Sag damping cable
A damping and damper technology, applied in the field of structural vibration reduction, can solve the problems of increased main cable tension, low lateral stiffness, structural deformation, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing deformation capacity, increasing energy dissipation capacity, and reducing deformation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
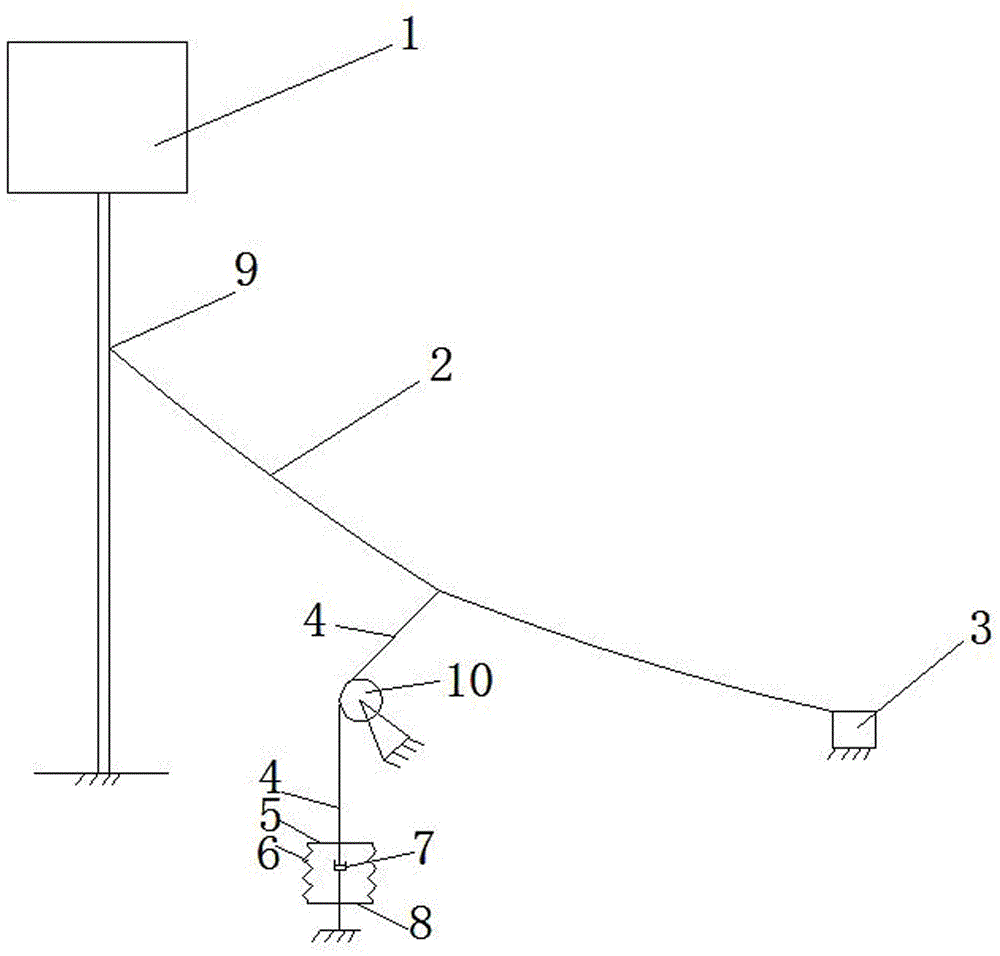
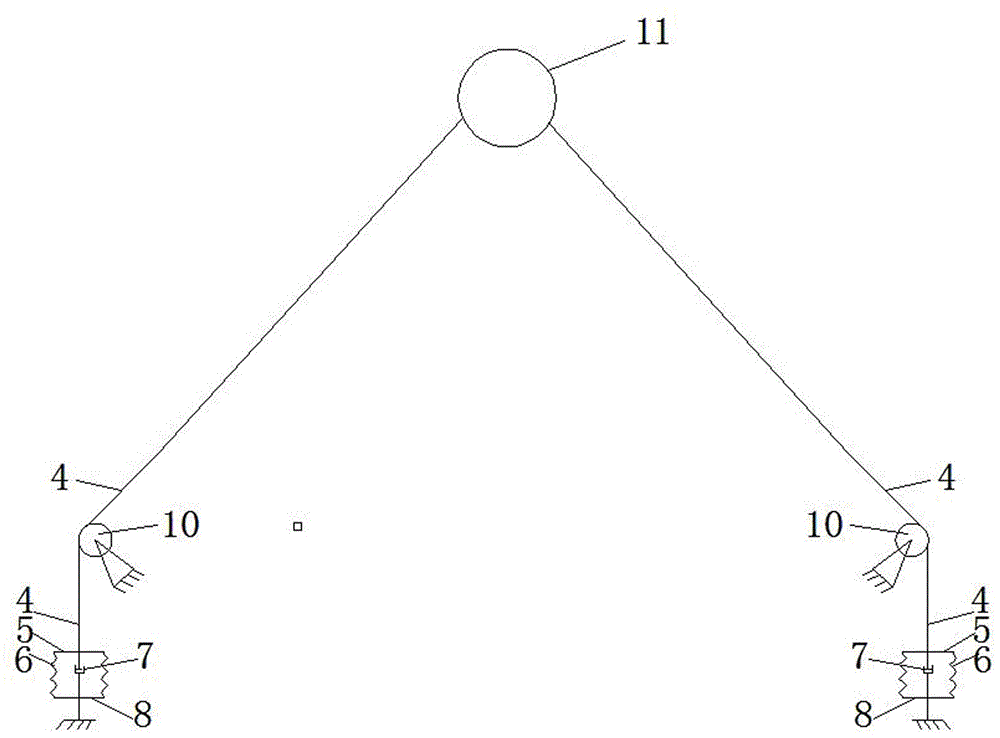
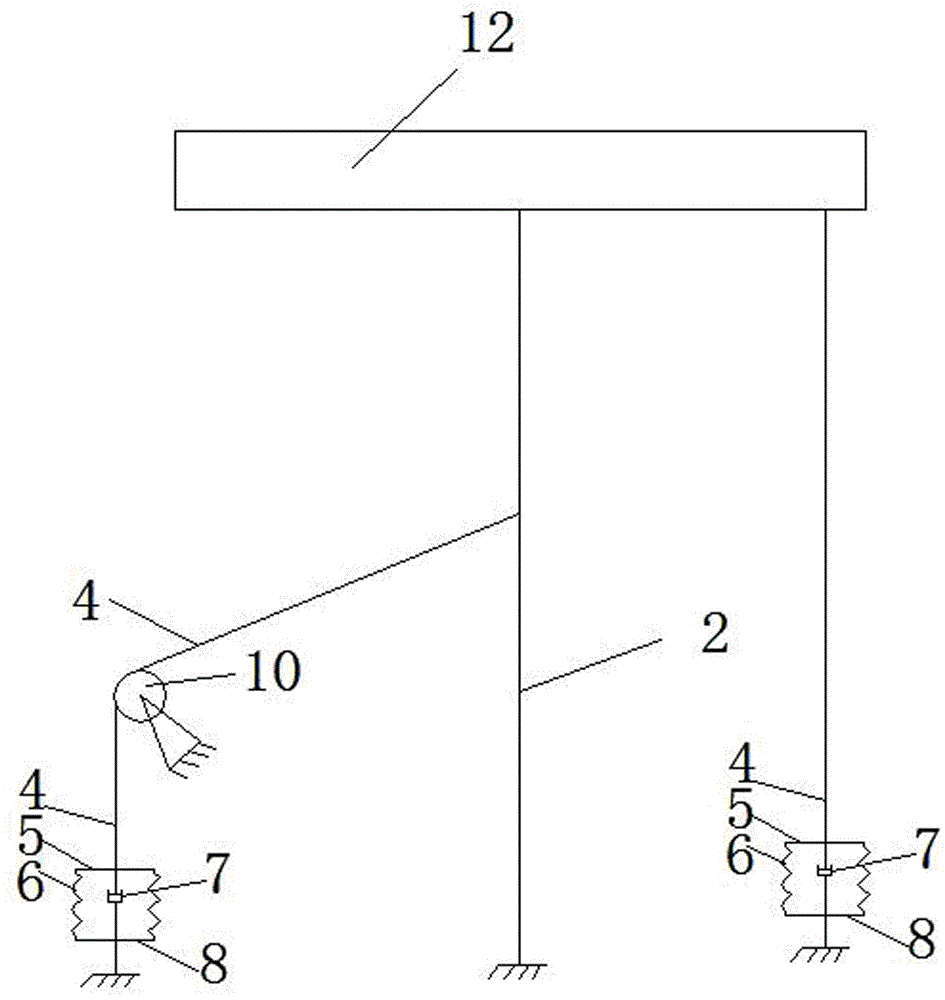
[0021] see figure 1 , taking the vibration reduction of towering structures such as transmission towers as an example, the towering structure vibrates under the action of strong wind (usually the structure swings from side to side), which is simplified as figure 1 The vibrating structure is shown in 1. From figure 1 It can be seen from the figure that the upper end of the main cable 2 is connected to the upper anchor point 9 fixed on the vibrating structure 1, and the lower end of the main cable 2 is connected to the anchorage 3 fixed on the ground. The main cable 2 sags or deforms laterally under the action of its own gravity or wind force, and deviates from the straight line connecting the upper and lower anchor points of the main cable 2. Generally, the distance from the midpoint of the main cable 2 to the straight line is the largest,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com