Label propagation method based on propagation limitation
A label propagation and labeling technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of different results, low application value, and poor algorithm stability, and achieve the effects of stable division results, reduced mutual interference, and accurate performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
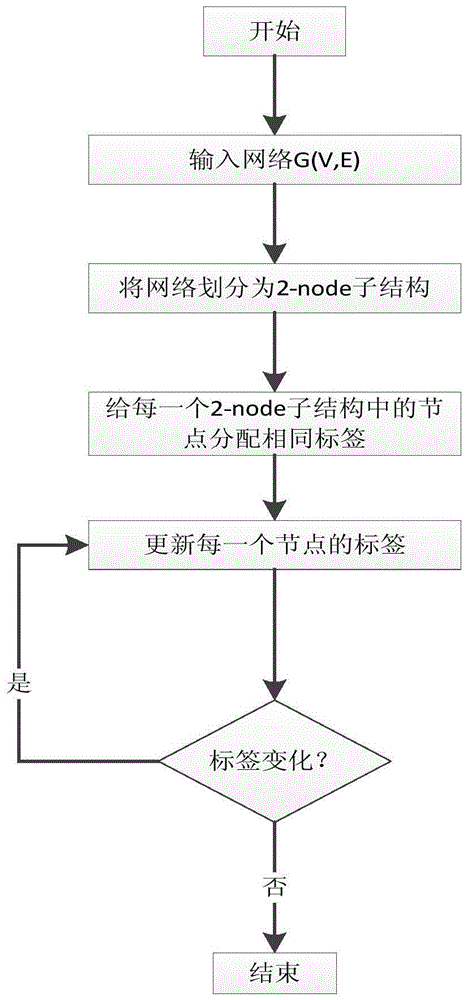
[0031] The present invention is a method based on propagation restriction label propagation, see figure 1 , use 2-node substructure modeling for complex networks to limit the label propagation between modules, reduce the mutual interference of label propagation between modules, and divide a large and complex network into multiple modules, including the following steps:
[0032] Step 1, input a large complex network, the given large complex network uses similarity formula to generate 2-node substructure,
[0033] There are many different natural modules in large complex networks, see figure 2 (a), when initializing, define a large complex network as G: Let is an undirected and unweighted network, V is a node set, E is an edge set, and for any edge ij of G=(V,E), use the similarity formula:
[0034] S i m = | N ( v i ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The label propagation method based on propagation restriction is the same as in embodiment 1, wherein in step 1, a similarity formula is used to generate a 2-node substructure, and the specific steps are:
[0045] 1.1. Initialize all nodes of the large complex network G(V,E) as unassigned nodes;
