A double-enzyme digestion simplified genome next-generation sequencing library construction method and supporting kit
A technology for a second-generation sequencing library and a construction method, which is applied in the field of matching kits for the construction of second-generation sequencing libraries, can solve the problems of limited library construction costs, cumbersome procedures, and complicated use of instruments, thereby reducing synthesis costs and simplifying library construction procedures. , the effect of improving the quality value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
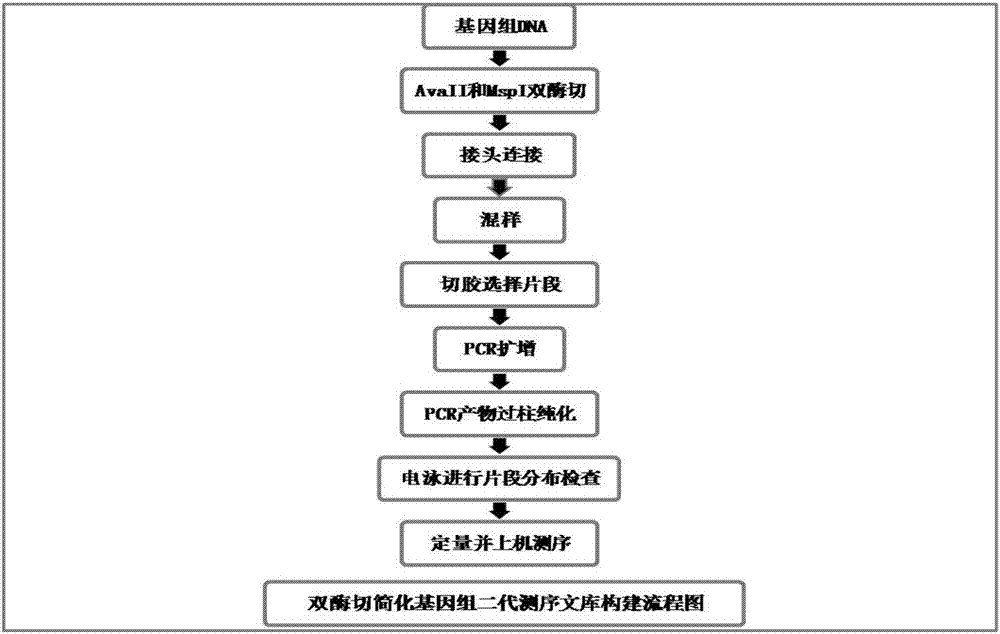
[0136] Double enzyme digestion simplifies the basic operation process of genome next-generation sequencing library construction:
[0137] The first step, the extraction of genomic DNA: using the improved CTAB method to extract the genomic DNA of fresh young bamboo leaves,
[0138] The second step, enzyme digestion of genomic DNA: use two common restriction endonucleases to digest genomic DNA to obtain DNA fragments with corresponding restriction enzyme sites at both ends;
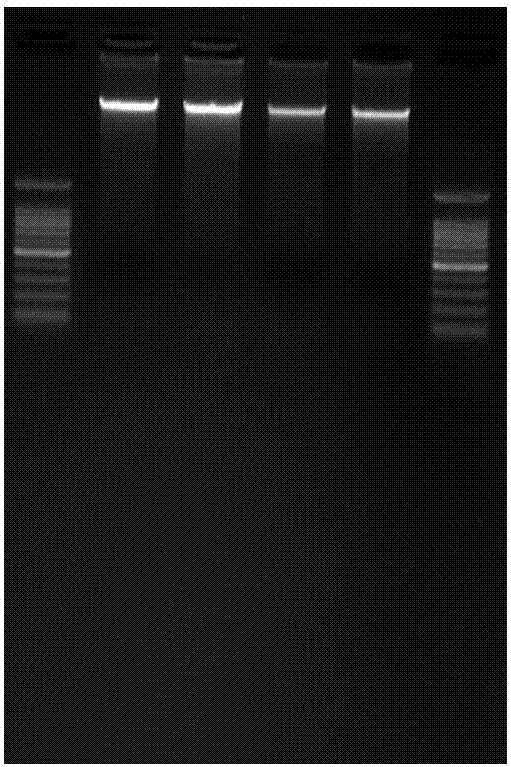
[0139] The genomic DNA has an obvious main band detected by agarose gel electrophoresis and the 260nm / 280nm value of the trace spectrophotometric purity test is between 1.8-2.2, and is diluted to 40-60ng / μl for use;
[0140] The common restriction endonuclease is preferably a restriction endonuclease recognizing a 4.5 base sequence and a restriction endonuclease recognizing a 4 base sequence, more preferably AvaII and MspI;
[0141] The third step is to use T4 DNA ligase to connect the A1 adapter (DNA barc...
