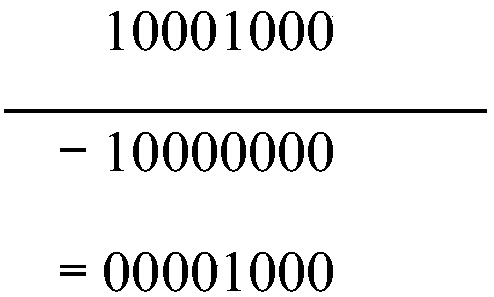modular inverse operator
A modular inverse operator and modular inverse operation technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as complex implementation, complex calculation process, and inability to calculate modulo with any non-zero integer, and achieve the effect of reducing hardware power consumption and improving computing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
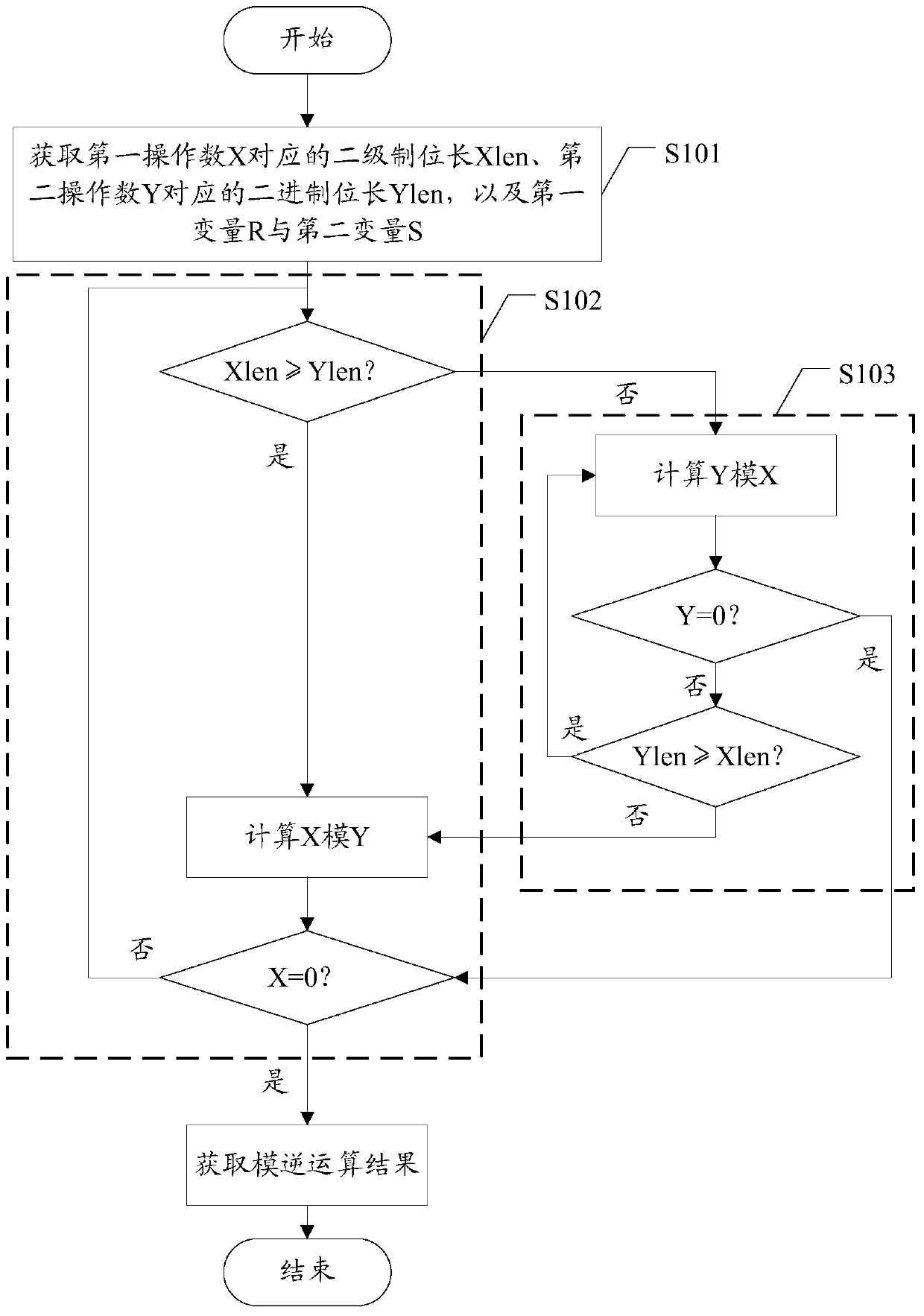
[0031] The existing binary extended Euclidean algorithm converts division into shift and addition and subtraction. However, in the process of shifting, the weight of operands has changed, and the final operation result contains 2 n (n is the bit length of the operand) item weight factor, the operation of dividing by 2 needs to be performed multiple times to remove the weight factor, therefore, the modulus must be an odd number. However, the existing binary extended Euclidean algorithm method still has certain limitations when performing modular inversion operations, and cannot perform modulo calculations for any non-zero integers, and the calculation process is relatively complicated.
