A motor control device that controls a motor based on the back EMF voltage of the motor winding
A technology of motor control and back electromotive force, applied in the direction of motor generator control, electromechanical transmission control, electronic commutation motor control, etc., can solve the problems of reducing productivity, correction amount error, phase lag, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
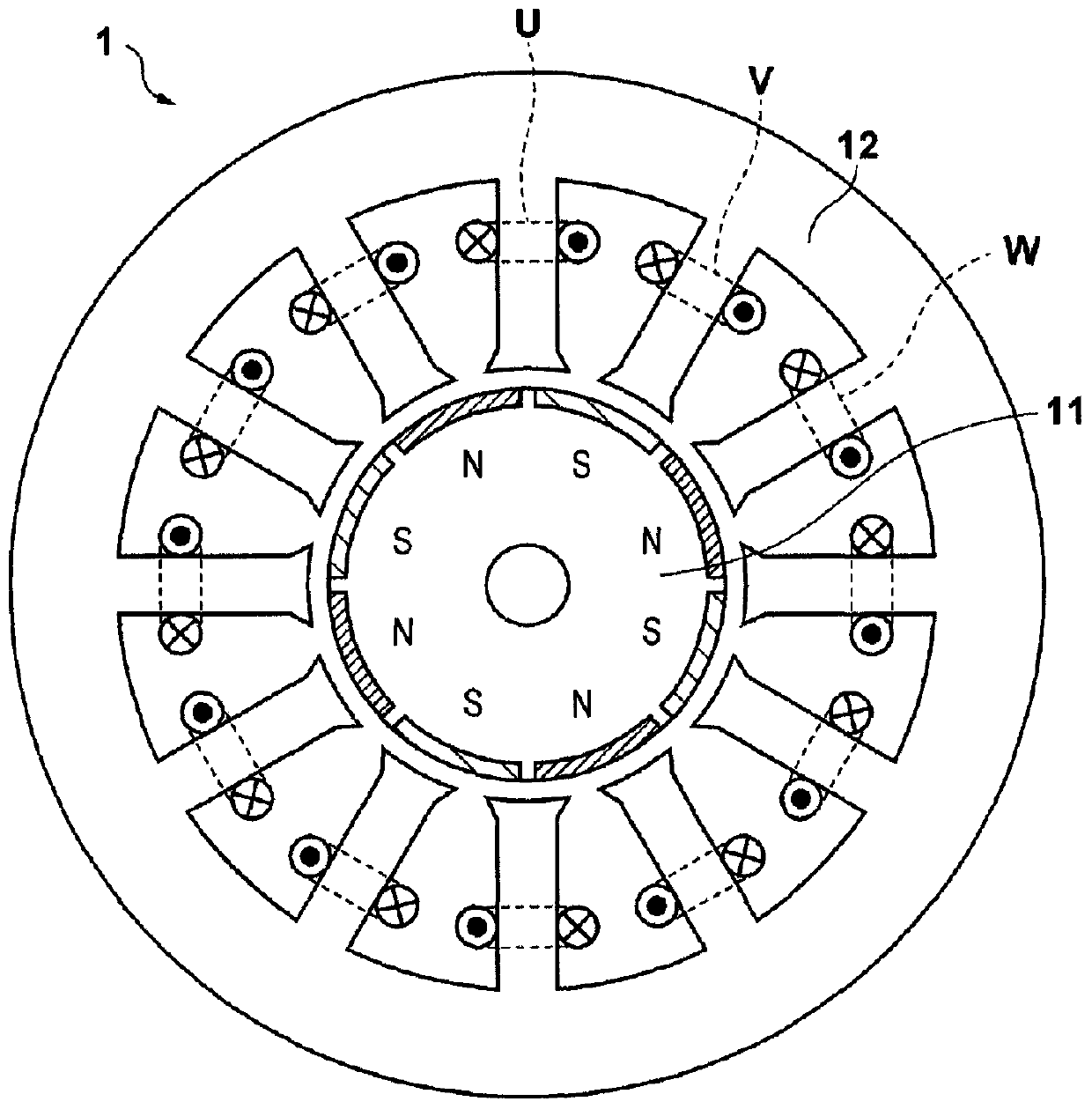
[0025] Hereinafter, the present embodiment will be described using a motor control device that controls a three-phase DC brushless motor having eight poles and twelve slots. Note that the motor controlled by the motor control device of the present invention is not limited to being a three-phase DC brushless motor with eight poles and twelve slots, and for example, the present invention can also be applied to other kinds of motors such as two-phase stepper motor. figure 2 The motor 1 of this embodiment is shown. Notice, figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the motor. The rotor 11 includes eight poles (four pairs) of permanent magnets. The stator 12 has twelve teeth (slots) arranged in 30 degree increments, and the windings U, V and W are wound around the slots. Note that windings U, V and W are arranged on different slots.
