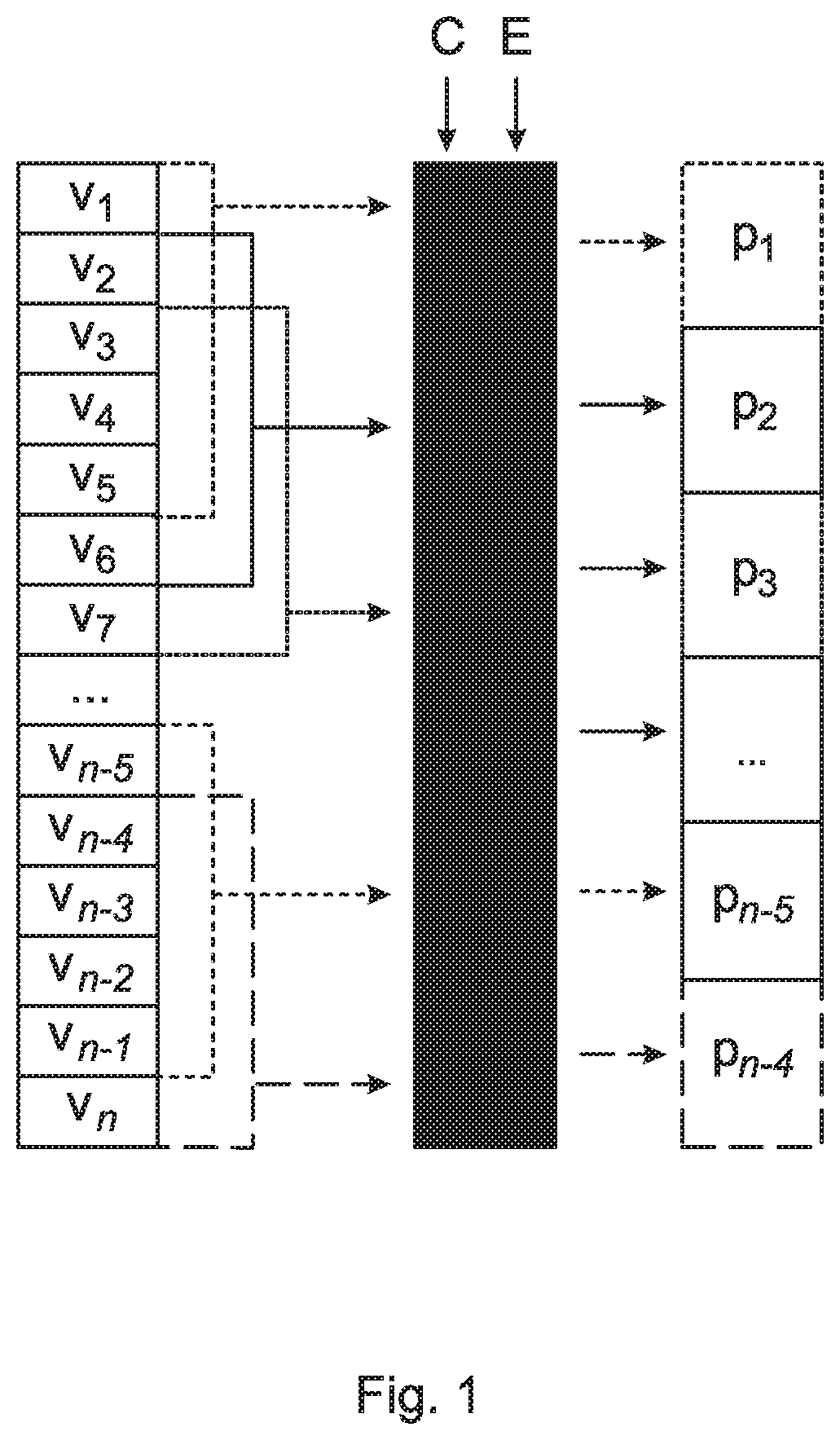
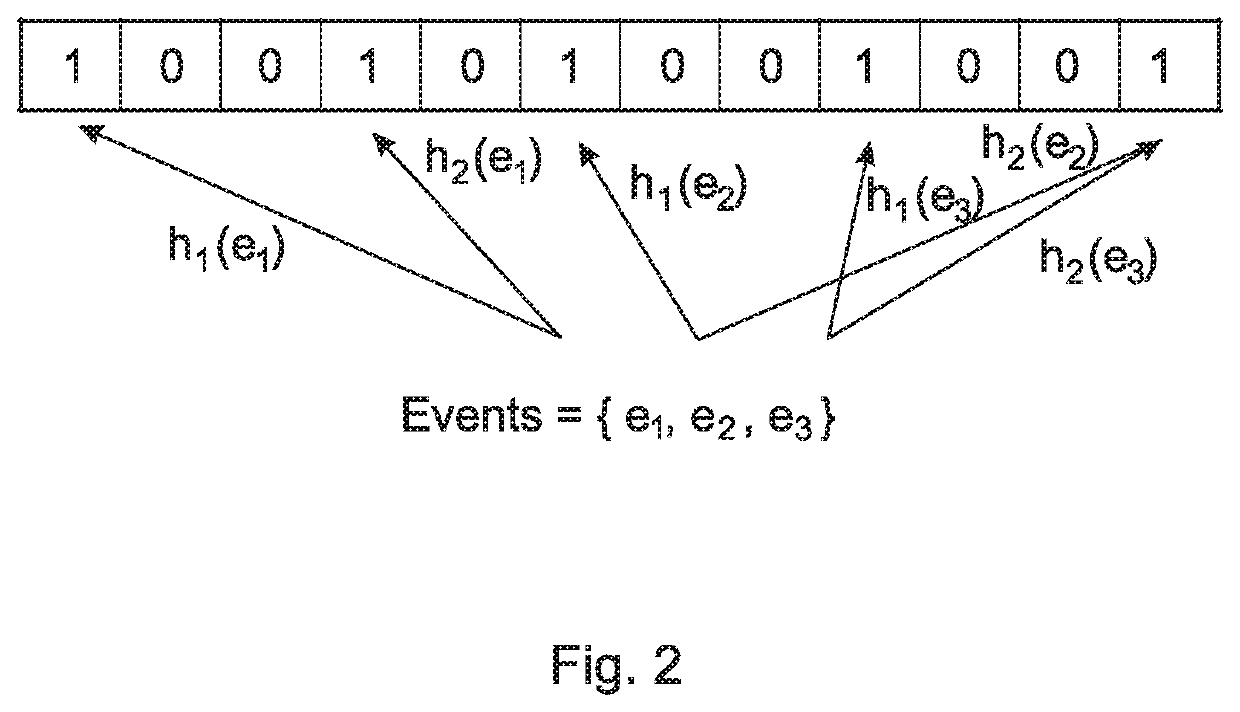
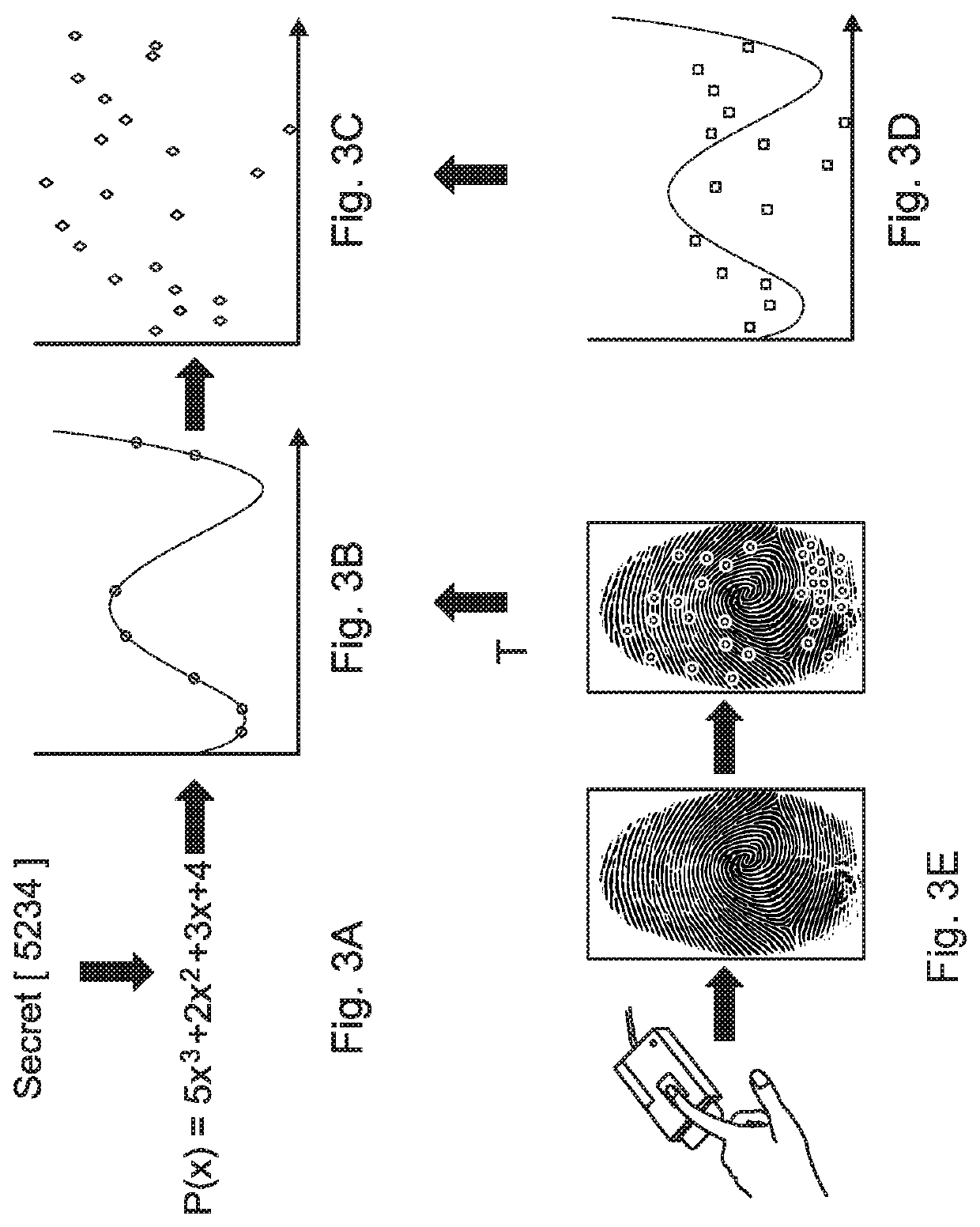
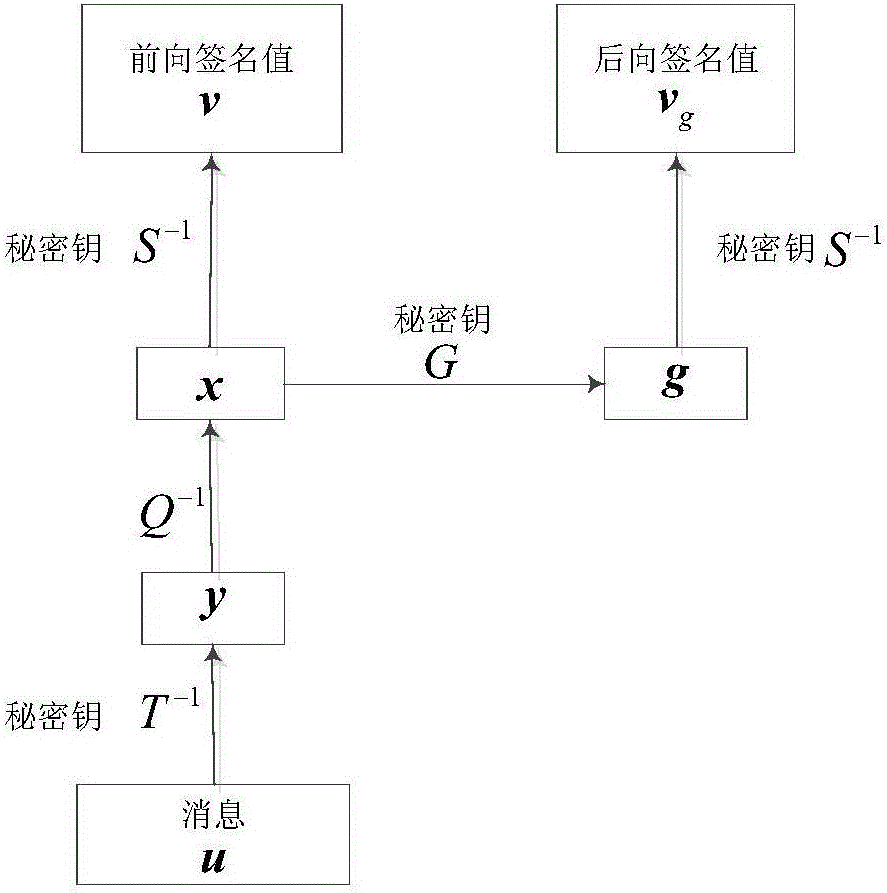
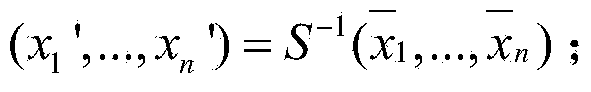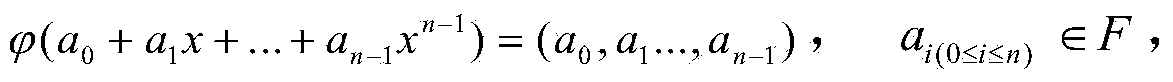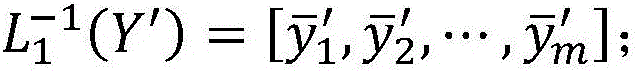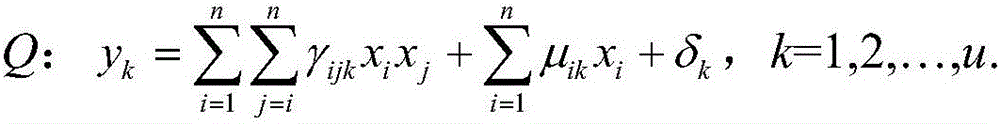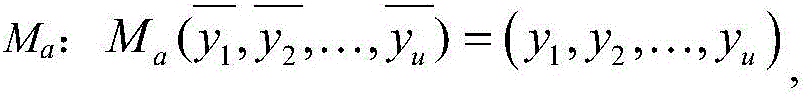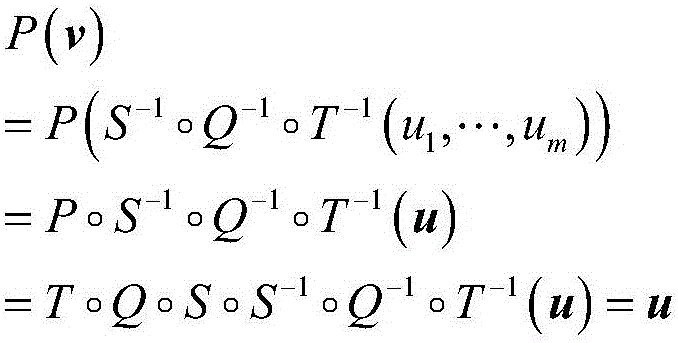Patents
Literature
41 results about "Multivariable polynomials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Asymmetric cryptosystem employing paraunitary matrices
InactiveUS20090010428A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationNon symmetricCiphertext
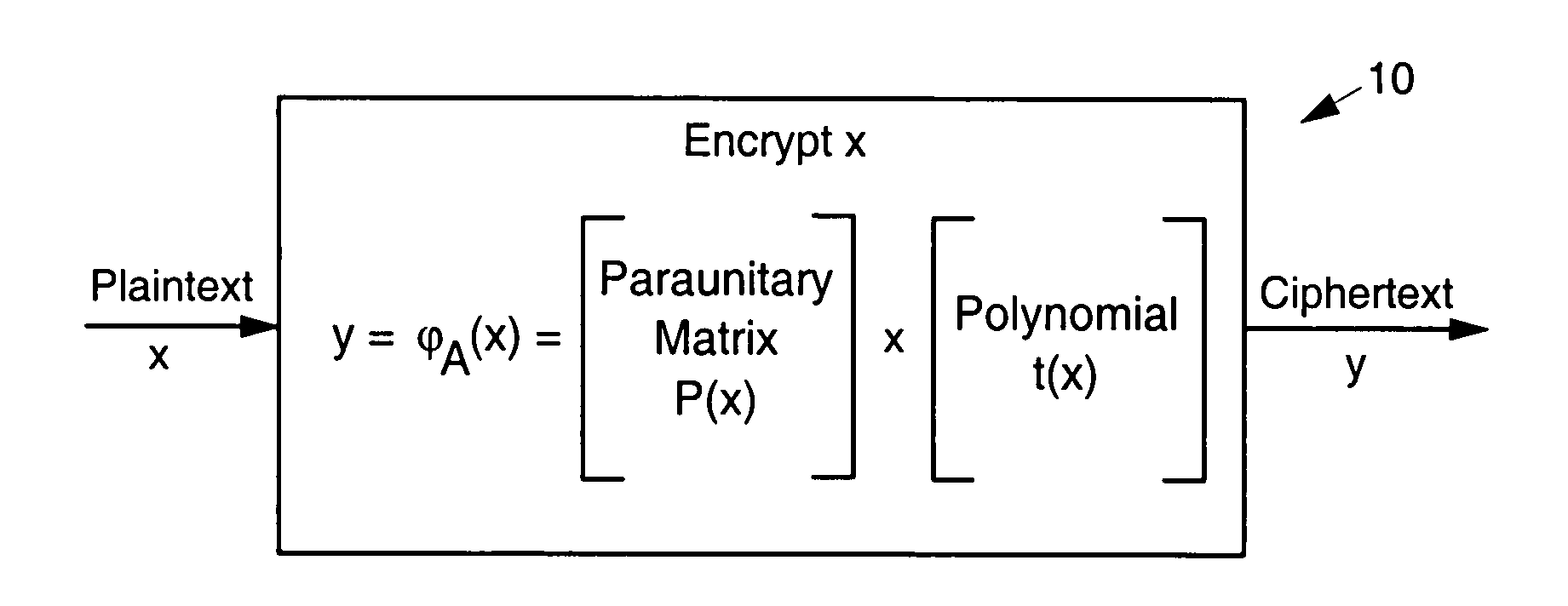
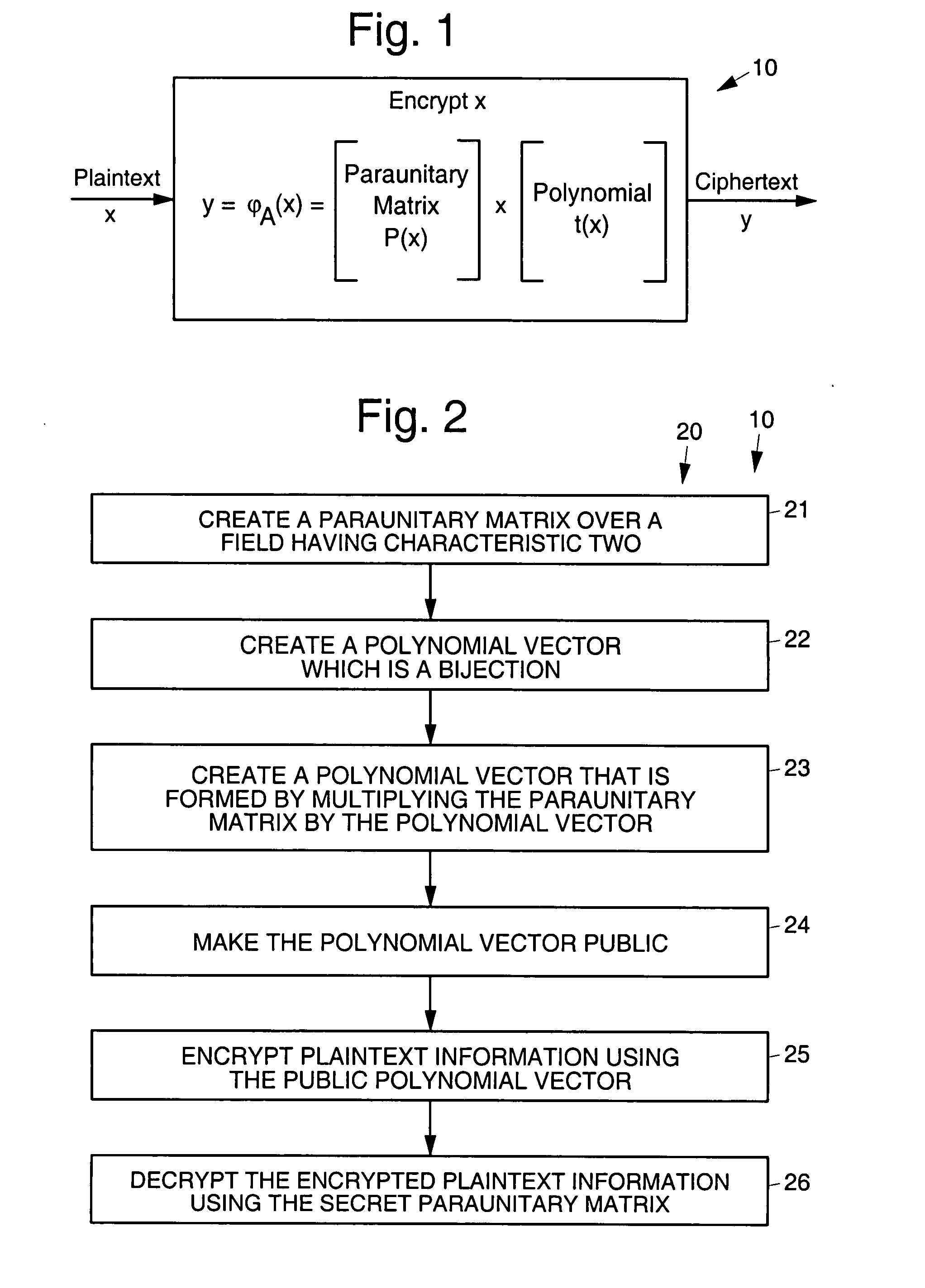
Disclosed are multivariate paraunitary asymmetric cryptographic systems and methods that are based on paraunitary matrices. An algebraic approach is employed in designing the multivariate cryptographic systems and methods. The cryptographic systems and methods are based on formulating a general system of multivariate polynomial equations by paraunitary matrices. These matrices are a family of invertible polynomial matrices that can be completely parameterized and efficiently generated by primitive building blocks. Using a general formulation that involves paraunitary matrices, a one-way function is designed that operates over the fields of characteristic two. To include a trapdoor, approximations are made to the paraunitary matrix. The result is a trapdoor one-way function that is efficient to evaluate, but hard to invert unless secret information about the trapdoor is known. An exemplary implementation operates on the finite field GF(256). In this example, the message block includes 16 to 32 symbols from GF(256), i.e., the block size n is an integer between 16 and 32. The ciphertext block takes its elements from the same field and has at least 10 extra symbols.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Cryptosystem using multivariable polynomials
InactiveUS20020001383A1Improve securityEasy to decryptPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationCiphertextCryptosystem
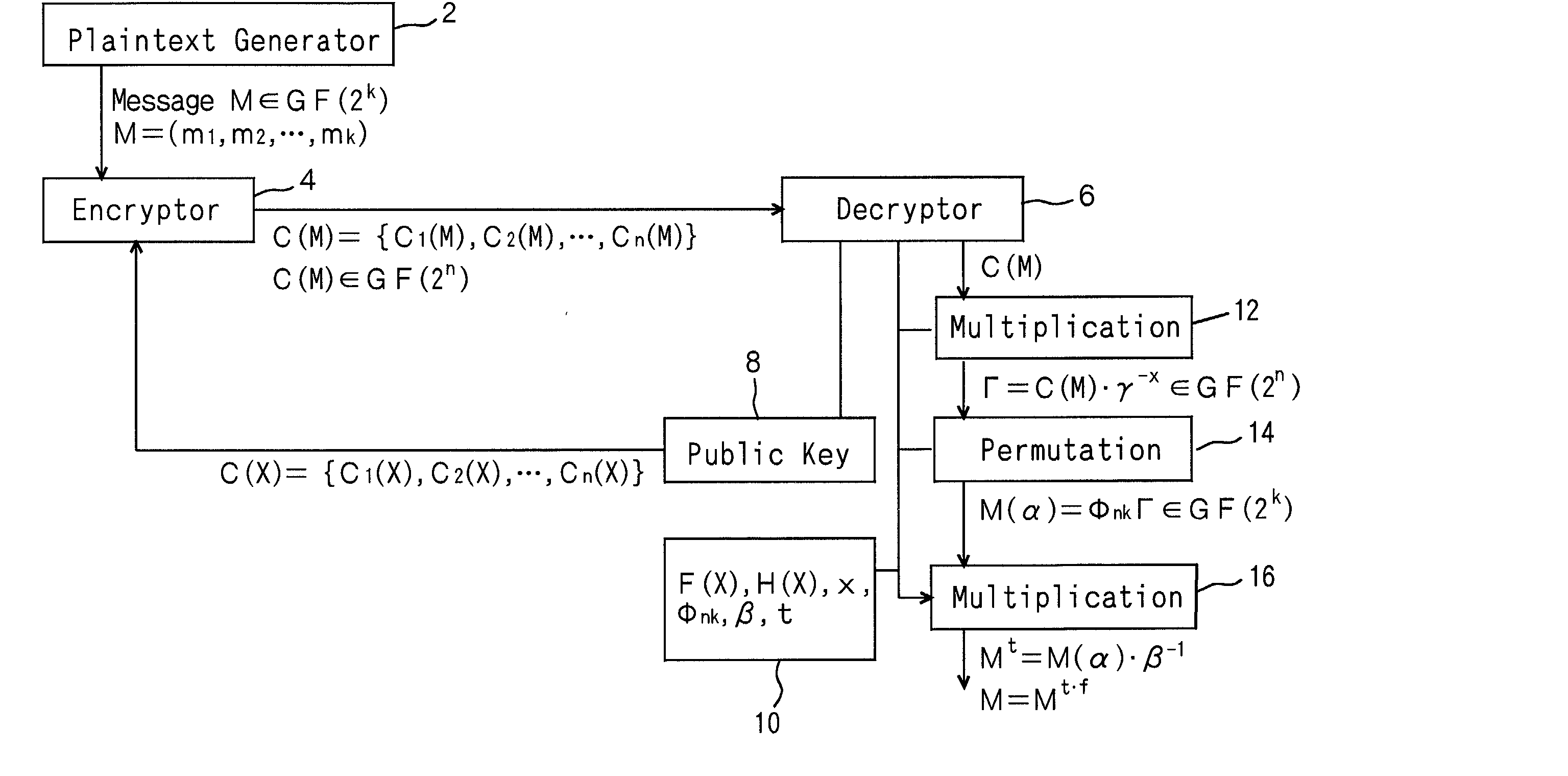
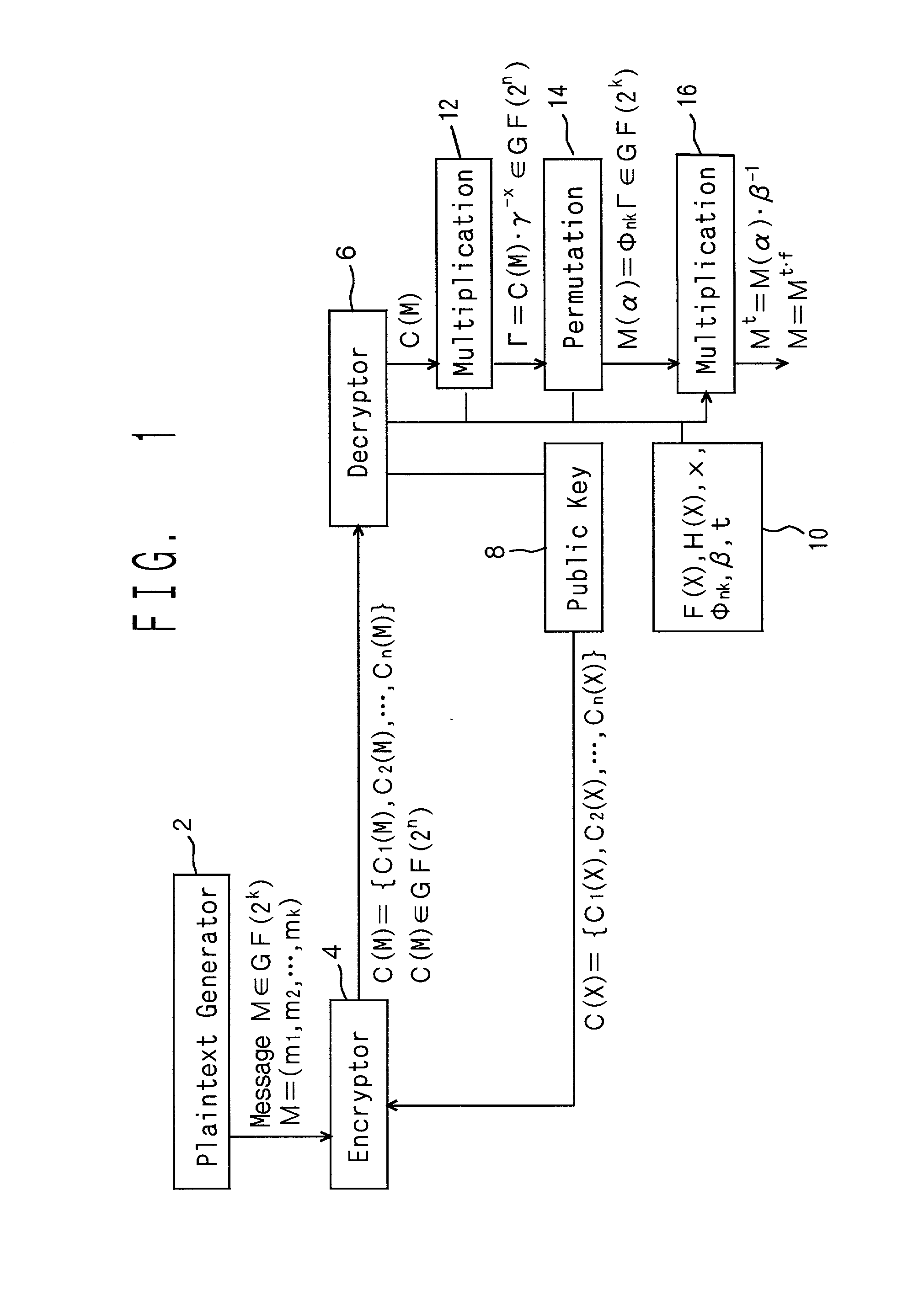
Let us consider a message M an element (m1,m2, . . . ,mk) in a Galois field GF (2k), and multiply it by a product of polynomials beta 1(alpha)-alpha t(alpha) into M(alpha).<paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>M(alpha)=Mbeta1(alpha).Mbeta2(alpha) . . . Mbetat(alpha)< / in-line-formula>Combine a noise vector r(alpha) of n-k to M(alpha) in series so that the data is expanded into degree n. Next, they are transformed into Γ by permutation. Γ is multiplied by an element gammax in the Galois field GF(2n) into cyphertext C(M), where gamma is a primitive root of the multiplicative group of the Galois field GF(2n). Practically, when the message M is substituted for X in a public key C(X), the cyphertext C(M) is obtained. The cyphertext C(M) is multiplied by gamma-x, is applied to an inverse permutation, and the noise vector r(alpha) is separated. Then, the inverse element of the product of beta1(alpha)-betat(alpha) is multiplied and is raised to an adequate index. Then the decrypted message is obtained.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD +1