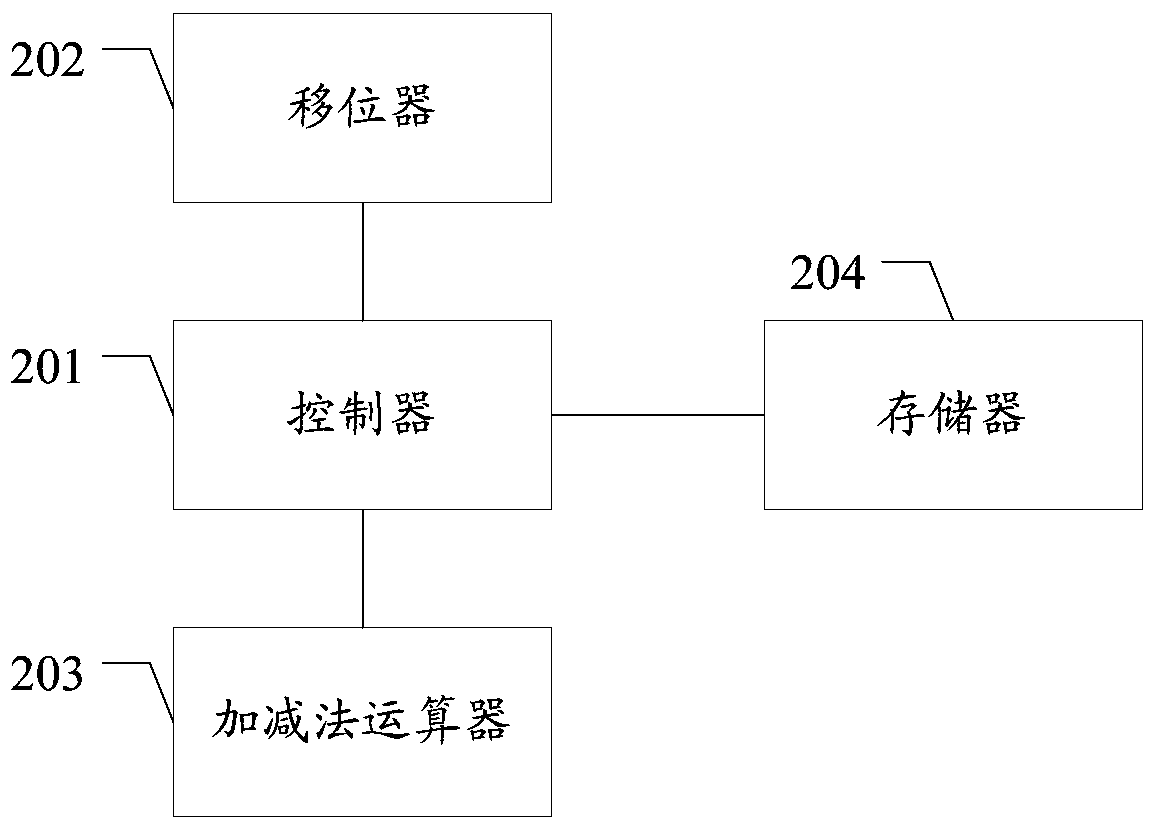
[0032] In the embodiment of the present invention, when the bit length of the first operand X is greater than that of the second operand Y, the redundant sign bit can be eliminated when X is shifted to the left, and the real-time bit length of X is recorded by the variable Xlen, and the weight o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com