Indoor positioning method and device
An indoor positioning and indoor map technology, applied in the field of navigation, can solve the problems of unfavorable real-time positioning of robots, reduced positioning accuracy and navigation accuracy, and high algorithm time complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] figure 1 This is a flowchart of the indoor positioning method provided by the first embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment can be applied to the situation of quickly and accurately positioning the position of the robot. The method can be executed by an indoor positioning device, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0022] Step 110: Determine an estimated pose, and determine a local map library according to the obtained indoor map library and the estimated pose.
[0023] Among them, in order to determine the position of the robot in the plane, a two-dimensional plane coordinate system is established. Take the starting point of the robot's movement in the indoor environment as the coordinate origin, and take the front of the robot when it starts to move as the positive direction of the X-axis. , the counterclockwise direction is positive, and the included angle ranges from -180° to 180°. Determine the current position of the robot through the s...
Embodiment 2
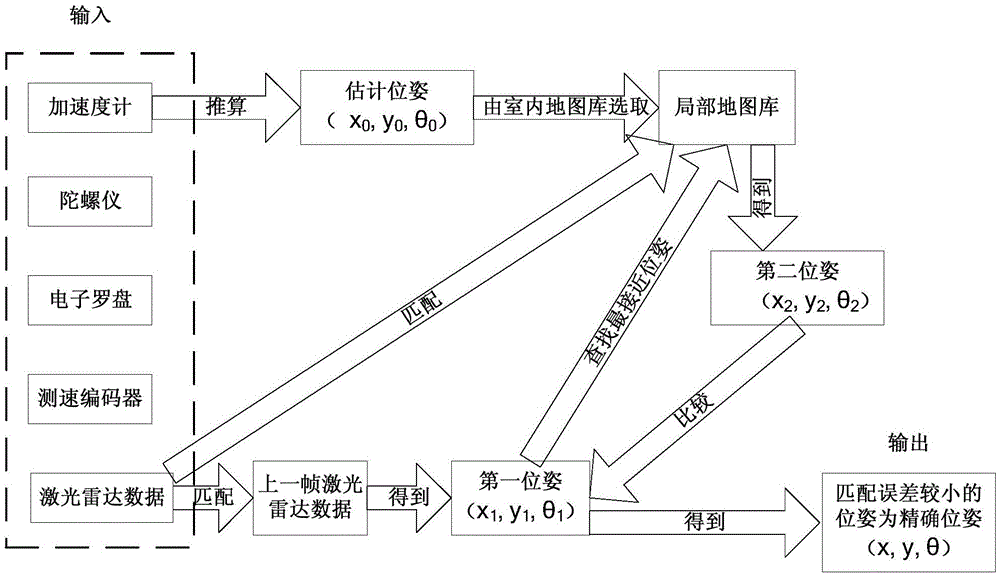
[0037] figure 2 This is a schematic diagram of data processing in an indoor positioning method provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and this embodiment may provide a preferred example based on the foregoing embodiment.
[0038] see figure 2 As shown, the input data includes the acceleration data collected by the accelerometer, the direction data collected by the gyroscope, the direction data collected by the electronic compass, the speed data collected by the speed encoder, the current frame lidar data and the indoor map library. The embedded chip in the robot acquires the acceleration data collected by the accelerometer set on the robot, the direction data determined by the gyroscope, the direction data determined by the electronic compass, and the speed data determined by the speed encoder (Hall sensors can also be used to replace the speed encoder. ), and estimate the position and attitude of the robot according to the data obtained above. For example, by ...
Embodiment 3
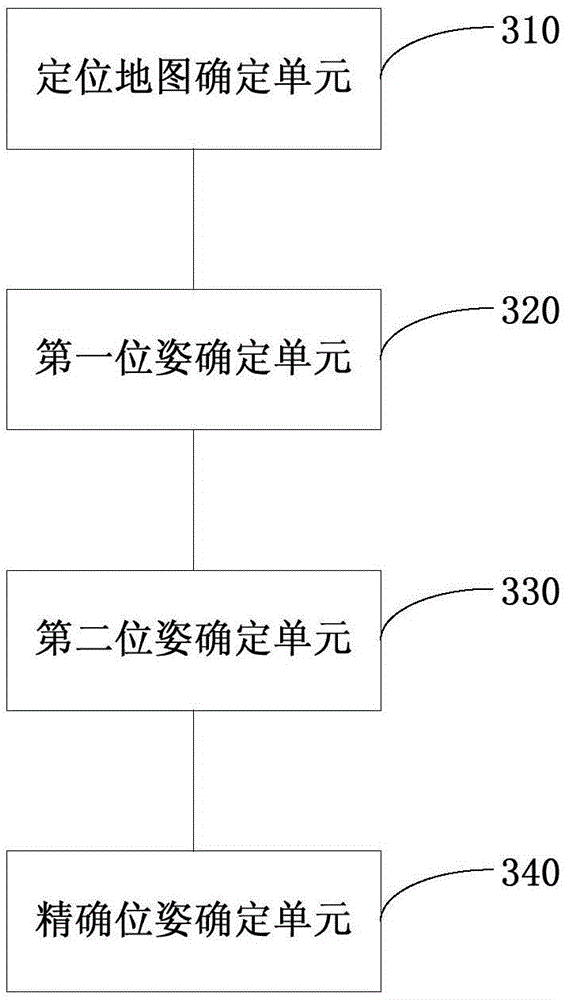
[0043] image 3 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of an indoor positioning device provided in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This embodiment can be applied to the situation of performing rapid indoor positioning of robots without pre-deploying auxiliary equipment in the indoor environment. The specific structure is as follows:
[0044] a positioning map determination unit 310, configured to determine an estimated pose, and determine a local map library according to the obtained indoor map library and the estimated pose;
[0045] a first pose determination unit 320, configured to match the collected lidar data of the current frame with the lidar data of the previous frame to determine the first pose;
[0046] The second pose determination unit 330 is configured to obtain the pose with the smallest offset from the first pose in the local map library, and compare the current frame lidar data with the pose with the smallest offset. The lidar data corresponding to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com