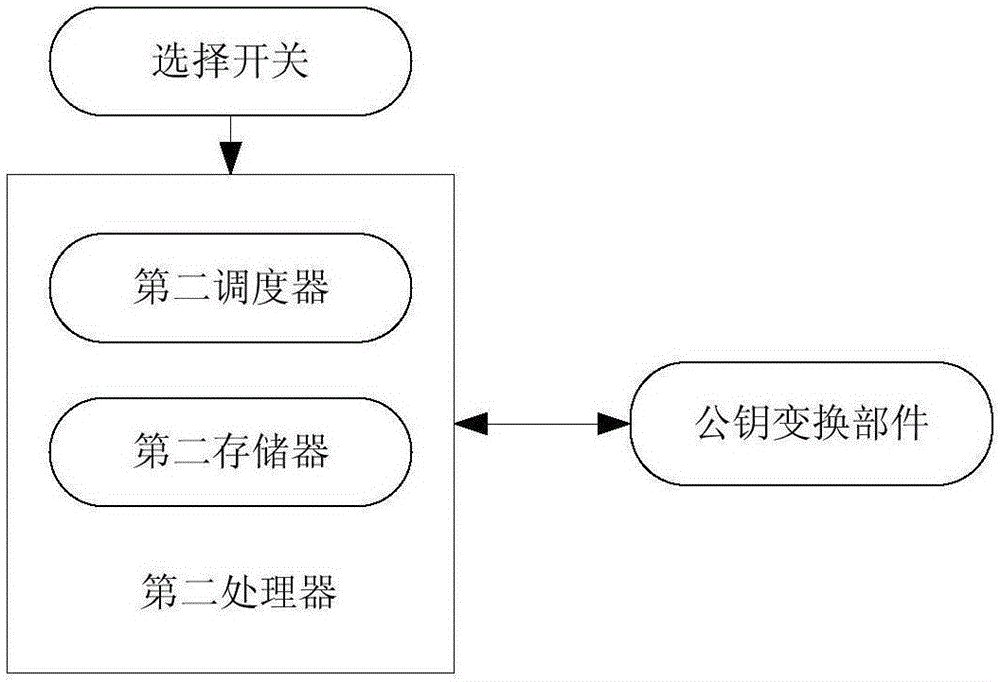
System and method for signing/verification of multivariable public key
InactiveCN103490897AImprove securityShorten the timeUser identity/authority verificationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsValidation methodsTrap door
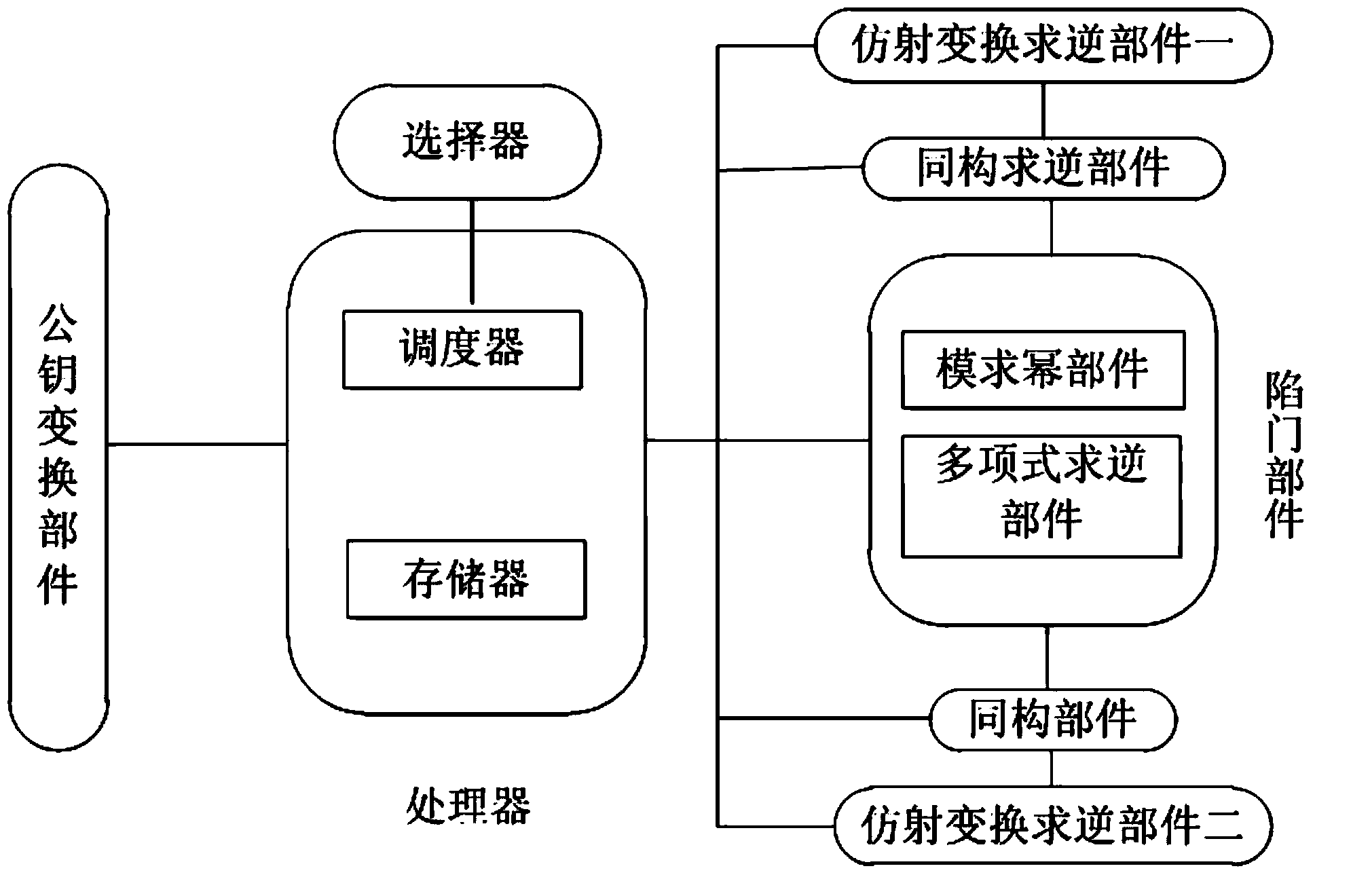
The invention discloses a system for signing / verification of a multivariable public key. The system comprises a signing module and a verification module. The signing module comprises a processor, a first affine transformation inversion component, an isomorphism inversion component, a trap door component, an isomorphism component and a second affine transformation inversion component. Corresponding operations are sequentially conducted on a message to be signed through the components, one or more groups of solutions are generated after the message is processed through the trap door component, at this time, one group of solutions are randomly selected and transmitted to the isomorphism component and the second affine transformation inversion component and are processed, and a generated signature and the message are transmitted to the processor together. The verification module comprises a processor and a public key transformation component, wherein the signature is transmitted to the public key transformation component through the processor, the signature is substituted into each multivariable polynomial in a public key map, and whether obtained data are equal to the message in a storage or not is judged through the processor; if yes, the signature is valid, and if not, the signature is invalid. According to the system and method for signing / verification of the multivariable public key, the safety and the operation efficiency are high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
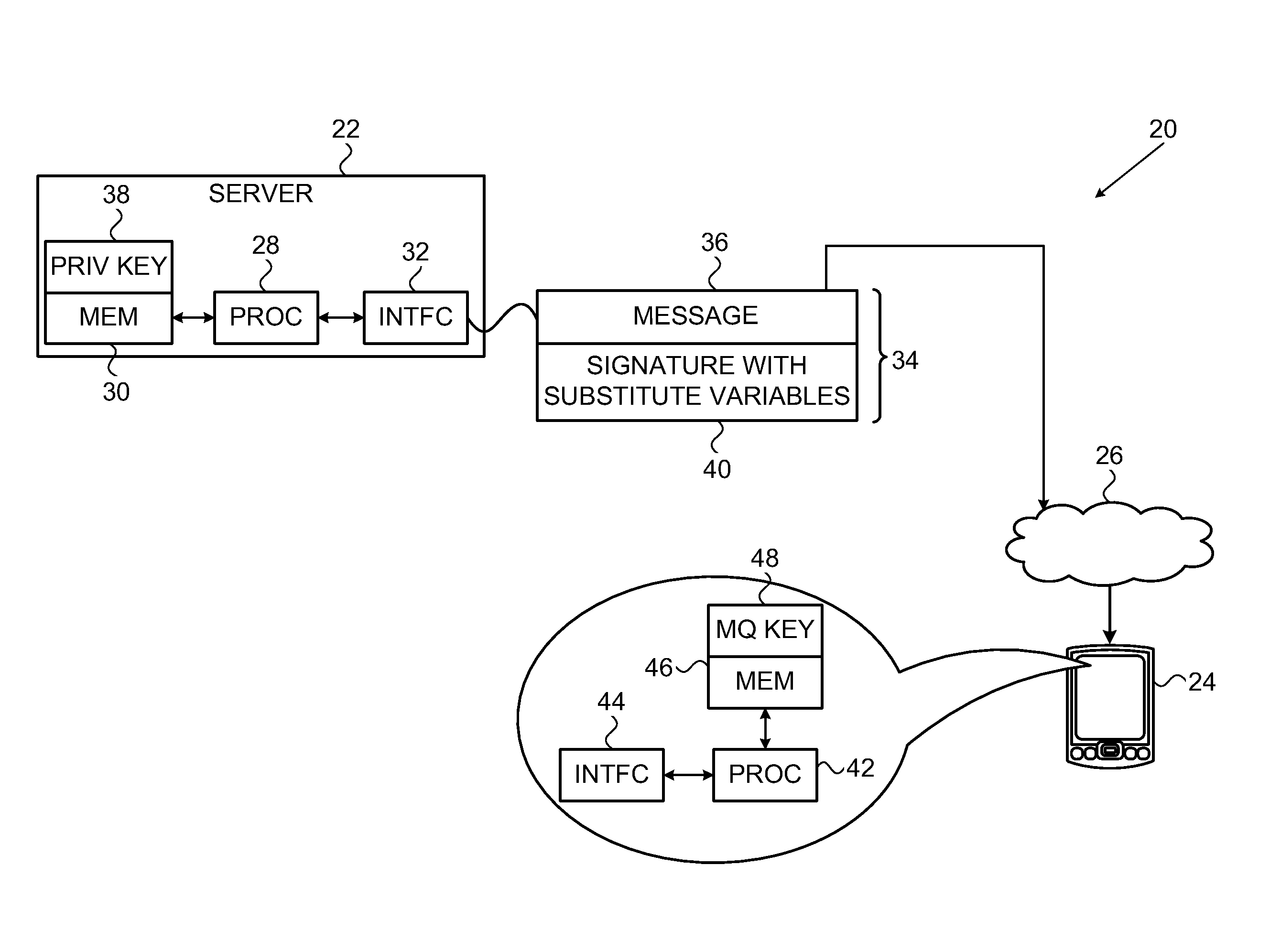
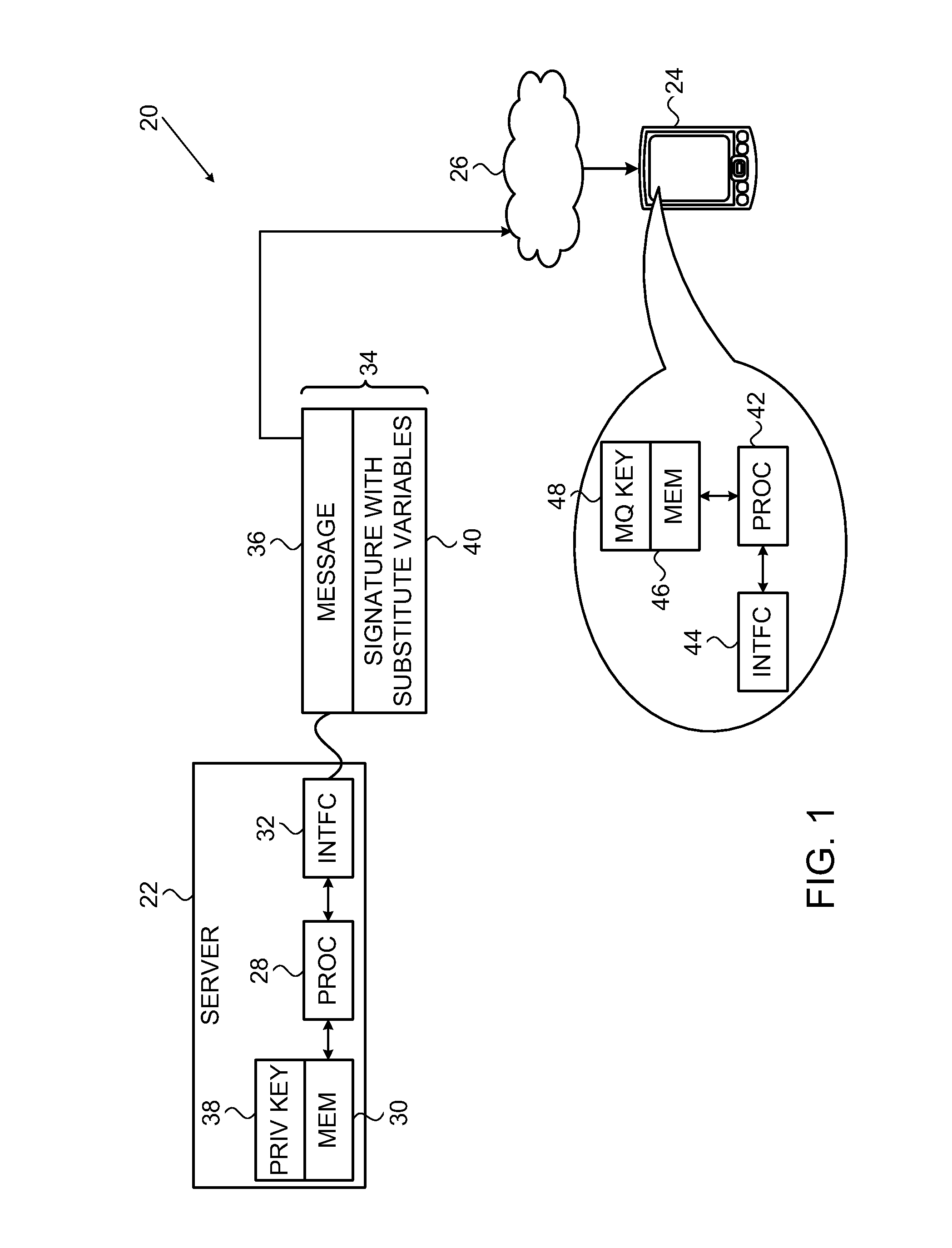
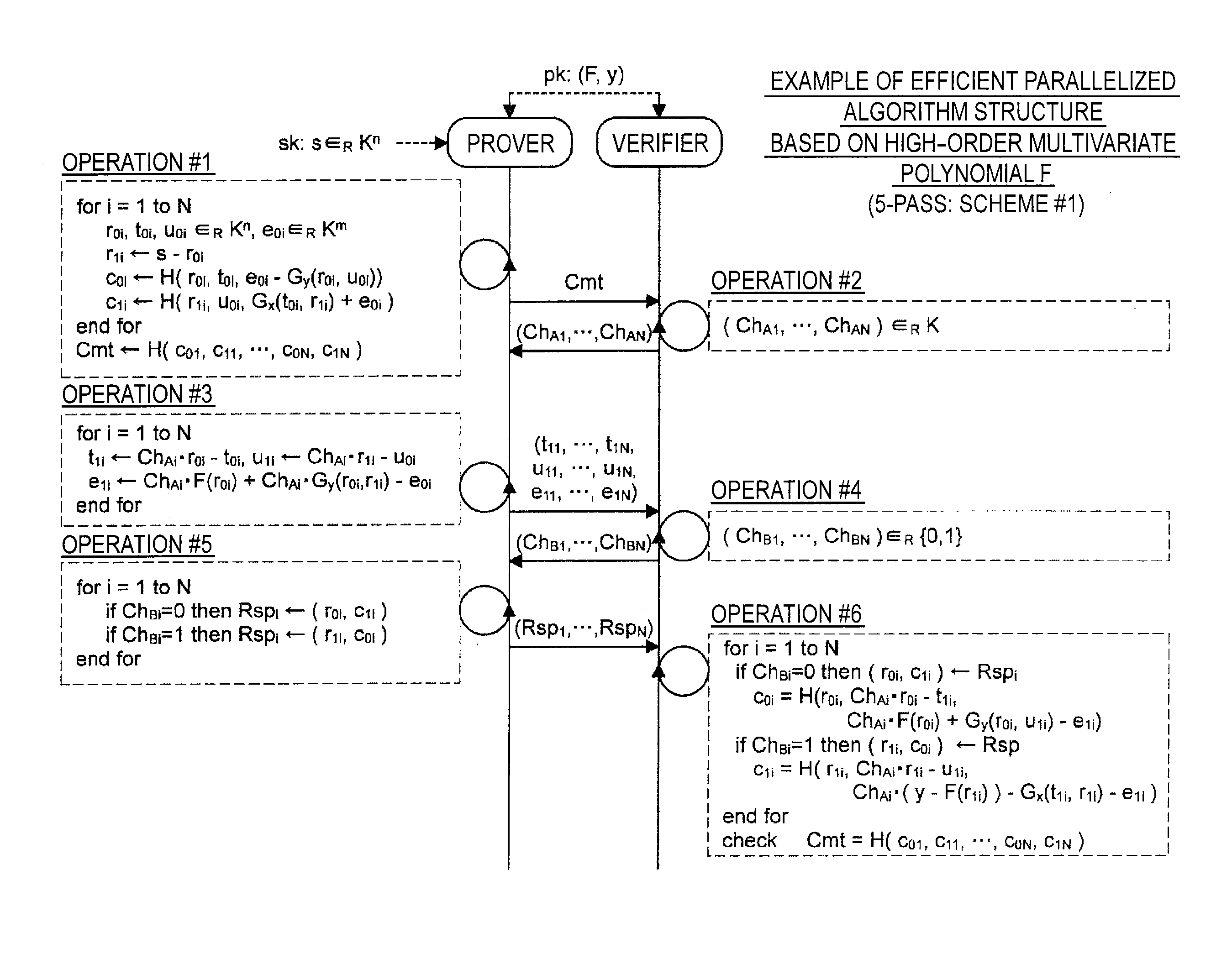
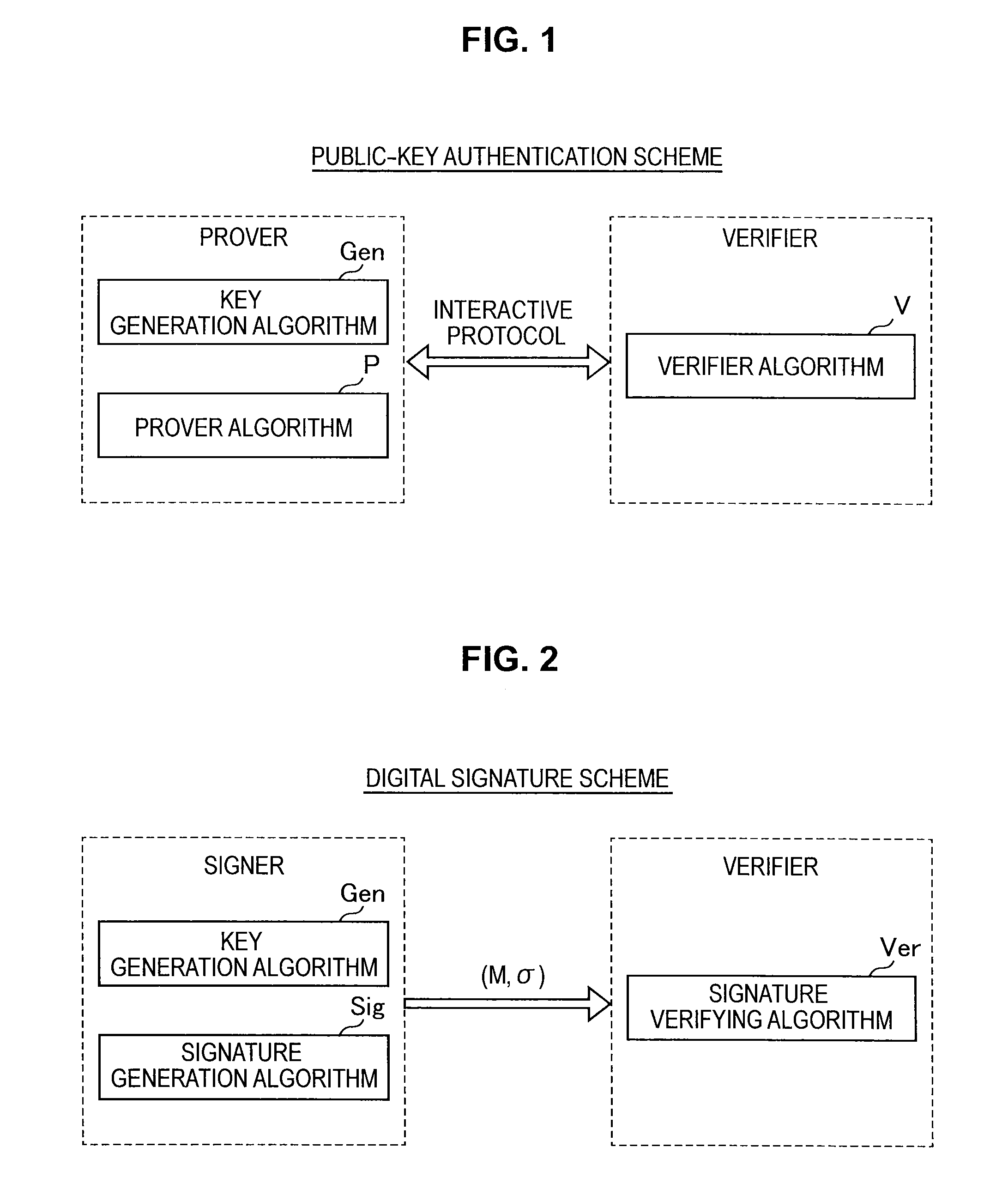
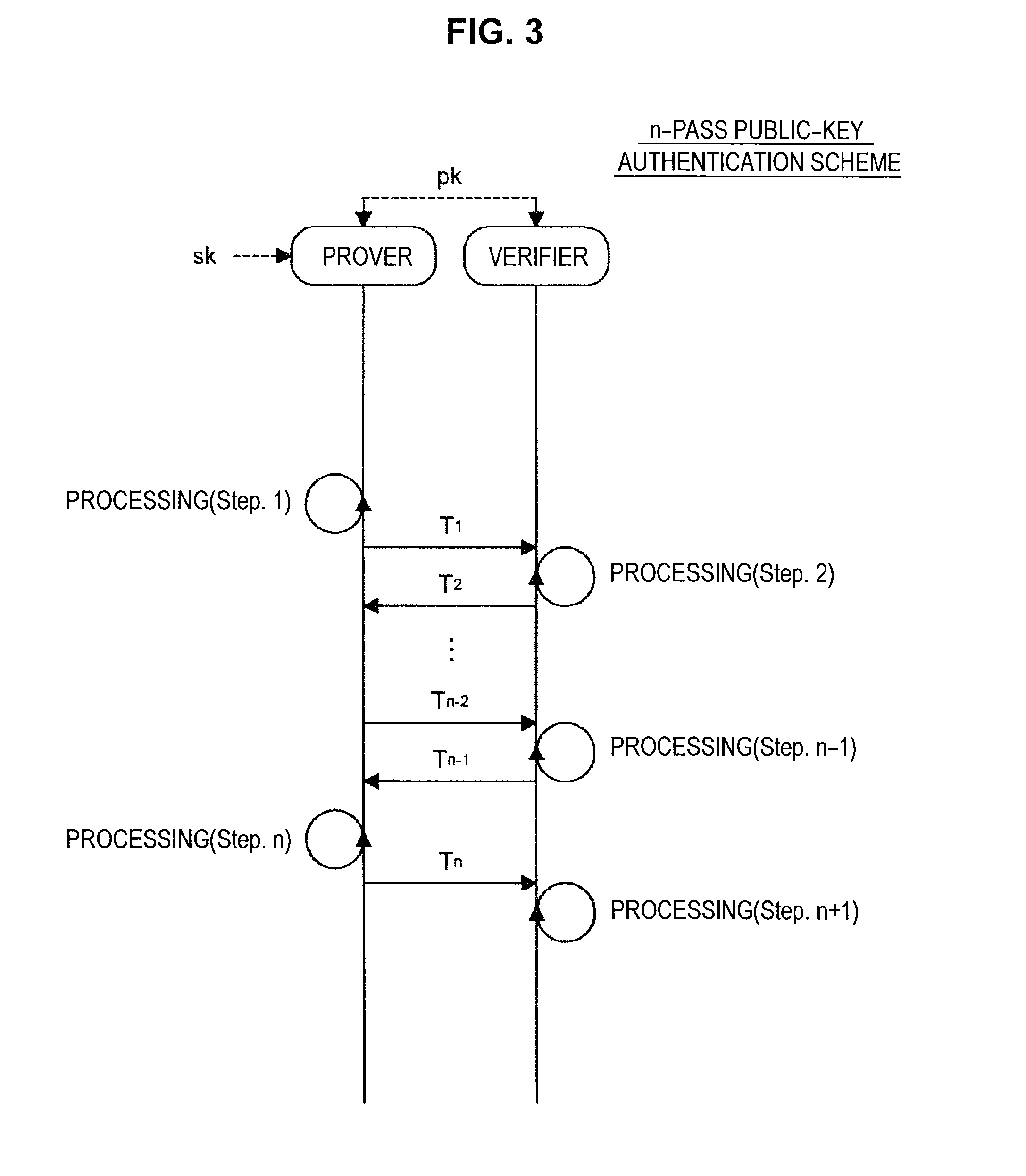
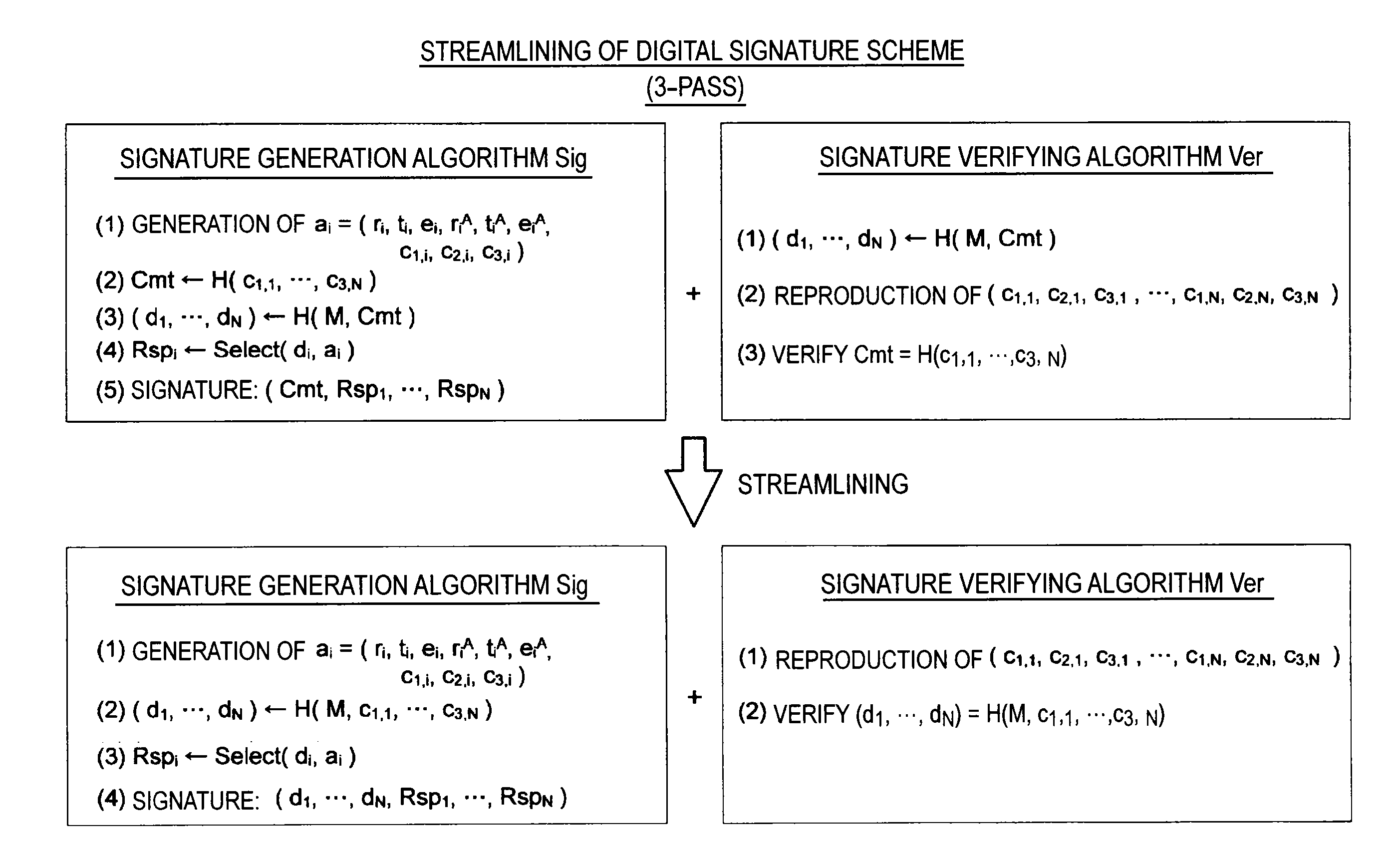
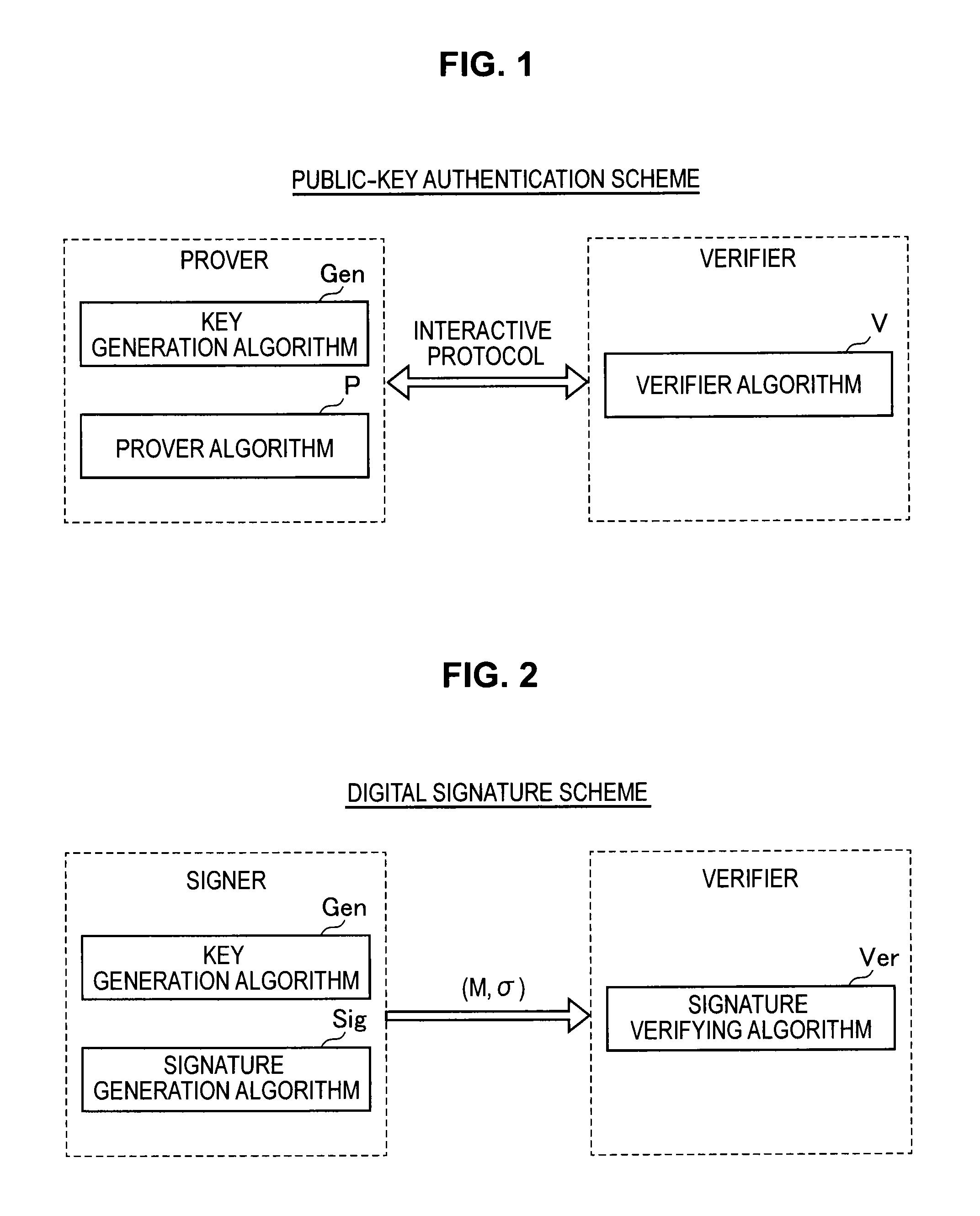
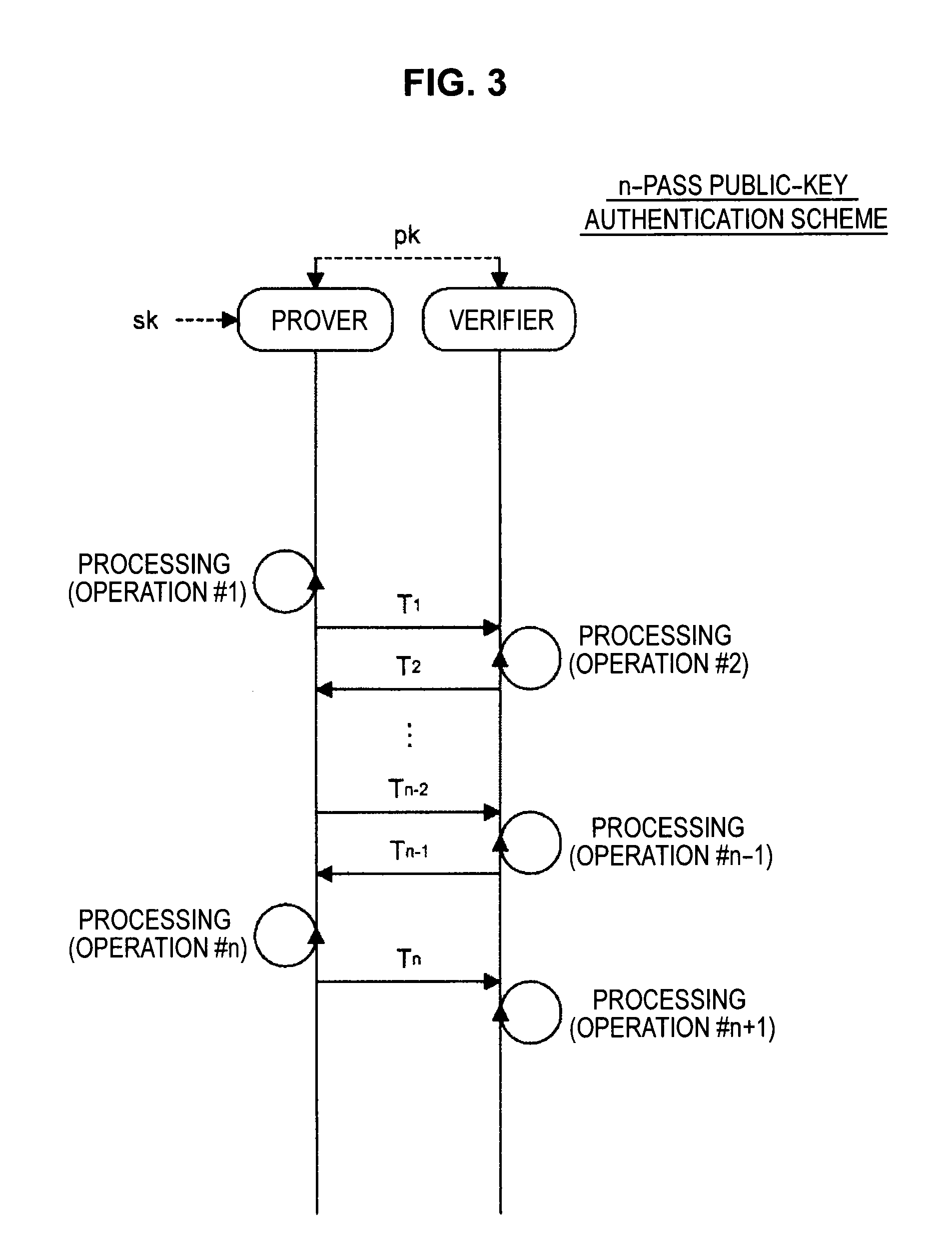
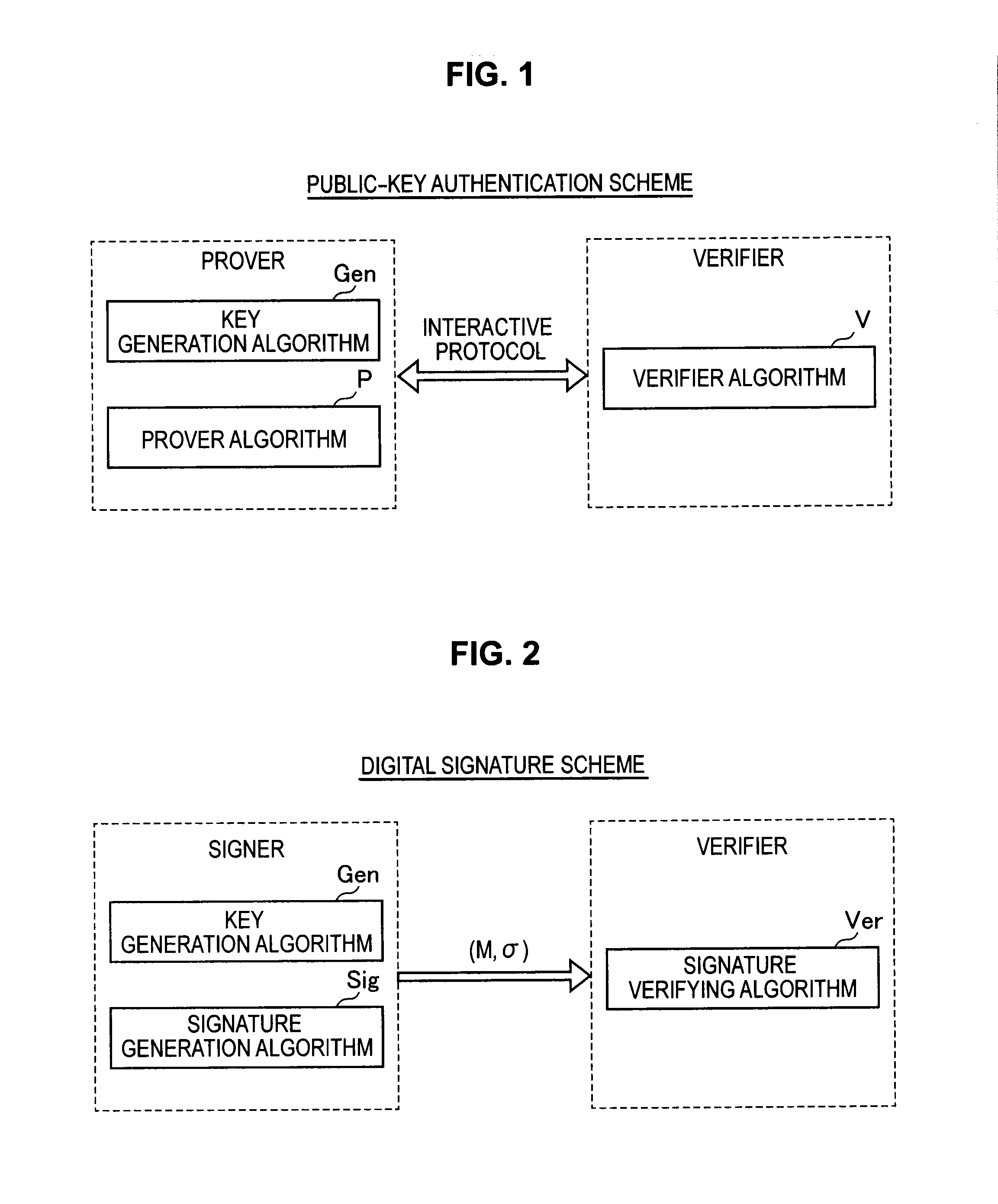
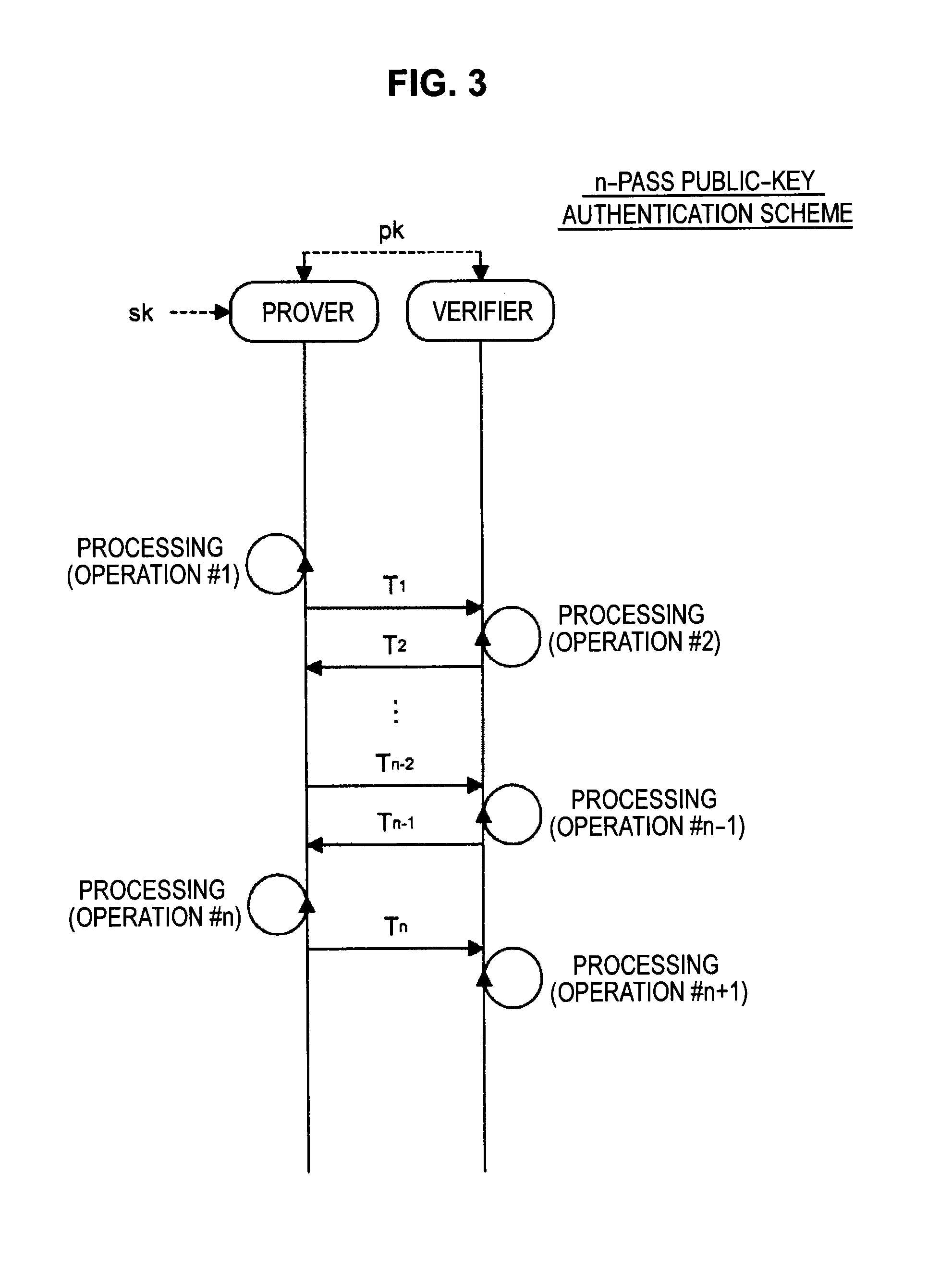
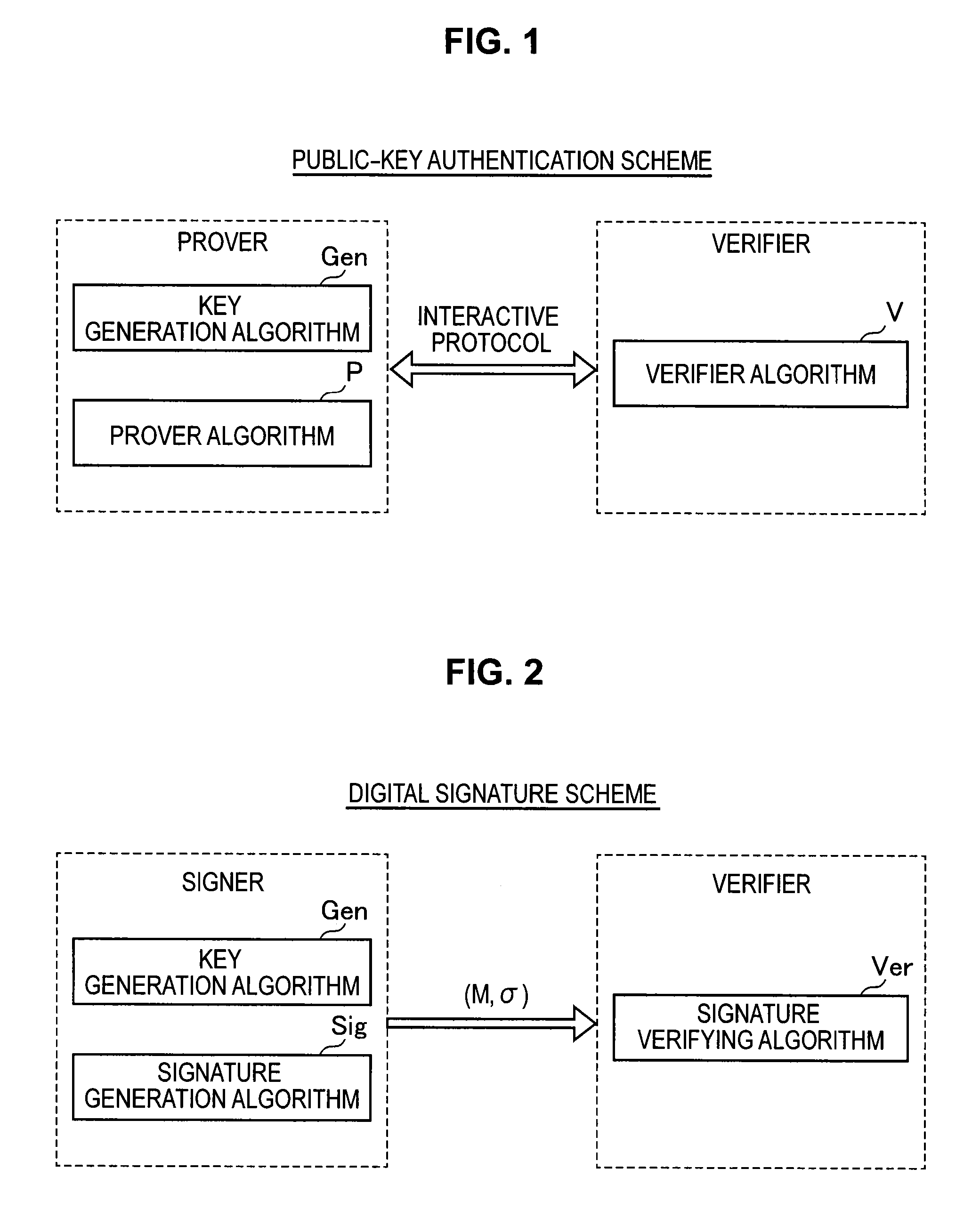
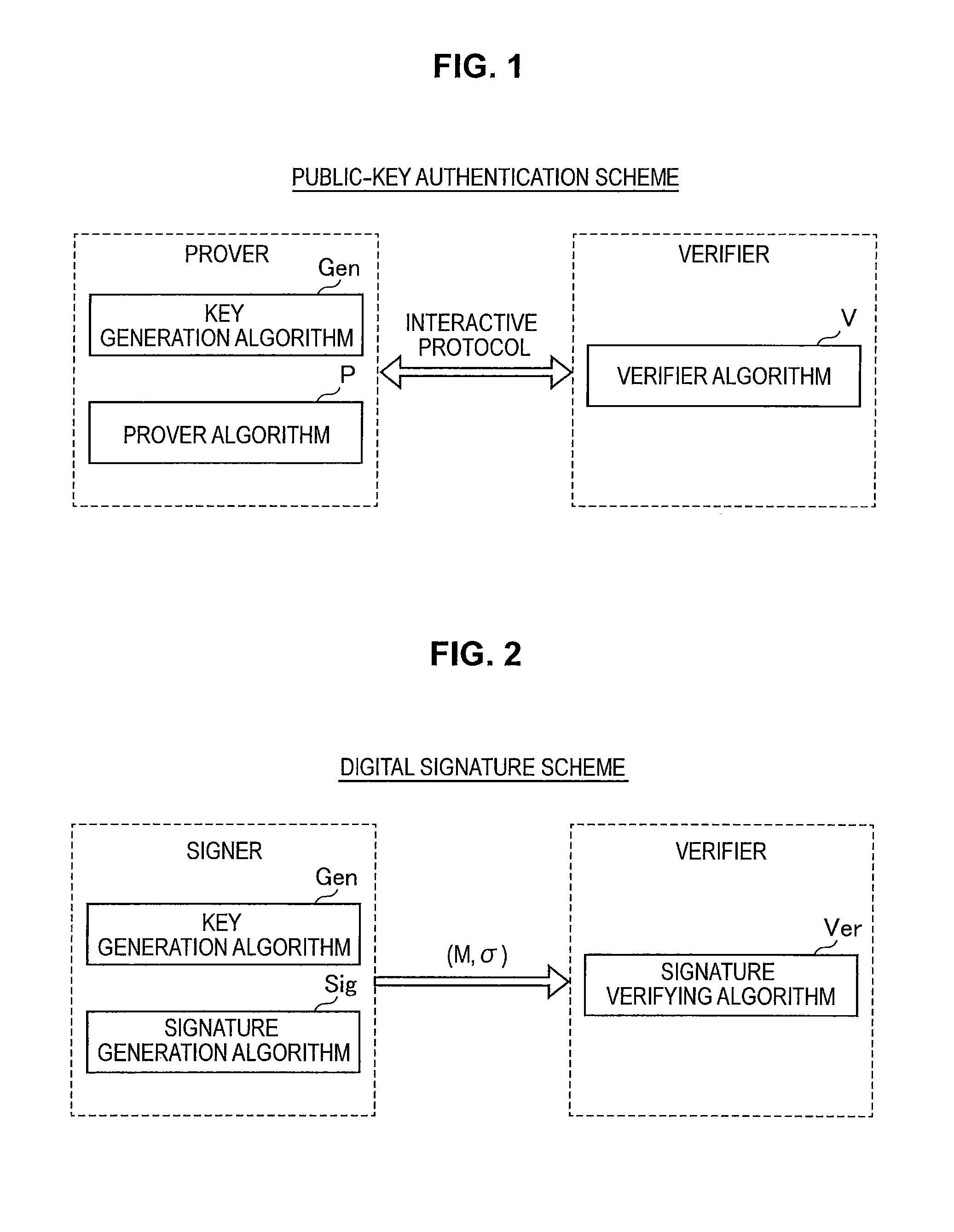
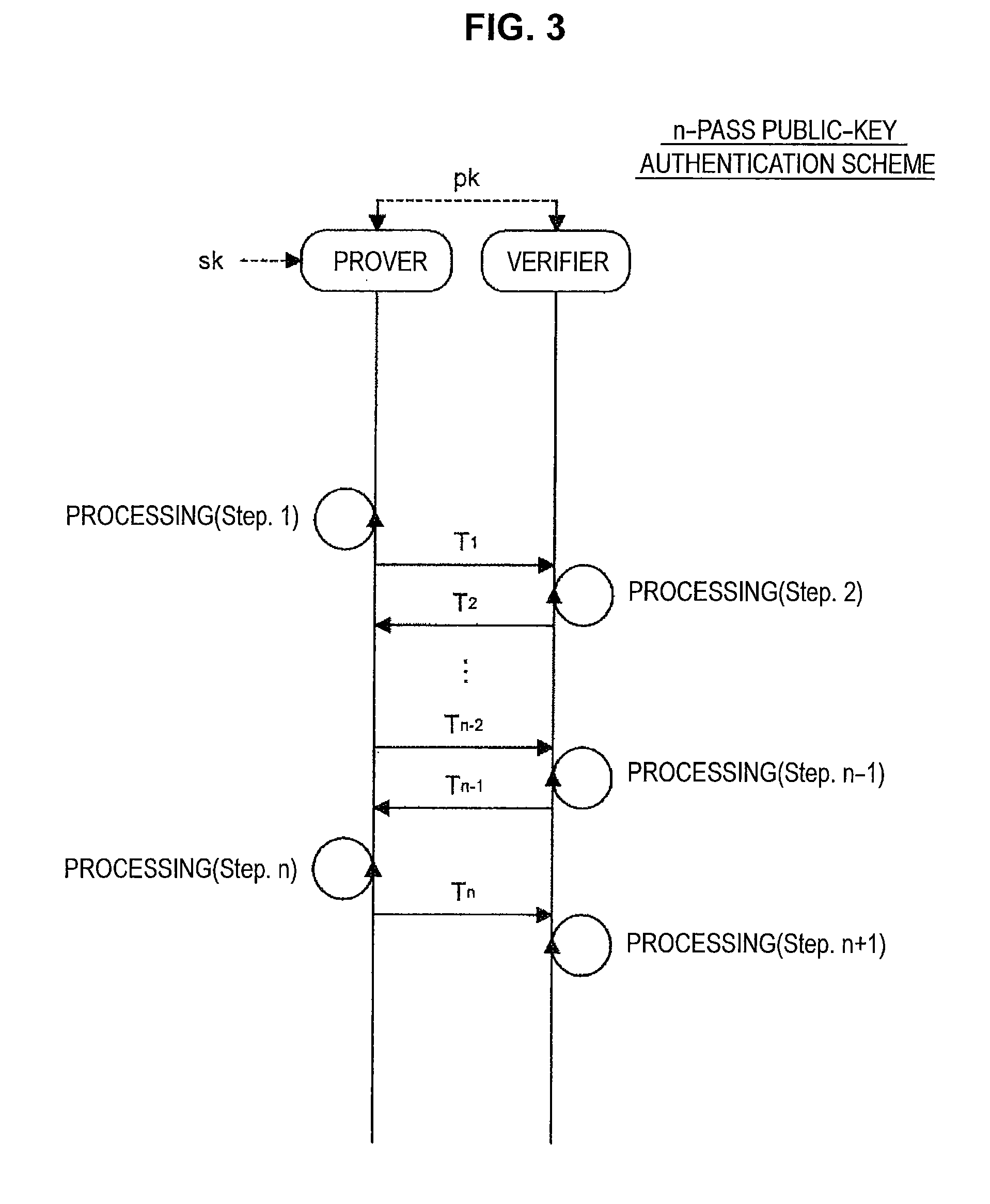
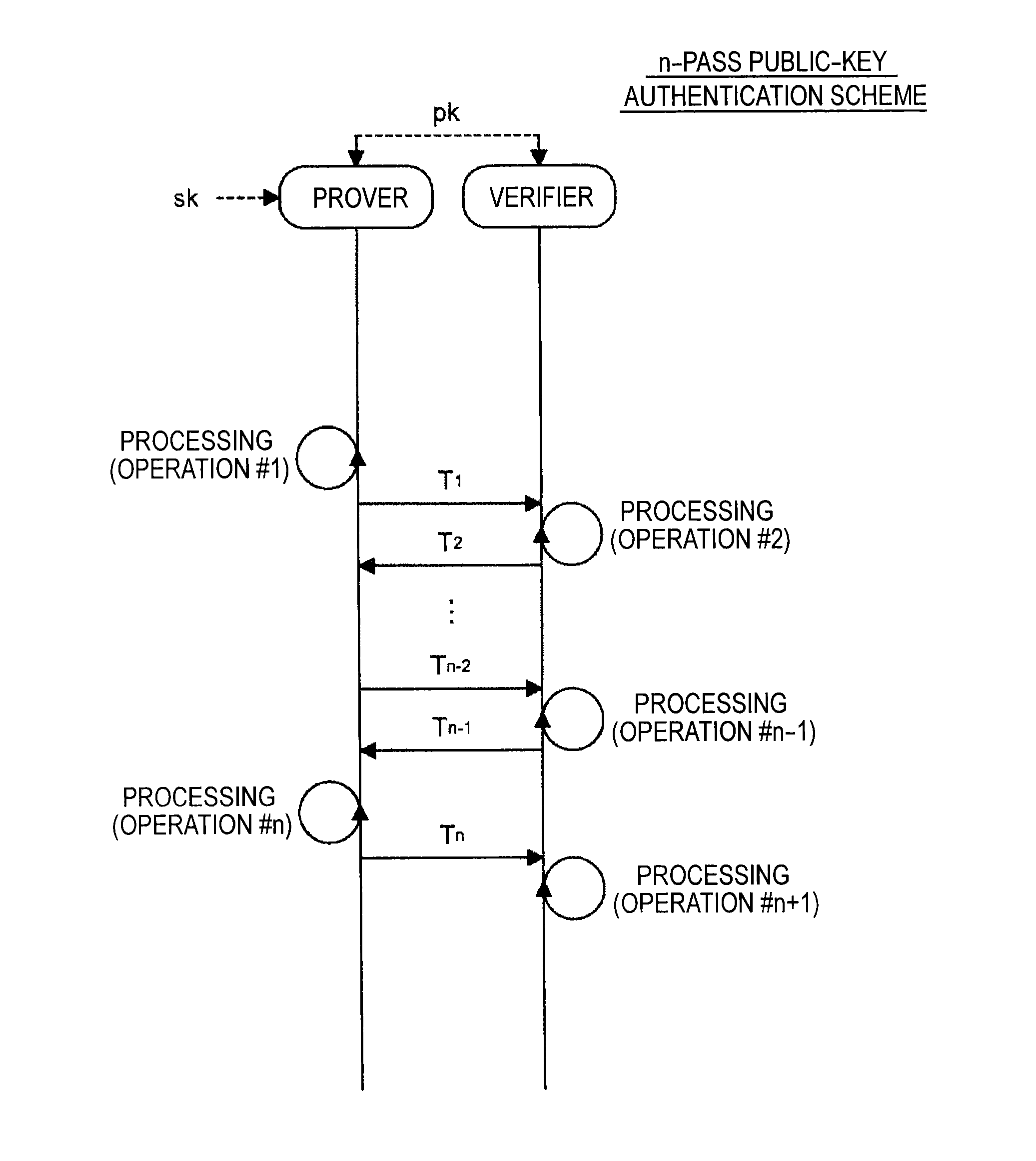
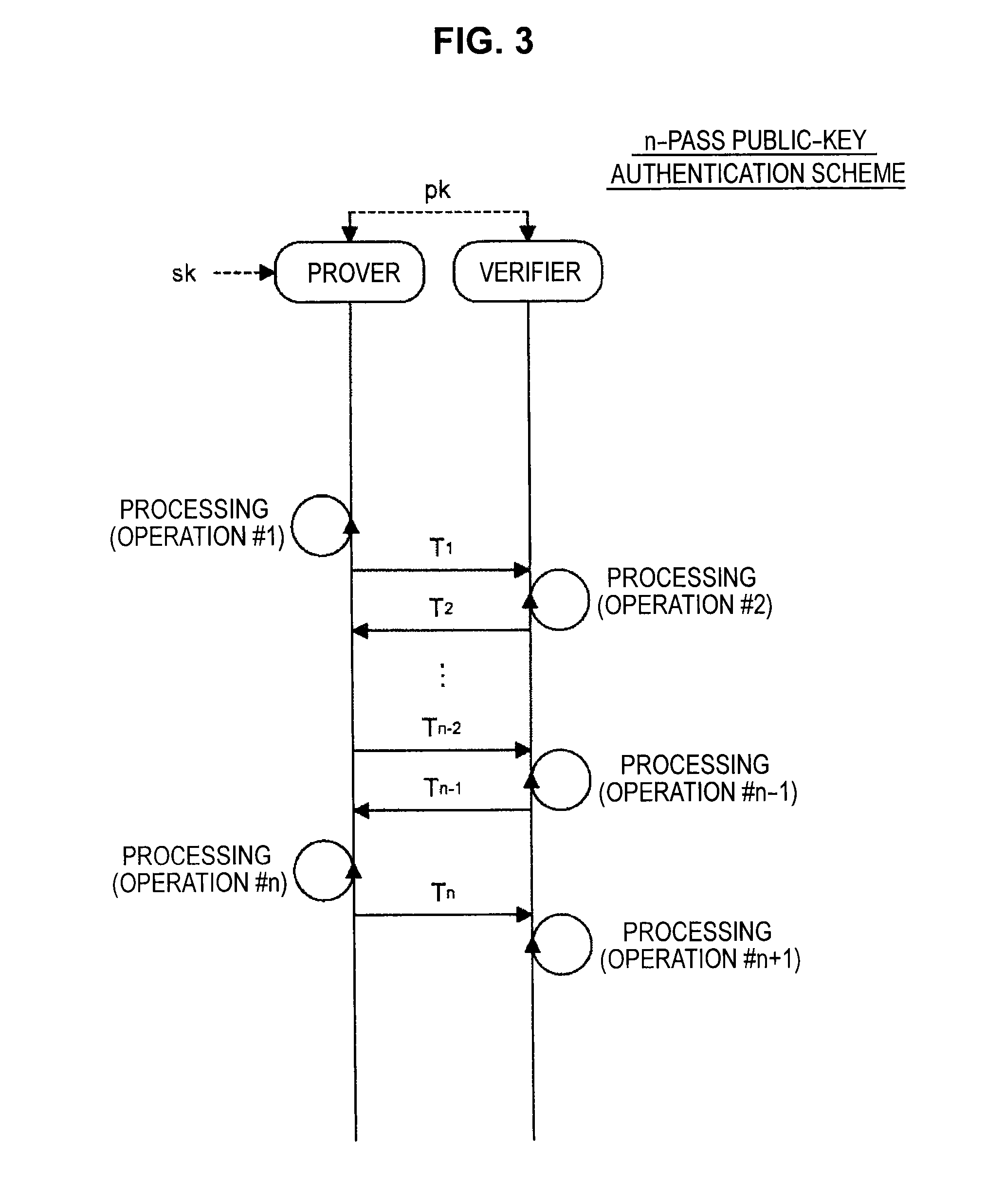
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program
