A Botrytis cinerea gene bcudc1 related to pathogenicity and its application
A technology of Botrytis cinerea, 1.bcudc1, applied in the application field of genes and their encoded proteins, can solve the problems of little known molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1B
[0025] Correlation analysis of embodiment 1BcUdc1 gene
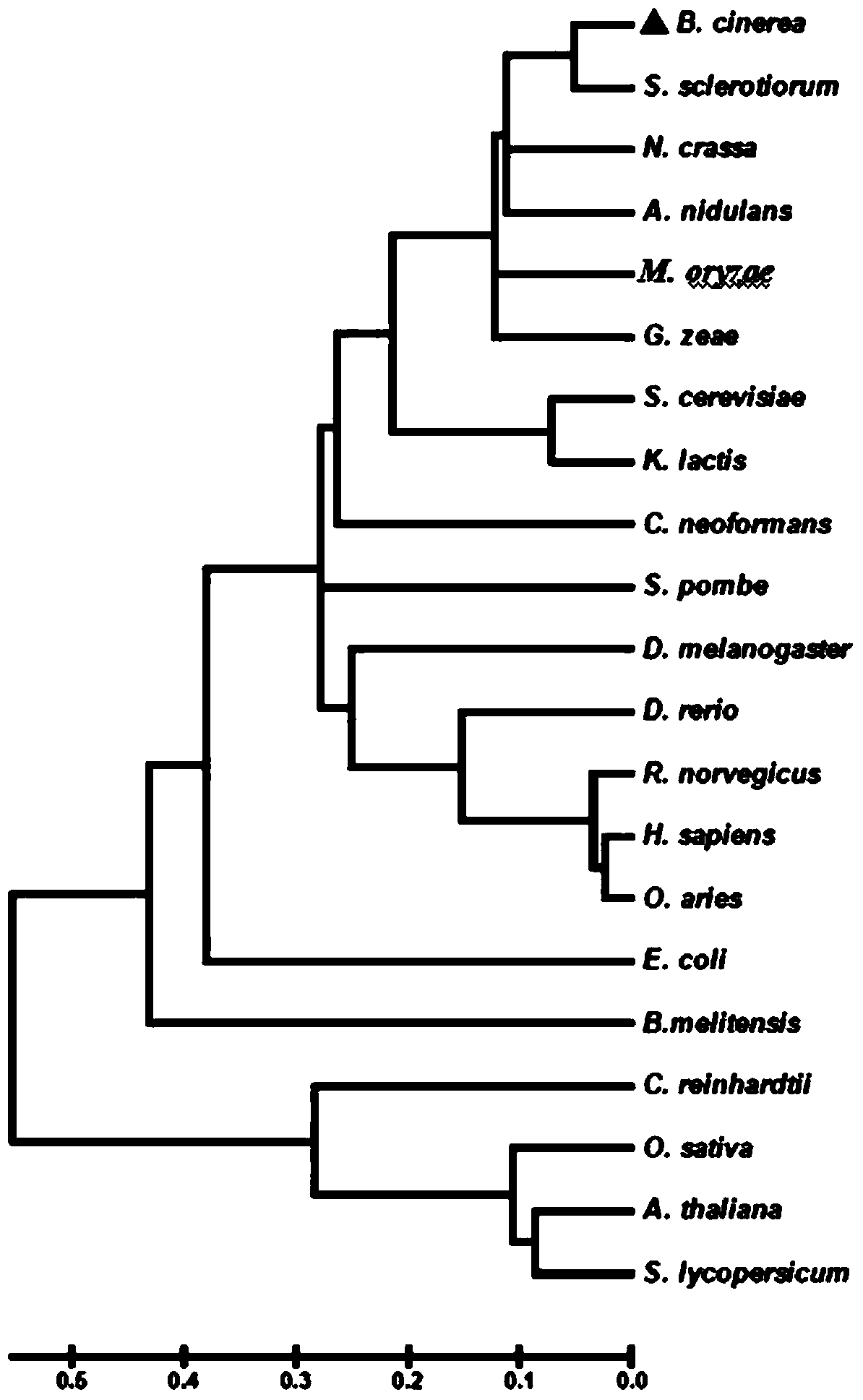
[0026] The open reading frame of the BcUdc1 gene of Botrytis cinerea consists of 1323 nucleotides, including 5 exons, the full-length cDNA of the coding region is 1095 nucleotides, and the encoded protein product consists of 364 amino acids. The BcUdc1 protein sequence was compared and analyzed (http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Blast.cgi), and it was found that Udc1 widely exists in cellular organisms such as animals, plants, fungi and bacteria. Phylogenetic tree analysis (http: / / phylogeny.lirmm.fr / phylo_cgi / simple_phylogeny.cgi) showed that the homology between filamentous fungal Udc1 proteins was high, among which BcUdc1 was closest to S. sclerotiorum Udc1; BcUdc1 was closely related to Yeast is a little further away, followed by animals, bacteria, and most distantly related to green algae and plants (see figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2B
[0027] Example 2 Knockout and Genetic Complementation of BcUdc1 Gene
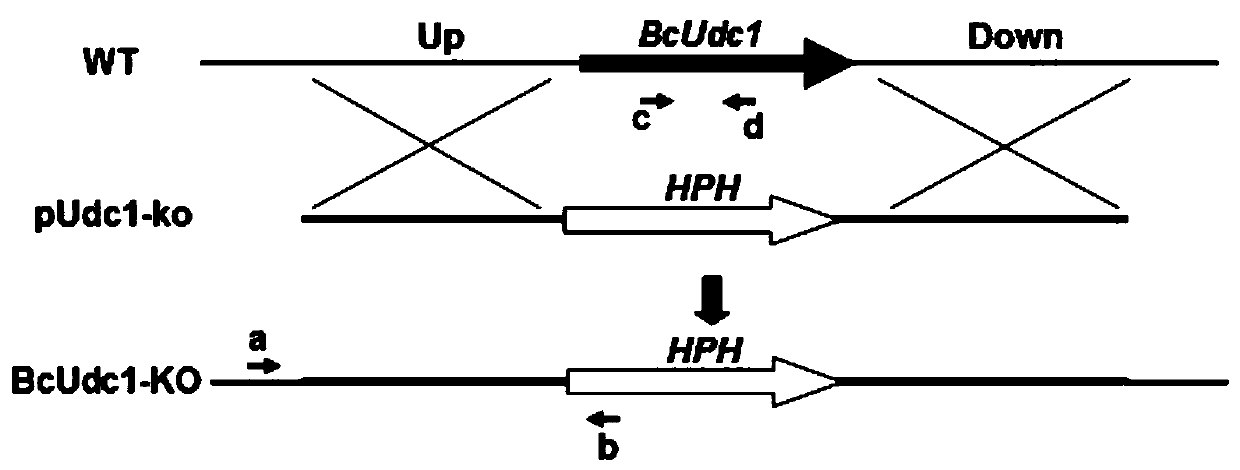
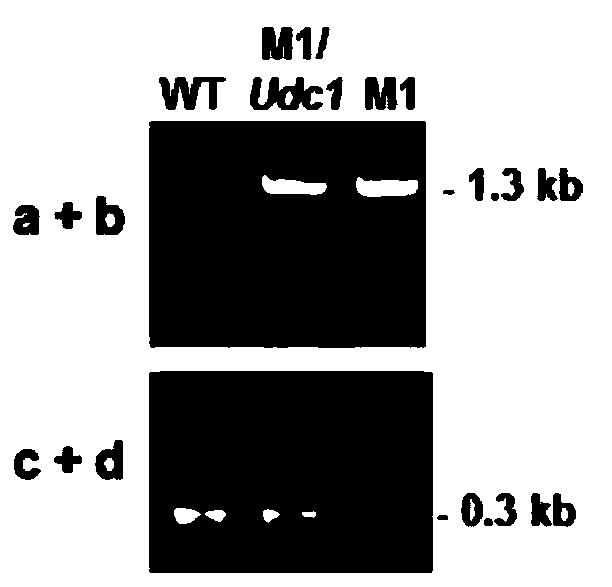
[0028] 1) Construction of knockout vector
