Method for determining fracture toughness and tensile strength of quasi-brittle materials from two-point loaded specimens
A brittle material, fracture toughness technology, applied in the analysis of materials, strength properties, preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of test sample production and test workload, and difficulty in completing sample preparation and test work.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
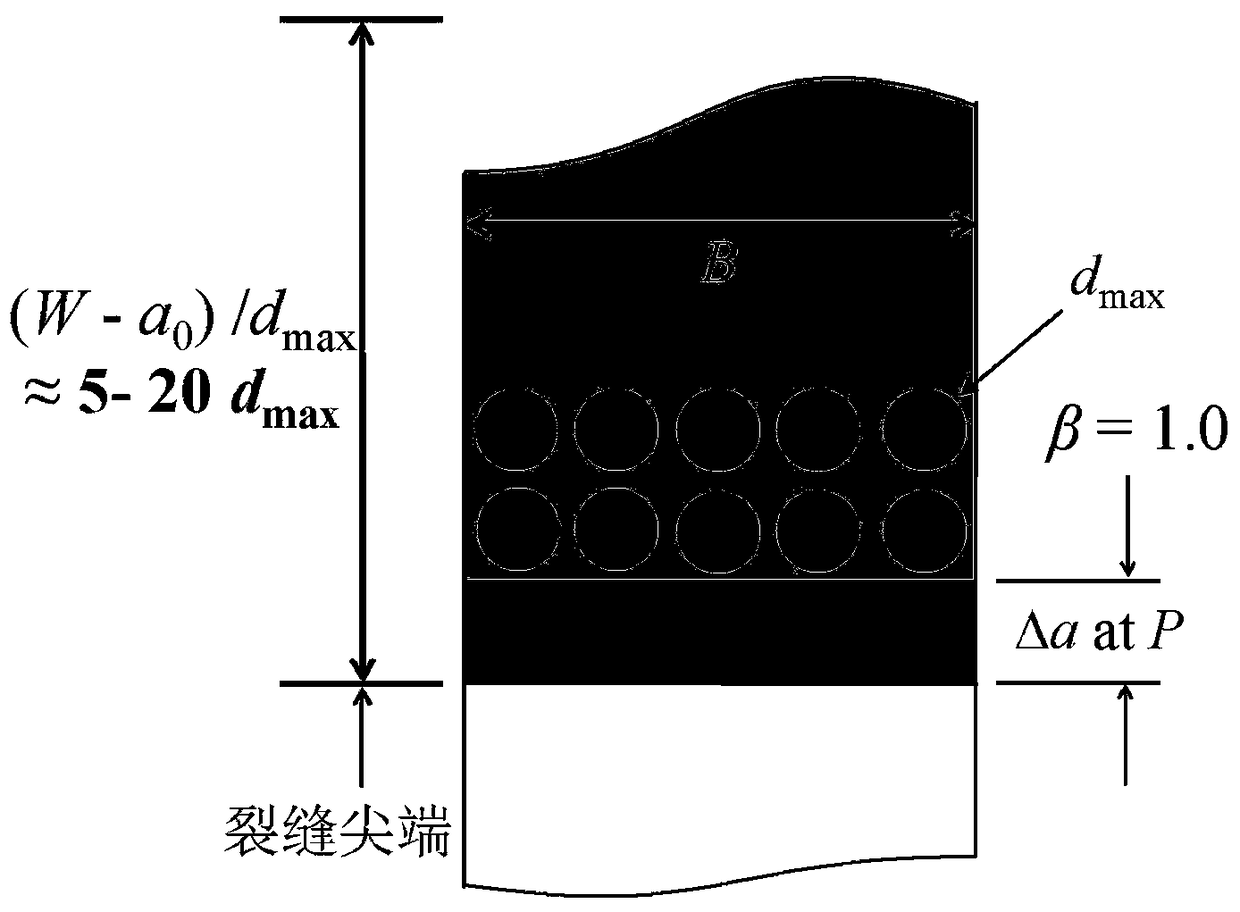
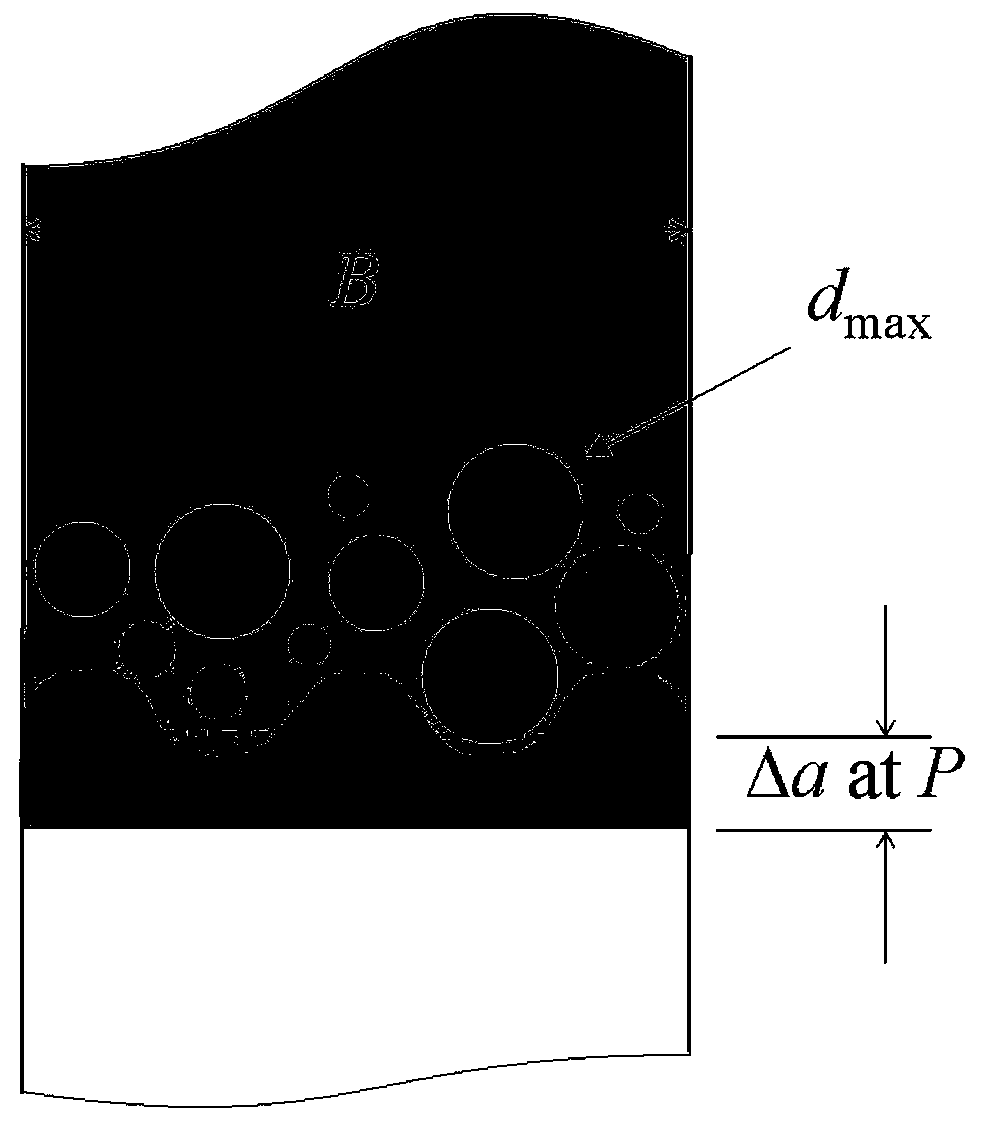
[0041] Example 1: The concrete specimen of the two-point loading type used in the test of this example, the maximum particle size of the concrete aggregate d max = 13mm, L x B x W = 806.4 × 152 × 203.2 mm, initial seam height ratio α = a 0 / W = 0.30, 0.35, 0.40, 0.45, 0.50, W / d max =15.6.