ActiveUS20140215222A1Efficient replacementPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingPublic key authentication
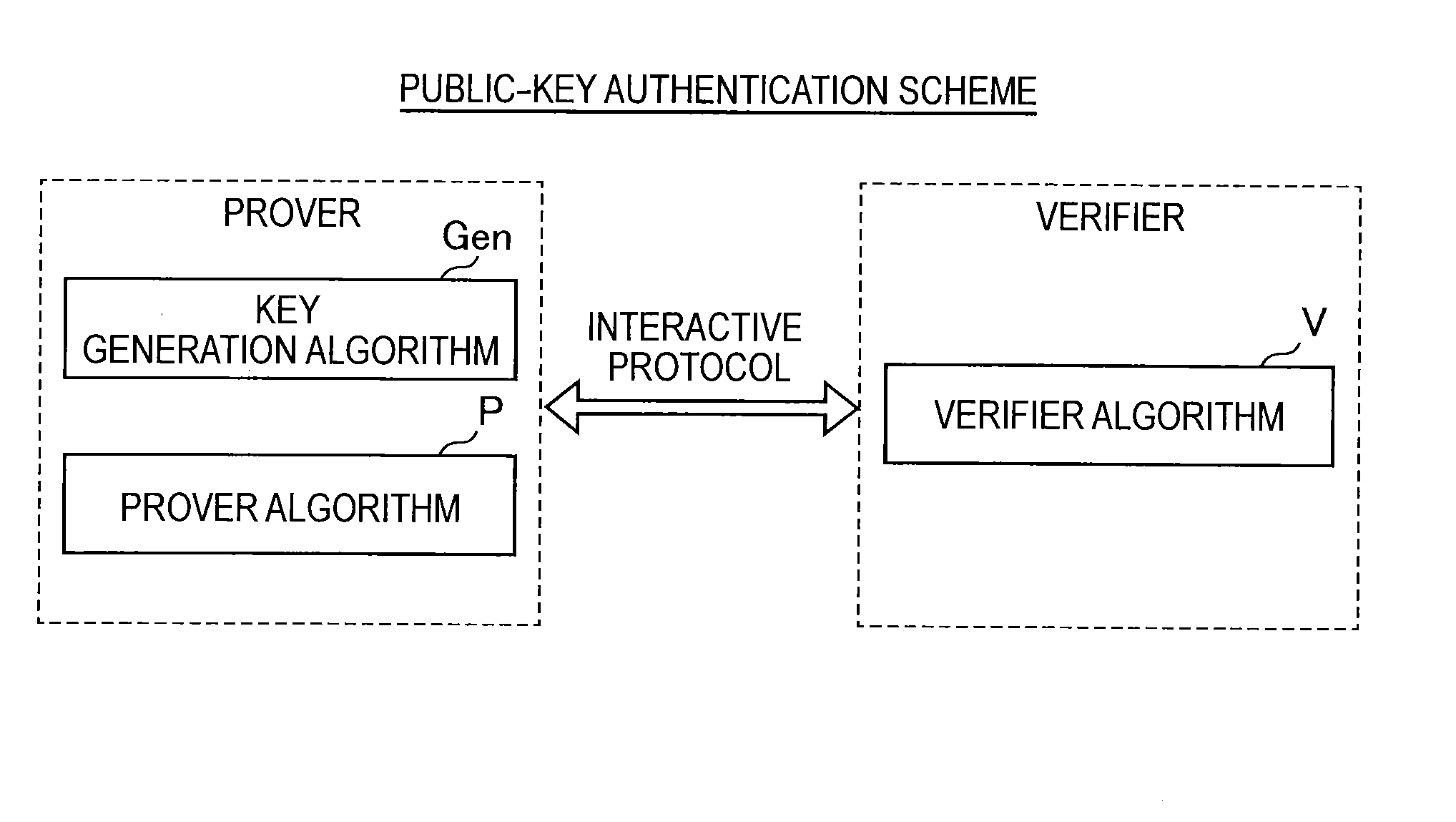
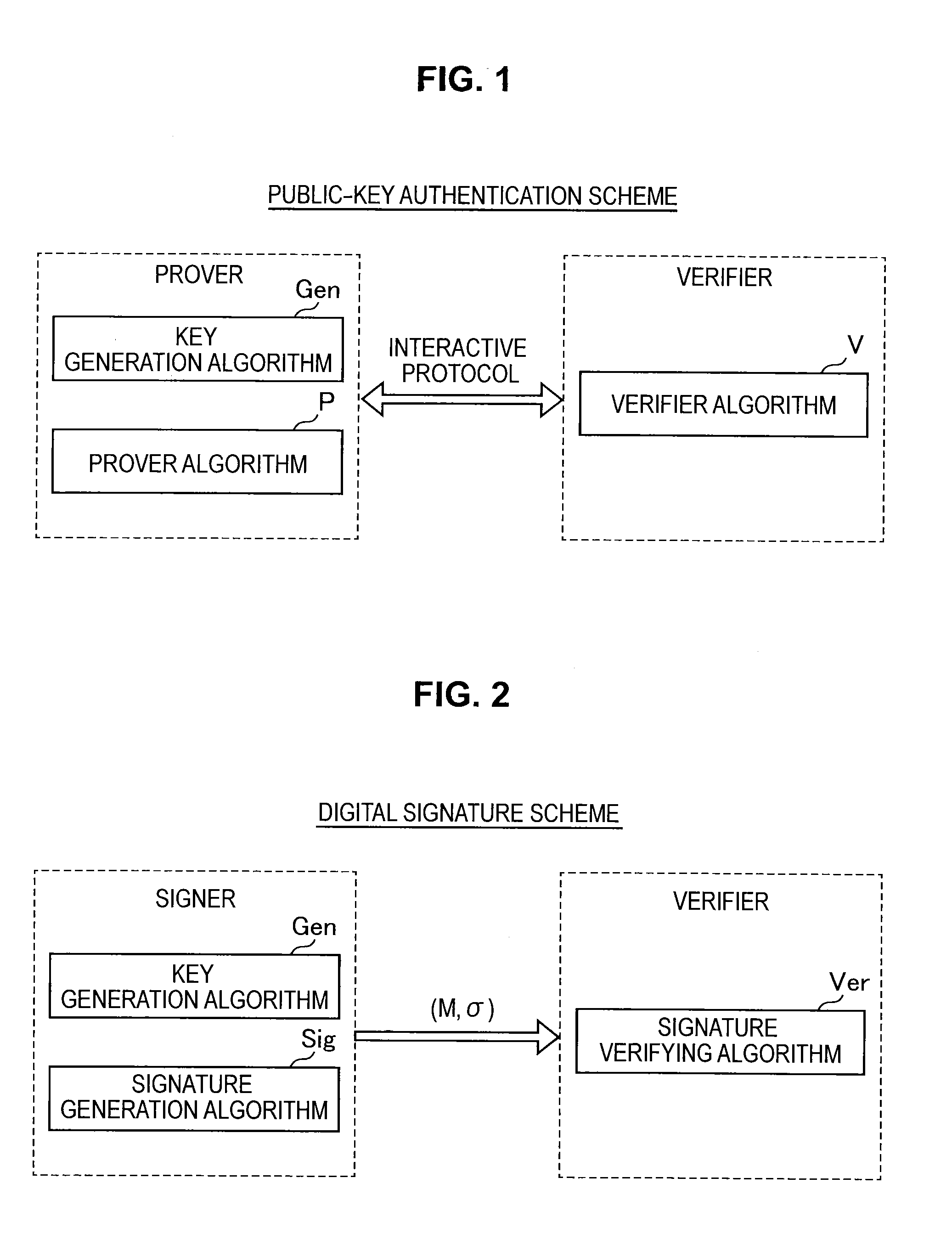
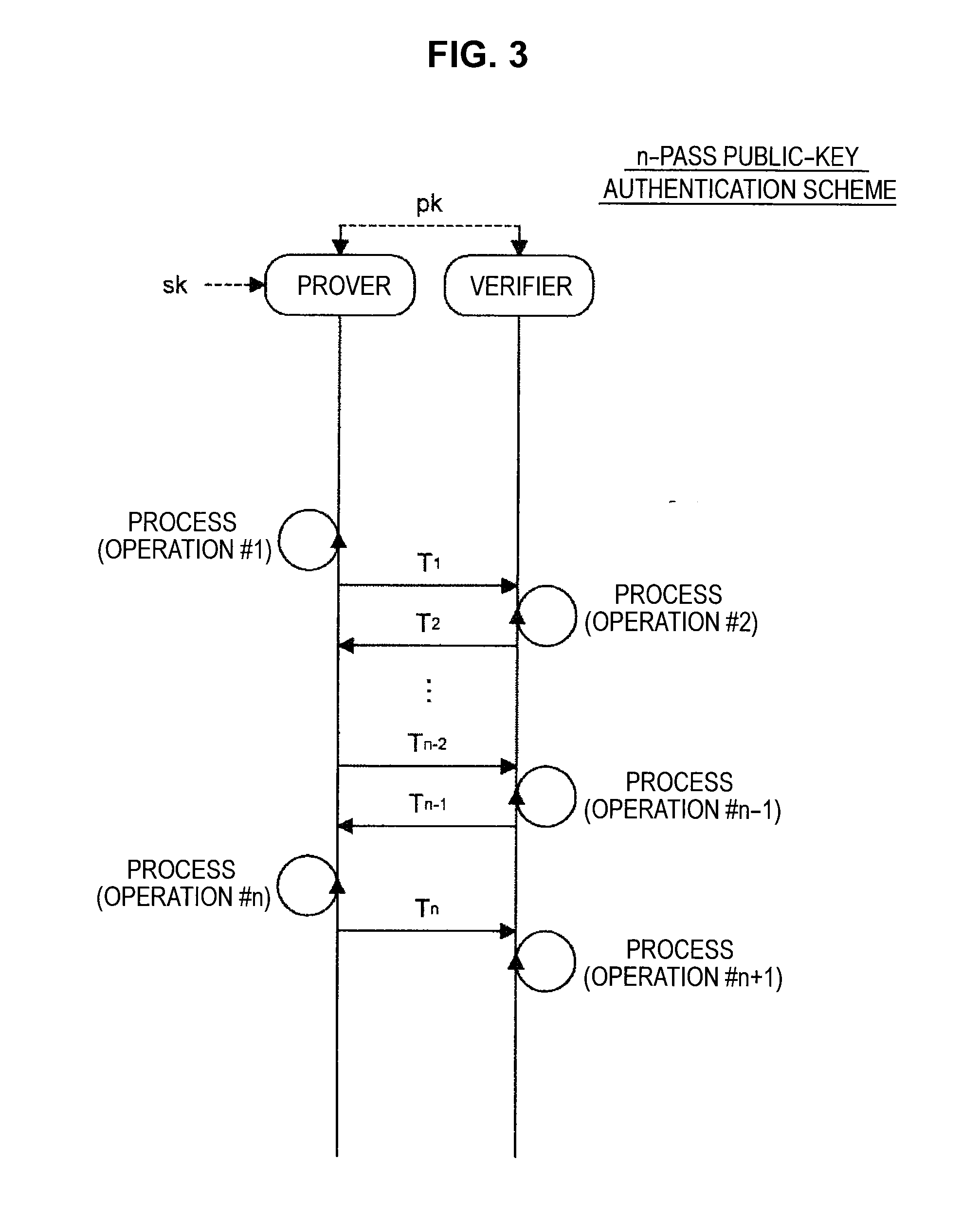
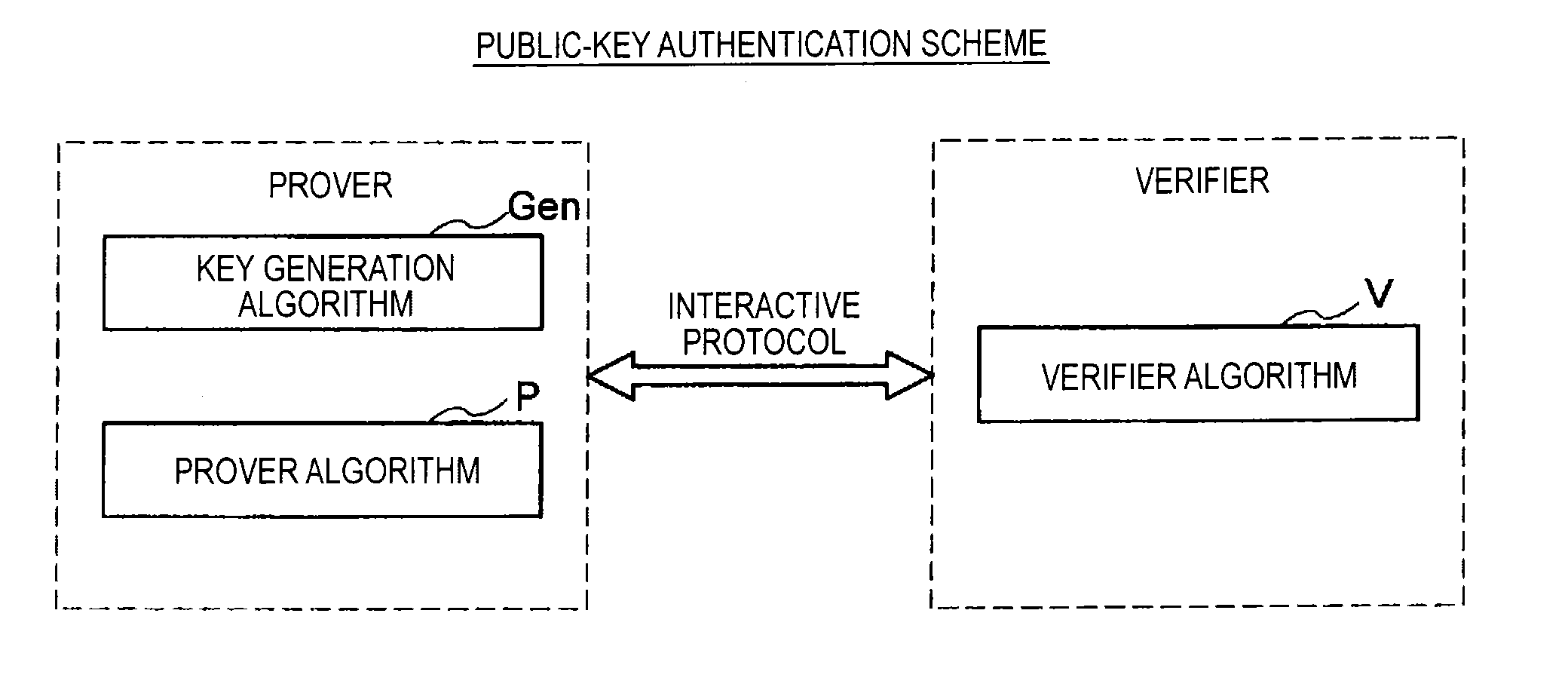
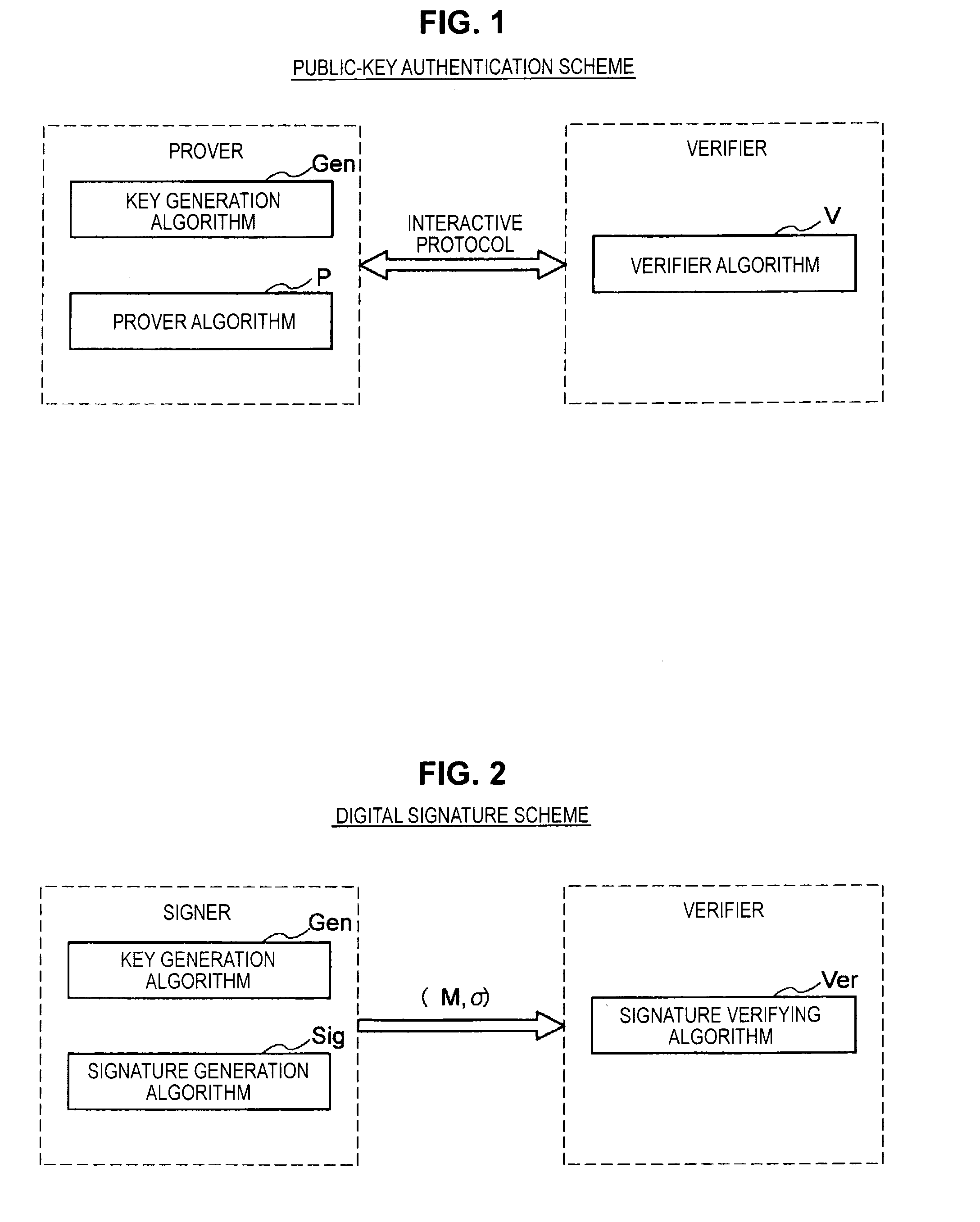
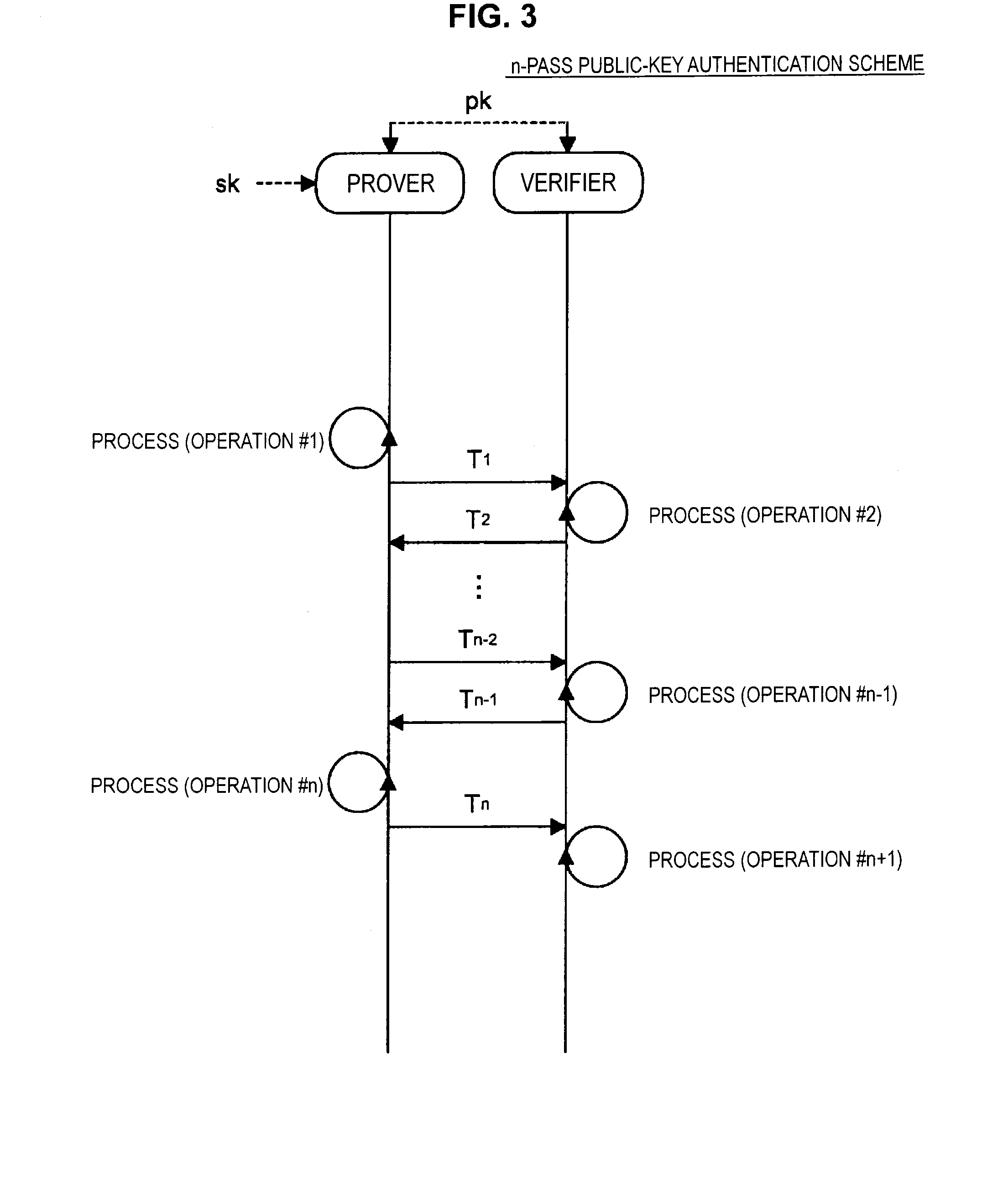
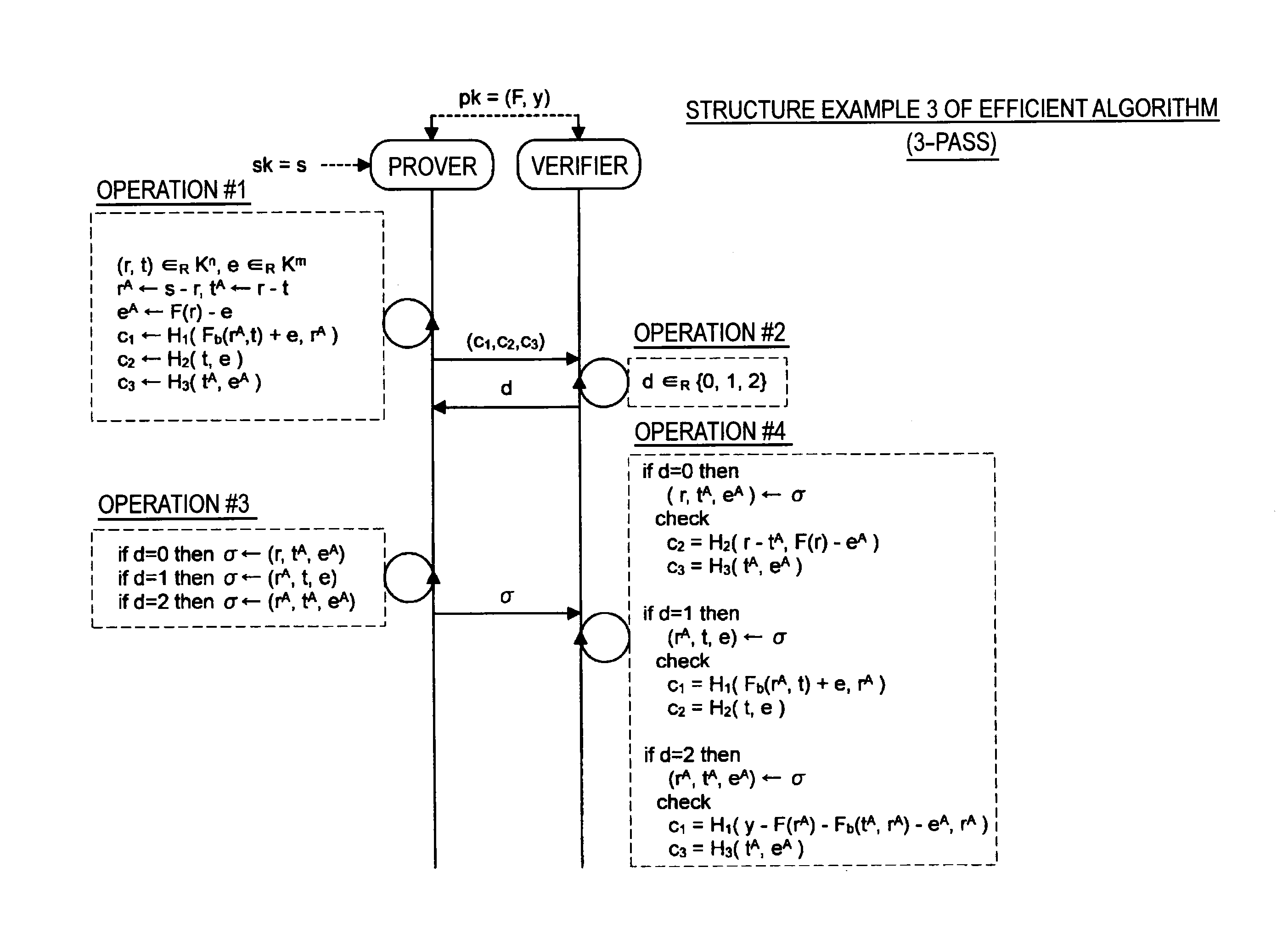
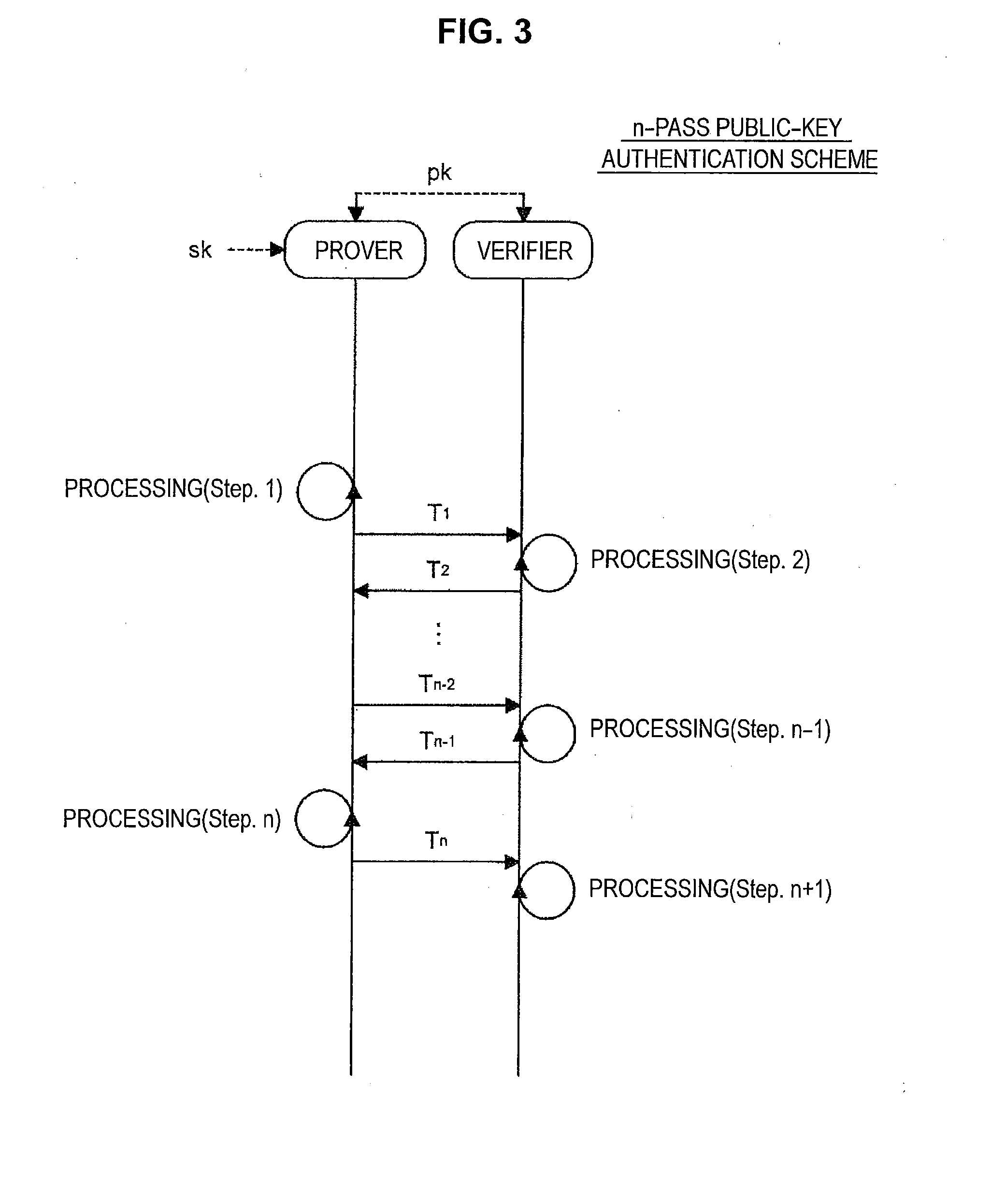
Provided an information processing apparatus including a number generation unit configured to generate numbers used in coefficients of terms included in a pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F=(f1, . . . , fm), using a predetermined function, from information shared between entities executing an algorithm of a public-key authentication scheme or a digital signature scheme that uses a public key including the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F, and an allocation unit configured to allocate the numbers generated by the number generation unit to the coefficients of the multi-order multivariate polynomials for which the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F are included in constituent elements.
Owner:SONY CORP
One-Round Secure Multiparty Computation of Arithmetic Streams and Evaluation of Functions
InactiveUS20210167946A1Key distribution for secure communicationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionSecret shareTheoretical computer science
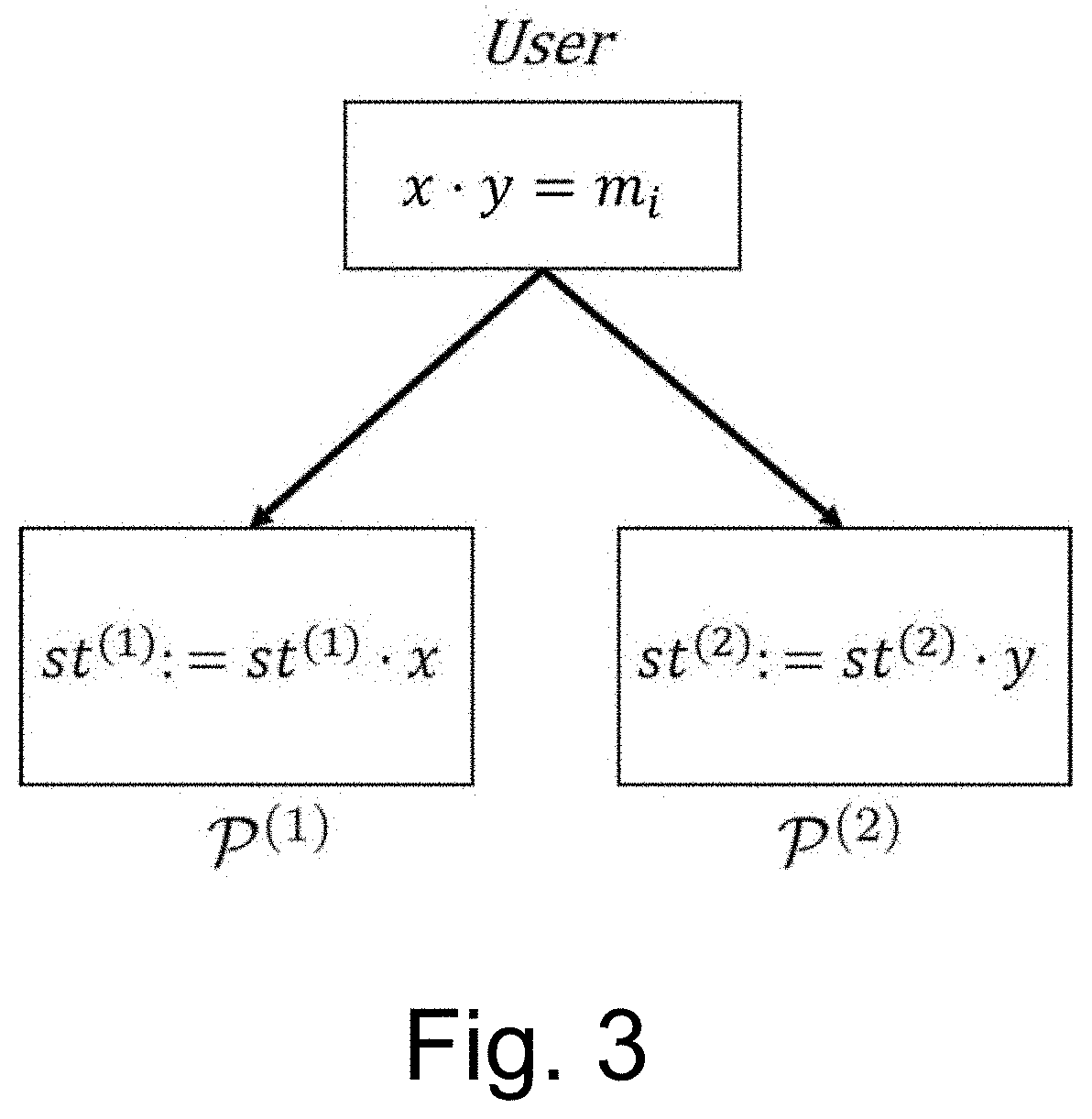
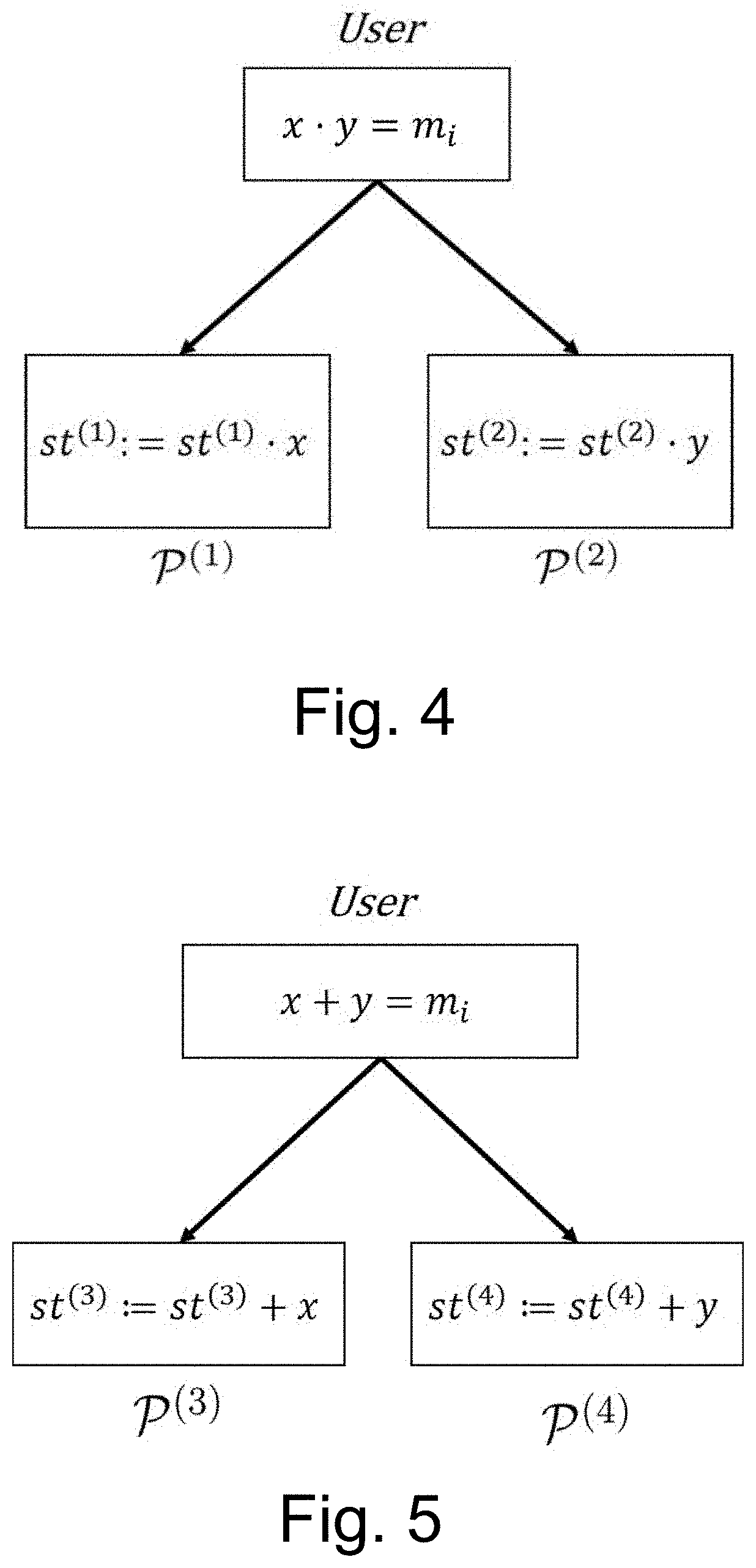
A method for performing, in a single round of communication and by a distributed computational system, Secure MultiParty Computation (SMPC) of an arithmetic function ƒ:pk→p represented as a multivariate polynomial over secret shares for a user, comprising the steps of sharing secrets among participants being distributed computerized systems, using multiplicative shares, the product of which is the secret, or additive shares, that sum up to the secret by partitioning secrets to sums or products of random elements of the field; implementing sequences of additions of secrets locally by addition of local shares or sequences of multiplications of secrets locally by multiplication of local shares; separately evaluating the monomials of ƒ by the participants; adding the monomials to obtain secret shares of ƒ.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD AT BEN GURION UNIV 907553
Attack-resistant multivariate signature scheme
InactiveUS8811608B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureTheoretical computer science
