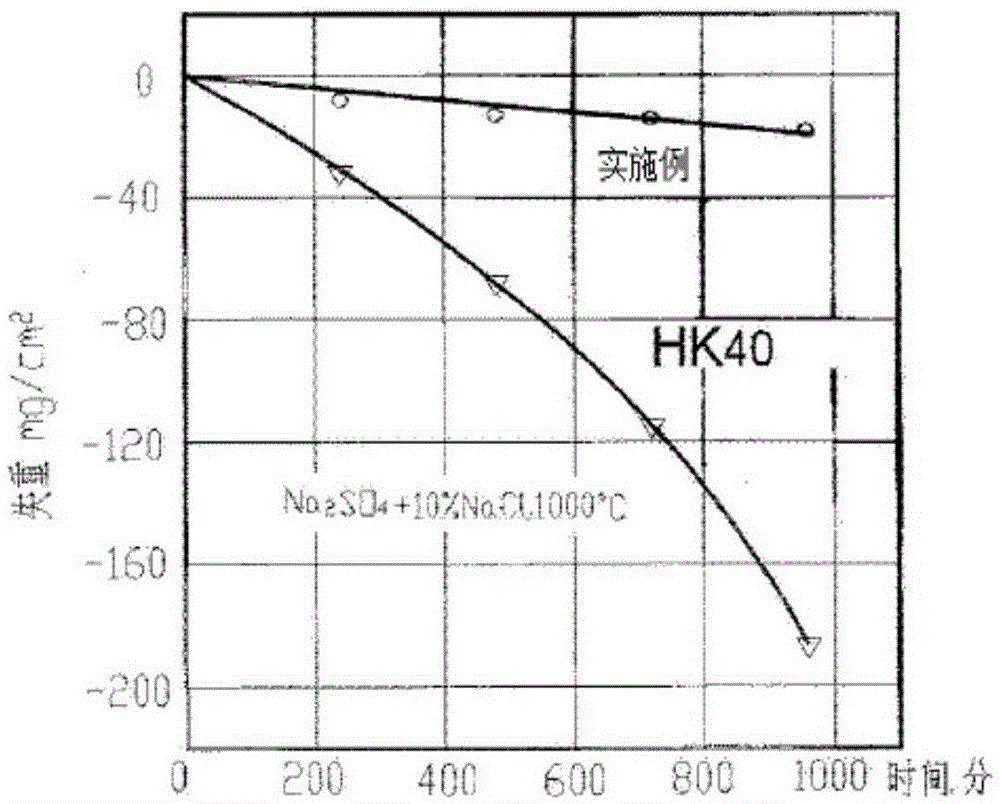
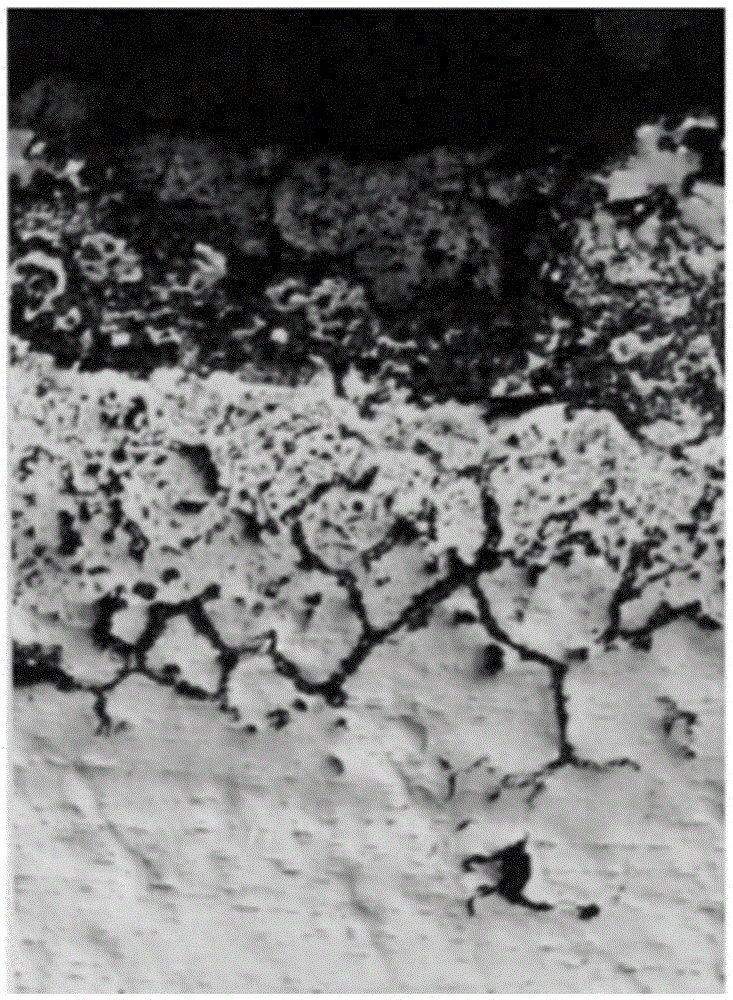
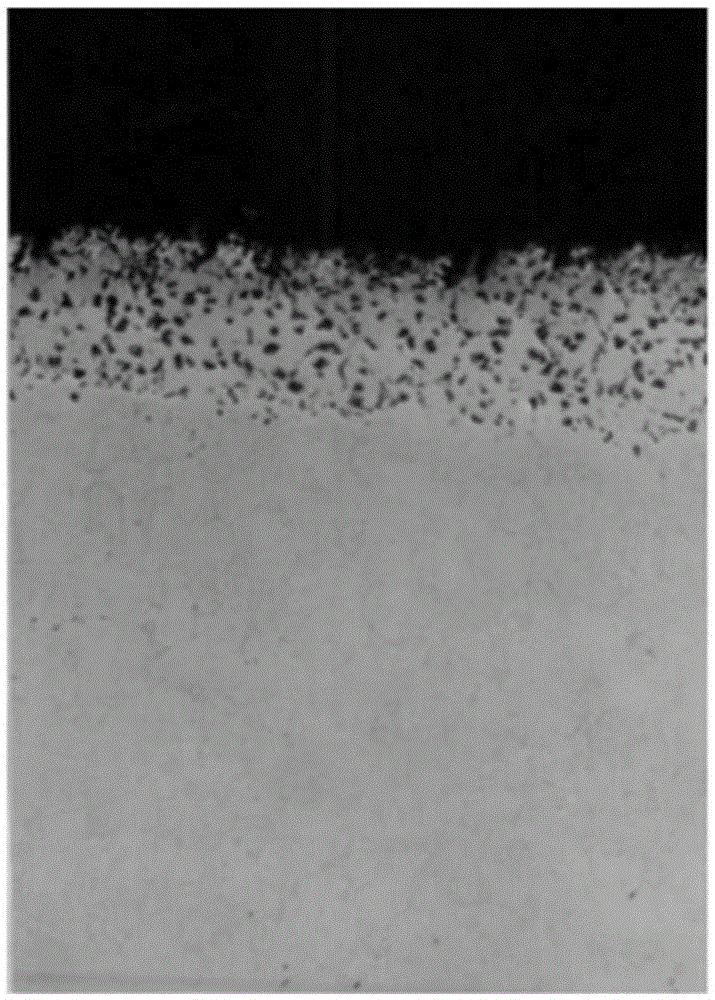
Heat-resistant alloy resisting to sulfur corrosion and rod production method thereof
A technology of heat-resistant alloy and production method, which is applied in the field of metal materials, can solve the problems of low service life and low corrosion resistance, and achieve the effects of increased fluidity, strong high-temperature sulfur corrosion resistance, and high-strength performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] First, the raw materials are melted in a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace. Under normal pressure, the melting temperature in the induction furnace is controlled at 1560 ° C. The mass percentage of molten steel obtained by melting is: C: 0.038%, Si: 1.41%, Mn: 1.13%, Cr: 24.32%, Ni: 19.92%, Nb: 1.23%, Mo: 0.38%, V: 0.08%, P: 0.032%, S: 0.025%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0039]Then the obtained molten steel is drawn into a Φ100mm master alloy rod through a horizontal continuous casting machine. Then put the finished master alloy rod into a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace for remelting. Under normal pressure conditions, control the melting temperature in the induction furnace at 1560 ° C, and add Al, Ce and La elements to the molten steel at the same time. Alloying, the mass percentage composition of the obtained remelted molten steel is: C: 0.038%, Si: 1.41%, Mn: 1.13%, Cr: 24.32%, Ni: 19.92%, Nb: 1.23%, Mo: ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] First, the raw materials are melted in a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace. Under normal pressure, the melting temperature in the induction furnace is controlled at 1600 ° C. The mass percentage of molten