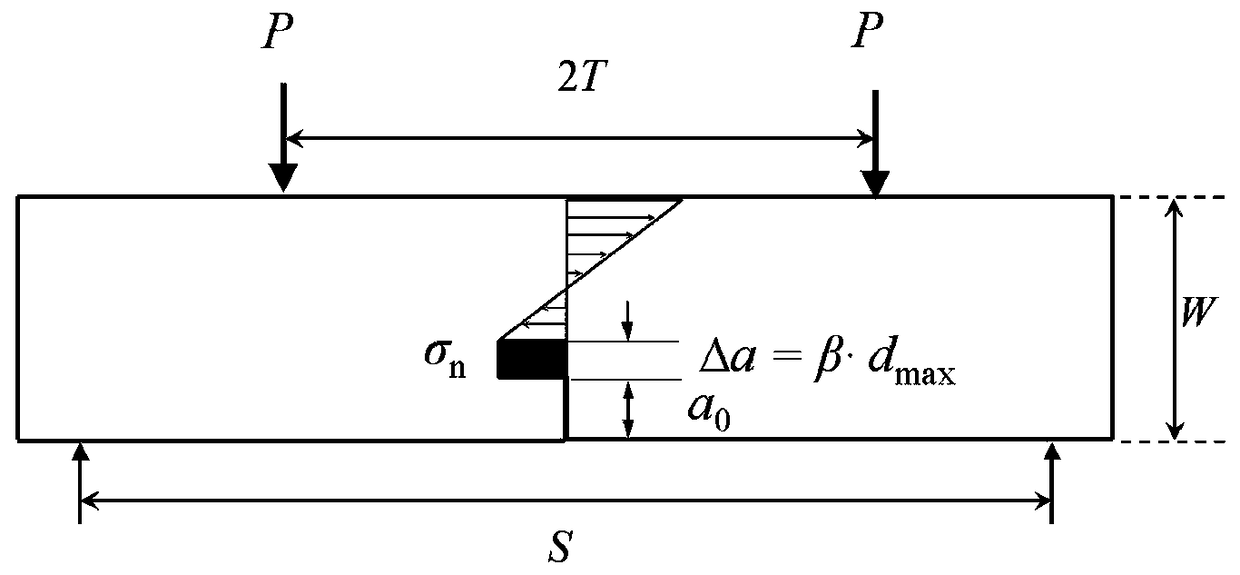
[0042] see figure 1 , considering concrete as a quasi-brittle material, the peak load P The stress distribution when figure 1 As shown, the corresponding crack growth Δ a = β · d max . Based on formula (2), the nominal strength of each specimen can be calculated from the measured peak load σ n .
[0043] Think Statistically β= 1.0, the average value of concrete fracture toughness and tensile strength can be calculated, see figure 2 . Considering the discreteness of the concrete test results and solving it accurately, it can make β= 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4..., calculate the exact values of the fracture toughness and tensile strength of concrete,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com