A tire safety monitoring device
A technology for safety monitoring and tires, applied in tire measurement, road vehicle tires, tire parts, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to measure tire wear, reduce service life, and safety hazards, and achieve the goal of simplifying tire maintenance and improving safety Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] "Front", "rear", "inside" and "outside" described in the present invention are the relative positions when the tire is installed on the automobile, and have nothing to do with the specific structure of the present invention.
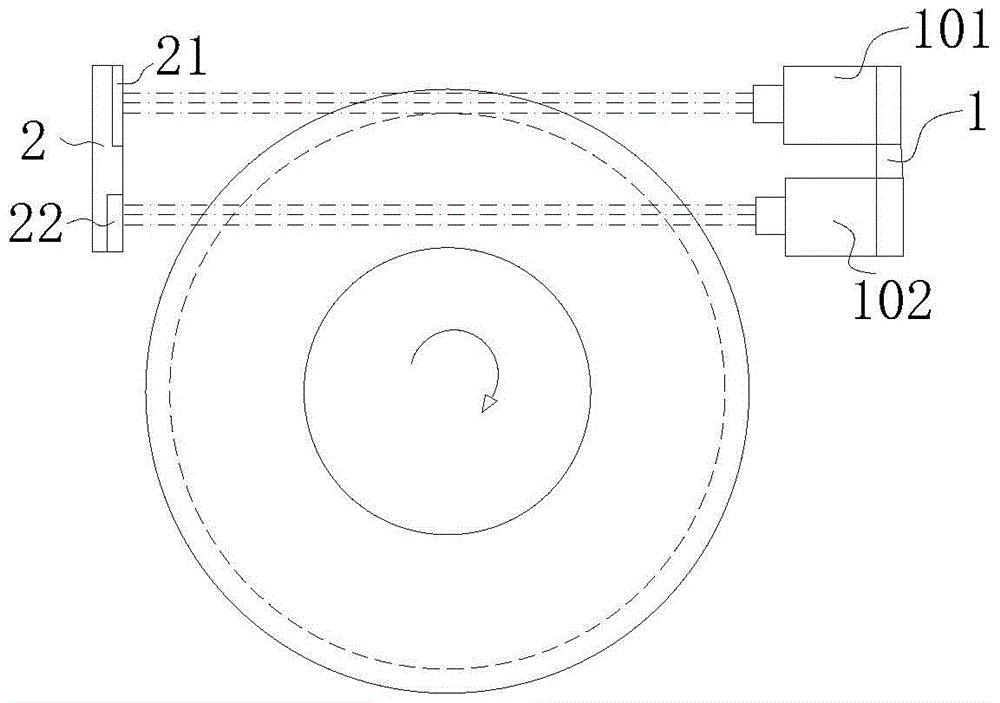
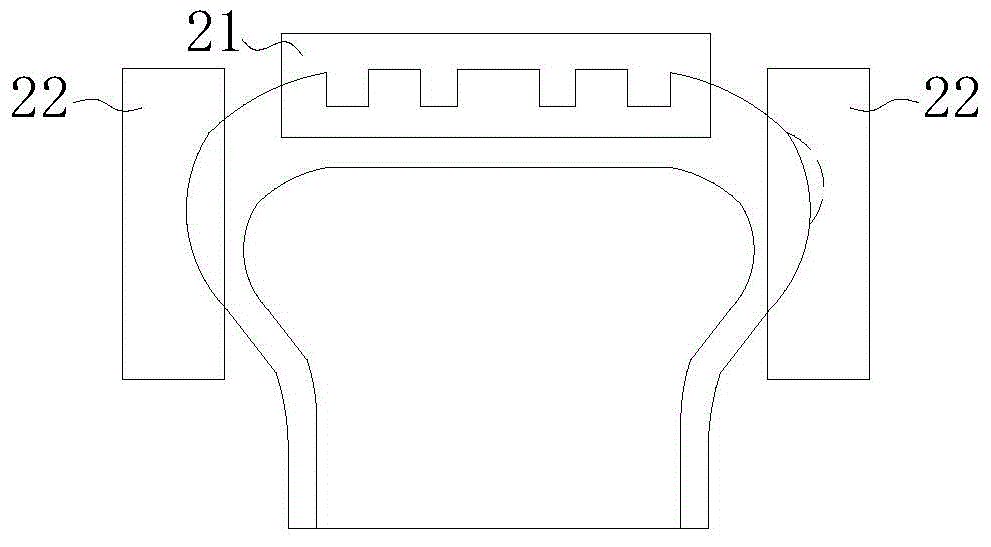
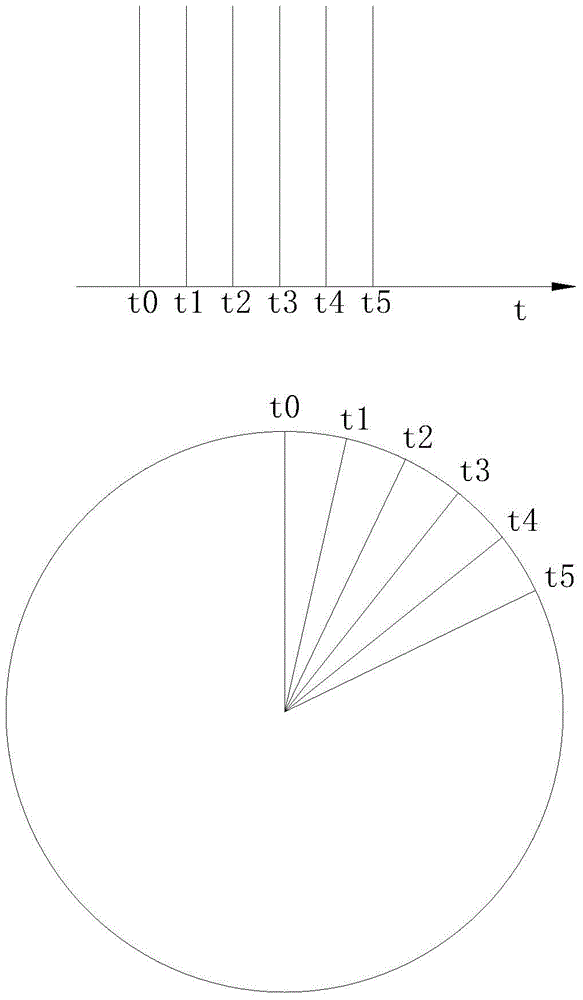
[0032] Such as Figure 1-5As shown, a tire safety monitoring device includes a limit block 61 installed on the tire for checking the depth of the longitudinal groove of the tire tread. The limit block 61 is provided with a metal calibration sheet. The tire front, A light source assembly 1 placed horizontally is installed on the inner lining of the fender of the automobile, and the light source assembly 1 includes a first lamp group 101, the height of the first lamp group 101 is consistent with the height of the upper surface of the tire, and the first lamp group The light emitted by 101 is perpendicular to the cross-section of the tire longitudinal groove passing through the center line of the tire and along the vertical direction. After passing t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com