A pharmaceutical composition for treating and/or preventing inflammatory pain and its application
A technology for inflammatory pain and composition, which is applied in the directions of drug combination, non-central analgesic, medical preparation containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of enhancing the analgesic effect of tetrahydropalmatine and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
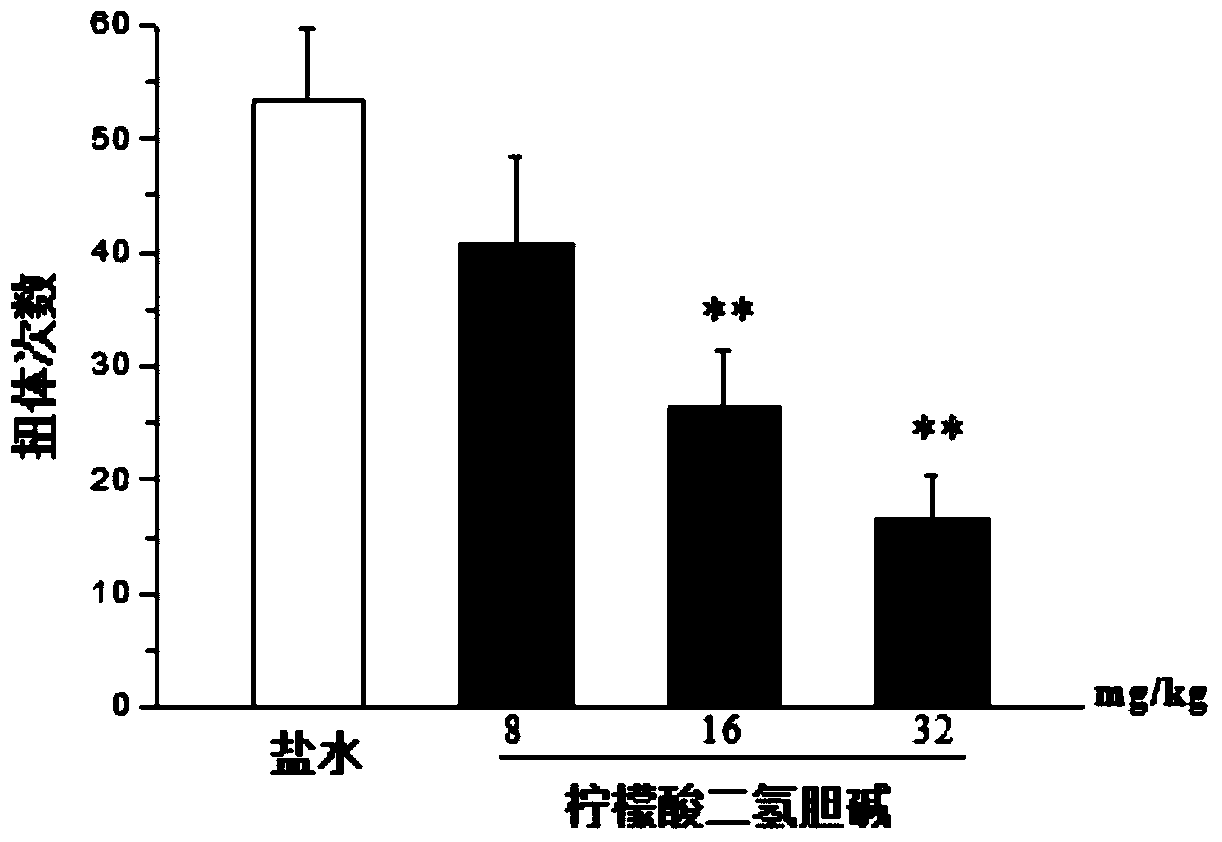
[0027] Embodiment 1: the analgesic effect of dihydrocholine citrate in acetic acid writhing experiment
[0028] Mice were injected with 0, 8, 16 and 32 mg / kg of dihydrocholine citrate into the tail vein, and 0.6% acetic acid solution 0.1ml / 10g was injected intraperitoneally after 120 minutes of administration, and the torque of the mice within 20 minutes after the injection of acetic acid was recorded. The body count was used to evaluate the analgesic effect of the drug. Data are expressed as mean±SEM, n=10, compared with saline group: * p** pfigure 1 shown. It shows that dihydrocholine citrate can dose-dependently reduce the number of writhing in mice induced by acetic acid.
