A method for hybrid breeding of Amorphophallus verruca
A technology of Amorphophallus verrucosum and hybrid breeding, which is applied in botany equipment and methods, plant gene improvement, application, etc. It can solve the problems of short flowering period, flowering is not fruitful, and the effect is not exerted, so as to achieve low cost and less virus accumulation. , the effect of high seed setting rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] In 2010, 26 flowering plants of Amorphophallus verruca were bred according to technical step A (the same below) in the experimental field of Dehong Prefecture Agricultural Science Institute; according to technical step E (the same below), assisted artificial pollination was carried out, and 1 plant was successfully induced to bear fruit. ~6 weeks later, the scape was as high as 91cm, and the appendages were separated from the mother body, and the growth was normal in the later period; the remaining 25 plants turned yellow and withered after 2 weeks of pollination, and the appendages remained; in late December, the berries of the surviving plants were fully mature and red. Harvest the seeds in batches according to the technical step F (the same below), and air-dry them on the spot; a total of 418 berries are harvested, the thousand-grain weight of the berries is 286g, and each berry contains 1-2 seeds. In March of the following year, seedlings were sown according to techn...
Embodiment 2
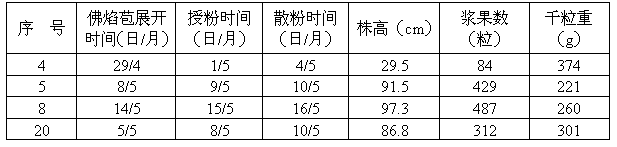
[0048] In 2011, 21 flowering plants of Amorphophallus verrucosum were cultivated; the pollen vigor was measured according to the technical step (B, the same below); the cross-pollination was carried out according to the technical step (C1), and the pollination time was between 19:00 and 21:00 (the following The same), respectively numbered observation records (see Table 1); after artificial pollination, 4 plants became fruitful, and the material numbers were: 4, 5, 8, 20; the remaining plants turned yellow and withered after 2 weeks; in late December, the surviving plants The berries were mature and the appendages were persistent. The seeds were harvested in batches and air-dried on the spot. A total of 1412 berries were harvested, with a thousand-grain weight of 289g (see Table 1). In March of the following year, 2125 seedlings were planted and 2125 seedlings were obtained; in mid-May, the field was transplanted, and the survival rate reached 88.3%; in mid-November, the plants...
Embodiment 3
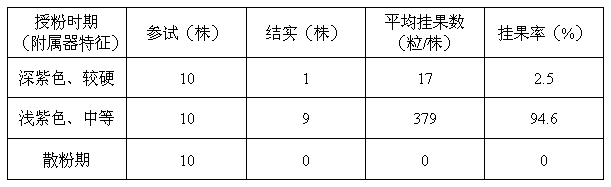
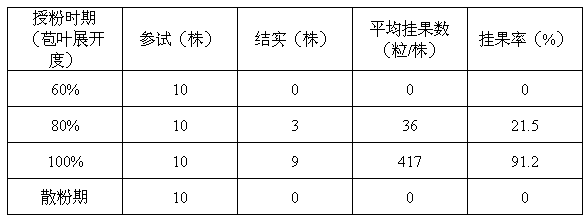
[0052] In 2012, 57 flowering plants of Amorphophallus verruca were bred. Measure the pollen viability according to the technical step (B); the first batch of flowering plants did not bear fruit after being pollinated by the same flower; select 40 plants to carry out the artificial assisted pollination experiment according to the technical step (C1), and set the bracts to be scattered 60%, 80%, and 100% ("Trumpet") and loose powder stage four treatments, each treatment 10 plants. The experimental results are shown in Table 2, fruit setting rate = number of plump fruits / number of seeds. The test results showed that the same pollination of Amorphophallus verrucoides did not bear fruit; the bract leaves unfolded for 1d to 2d, and the seed setting rate was the highest; by the pollination stage, the female flowers had completely lost their vigor and could not bear fruit.
[0053] Table 2 Morphological characteristics of Amorphophallus konjac bracts and hybrid seed setting rate
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com