A cryptographic method, apparatus, and system, including selecting a first multivariate polynomial mapping, which includes first multivariate polynomial equations over first variables in a finite field, defining a second multivariate polynomial mapping, which includes at least some of the first multivariate polynomial equations and further includes second multivariate polynomial equations over the first variables together with second variables in the finite field, generating a public key based on the second multivariate polynomial mapping, and digitally signing a message, using a processor, with a digital signature that is verifiable using the public key and is generated by solving the first multivariate polynomial mapping to find respective first values of the first variables, solving a set of linear equations using the first values to find respective second values of the second variables, and applying a transform to the first and second values so as to generate a vector corresponding to the digital signature, wherein the second values are chosen so that a predefined group of elements of the vector will be zero. Related methods, apparatus, and systems are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method to produce new multivariate public key cryptosystems
ActiveUS7961876B2Improve any MPKCMore efficientPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationMultivariable polynomialsAuthentication
Owner:DING JINTAI
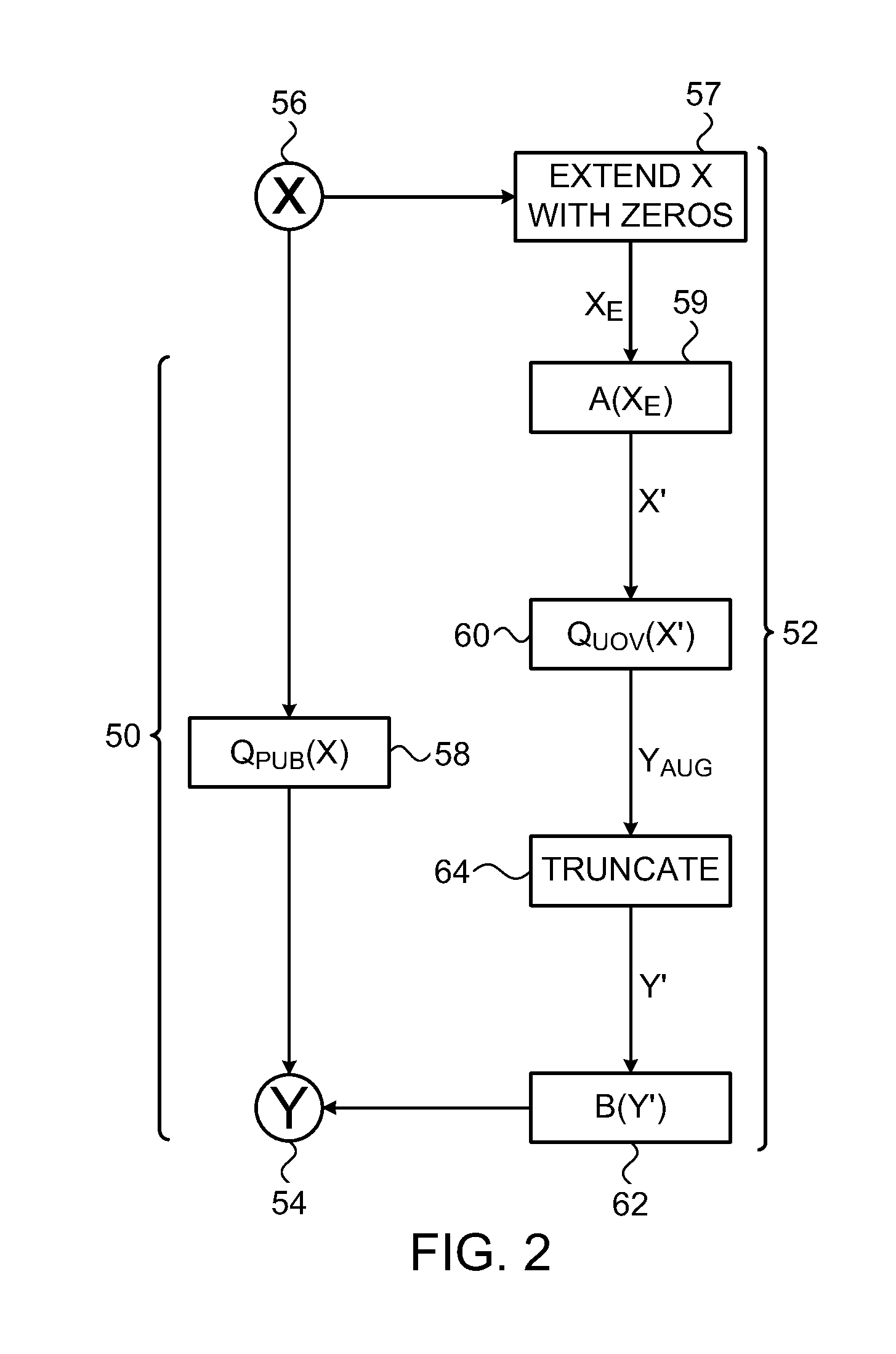
High rate locally decodable codes
ActiveUS20120246547A1Efficient accessImprove noise immunityReed-muller codesCode conversionReed–Muller codeHigh rate
Data storage techniques and solutions simultaneously provide efficient random access to information and high noise resilience. The amount of storage space utilized is only slightly larger than the size of the data. The solution is based on locally decodable error-correcting codes (also referred to as locally decodable codes or LDCs). Locally decodable codes are described herein that are more efficient than conventional locally decodable codes. Such locally decodable codes are referred to as “multiplicity codes”. These codes are based on evaluating multivariate polynomials and their derivatives. Multiplicity codes extend traditional multivariate polynomial based (e.g., Reed-Muller) codes. Multiplicity codes inherit the local decodability of Reed-Muller codes, and at the same time achieve substantially better parameters.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Target algorithm fitting method based on neural network, terminal and application
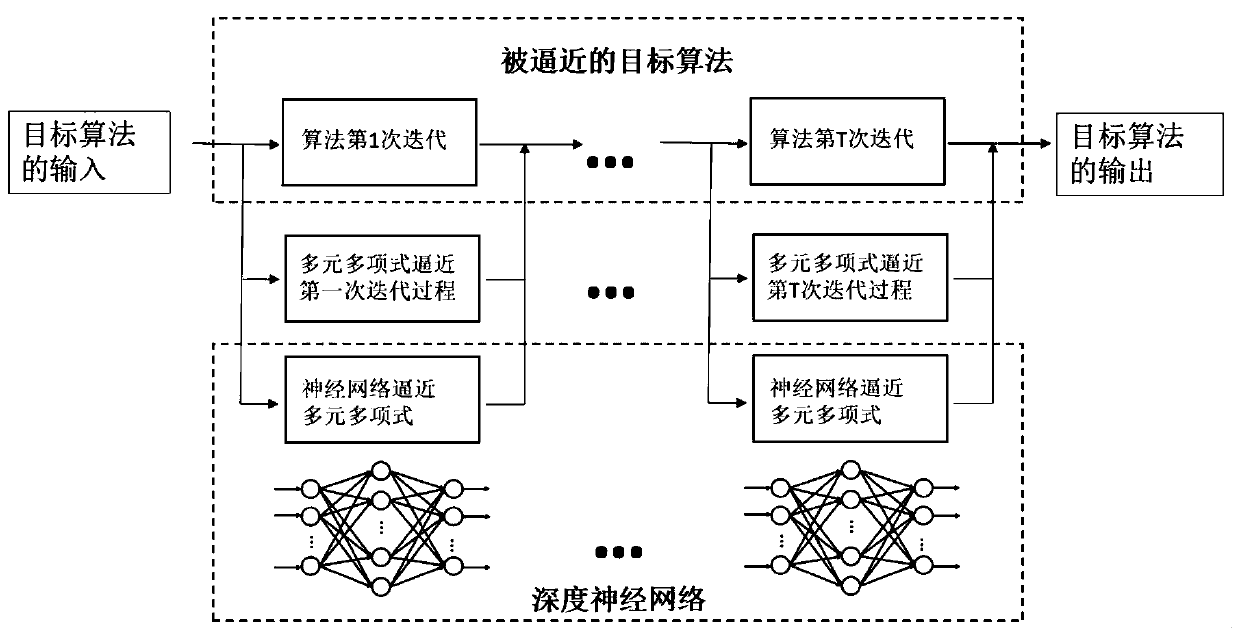
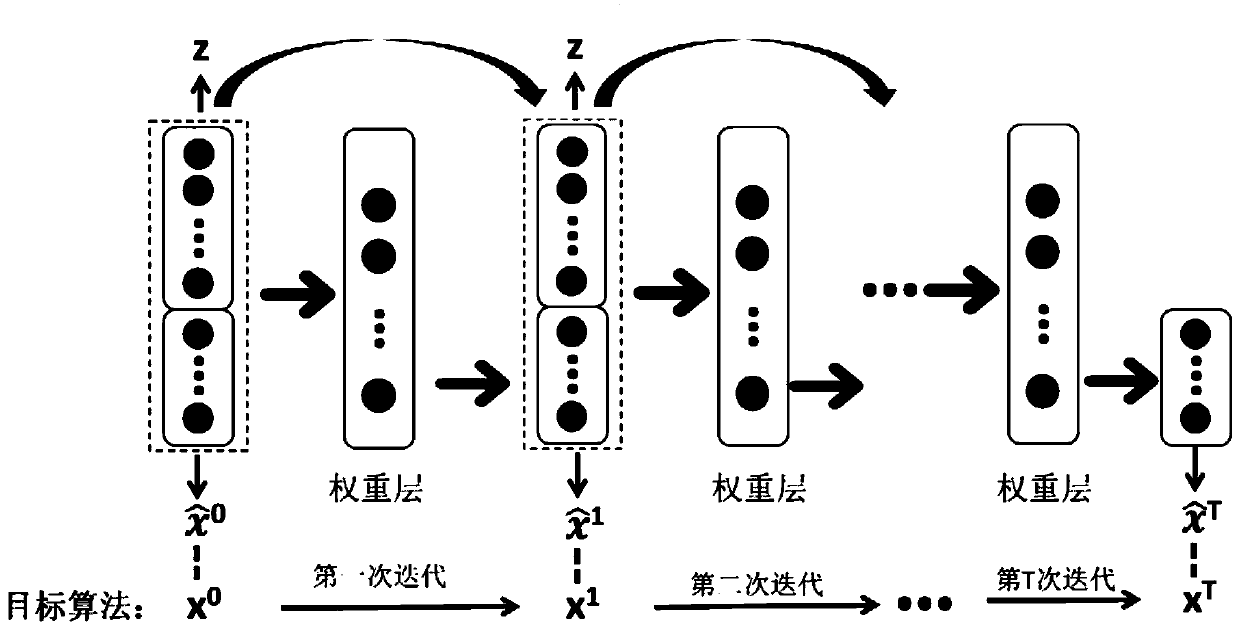
ActiveCN111126562ASolve the fitting problemShorten operation timeRadio transmissionOrthogonal multiplexPattern recognitionHidden layer
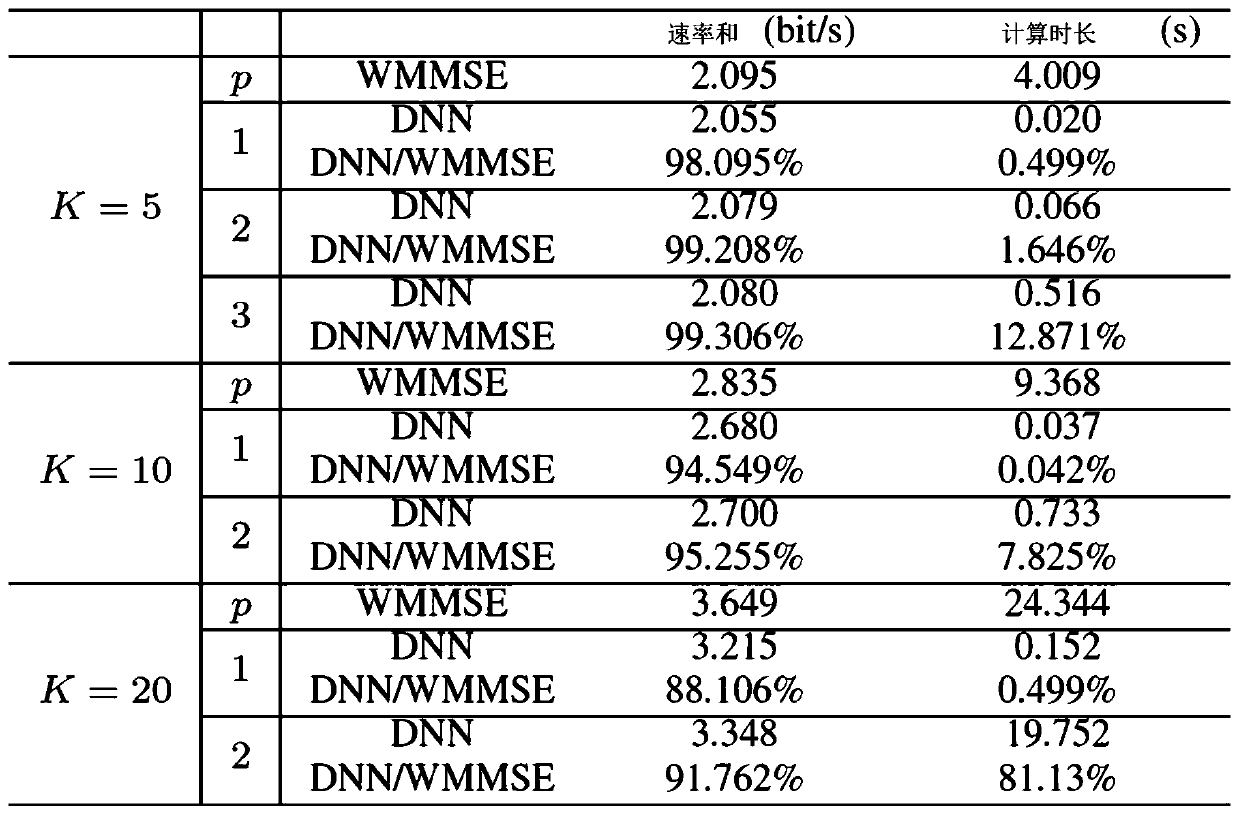
The invention provides a target algorithm fitting method based on a neural network. The method comprises the steps: acquiring a target algorithm capable of being approximated by the neural network; performing one-time iteration on the target algorithm to obtain data sets of different input and output variables; using the input variable as an independent variable, using the output variable as a dependent variable, and using a multivariate polynomial to fit the input and output variables of