Embodiment 2
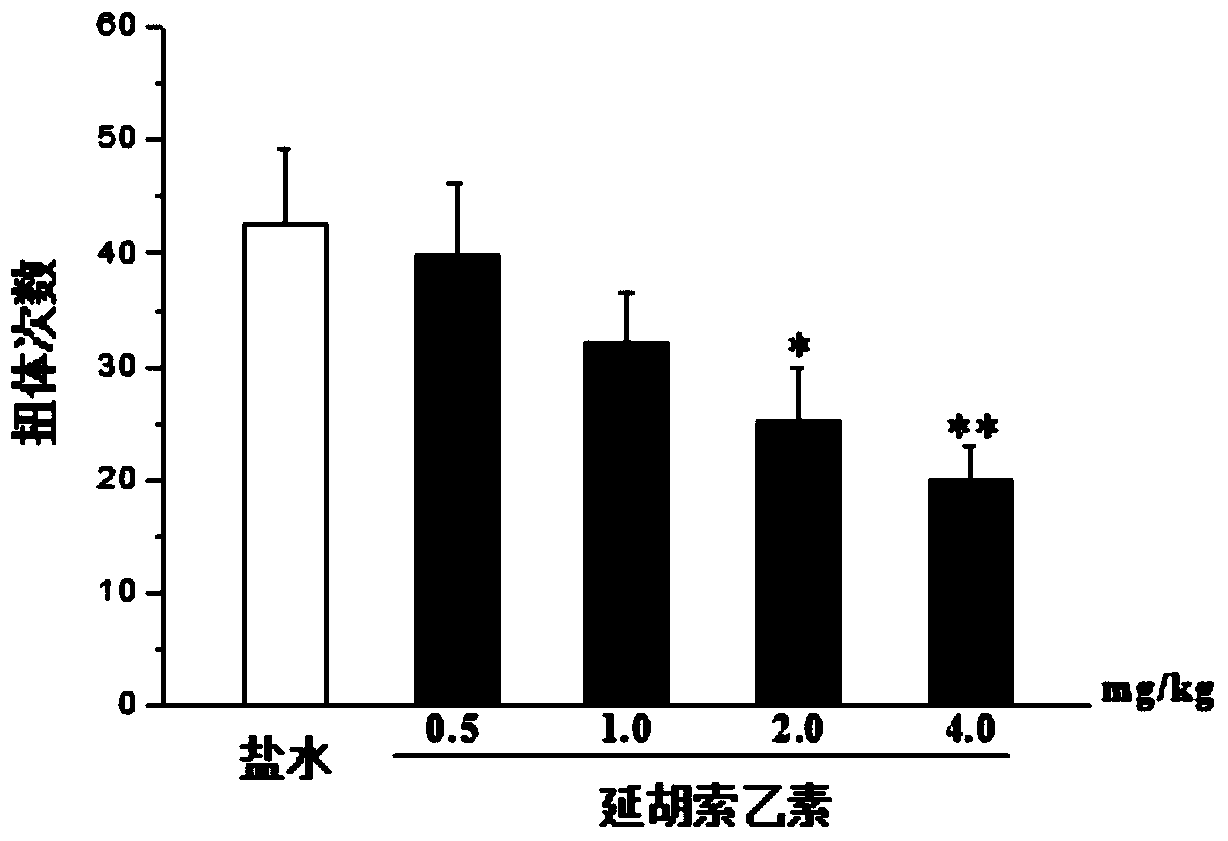
[0029] Embodiment 2: Analgesic effect of tetrahydropalmatine in acetic acid writhing experiment
[0030] Mice were intraperitoneally injected with Tetrahydropalmatine 0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mg / kg, and 0.6% acetic acid solution 0.1ml / 10g was injected intraperitoneally after administration for 15 minutes, and the writhing of mice within 20 minutes after acetic acid injection was recorded The number of times used to evaluate the analgesic effect of the drug. The data are expressed as mean±SEM, n=10, compared with the saline group: *p figure 2 shown. Show that tetrahydropalmatine can dose-dependently reduce the number of mice writhing caused by acetic acid.
