Performance analysis method of d2d cellular heterogeneous network based on queuing theory
A heterogeneous network and analysis method technology, applied in transmission monitoring, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient consideration of random arrival reliability requirements and low complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Step 1: Establish a system model;
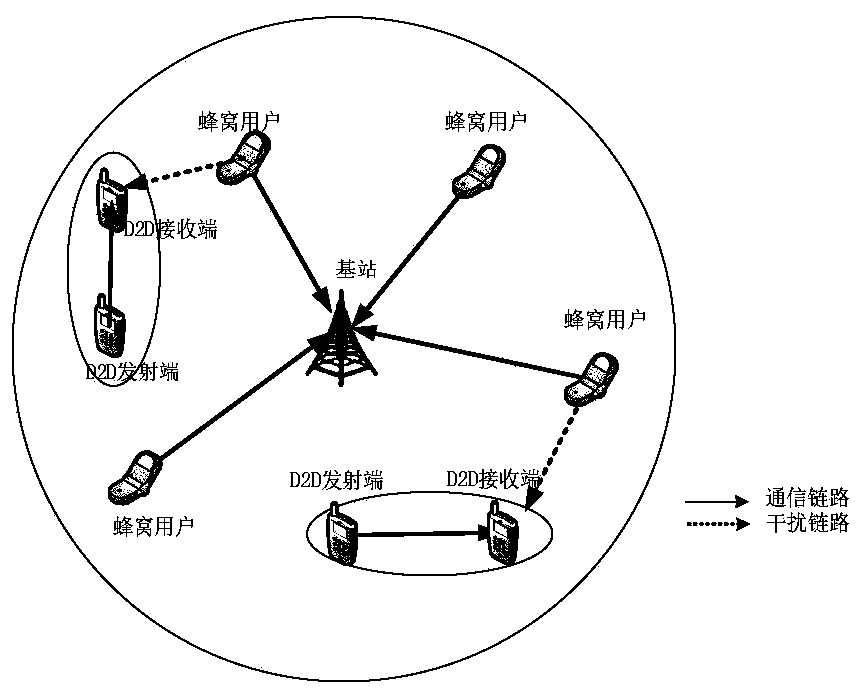
[0081] The present invention is aimed at a special application scene, comes from practical application, and the scene setting is meticulous and reasonable, and has practical guiding significance. Such as figure 1 As shown in , assuming that in a single-cell scenario, N cellular users occupy N orthogonal channels, record their set as There are M D2D user pairs in total, and the set is D={1, 2,..., M}. Cellular users and D2D users are uniformly distributed in the cell. Assuming N>M, a pair of D2D users only multiplex one cell For the user's uplink channel, in order to reduce system overhead, the D2D user randomly selects a multiplexed channel, and any D2D receiving end is only interfered by the cellular user sharing the channel with it. This paper only considers large-scale fading, and the path loss model can be expressed as P(d)=P·d -α , where P represents the transmitted power, P(d) represents the received power measured at a dist...
Embodiment 2
[0111] In order to analyze the system performance from the perspective of ease of practical application, considering that the transmission performance of D2D is affected by the distance between the cellular user and the D2D receiver, the complexity of the algorithm is reduced, which is conducive to accurate analysis of system performance in real time. The present invention is further improved on the basis of Embodiment 1, specifically:
