A lithium-ion power battery charging method based on temperature-controlled battery attenuation
A charging method and power battery technology, applied in secondary battery charging/discharging, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc., can solve problems such as not considering the influence of temperature on battery charging characteristics, affecting battery life, and accelerating side reactions, etc. Achieve the effects of improving service life, reducing battery attenuation, and controlling attenuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0035] The embodiment uses the battery q of 50Ah battery, starting temperature T and V 临界 The relationship between them is (Table 1):
[0036] q (unit is %)
[0037] V within Table 1 above 临界 Values are V at the temperature in brackets 临界 , where V at -20°C 临界 Specifies the theoretical charging upper limit voltage for the battery, V at -15 and 10°C 临界 It is the lithium analysis voltage; when the battery is charged to 4.2V with a standard current constant current at -20°C, q=9.7%. At this time, the charging capacity is low, and the battery has not reached the lithium analysis voltage. From the table above, the T of the battery 1 -20°C, T 2 is 0°C.
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: T=-15°C, T 1 2
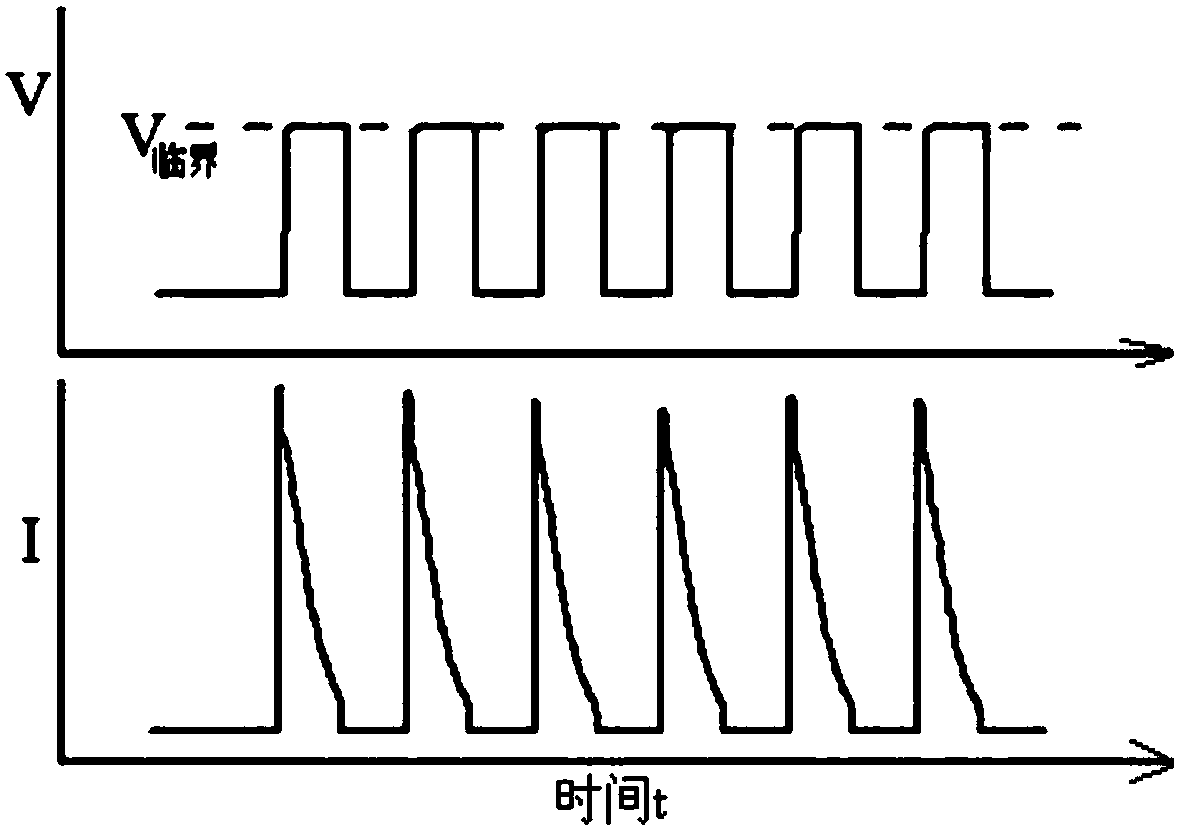
[0042] Measure the initial temperature of the battery at -15°C, V 临界 is 4.07V. The battery is charged with a constant voltage pulse from -15°C. As the charge progresses, the battery temperature rises to Tc>T 2 When the temperature is set at 2°C (>0°C), stop the constant voltage pulse charging; at this time, charge with a constant current of 1 / 3C to 4.107V (2°C), then switch to a constant voltage of 4.107V to charge until the current is about 1 / 3C 30C or constant pressure time 1h. Among them, the pulse charging adopts a 4-step pulse process, and the pulse voltages are 4.07V (-15°C), 4.08V (-10°C), 4.09V (-5°C), and 4.10V (0°C), and the pulse voltages are respectively in brackets V at internal temperature 临界 . The temperature intervals were 5°C (heating to 0°C) and 2°C (heating to the target 2°C), the single pulse time was 0.2s, and the rest time after a single pulse was 0.2s.
[0043] The constant voltage pulse charging parameters are s...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: T=10°C, T>T 2
[0050] Battery test temperature 10°C, V 临界 is 4.13V. The charging method of the battery at 10°C adopts 1C constant current charging to 4.13V (V 临界 ) and then switch to constant voltage (4.13V) to charge until the current drops to 0.1C or the constant voltage time is 1h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com