steel obtained by melting is: C: 0.017%, Si: 1.83%, Mn: 1.42%, Cr: 25.87%, Ni: 21.35%, Nb: 1.47%, Mo: 0.41%, V: 0.32%, P: 0.028%, S: 0.025%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0043] Then the obtained molten steel is drawn into a Φ100mm master alloy rod through a horizontal continuous casting machine. Then put the finished master alloy rod into a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace for remelting. Under normal pressure conditions, control the melting temperature in the induction furnace at 1600 ° C, and add Al, Ce and La elements to the molten steel at the same time. Alloying, the mass percentage composition of the obtained remelted molten steel is: C: 0.017%, Si: 1.83%, Mn: 1.42%, Cr: 25.87%, Ni: 21.35%, Nb: 1.47%, Mo:...
Embodiment 3
[0046] First, the raw materials are melted in a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace. Under normal pressure conditions, the melting temperature in the induction furnace is controlled at 1580 ° C. The mass percentage of molten steel obtained by melting is: C: 0.21%, Si: 2.12%, Mn: 2.01%, Cr: 24.92%, Ni: 22.03%, Nb: 1.62%, Mo: 0.42%, V: 0.54%, P: 0.030%, S: 0.020%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0047] Then the obtained molten steel is drawn into a Φ100mm master alloy rod through a horizontal continuous casting machine. Then put the finished master alloy rod into a non-vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace for remelting. Under normal pressure conditions, control the melting temperature in the induction furnace at 1580°C, and add Al, Ce and La elements into the molten steel at the same time. Alloying, the mass percentage composition of the obtained remelted molten steel is: C: 0.21%, Si: 2.12%, Mn: 2.01%, Cr: 24.92%, Ni: 22.03%, Nb: 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com