A fine and intelligent dismantling process and device for waste lead-acid batteries
A technology for waste lead-acid batteries and batteries, used in battery recycling, solid waste removal, waste collector recycling, etc., can solve the problems of low recovery rate, easy to be brought into other follow-up equipment and equipment, reducing equipment service life, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0081] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the solution of the present invention, and to make the above-mentioned purpose, features and advantages of the present invention more obvious and understandable, the following in conjunction with the attached Figure 1-23 The present invention is described in further detail with the following examples.
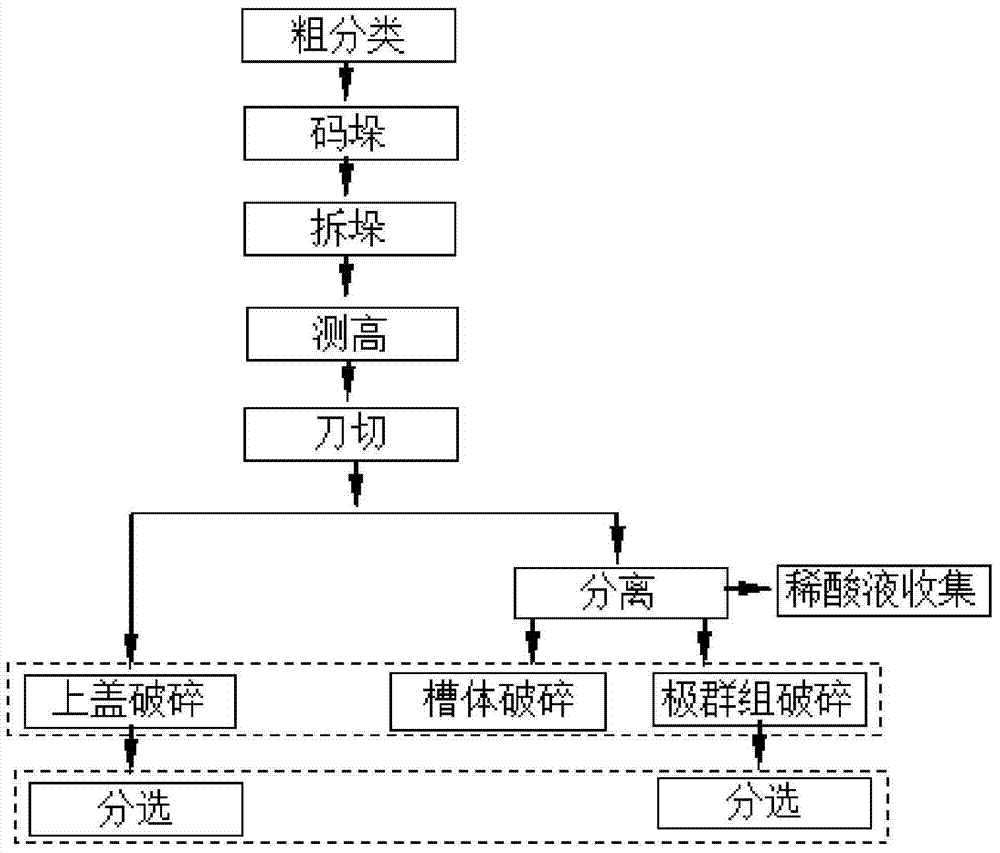
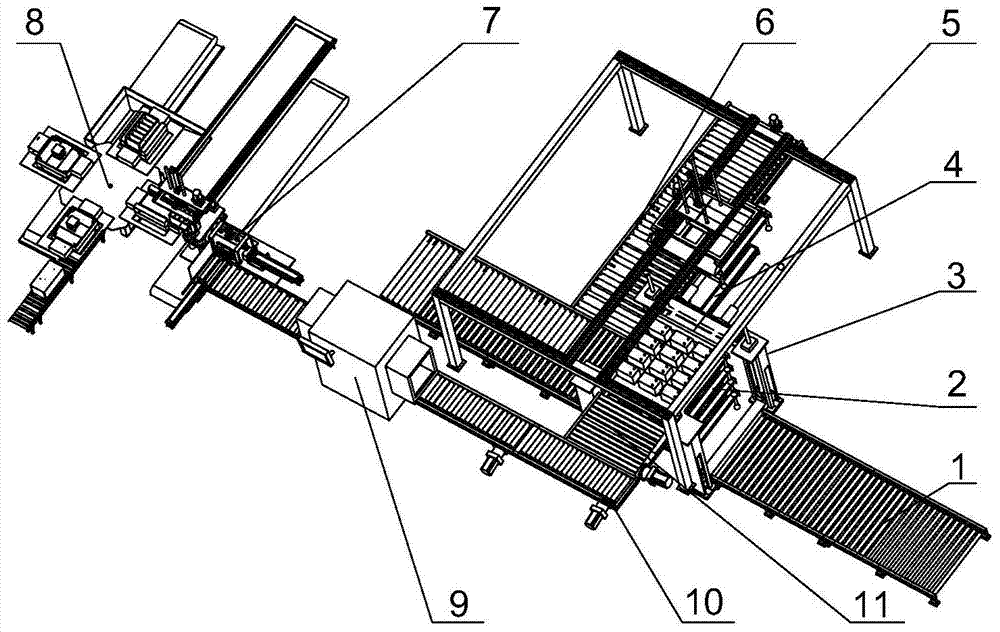
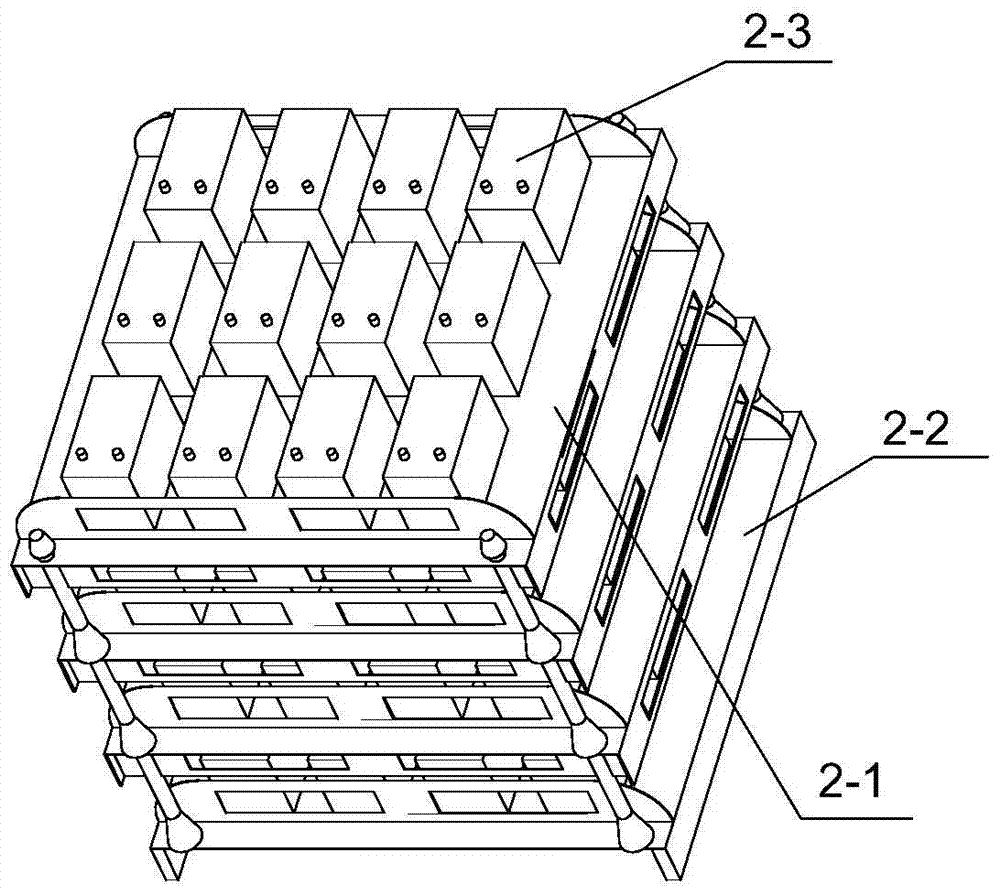
[0082] Such as figure 1 and 2 , the process and the device of the processing waste lead-acid battery implemented according to the present invention are specifically as follows:
[0083] 1. Primary classification
[0084] There are many types of batteries produced by lead-acid battery factories, so there are various types of waste lead-acid batteries when recycling them. In order to improve the efficiency of battery recycling, firstly, all recycled waste lead-acid batteries are roughly classified, and the width and size of batteries can be known through statistics. Between 128mm and 269mm, batteries are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com