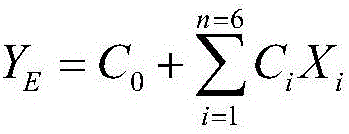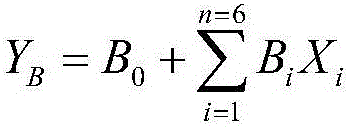An identification method for microseismic and blasting events based on source parameters
An identification method and event technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of overlapping effects, signal aliasing of different frequency bands, etc., to improve accuracy, weaken the impact of monitoring results, Applicable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] (1) Obtain the source parameters of a total of 50 groups of microseismic events and blasting events that have been determined through the microseismic monitoring system;
[0095] Including: the ratio of S wave to P wave energy E S / E P , seismic moment M, static stress drop SSD, dynamic stress drop DSD, source seismic time t and moment magnitude M m ;
[0096] (2) For the parameter E obtained in step (1) S / E P , M, SSD and DSD take logarithms respectively, and the obtained result is log E S / E P , logM, logSSD, and logDSD;
[0097] (3) Processing time t of seismic source earthquake;
[0098] Calculate the source vibration time t corresponding to the microseismic event or blasting event and the source vibration time t corresponding to the adjacent previous microseismic event or blasting event0 The time difference Δt=t-t 0 ;
[0099] (4) Calculate the value of the probability density function [generalized logistic distribution]:
[0100] The probability density...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com