one iteration; determining a single hidden layer neural network structure of a multivariate polynomial ina fitting single iteration process; and repeating the iteration process, and connecting the iteration processes of each time in series to obtain the deep neural network which can finally fit the wholetarget algorithm. Meanwhile, the invention provides a deep neural network obtained based on the method, a channel capacity and energy distribution optimization method based on a WMMSE algorithm and aterminal used for executing the method. According to the method, the fitting problem of a complex algorithm is solved, and the structural design of the neural network and the selection of the numberof layers and neurons of the neural network can be practically guided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
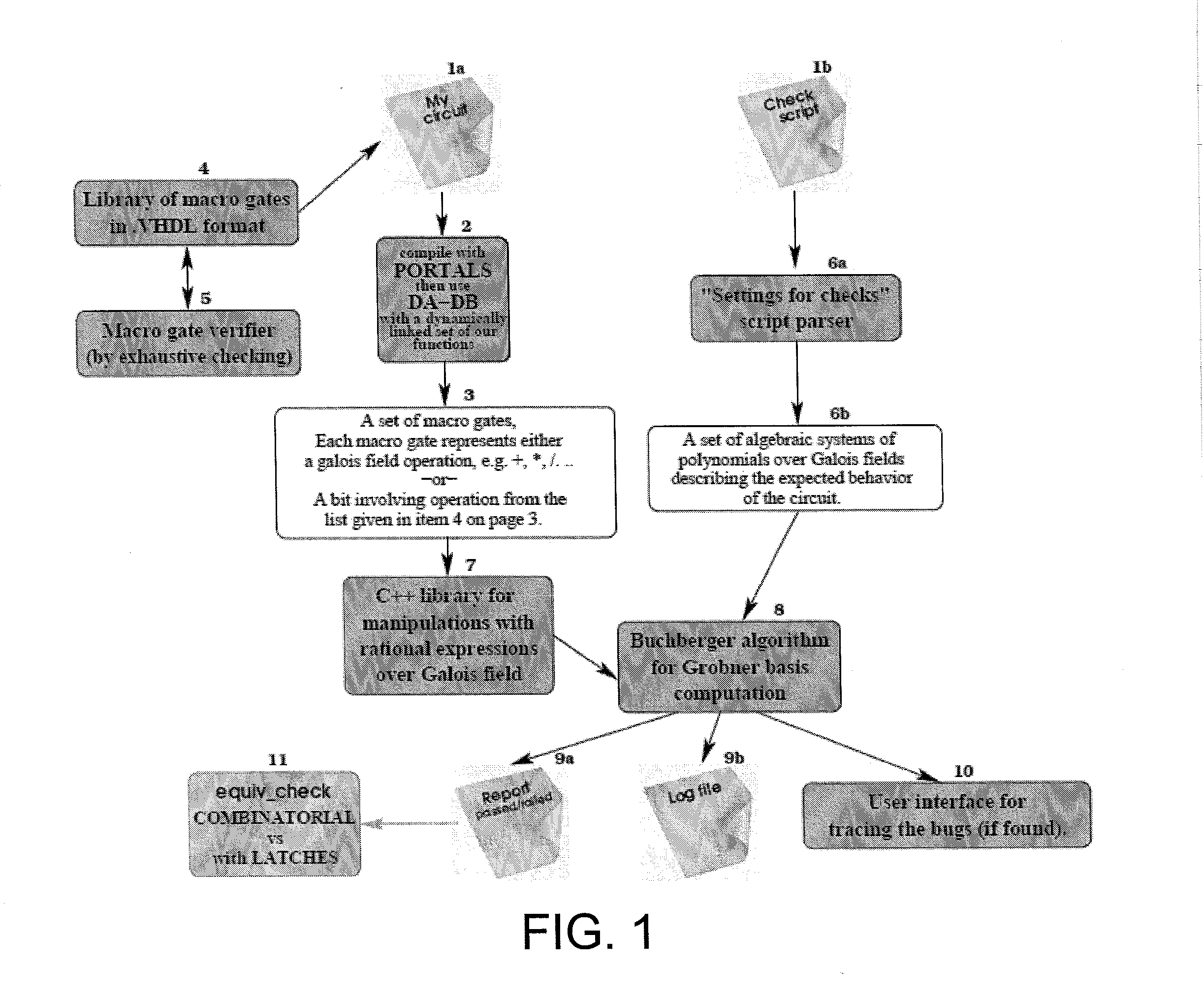
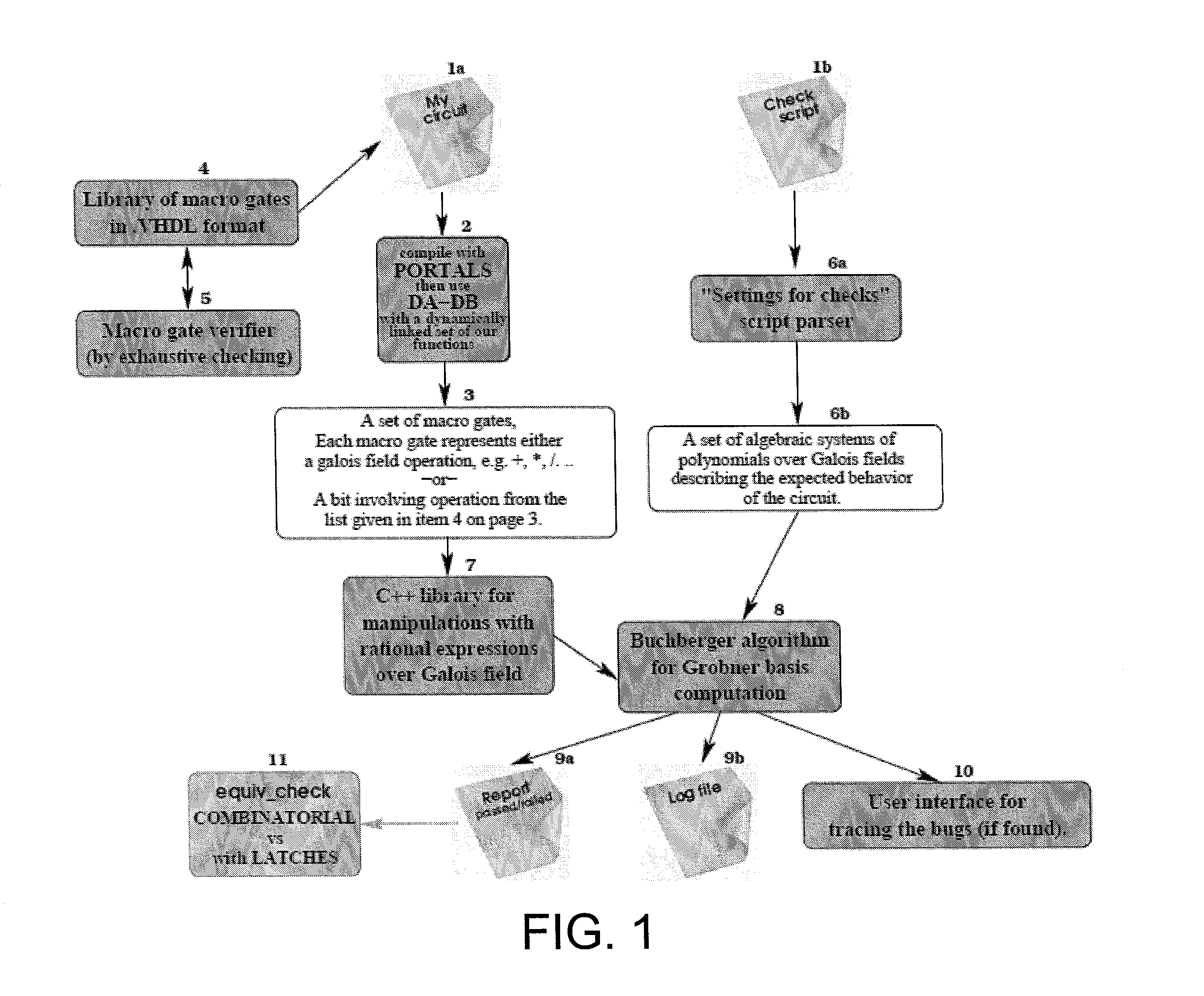
Circuit verification using computational algebraic geometry
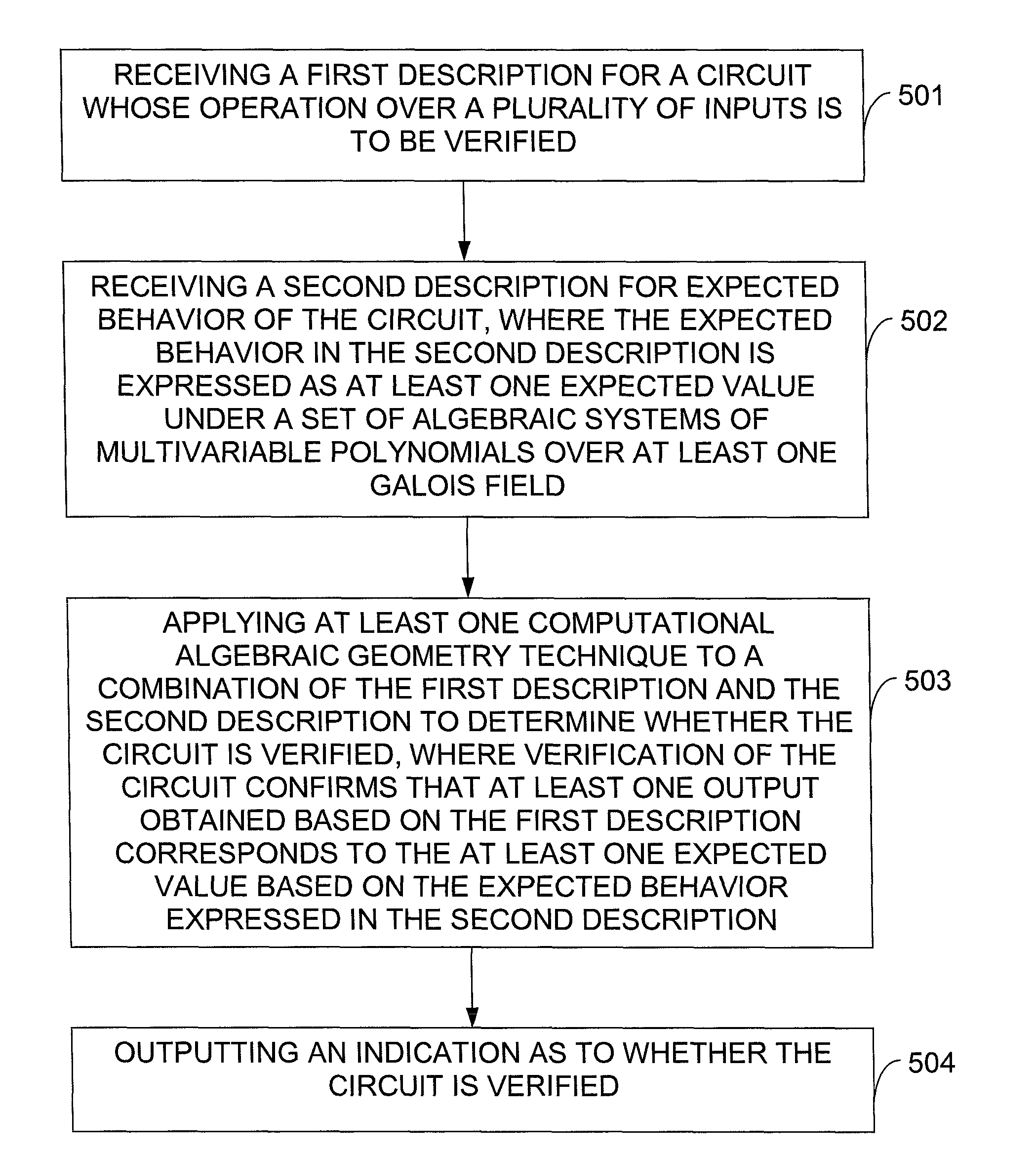
InactiveUS20130198705A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceMultivariable polynomials
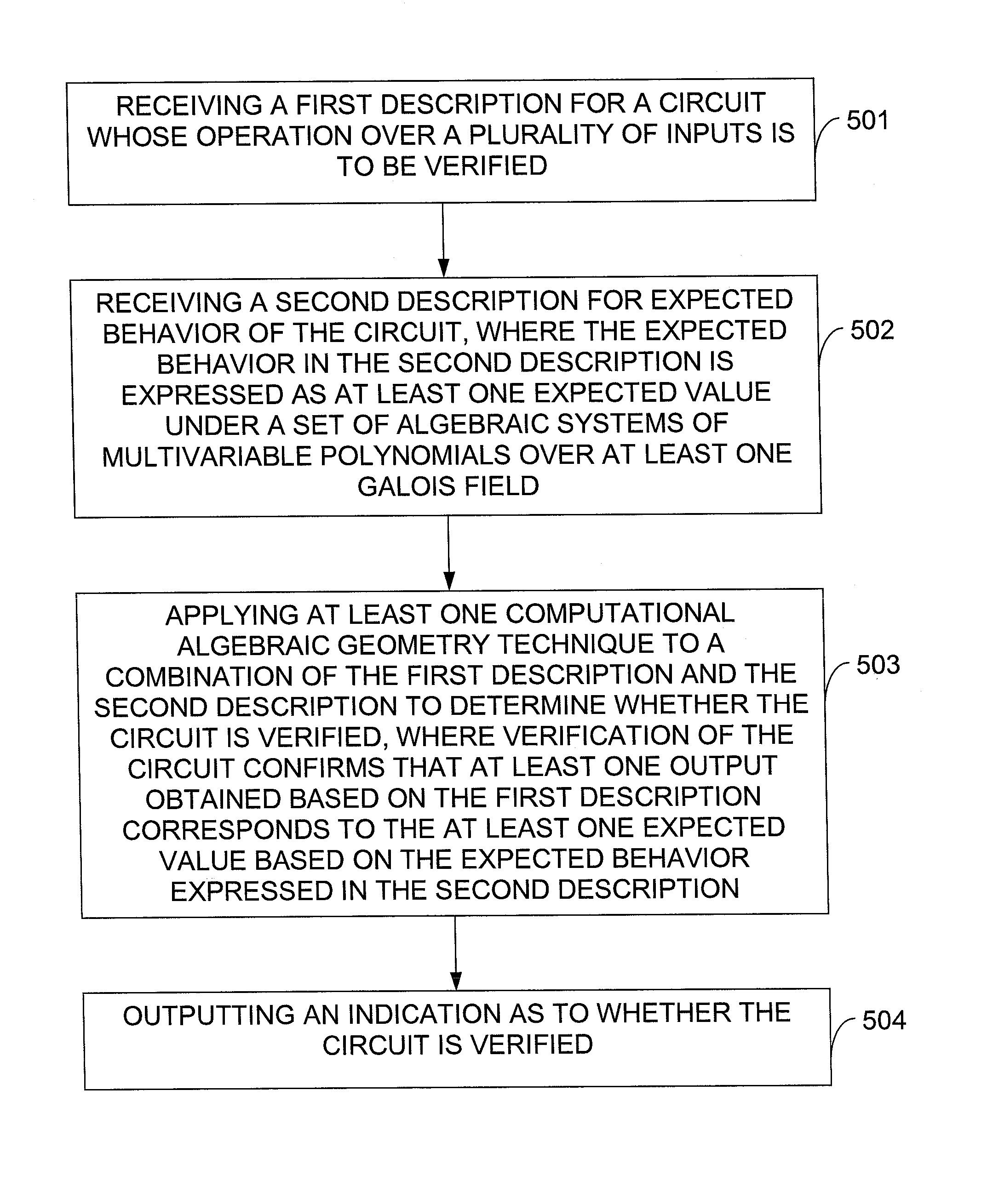
In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a method includes: receiving a first description for a circuit whose operation over a plurality of inputs is to be verified; receiving a second description for expected behavior of the circuit, where the expected behavior in the second description is expressed as a set of algebraic systems of multivariable polynomials over at least one Galois field; applying at least one computational algebraic geometry technique to a combination of the first description and the second description to determine whether the circuit is verified, where verification of the circuit confirms that at least one output obtained based on the first description corresponds to at least one expected value based on the expected behavior expressed in the second description; and outputting an indication as to whether the circuit is verified.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Attack-Resistant Multivariate Signature Scheme
InactiveUS20130177151A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureTheoretical computer science
A cryptographic method, apparatus, and system, including selecting a first multivariate polynomial mapping, which includes first multivariate polynomial equations over first variables in a finite field, defining a second multivariate polynomial mapping, which includes at least some of the first multivariate polynomial equations and further includes second multivariate polynomial equations over the first variables together with second variables in the finite field, generating a public key based on the second multivariate polynomial mapping, and digitally signing a message, using a processor, with a digital signature that is verifiable using the public key and is generated by solving the first multivariate polynomial