Equipment area provable security verification method with resistance to collusion attack
A security verification and anti-collusion technology, applied in the field of network security, can solve the problems of not satisfying security, lack of password verification methods, unable to help verify the specific location of the verified person, etc., to achieve the effect of high security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
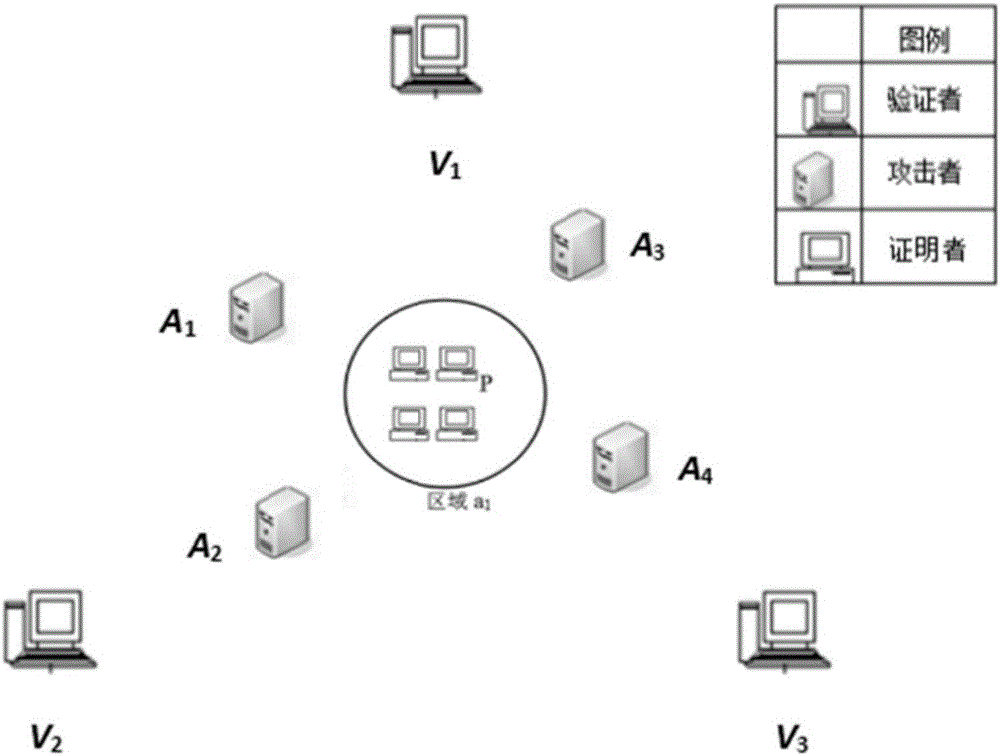
[0047] With the development of Internet and mobile communication technology, location information has become increasingly important, and secure location verification is essential. The current existing research technologies mainly include positioning based on network technology, wireless security positioning and location verification, security distance constraint technology and positioning technology based on location cryptography, but the positioning technology based on network technology does not consider the security of positioning in the environment where attacks exist Problem: The protocol scheme given by wireless security positioning and location verification is not provably safe under collusion attacks, and can only resist the attacks of a single or two attackers without collusion; the security distance constraint can only verify whether the verified person is Within a certain distance, it cannot help to verify the specific location of the prover; location-based cryptogra...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The device area provable security verification method against collusion attacks is the same as that in Embodiment 1, wherein the process of sending the verifier message in step (4), the specific steps are as follows:
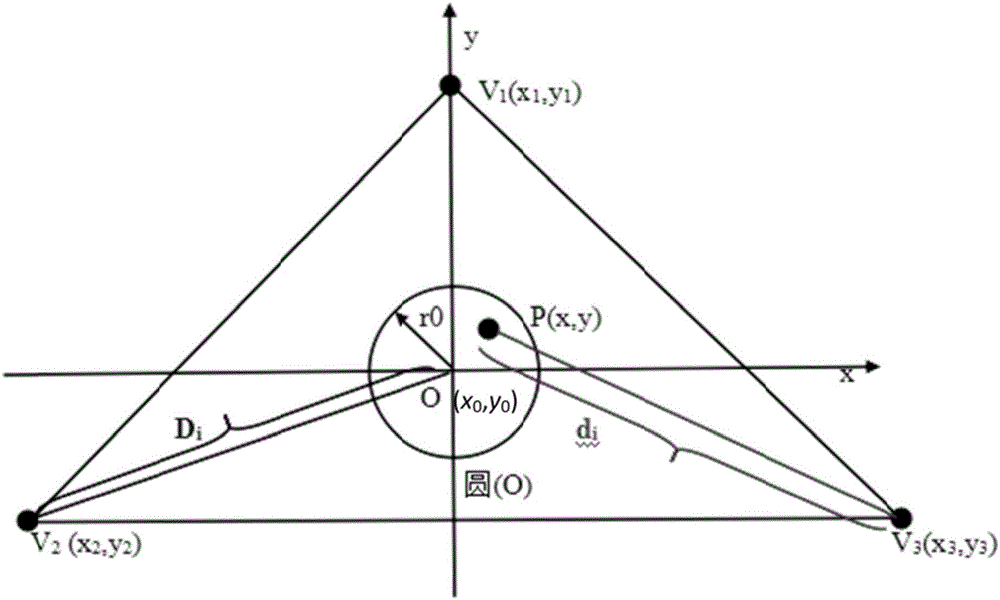
[0067] (4a) Let the verifier V 1 , V 2 , V 3 The first message sent reaches the center O at the same time T, O(x 0 ,y 0 ) represents the coordinates of the center of the circle, and the second message arrives at O at the time T', where T'=T+Δt, Δt=2r 0 / v, r 0 Indicates the radius of the target area circle, and v indicates that the verifier sends messages at the speed of radio waves;
[0068] (4b) The distance between the verifier and the center O is different, and the message needs to reach the center of the circle at the same time, so the verifier V i The moment of sending the message is different, let V 1 , V 2 , V 3 The time of sending the first message is respectively represented by T 1 ,T 2 ,T 3 Indicates that the time to send the seco...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The device area provable security verification method against collusion attacks is the same as that in Embodiment 1, wherein in step (5) the prover P receives all verifiers V i The first message M sent i time t i , and the prover P receives all verifiers V i The second message M sent i ’ time t i ’ is calculated as follows:
[0078] t 1 =T 1 +d 1 / v,t 1 '=t 1 +Δt;
[0079] t 2 =T 2 +d 2 / v,t 2 '=t 2 +Δt;
[0080] t 3 =T 3 +d 3 / v,t 3 '=t 3 +Δt;
[0081] d 1 , d 2 , d 3 Denotes the verifier V 1 (x 1 ,y 1 ), V 2 (x 2 ,y 2 ), V 3 (x 3 ,y 3 ) is the distance from the prover P(x,y).
[0082] Both the first message and the second message sent by the verifier are sent in the form of broadcast, because the prover is in the circular area, so the prover can receive all the messages sent by each verifier. The moment when each message is received by the prover in the area is equal to the moment when the verifier sends the message plus the time requ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com