Control method of air conditioner and air conditioner
A control method and technology for air conditioners, which are applied in the field of air conditioner control and air conditioners, can solve problems such as user discomfort, and achieve the effects of improving comfort and solving supercooling and overheating.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
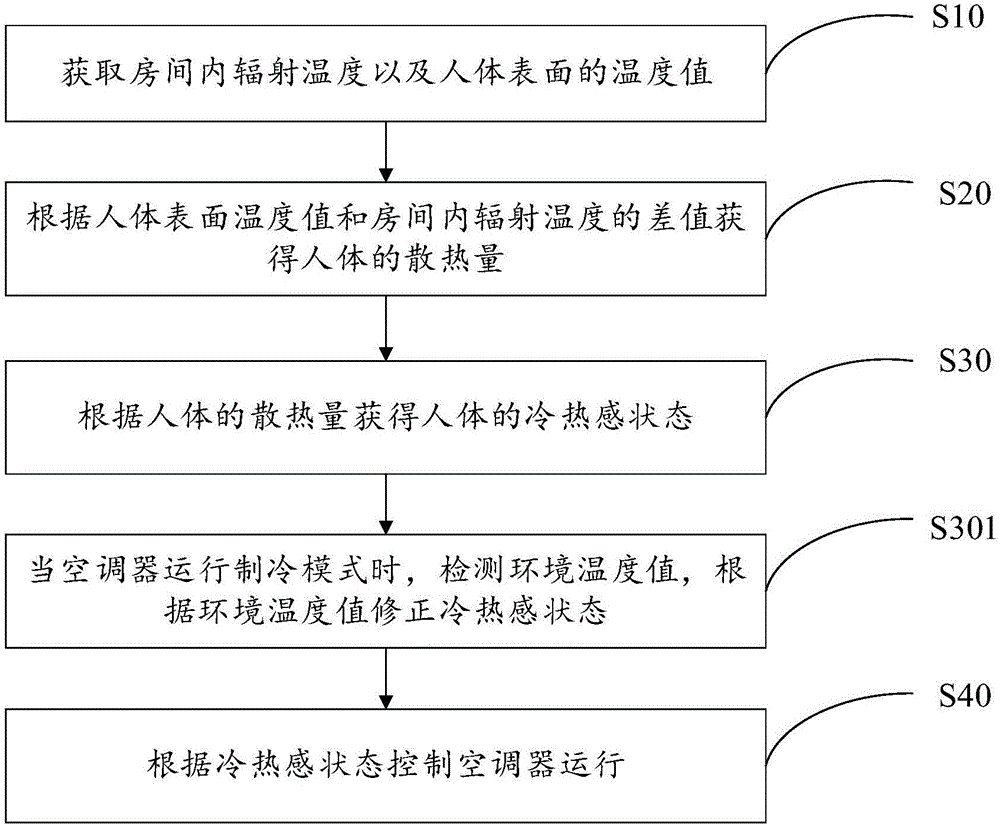
[0053] Further, refer to figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of an air conditioner control method according to another embodiment of the present invention, based on the first embodiment of the air conditioner control method of the present invention described above, in this embodiment, after the above step S30, further includes:
[0054] Step S301, when the air conditioner is running in the cooling mode, the ambient temperature value is detected, and the temperature value is corrected according to the temperature value.
[0055] After calculating the human body's thermal sensation state value based on the amount of heat dissipation, if the air conditioner operates in cooling mode, the thermal sensation state value can be further corrected according to the detected ambient temperature value.
[0056] The specific adjustment rules are as follows:
[0057] Obtain the ambient temperature value T1 detected by the air conditioner, and correct the state value M of cold...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com