mapping to find respective first values of the first variables, solving a set of linear equations using the first values to find respective second values of the second variables, and applying a transform to the first and second values so as to generate a vector corresponding to the digital signature, wherein the second values are chosen so that a predefined group of elements of the vector will be zero. Related methods, apparatus, and systems are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Information processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
InactiveUS20150010144A1Effective calculationKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationInformation processingPublic key authentication
Provided is an information processing apparatus including a number acquisition unit configured to acquire a number used for a coefficient of each term constituting a set of a multi-order multivariate polynomial F=(f1, . . . , fm), the number generated using a predetermined function from information shared between entities that execute an algorithm of a public-key authentication scheme or a digital signature scheme that uses a public key including the set of the multi-order multivariate polynomial F, and a polynomial calculation unit configured to calculate a multi-order multivariate polynomial for an input value of a variable by allocating the number acquired by the number acquisition unit to coefficients of the multi-order multivariate that includes the set of the multi-order multivariate polynomial F as a structural element. The polynomial calculation unit skips a calculation process for a term in which an input value of at least one variable is 0
Owner:SONY CORP
Circuit verification using computational algebraic geometry
InactiveUS8640065B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceMultivariable polynomials
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Nformation processing apparatus, signature generation apparatus, information processing method, signature generation method, and program
InactiveUS20140189361A1High safetyImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionTheoretical computer scienceAlgorithm
Provided is an information processing apparatus including a message generation unit that generates a message based on a pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F=(f1, . . . , fm) defined in a ring K and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a message supply unit that supplies the message to a verifier storing the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F and vectors y=(y1, . . . , ym)=(f1(s), . . . , fm(s)), a response supply unit that supplies the verifier with response information corresponding to a verification pattern which the verifier selects from among k (where k≧3) verification patterns. The vector s is a secret key. The pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F and the vectors y are public keys.
