Data consistency and wear leveling-based memory file system management method
A memory file system and wear leveling technology, applied in memory systems, electrical digital data processing, memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve problems such as high overhead and performance reduction of memory file systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Abbreviations and key terms involved in this embodiment are defined as follows:
[0104]NVM, Non-Volatile Memory, non-volatile memory;
[0105] SCM, Storage Class Memory, storage class memory;
[0106] The file is updated in place, the internal data of the file is modified, and the file size remains unchanged;
[0107] File appending, content is added at the end of the file, and the file size becomes larger;
[0108] Adding part of the file, modifying the file data and adding content at the end, the file size becomes larger;
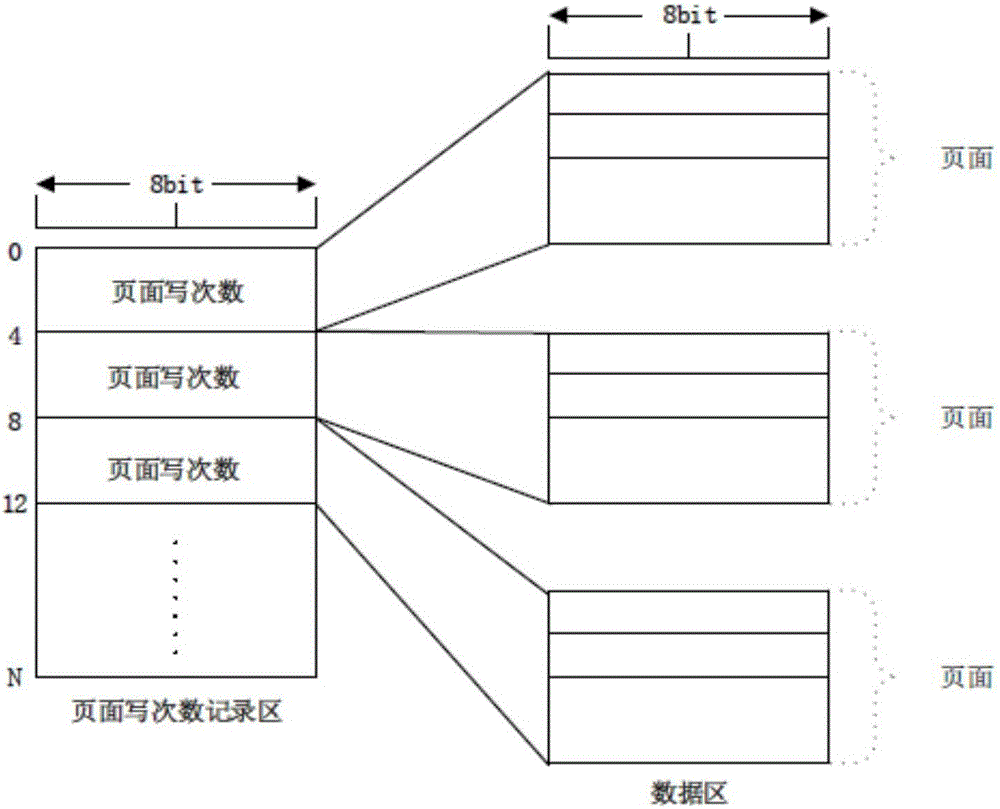
[0109] Page write count recording area, which records the number of times memory page data is updated;
[0110] The free page management module is a system function module responsible for allocating and reclaiming free memory pages.
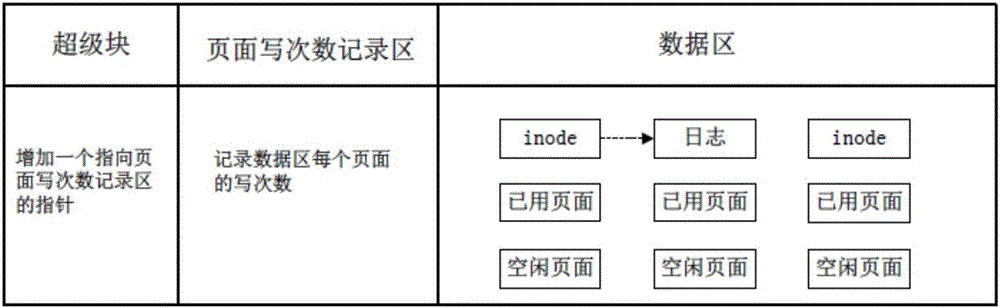
[0111] As shown in the figure, the persistent memory file system provided by this embodiment divides the non-volatile storage area into three parts: a super block, a page write count recording area, and a data ar...