[0029] Udc1-UP-F(5'-CTCGAGGCTCCGTGGAAACACCTACA-3)' and Udc1-UP-R(5'-GAATTCAAATAAGTTGACAGGGACGAGA-3') were used to amplify the upstream of BcUdc1 gene using the genomic DNA of Botrytis cinerea strain B05.10 as a template 655bp fragment, use Udc1-DN-F (5'-GGATCCAAACCGCCCAGTTGTCTTCC-3') and Udc1-DN-R (5'-CTGCAGAGAAACCCTCGCCATCAAAC-3') to amplify the downstream 699bp fragment of Botrytis cinerea BcUdc1 gene, the reaction system is: 10mmol / L dNTP Mixture, 0.5 μL; 10×PCR buffer, 2.5 μL; each 1 μL of upstream and downstream primers (10 μmol / mL); template DNA, 1 μL; Ex-Taq, 0.2 μL (5U); ddH 2O, 18.8 μL; amplification program: 94°C pre-denaturation for 3 minutes, then (1) 94°C, denaturation for 50 seconds; (2) 58°C, annealing for 50 seconds; (3) 72°C, extension for 60 seconds; (4) ) cycled 30 times; (5) extended at 72°C for 10 minutes. The above two DNA amplification p...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The role of embodiment 3 BcUdc1 gene in the process of conidia germination of Botrytis cinerea
[0042] The variation of conidia germination of BcUdc1 mutant was determined by slide culture method. PDB (20% potato boiled and filtered, glucose 2%) spore suspension (5×10 4 mL- 1 ) was dropped on the glass slide, incubated at 20°C with moisture, and microscopically observed after 12h and 24h respectively. The experimental results showed that the conidia of the wild-type strain of Botrytis cinerea had germinated within 12 hours, and grew long germ tubes (60-100 μm), while only a small amount of conidia of the BcUdc1 mutant germinated, and the growth was small , even at 24h, it is only about 20 μm, indicating that the BcUdc1 gene plays an important role in the germination of Botrytis cinerea conidia (see Figure 4 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com