Owner:SONY CORP
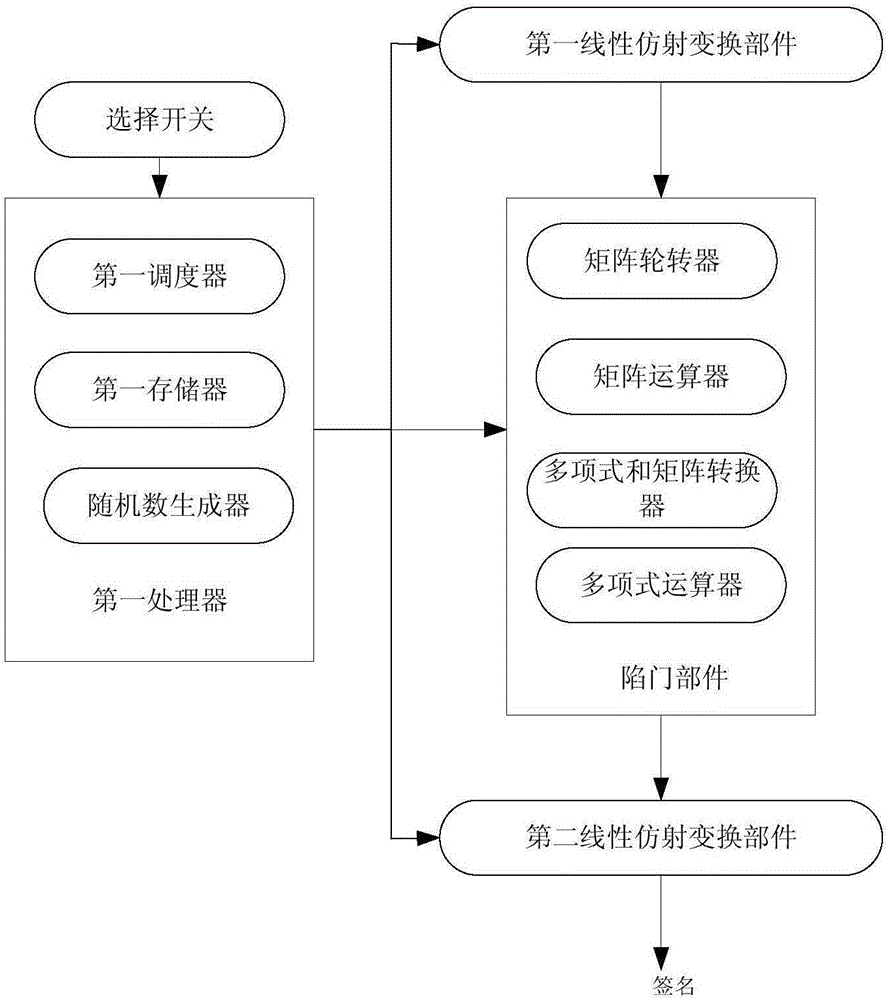
Multivariable public key signature system and multivariable public key signature method
ActiveCN106330463AReduce storageHigh speedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPasswordMultivariable polynomials
The invention discloses a multivariable public key signature system and a multivariable public key signature method. The signature system comprises a first processor, a first linear affine transformation part, a trap door part, and a second linear affine transformation part. The first processor is used to generate a random number, and is used to receive to-be-signed massage, and is used to transmit the to-be-signed massage to the first linear affine transformation part. The first linear affine transformation part is used for the affine transformation of the to-be-signed massage, and the trap door part is used to generate a multivariable polynomial equation group according to a private key parameter, and is used to substitute the received random number and the affine transformation result into the multivariable polynomial equation group for the solution, and the second linear affine transformation part is used for the affine transformation of the solution acquired by the trap door part, and a signature is acquired. Under a condition of guaranteeing the unforgeability of the signature, the speed of the multivariable public key password signature is accelerated, and at the same time, the memory size of the private key is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Information processing apparatus, signature providing method, signature verifying method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20140164780A1Improve securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingDigital signature
An information processing apparatus including a message generating unit that generates N sets of messages based on a multi-order multivariate polynomial set F=(f1, . . . fm) defined on a ring K and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a first information selecting unit that inputs a document M and the N sets of messages to a one-way function that selects one piece of first information from among k (where k≧3) pieces of first information in response to a set of input information, and selects N pieces of first information, a second information generating unit that generate N pieces of second information, and a signature providing unit that provides a verifier with the N pieces of first information and the N pieces of second information as a digital signature.
Owner:SONY CORP
Proxy re-signature method based on IP signature
InactiveCN106789066AThe proxy re-signature method is guaranteed to be quantum-resistantResistant to Quantum AttacksKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer networkMultivariable polynomials
The invention discloses a proxy re-signature method based on IP signature for solving the technical problem of poor quantum aggression defense of the existing proxy re-signature method. The technical scheme is as follows: performing secret affine transformation on private keys of a trustee and a client to construct a re-signature key, designing a proxy re-signature and a verification process of the proxy re-signature based on a polynomial isomorphism (IP) problem, and thus the quantum aggression defense of the proxy re-signature method is ensured; and in addition, the affine transformation of a quadratic multivariable polynomial group mainly executes multiplication, so the amount of computation is small, and the proxy re-signature method has relatively high computation efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
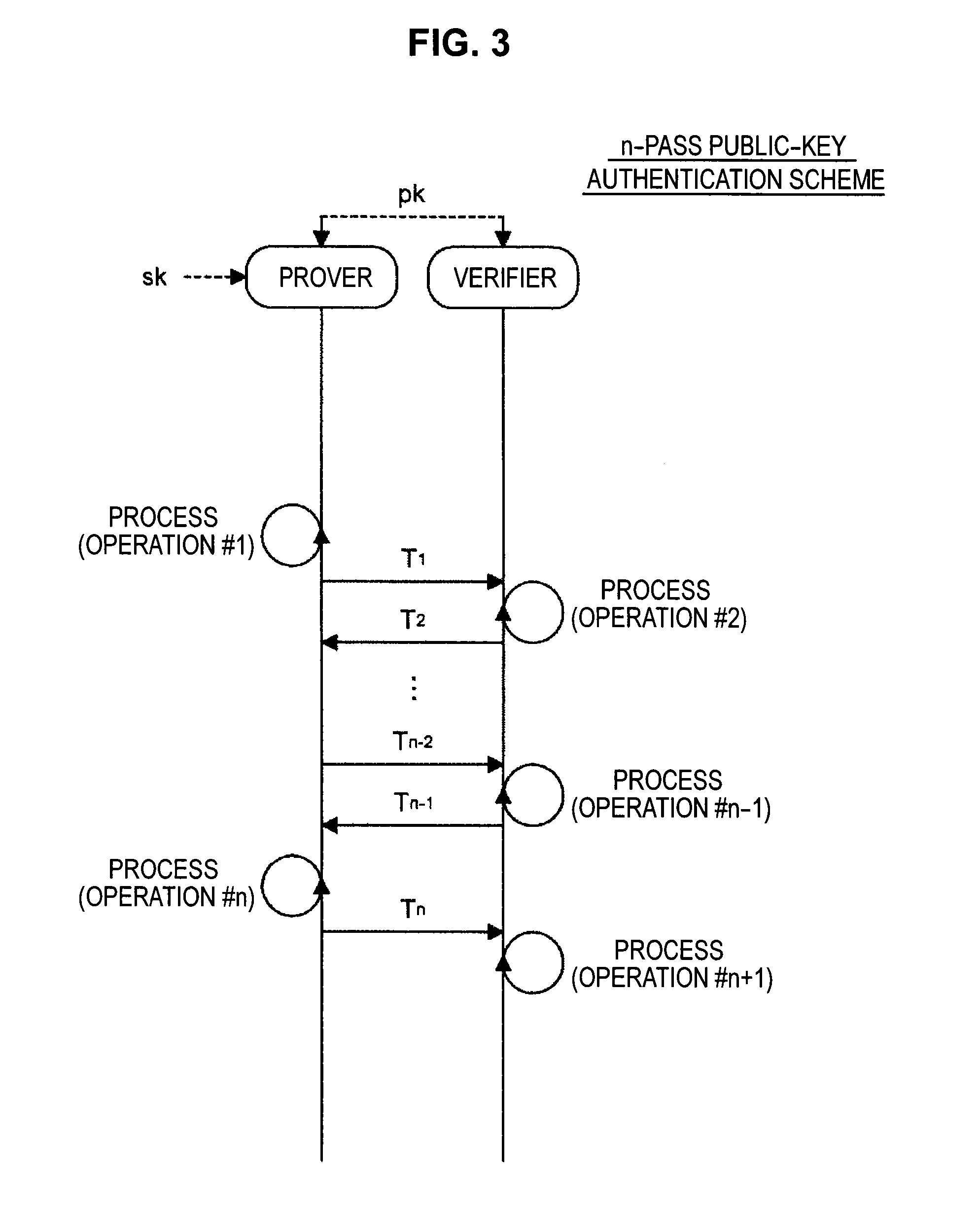
Information processing apparatus, key generation apparatus, signature verification apparatus, information processing method, signature generation method, and program
InactiveUS20120233704A1Ensure safetySafety from chosen-message attacks can be securedDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInformation processingTheoretical computer science
Provided is an information processing apparatus for realizing an electronic signature system of the MPKC signature method capable of safety certification with respect to chosen-message attack. An information processing apparatus including a first inverse transformation unit that transforms an element y of a finite ring Kn containing elements constituted of n numbers into an element y′ of the finite ring Kn by an inverse transformation T−1 of a first secret polynomial T, an element computation unit that considers the element y′ of the finite ring Kn obtained here as an element Y of an n-order extension A of a finite ring K and computes an element Xε{Z|f(Z)=Y} of an inverse image of mapping f: A→A represented by a predetermined multivariable polynomial by using the element Y, an element selection unit that selects one element X of the inverse image with a probability p proportional to a number of elements α of the inverse image and outputs an exception value with a probability (1-p), and a second inverse transformation unit that considers the element X selected here as an element x′ of the finite ring Kn and transforms the element x′ of the finite ring Kn into an element x of the finite ring Kn by an inverse transformation S−1 of a second secret polynomial S is provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
ActiveUS20140136843A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingMultivariable polynomials
Provided is an information processing apparatus including a message generating unit that generates a message based on a multi-order multivariate polynomial set F=(f1, . . . ,fm) defined on a ring K and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a message providing unit that provides the message to a verifier holding the multi-order multivariate polynomial set F and a vector y=(y1, . . . ,ym)=(f1(s), . . . ,fm(s)), and a response providing unit that provides the verifier with response information corresponding to a verification pattern selected by the verifier from among k (where k≧3) verification patterns. The vector s is a secret key. The multi-order multivariate polynomial set F and the vector y are public keys. The message is information obtained by performing an operation prepared for a verification pattern corresponding to the response information in advance using the public keys and the response information.
Owner:SONY CORP
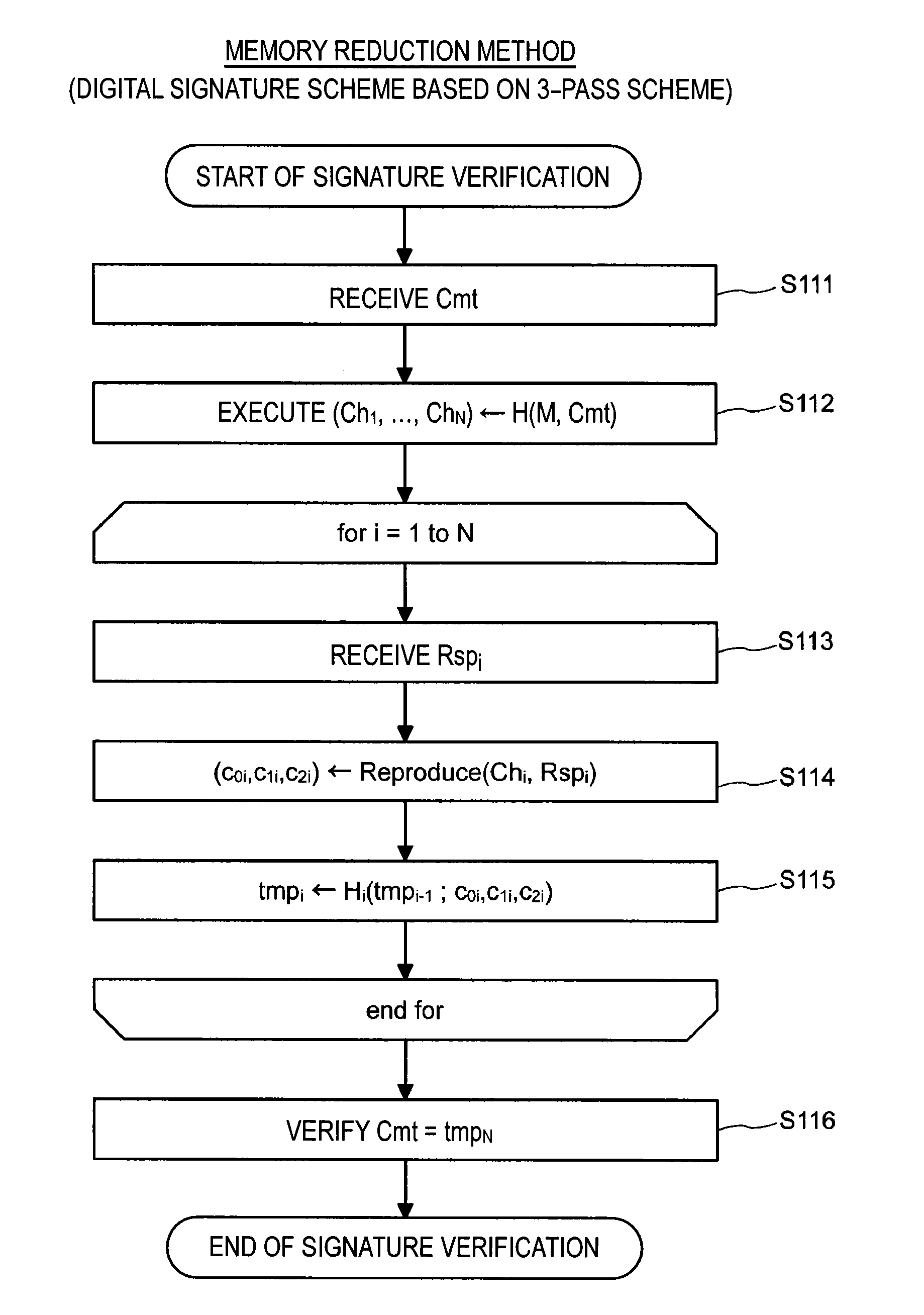
Signature verification apparatus, signature verification method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS9129122B2Improve securitySmall memoryPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureMultivariable polynomials
A signature verification apparatus including a signature acquisition unit configured to acquire a digital signature including first information generated based on a pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F=(f1, . . . , fm) defined in a ring K, a signature key s which is an element of a set Kn, and a document M and a plurality of pieces of second information for verifying that the first information is generated using the signature key s based on the data M, the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F, and vectors y=(f1(s), . . . , fm(s)), and a signature verification unit configured to verify legitimacy of the document M by confirming whether or not the first information is restorable using the plurality of pieces of second information included in the digital signature. The pair of multivariate polynomials F and the vectors y are public keys.
Owner:SONY CORP
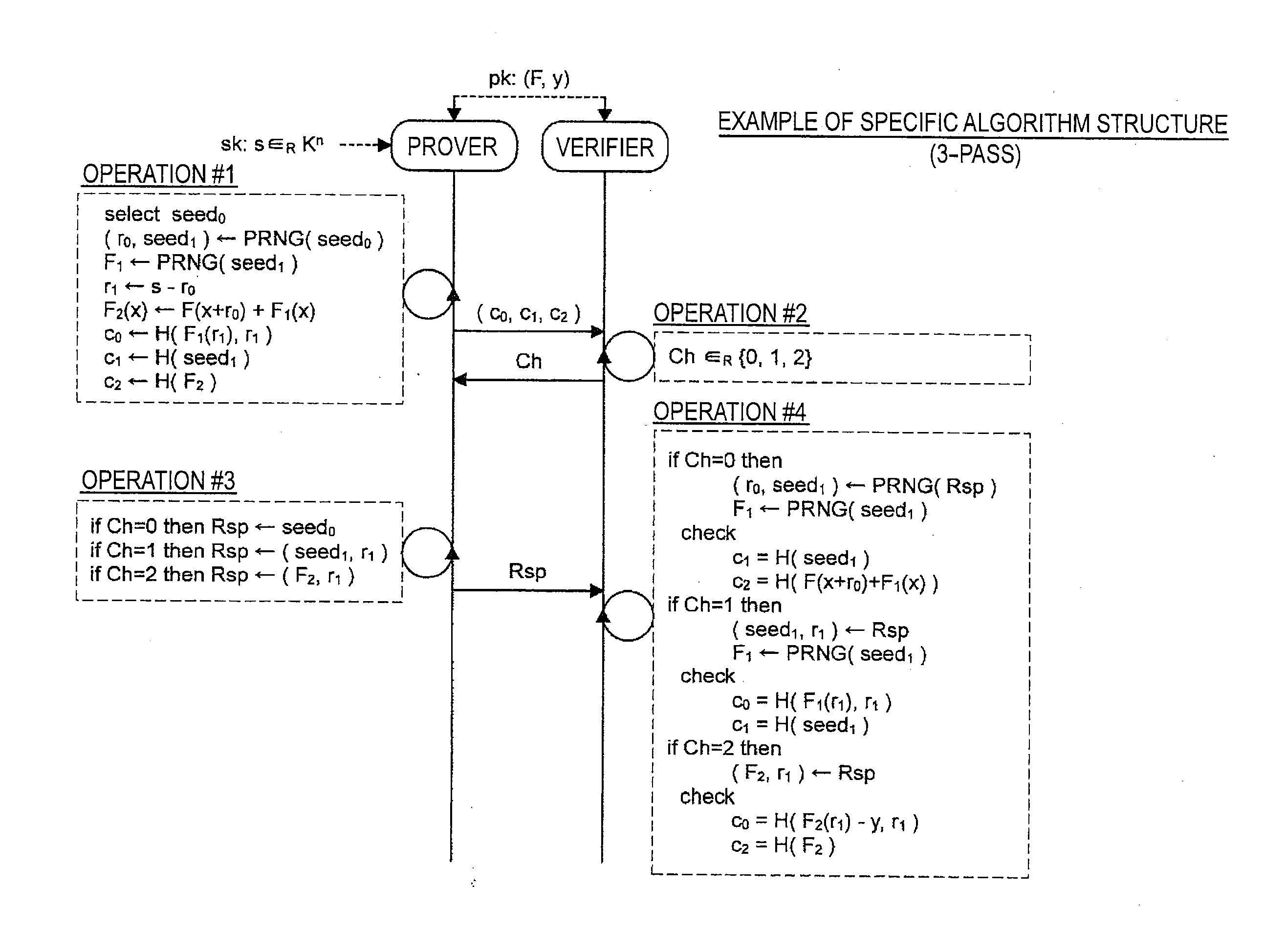
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20140153717A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationInformation processingMultivariable polynomials
Provided an information processing apparatus including a message generation unit that generates a message based on a pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F=(f1, . . . , fm) and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a message supply unit that supplies the message to a verifier storing the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F and vectors y=(y1, . . . , ym)=(f1(s), . . . , fm(s)), an intermediate information generation unit that generates third information based on first information randomly selected by the verifier and second information obtained at a time of generation of the message, an intermediate information supply unit that supplies the third information to the verifier, and a response supply unit that supplies the verifier with response information corresponding to a verification pattern which the verifier selects from among k (where k≧2) verification patterns.
Owner:SONY CORP
Using Geometric Wavelets Based on Active Contours for Signal Processing
Certain embodiments provide systems and methods for using geometric wavelets based on active contours for signal processing. Certain embodiments may allow image processing. A system includes providing an image processing circuitry that computes a segmentation tree using active contours for an input image data; creates a geometric wavelets representation using the segmentation tree; and then generate an image based on geometric wavelet sparse representation extracted from the geometric wavelets representation. The geometric wavelet sparse representation may comprise M most active geometric wavelets from a set of N geometric wavelets in the geometric wavelets representation. The image processing circuitry may recursively find sub-domains and multivariate polynomials for each domain at each stage in the computing of the segmentation tree. Each of the sub-domains is a domain for a succeeding stage for the segmentation tree. The recursively finding may be terminated, for example, when each domain at a stage comprises less than a determined number of pixels.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for calling agent model
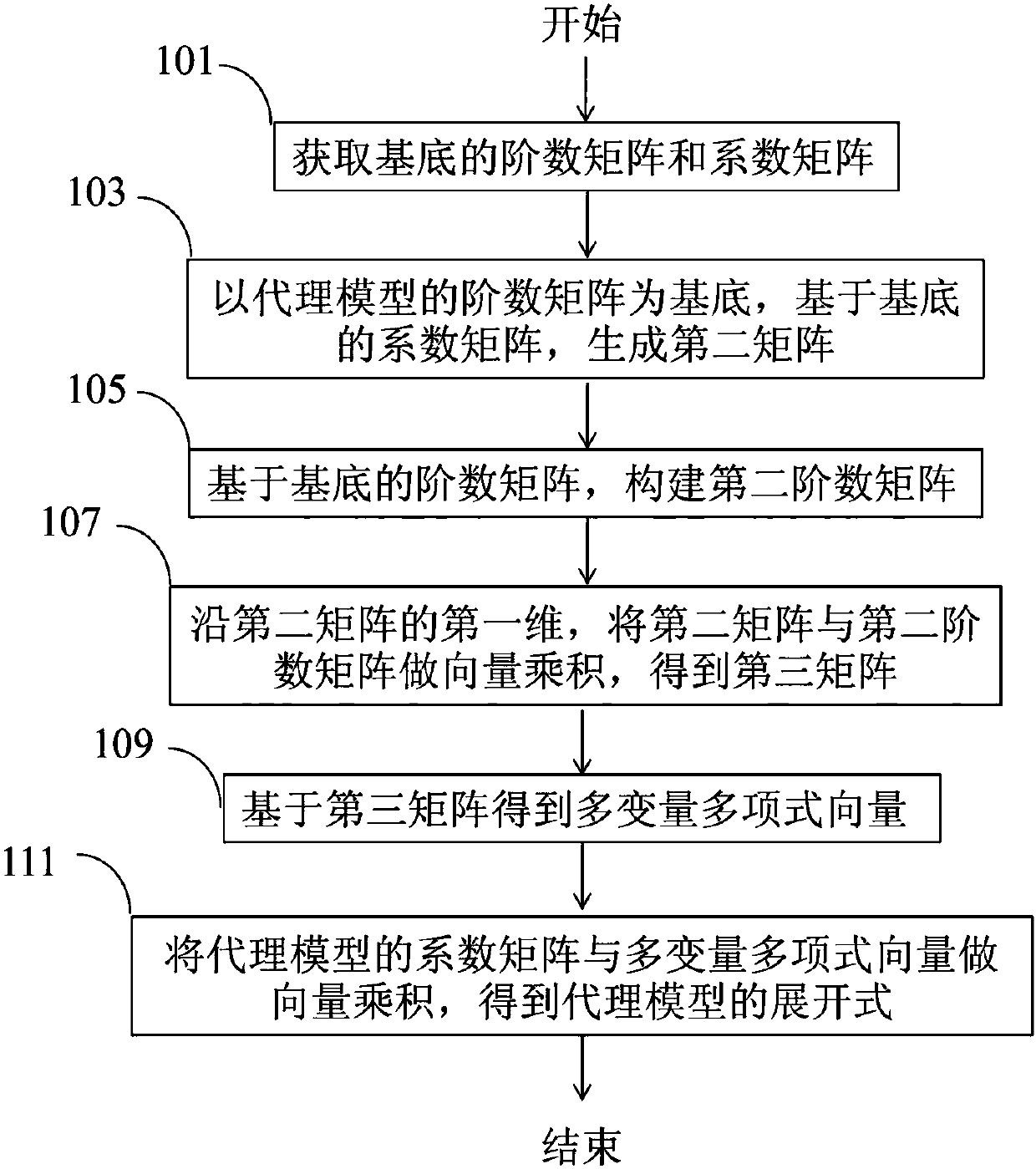
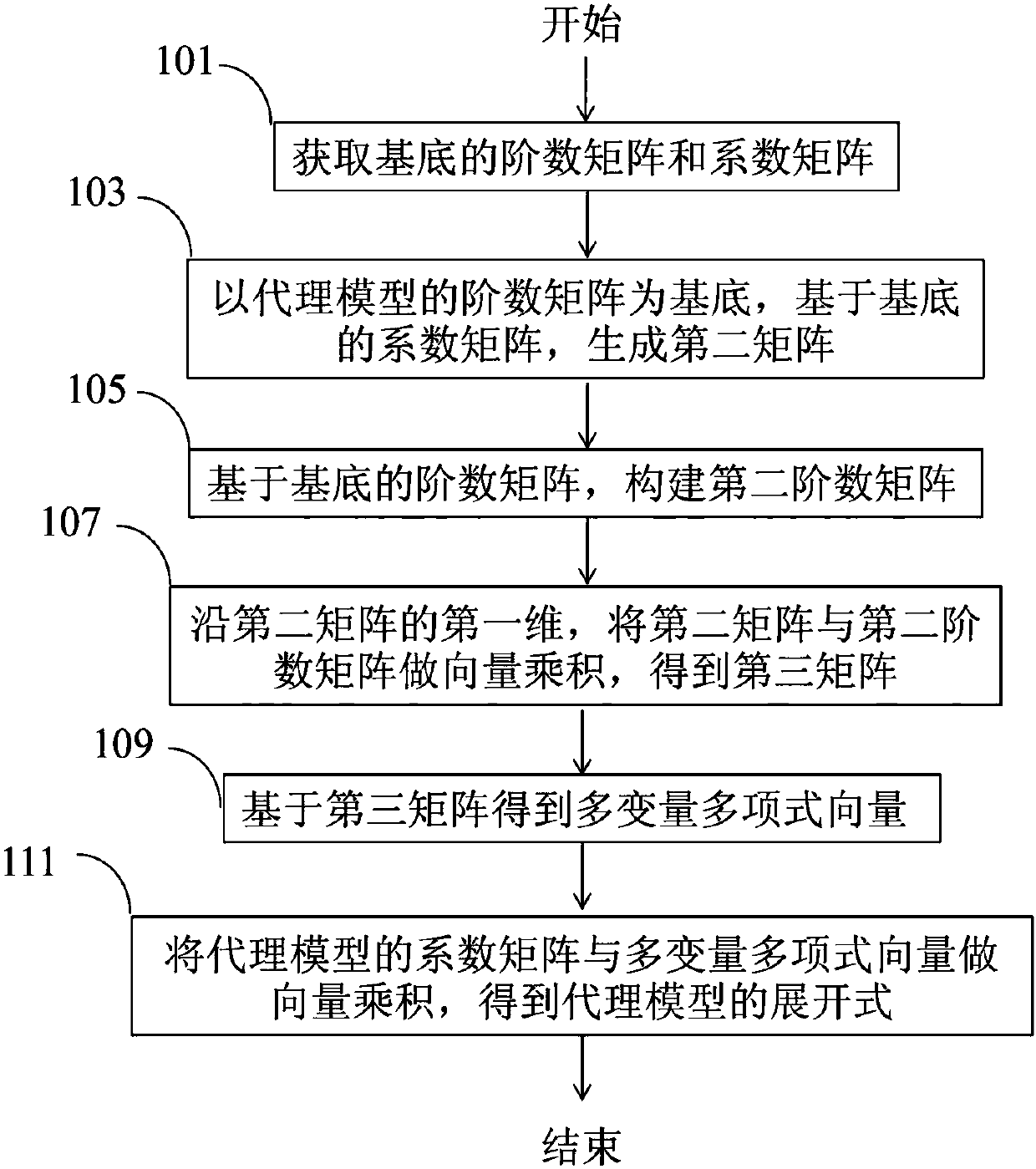
PendingCN109960775AImprove computing efficiencyImplement vectorizationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmMultivariable polynomials
The invention provides a method and a device for calling an agent model. The method comprises the steps of acquiring an order matrix of a multivariable polynomial substrate to serve as a first order matrix, and acquiring a coefficient matrix of the multivariable polynomial substrate to serve as a first coefficient matrix; generating a three-dimensional second matrix based on the first coefficientmatrix by taking the order matrix of the agent model as a base mark; constructing an order matrix of variables as a second order matrix based on the first order matrix; carrying out vector product onthe second matrix and the second order matrix along the first dimension of the second matrix to obtain a third matrix; obtaining a multivariable polynomial vector based on the third matrix; and working out a vector product on the coefficient matrix of the agent model and the multivariate polynomial vector to obtain the expansion of the agent model. According to the method, when the agent model iscalled, the calculation efficiency for calling the agent model is improved while the precision is ensured not to be lost, and effective application of the agent model is realized.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS9178700B2Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationInformation processingMultivariable polynomials
Provided an information processing apparatus including a message generation unit that generates a message based on a pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F=(f1, . . . , fm) and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a message supply unit that supplies the message to a verifier storing the pair of multi-order multivariate polynomials F and vectors y=(y1, . . . , ym)=(f1(s), . . . , fm(s)), an intermediate information generation unit that generates third information based on first information randomly selected by the verifier and second information obtained at a time of generation of the message, an intermediate information supply unit that supplies the third information to the verifier, and a response supply unit that supplies the verifier with response information corresponding to a verification pattern which the verifier selects from among k (where k≧2) verification patterns.