Embodiment 3
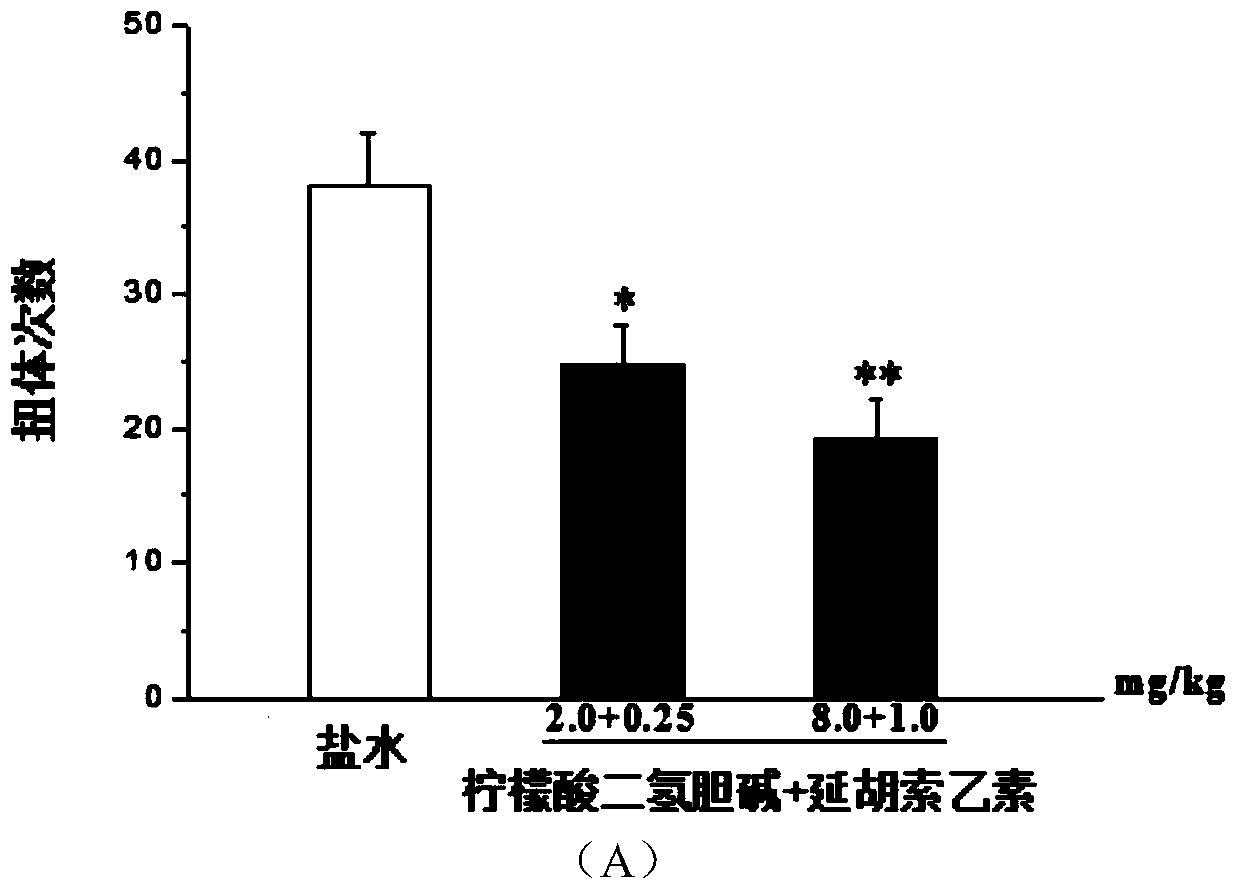
[0031] Example 3: Analgesic effect of combined application of different doses of dihydrocholine citrate and different doses of tetrahydropalmatine in acetic acid writhing test
[0032]Mice were injected with dihydrocholine citrate 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.50, 1.00, 2.00 and 8.00 mg / kg into the tail vein respectively, and intraperitoneally injected with tetrahydropalmatine 0, 0.015, 0.03, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25 and 105 minutes after administration. 1.00mg / kg, intraperitoneally inject 0.6% acetic acid solution 0.1ml / 10g in mice 15 minutes after administration, and record the number of writhing times of mice within 20 minutes after acetic acid injection to evaluate the analgesic effect of the drug. Data are expressed as mean±SEM, n=10, compared with saline group: * p** p image 3 A, 3B shown. It shows that the combined application of choline and tetrahydropalmatine can synergistically reduce the number of writhing in mice caused by acetic acid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com