Embodiment 2
[0127] A data consistency and wear leveling memory file system management method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
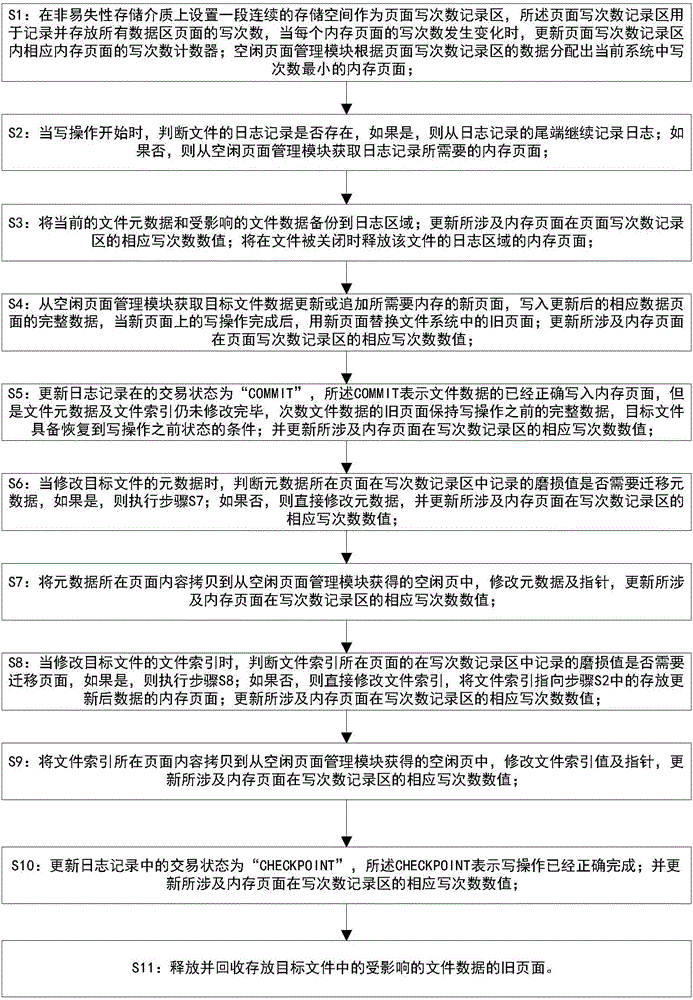
[0128] S1: Set a continuous storage space on the non-volatile storage medium as the page write count recording area, the page write count recording area is used to record and store the write count of all data area pages, and the write count of each memory page Update the write times counter of the corresponding memory page in the recording area when a change occurs; the free page management module can allocate the memory page with the smallest write times in the current system according to the data recorded in this area; as long as the system follows the architecture proposed by the patent of this embodiment and method implementation, the write operations in the page write count recording area itself are relatively evenly distributed, and will not exceed the maximum tolerable write count of the non-volatile memory before any other memory p...
Embodiment 3
[0147] Such as Figure 5 as shown, Figure 5 It is a flow chart of opening the file in the present invention, and the specific process is as follows:
[0148] Open the file to determine whether the file exists. If it exists, open the file. If the file does not exist, perform the process of creating a file. The process of creating a file is as follows:
[0149] Step 1: Generate metadata to determine whether to apply for a page; if you need to apply for a new page, go to step 2; if you don’t need to apply for a new page, go to step 3;
[0150] Step 2, apply for a page with the least number of writes from the free page management module, write metadata, modify relevant data, and execute step 4;
[0151] Step 3, write metadata to the page, go to step 4;
[0152] Step 4, increase the corresponding write count value of the involved memory page in the page write count recording area, and execute step 5;
[0153] Step 5, complete.
[0154] in, Figure 6 It is a flow chart of upd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com