Memory-based frequent pattern mining method
A frequent mode and memory technology, applied in the field of memory, can solve the problems of limited number of NVM write operations, reduced NVM service life, time and energy consumption, etc., to achieve rapid construction, reduce a large number of intensive write operations, and prolong life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
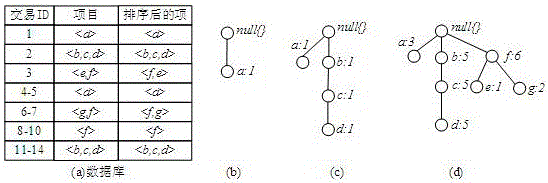
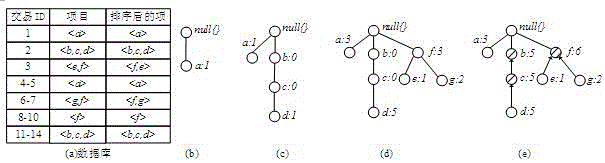
[0052] image 3 An example of constructing a frequent pattern tree for the present invention, the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0053] Step 1, according to image 3 (a) The database constructs the initial tree of frequent patterns, the specific process is as follows:
[0054] Such as image 3 As shown in (b), create a node with a label of null as the root node of the entire frequent pattern tree; after scanning the first transaction record, create node a, and set the count field value of node a to 1, indicating item a appears 1 time;
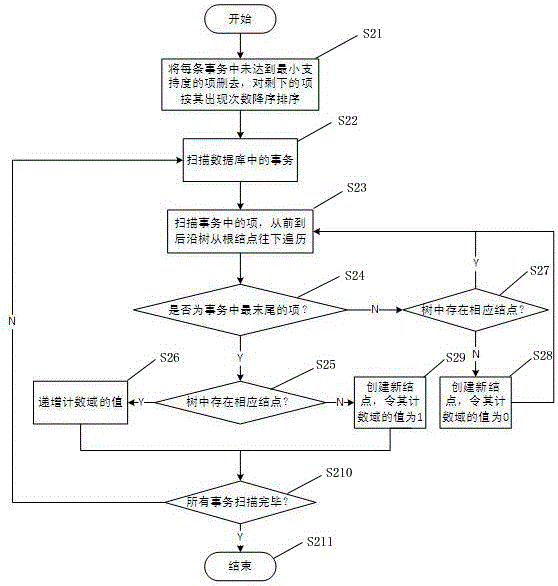
[0055] Such as image 3 As shown in (c), after scanning the second transaction record, build nodes b, c, and d, and set the count field value of b and c to 0, and the count field value of d to 1, indicating that item d appears once (this In order to reduce redundant writing when building a frequent pattern tree, the number of occurrences of b and c is not recorded, only the number of occurrences of item d at the end of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com