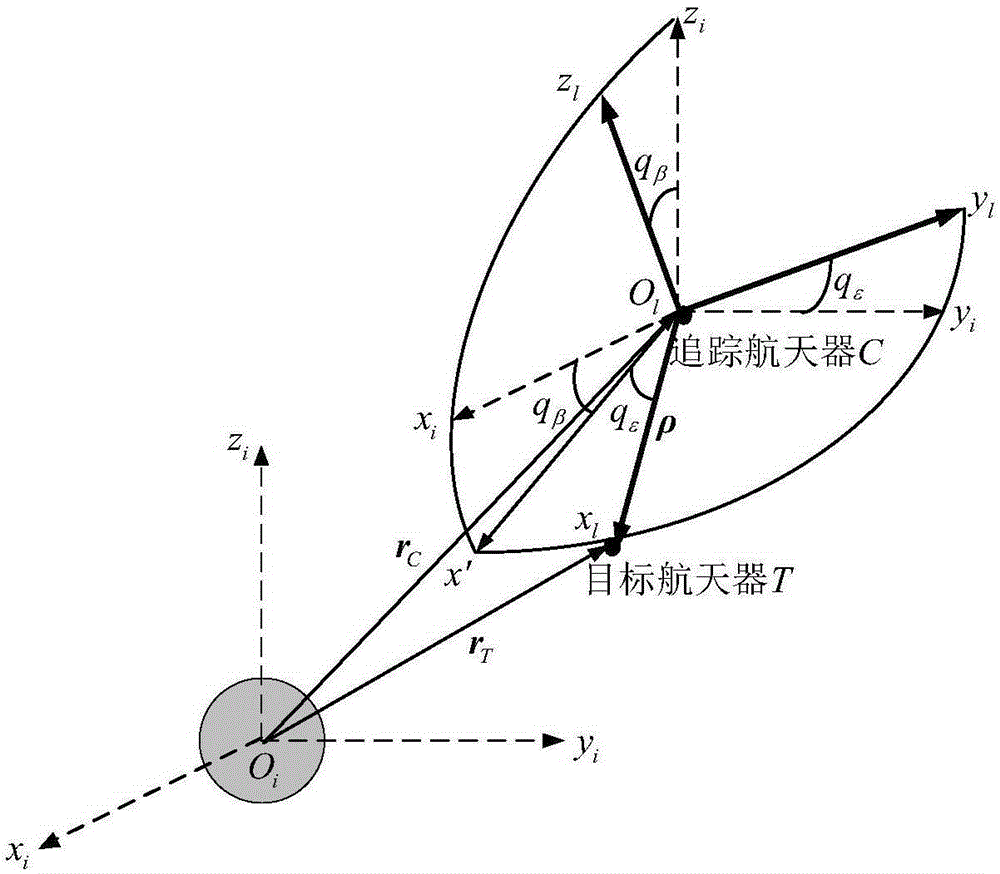
[0051] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the finite-time fault-tolerant control method of approaching and tracking space non-cooperative targets in this embodiment, the process of establishing the relative orbital dynamics model in the form of components described in Step 1 is as follows: set the geocentric inertial coordinate system o i x i the y i z i and line of sight coordinate system O l x l the y l z l and its relationship, such as figure 1 The relative position vectors of the Earth, the target spacecraft, and the tracking spacecraft are shown, O l is the origin of the line-of-sight coordinate system, located at the center of mass of the tracking spacecraft, x l The axis coincides with the line of sight, that is, the tracking spacecraft points to the target spacecraft, y l axis is located by x l axis and y i axes together form the longitudinal plane, with the x l Axis vertical, z l The axes are determined by the right-hand rule; q ε is the line-of...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Different from the first or second specific embodiment, the finite-time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking a space non-cooperative target in this embodiment is characterized in that: the process of obtaining the derivative relationship between the attitude angular velocity and the attitude angle described in step one As, define the rotation angles of the tracking spacecraft around the x, y, and z axes of the body as θ, ψ, the attitude matrix described by the Euler angles is:
[0054] Track the attitude angular velocity of the spacecraft:
[0055]
[0056] For simplicity, define the matrix:
[0057]
[0058] Then there is the attitude angle:
[0059]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com