Owner:SONY CORP
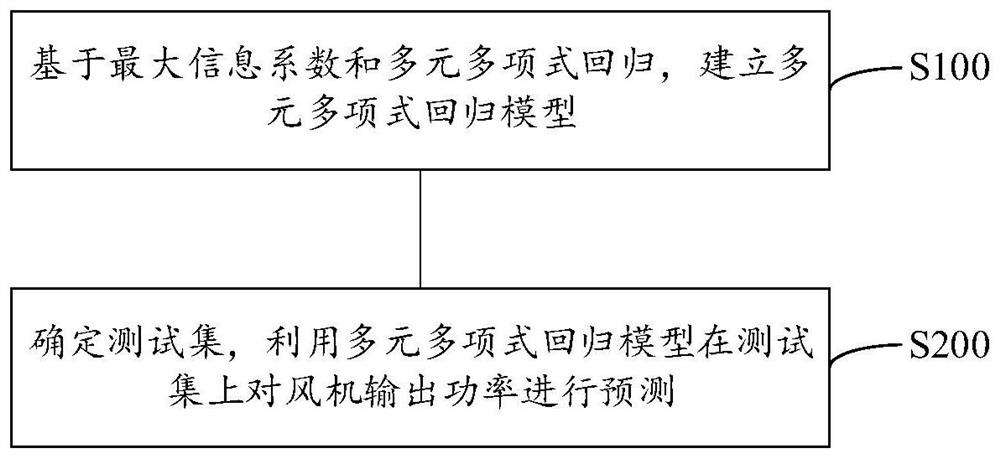
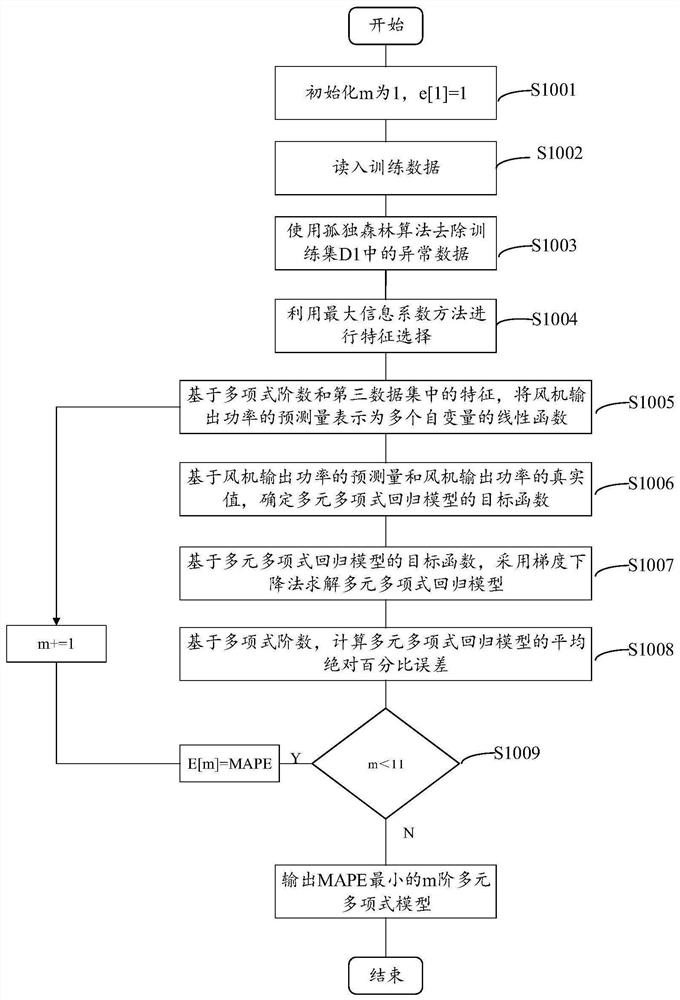
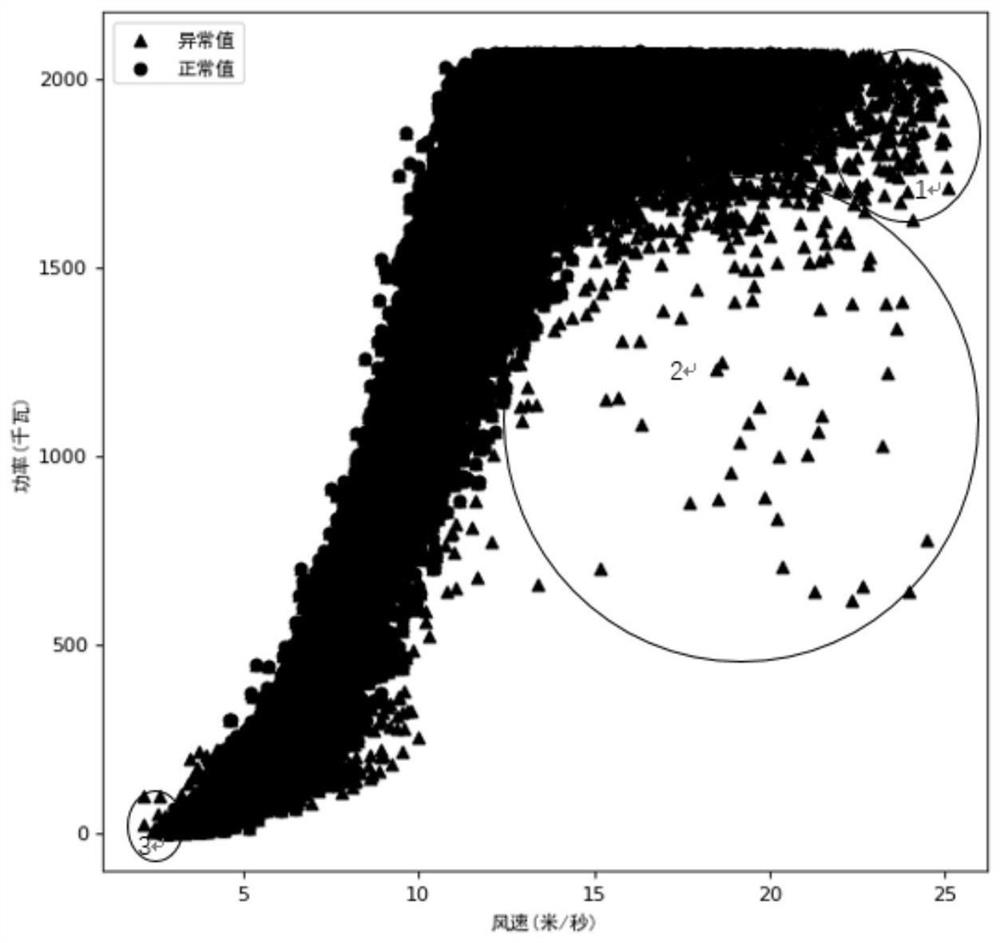
Fan output power prediction method and system
PendingCN113821931ASolve the problem of insufficient analysisImprove accuracyForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationPolynomial methodPolynomial regression model
The invention discloses a fan output power prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a multivariate polynomial regression model based on a maximum information coefficient and multivariate polynomial regression; and then, determining a test set, and predicting the output power of the fan on the test set by using the multivariate polynomial regression model. In addition, the invention further provides a fan output power prediction system. According to the method and system, the maximum information coefficient is used for selecting the important variables influencing the output power of the fan in the process of establishing the multivariate polynomial regression model, multiple important variables are comprehensively considered, the problem that analysis is not comprehensive enough due to the fact that influence factors of the output power of the fan are analyzed manually is solved, and further, the relation between multivariable and the fan output power is modeled through a polynomial method, so that prediction of the fan output power has high accuracy and low model complexity.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
ActiveUS20140205088A1Improve securityPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationInformation processingMultivariable polynomials
Provided is an information processing apparatus including a message generating unit that generates a message based on a multi-order multivariate polynomial set F=(f1, . . . , fm) defined on a ring K and a vector s that is an element of a set Kn, a message providing unit that provides the message to a verifier holding the multi-order multivariate polynomial set F and a vector y=(y1, . . . , ym)=(f1(s), . . . , fm(s)), and a response providing unit that provides the verifier with response information corresponding to a verification pattern selected by the verifier from among k (where k≧3) verification patterns. The vector s is a secret key. The multi-order multivariate polynomial set F and the vector y are public keys. The message is information obtained by performing an operation prepared for a verification pattern corresponding to the response information in advance using the public keys and the response information.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for protecting biometric templates, and a system and method for verifying a speaker's identity
ActiveUS20200335107A1Low accuracyReduce precisionSpeech analysisDigital data protectionAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Owner:FOUND OF THE IDIAP RES INST IDIAP
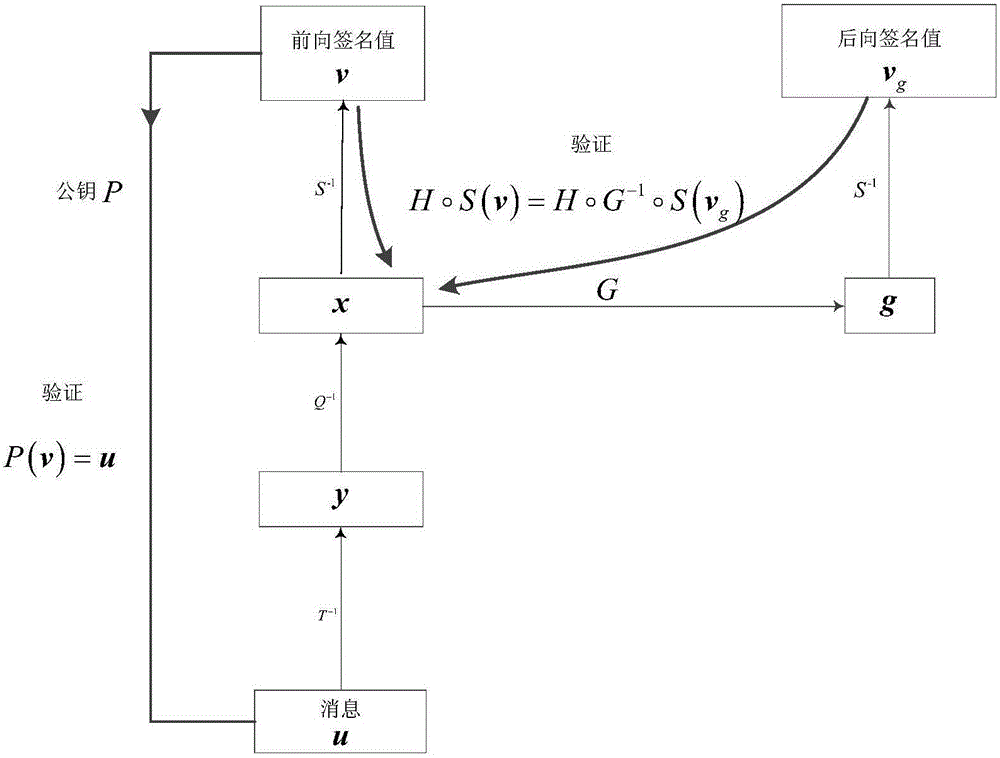
Multivariable signature method capable for resisting forged signature attack
ActiveCN106209376ASystem Efficiency and SafetyIncrease the difficultyUser identity/authority verificationCryptographic attack countermeasuresDigital signatureThree stage
The invention discloses a multivariable signature method capable for resisting a forged signature attack, which is characterized in that by adding a vector called as signature additional value, a verification condition related to internal information is added during signature verification, so that the forged signature attack can be revisited effectively. The multivariable signature method particularly comprises three stages of data pre-processing, signature generation and signature verification. By taking a multivariable public key cryptosystem as a theoretical basis, a message signature and verification scheme is established according to a multivariable polynomial equation set in a finite field, so that the model defect of the conventional multivariable signature scheme is overcome, and under the condition of resisting a quantum attack, signature verification not only is dependent on public key verification, but also involves a user's legal private key. Therefore, the multivariable signature method can provide a basic technological support for information security of the quantum computer era and establishment of a trust system, and is suitable for secure digital signature in the quantum computer era; and moreover, due to relatively high efficiency and security, the multivariable signature method is particularly suitable for occasions where memory space and operation time are limited.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Information processing device, key generating device, signature verifying device, information processing method, signature generating method, and program
InactiveCN102640451AEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingTheoretical computer science
Disclosed is an information processing device for realizing an electronic signature system using the MPKC scheme capable of certifying security against attacks on selected documents. Specifically disclosed is an information processing device which comprises a first inverse transforming unit that transforms elements y of a finite ring Kn including n elements into elements y' of the finite ring Kn using inverse transformation T-1 of a first secret polynomial T; a component calculating unit that calculates components X is an element of a set {Z is an element of a set | f(Z) = Y} of an inverse image of a mapping f:A->A expressed by a predetermined multivariable polynomial using elements Y of a degree n extension A of a finite ring K, letting the elements y' of the finite ring Kn obtained above be the elements Y; a component selecting unit that selects a component X of the inverse image with a probability p proportional to the number alpha of the components of the inverse image and that outputs an exception value with a probability (1 - p); and a second inverse transforming unit that transforms elements x' of the finite ring Kn into elements x of the finite ring Kn using inverse transformation S-1 of a second secret polynomial S, letting the component X selected above be the elements x' of the finite ring Kn.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Apparatus and method for detecting signal using multivariate polynomial in multiple input multiple output communication system
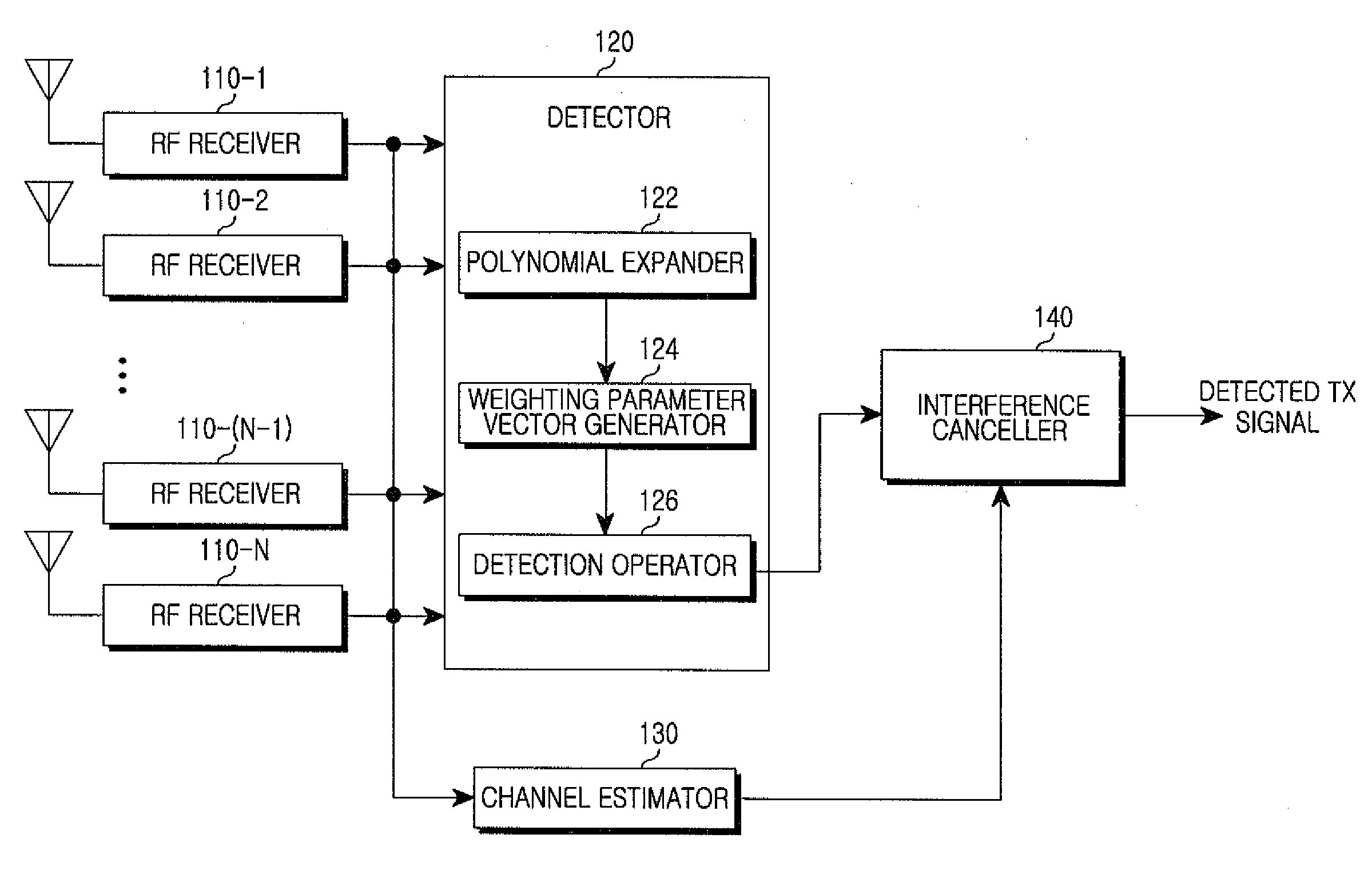
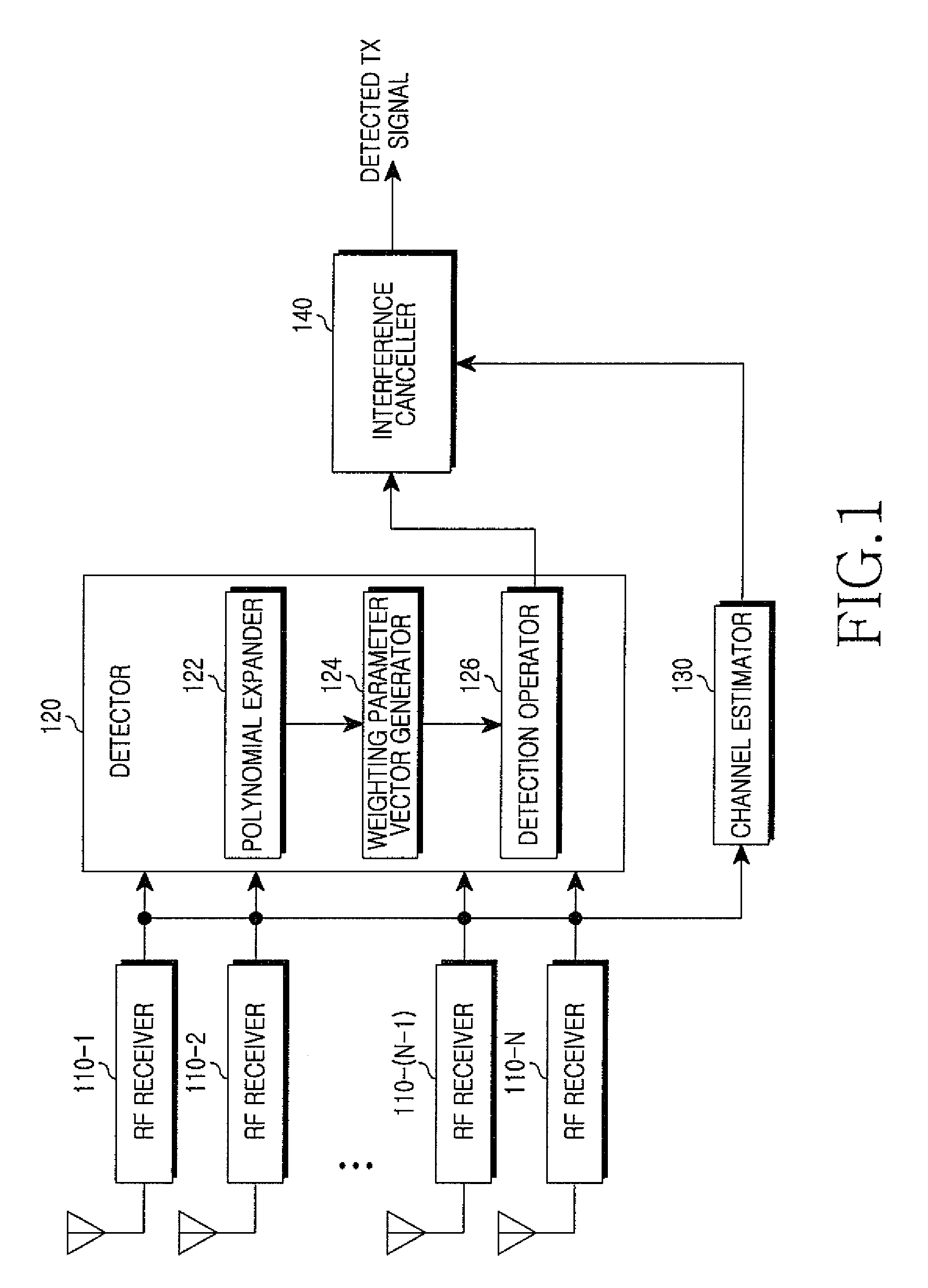
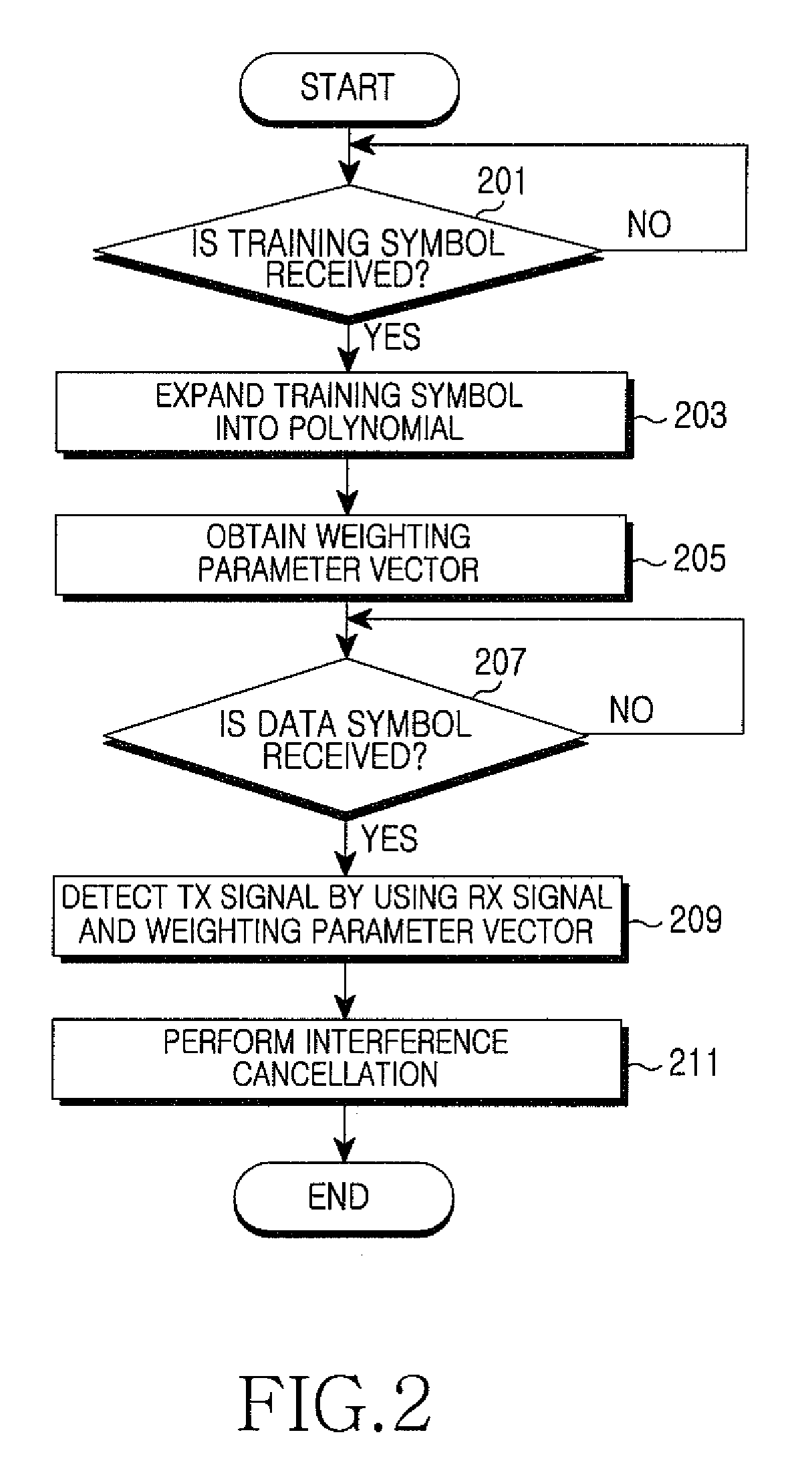
ActiveUS8130859B2Reduce complexityMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemRound complexity
A signal detection apparatus and method in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a receiver for receiving training symbol vectors and a data signal vector from a transmitting end through a plurality of receive (Rx) antennas and a detector for expanding the training symbol vectors into second- or higher-order polynomials, for generating a weighting parameter vector for multivariate polynomial expansion of the data signal vector by using the polynomials expanded from the training symbol vectors and thereafter for expanding the data signal vector into a second- or higher-order multivariate polynomial using the weighting parameter vector, and for detecting Transmit (Tx) values of the data signal vector from the multivariate polynomial. Therefore, signal detection performance in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system resembles that of a non-linear scheme while complexity resembles that of a linear scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com