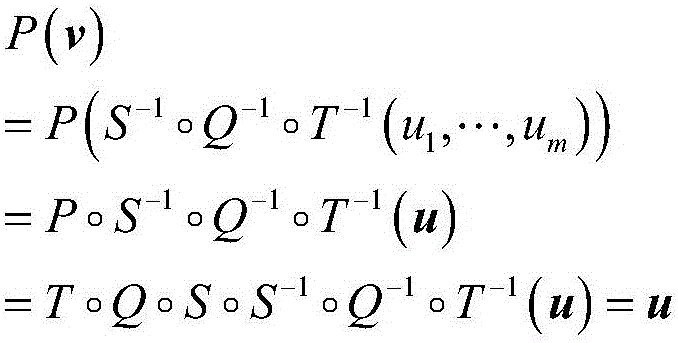Multivariable signature method capable for resisting forged signature attack
A multi-variable, polynomial equation technology, applied in multi-variable public key cryptography, multi-variable digital signature against counterfeit signature attacks, can solve the problem of reducing difficulty, does not verify whether the forger has a legal key, and does not involve internal secret information and other issues to achieve the effect of resisting forgery attacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
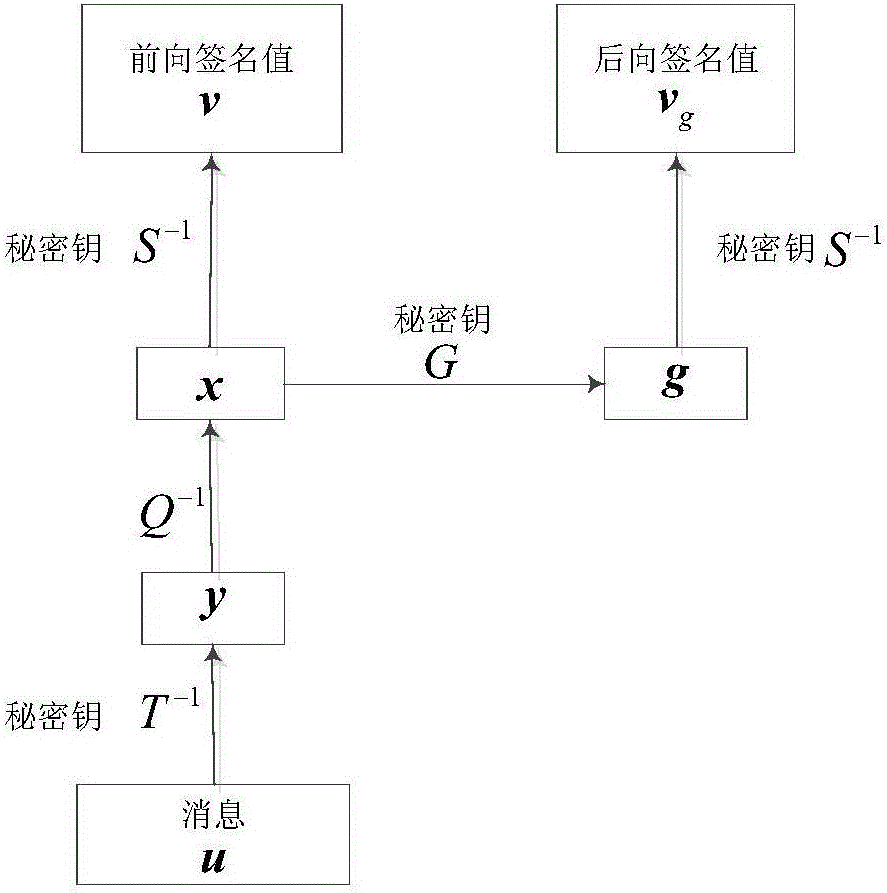
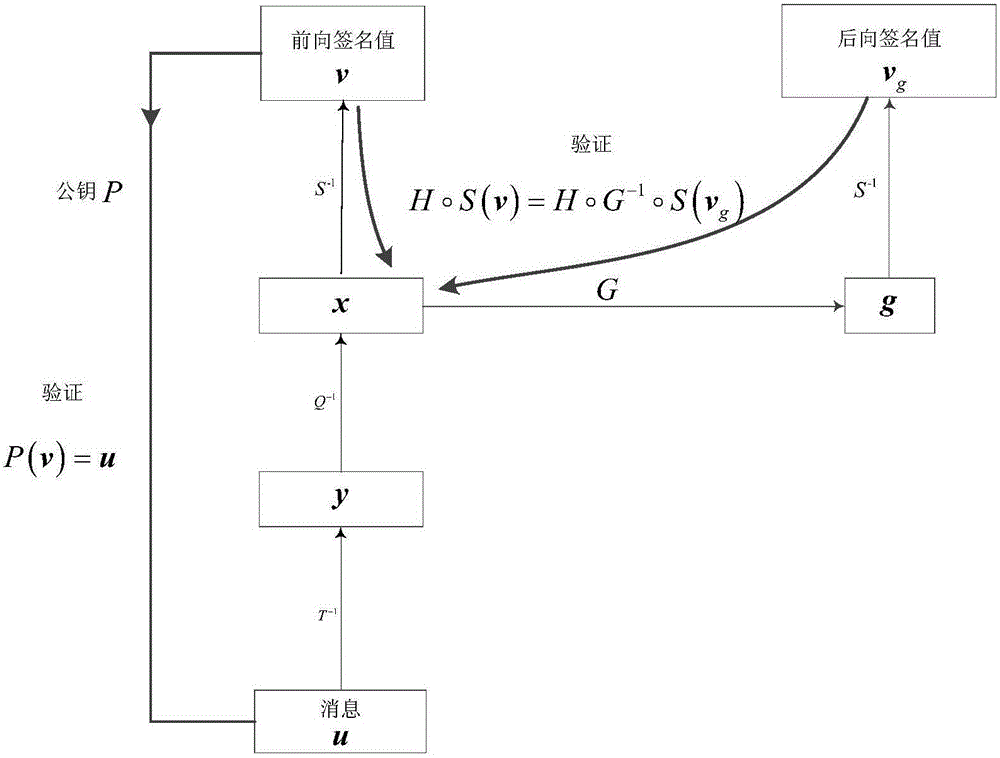
[0132] Taking the central mapping of the Matsumoto-Imai multivariate [MI] system as an example, the signature scheme is as follows:
[0133] (1) Original MI scheme.
[0134] Assume is a q-order finite field, yes The n times of expansion domain, is the isomorphic mapping from the extended domain to the vector space, which is π(a 0 +a 1 x+…+a n-1 x n-1 )=(a 0 ,...,a n-1 ). positive integer satisfies gcd(q n -1,q λ +1)=1, at Take a one-to-one mapping on:
[0135]
[0136] is a reversible transformation, and where t(q λ +1)=1 mod q n -1. Center map Q(x 1 ,...,x n )yes arrive The mapping is:
[0137]
[0138] Among them, q i (x 1 ,...,x n ), i=1,..., m are quadratic polynomial equations of n variables. Let S, T be Two random reversible affine transformations on , then there is a public key Here each polynomial is quadratic.
[0139] This system is used as a signature algorithm, and the process is as follows. Alice wants to send Bob ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com