Distributing Connection Publishing in a Load Balancer
A load balancer, a technology for distributing loads, applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
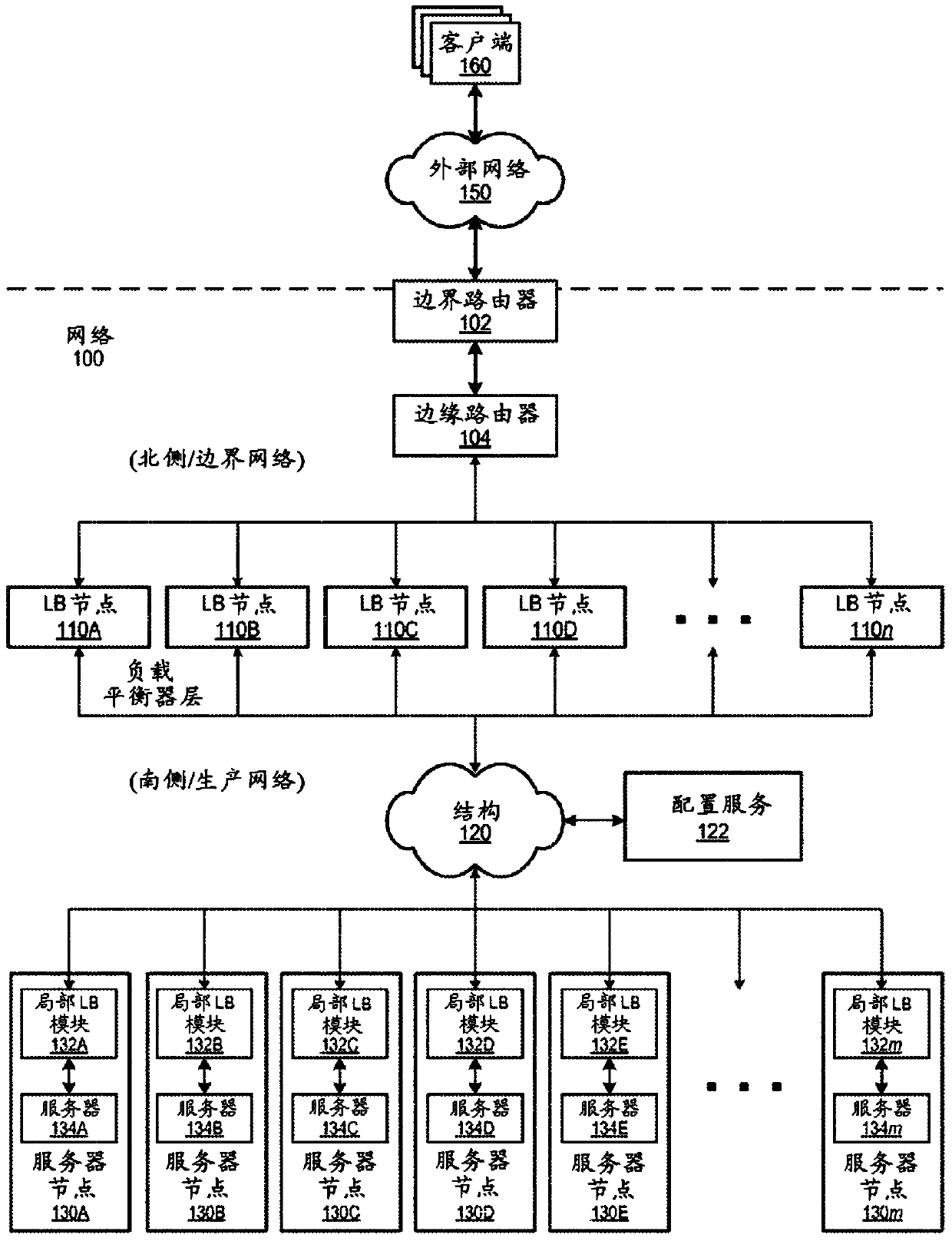
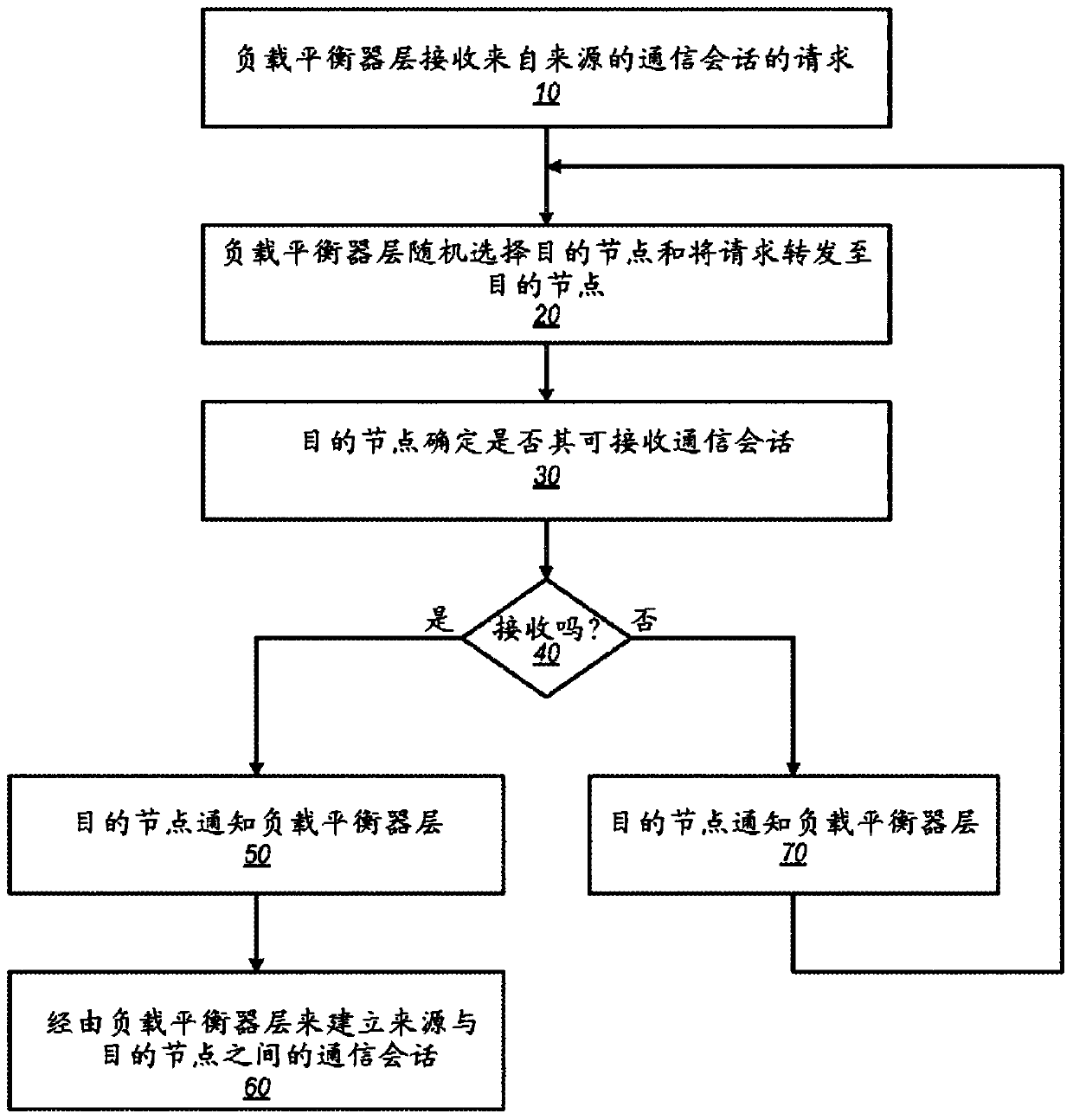
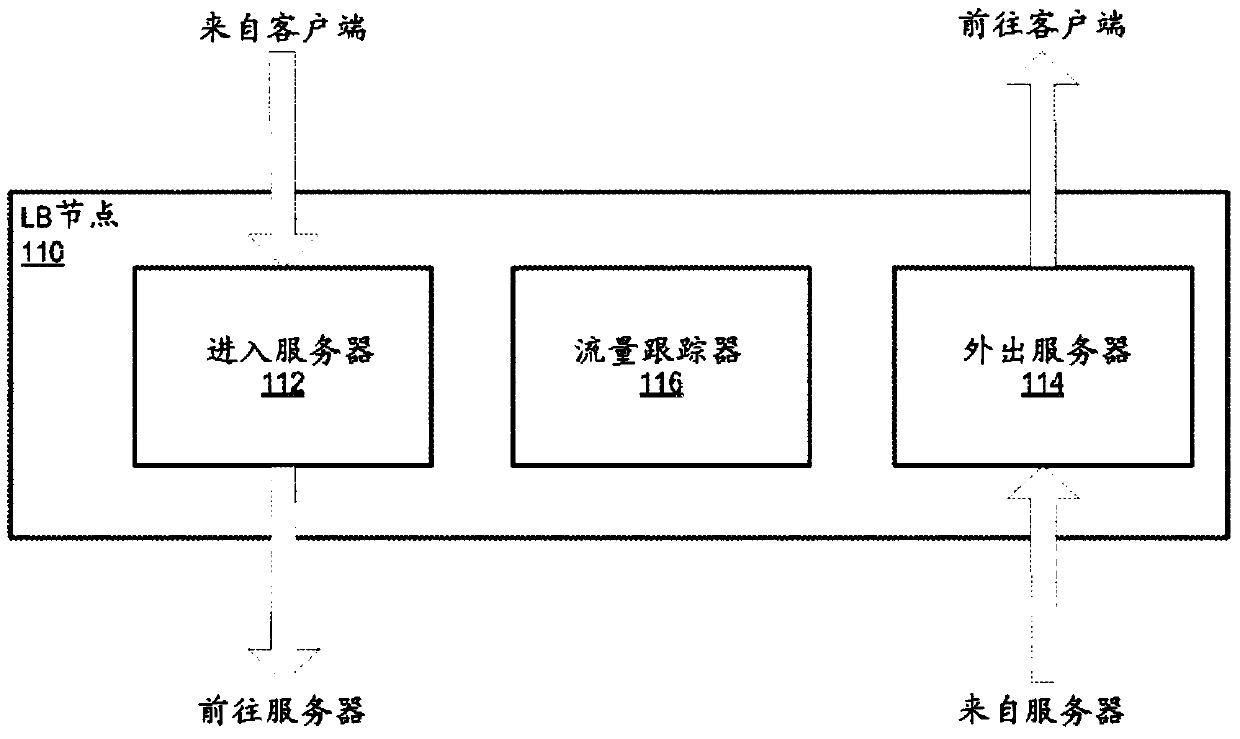
[0043] Various embodiments of methods and systems for distributed load balancing in a network environment are described. Embodiments of distributed load balancing methods and systems are described that may be implemented in accordance with embodiments of distributed load balancers in various network environments. An implementation of a distributed load balancer can be used, for example, to facilitate and maintain clients on an external network, such as the Internet, with a local network, such as Figure 33A and 33B The illustrated destinations on provider network 1900 are typically packet flows, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) technology packet flows, between servers (eg, web servers, application servers, data servers, etc.). Although embodiments are described herein primarily with respect to processing TCP packet streams, it should be noted that embodiments are applicable to other data communication protocols besides TCP, and to other applications besides process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com