[0046] 1.2. Randomly select a node v that is not assigned a network i , if v i If there are unassigned neighbor nodes, choose from them with v i Vertex v with maximum vertex similarity j , put v i and v j as a 2-node substructure; otherwise v i Form a 2-node substructure by itself;
[0047] 1.3. Repeat step 2 until all nodes in the large complex network are allocated.
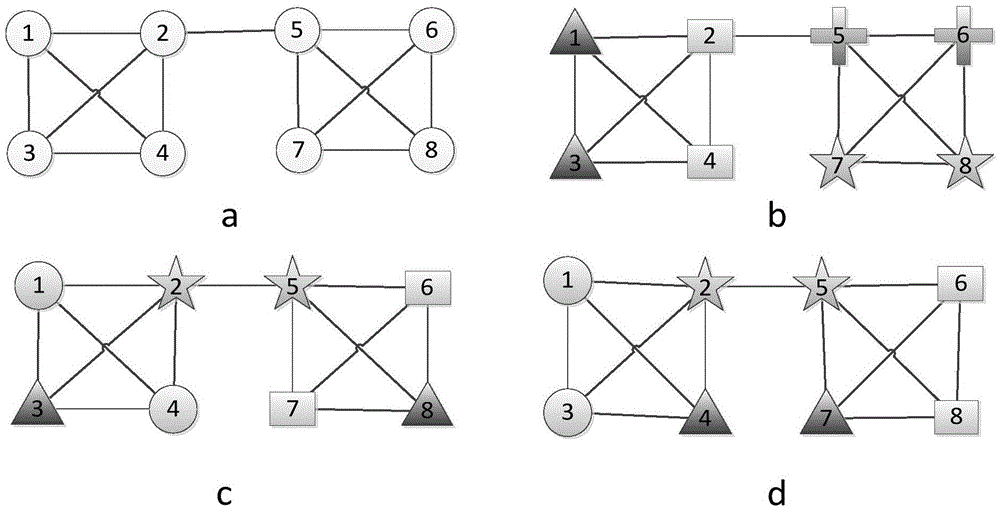
[0048] see figure 2 , figure 2 a is a schematic diagram of the original network data, nodes 1, 2, 3, and 4 belong to the same module, and nodes 5, 6, 7, and 8 belong to the same module. figure 2 b is the 2-node substructure divided by the present invention. In the figure, the triangle 1,3 nodes, th...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Based on the propagation restriction label propagation method, the same as in embodiment 1-2,
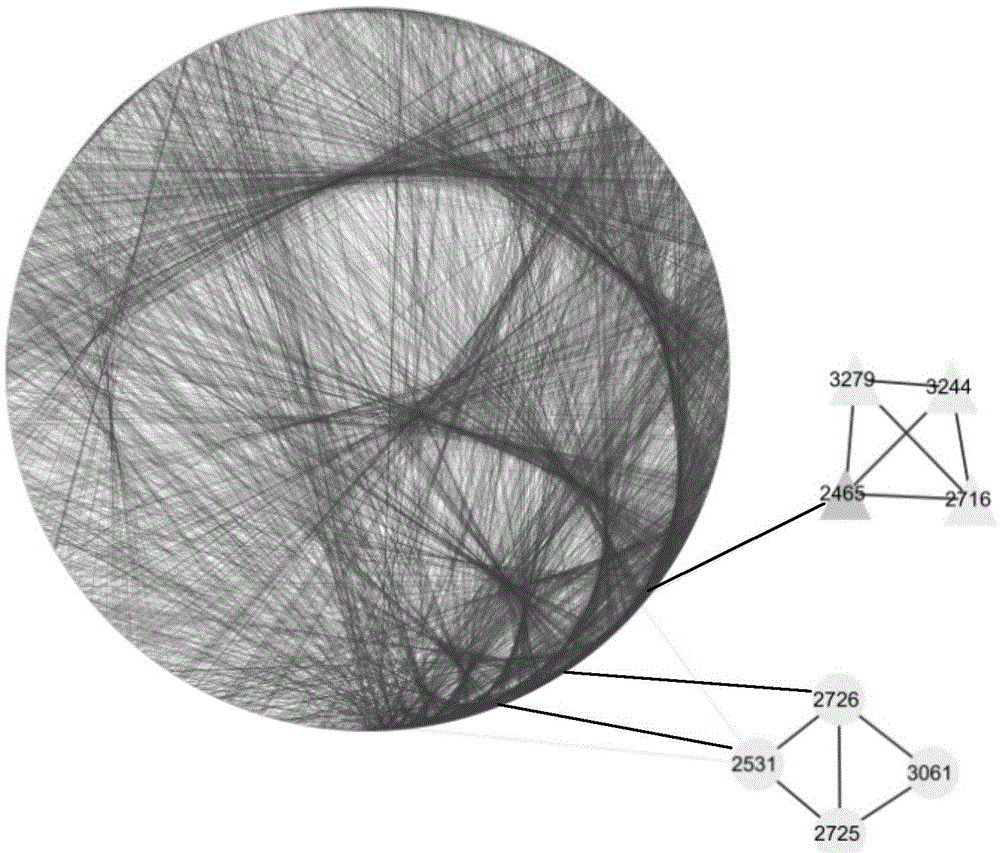
[0053] In this example, the module mining in the topological network of the national power grid in the western cities of the United States is completed by using the present invention. see image 3 There are 4,941 nodes and 13,188 edges in the topological network of the National Grid of western cities in the United States. There are no self-loops and repeated edges in the network, that is, there is no edge from node A to node A, and there is at most one edge between any two nodes.
[0054] see image 3 , utilize the implementation steps of the present invention as follows:
[0055] The first step is to preprocess the topological network data of the national power grid in the western cities of the United States, and obtain the network data G=(V,E);
[0056] In the second step, the network G=(V, E) is processed, and G=(V, E) is divided into 2-node substructures using the met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com