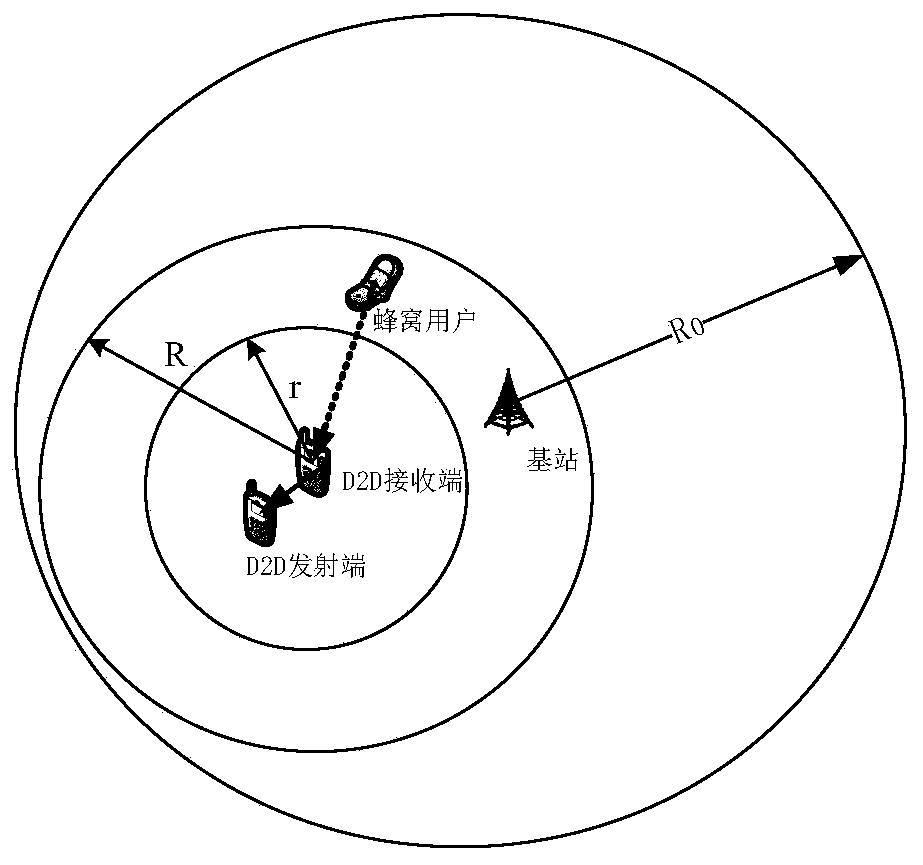
[0112] Such as figure 2 As shown, consider that in a single macro cell, a D2D receiver is divided into three ring-shaped areas centered on a D2D receiving end, divided by radius r, R, assuming that the maximum radius is still within the coverage of the macro cell, and R is the macro user’s D2D The maximum interference distance of the user, that is, when the distance between the macro user and the D2D receiving end is greater than R, the interference of the macro user to the D2D user can be ignored. When the macro user falls into the ring dom...
Embodiment 3
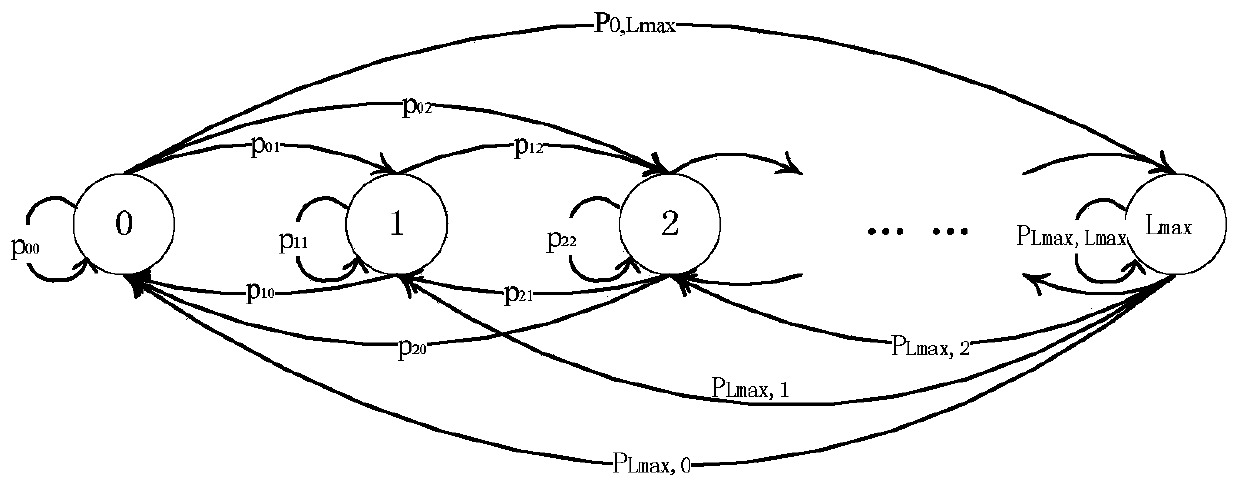
[0118] The present invention further improves on the basis of Embodiment 1. Under the assumed conditions of finite-state Markov model and Poisson service arrival, a two-dimensional Markov system model including channel and queue state is constructed for the D2D user system. , using the steady-state probability analysis system performance, high reliability. Specifically, the solution to the steady-state transition probability includes the following steps:
[0119] when Time:
[0120]
[0121] The above formula shows that when the queue length is less than the minimum sending rate of the time slot ΔT, no matter which sending rate it is in, all data packets in the queue can be sent completely.
[0122] when and Time:
[0123]
[0124] The above formula shows that at this time with the minimum sending capability (i.e.γ 1 ), can’t achieve state transfer, only with γ 2 and gamma 3 Send data, and can clear the original captain.
[0125] when and Time:
[0126] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com