Embodiment 2
[0188] The establishment of double enzyme digestion simplified genome next-generation sequencing library construction method:
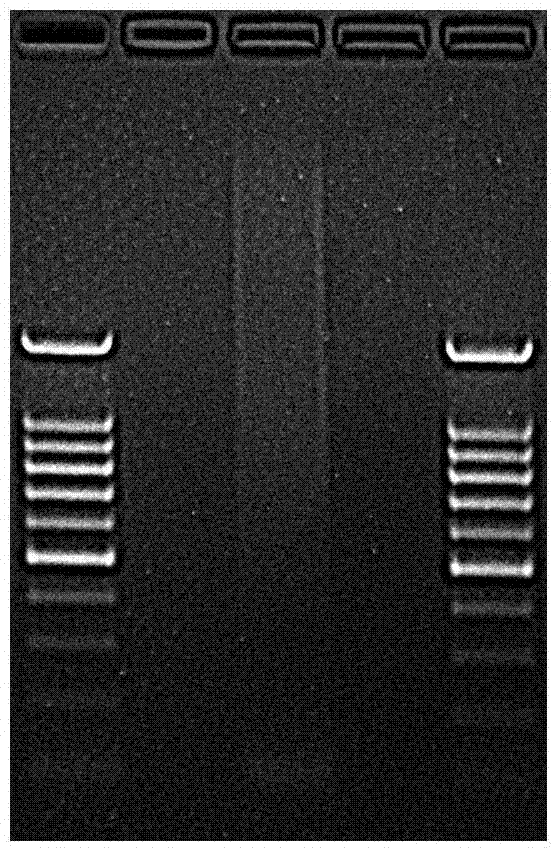
[0189] This embodiment selects Gramineae Bamboo subfamily Phyllostachysviridi-glaucescens (Carr.) A.et C.Riv. and Pseudosasa japonica (Sieb.et Zucc.) Makino) two Bamboo was used as the experimental material, and the basic operation process of double-enzyme digestion simplified genome next-generation sequencing library construction is shown in figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0190] The first step, genomic DNA extraction
[0191] Whole-genome DNA was extracted from the young leaves of P. viridi-glaucescens (Carr.) A. et C. Riv. and P. japonica (Sieb. et Zucc.) Makino) by modified CTAB method ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0192] (1) Take 10ml of 4% CTAB and preheat it at 60°C, add 2‰ dithiothreitol DTT and mix well.
[0193] (2) Weigh 60 mg of fresh young leaves, add liquid nitrogen to quickly grind them into powder, transfer to a 2m...
Embodiment 3
[0263] Genome-wide interspecific variation SNP detection of 20 temperate woody bamboo species:
[0264] Use double-digestion simplified genome next-generation sequencing library construction kit for research. Double Digestion Simplified Genome Next Generation Sequencing Library Construction Kit contains:
[0265] 1) A1 linker sequence pairs consisting of 20 sequences, each sequence structure is:
[0266] Positive strand: 5'TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTXXXXX3',
[0267] Negative strand: 5'GWCYYYYYAGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTA3'.
[0268] Wherein: XXXXX in the positive strand represents the DNA barcode sequence, YYYYY in the negative strand represents the sequence complementary to the DNA barcode, and W represents the base A or T. This kit only provides the A1 linker sequence pair corresponding to AvaII, and the A1 linker sequence pair corresponding to the rest of the enzymes can be directly synthesized from biological companies.
[0269] 2) A2 linker sequence, specifically:
[0270] Posit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com