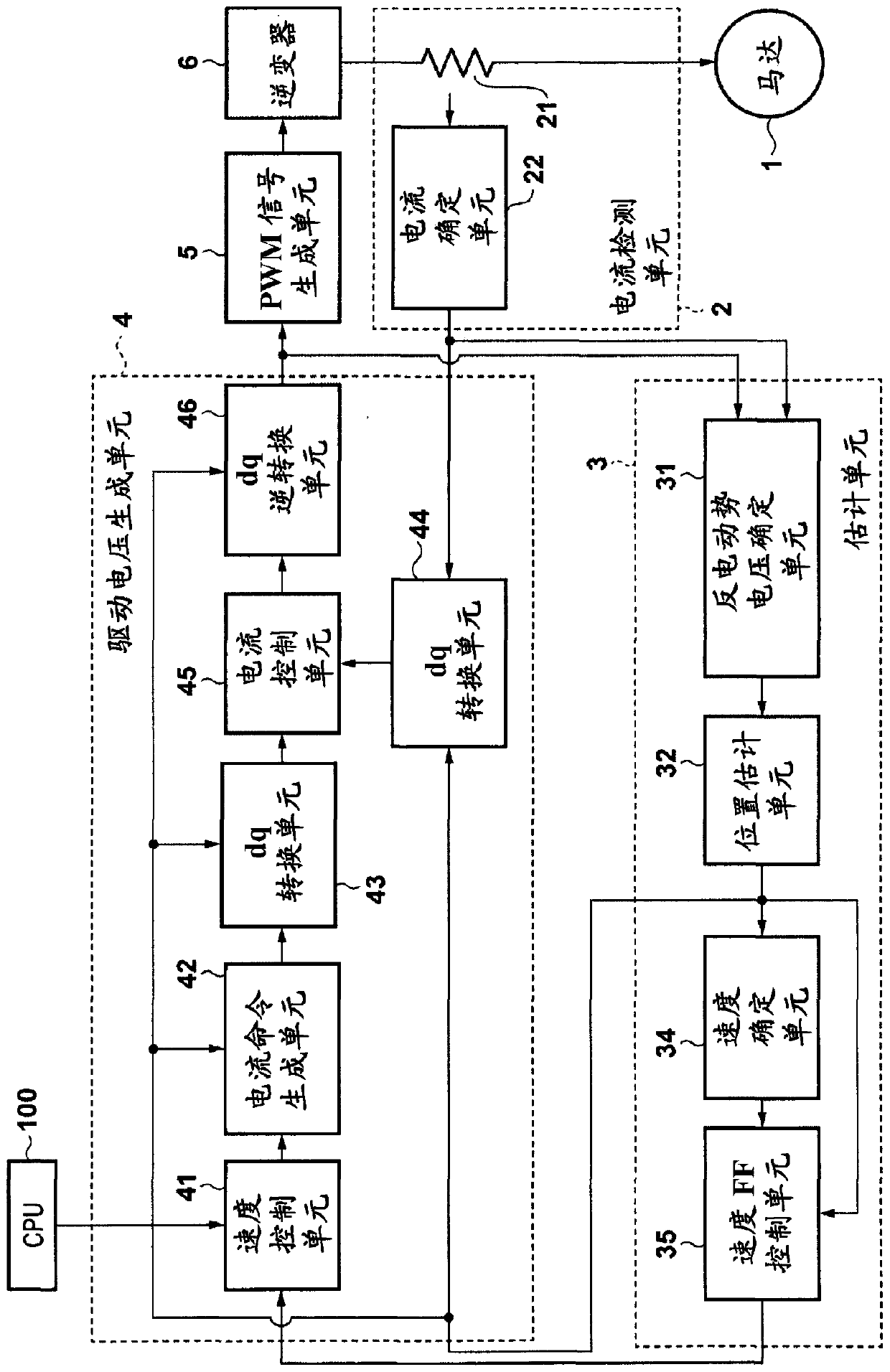
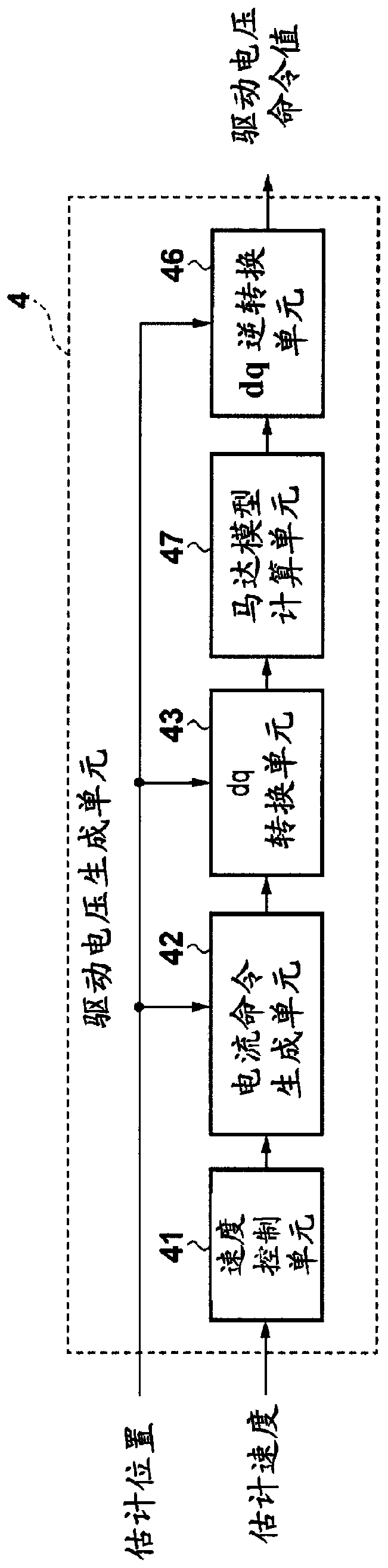
[0026] figure 1 is a diagram showing the overall configuration of the motor control device according...
no. 2 example
[0075] Next, a second embodiment having points of interest different from points of the first embodiment will be described. Figure 12 is a diagram showing the configuration of the motor control device according to the present embodiment. The configuration of the estimation unit 3 is different from that of the estimation unit 3 in the first embodiment, and hereinafter, it will be described in Figure 12 Estimation unit 3 shown in . exist Figure 12 In the estimating unit 3 of this embodiment shown in , the back EMF voltage determining unit 31 and the position estimating unit 32 are similar to figure 1 The counter electromotive voltage determining unit 31 and the position estimating unit 32 in the first embodiment shown in , and thus, the position estimating unit 32 outputs the estimated position θ_est. The position FF control unit 73 reduces an error caused by harmonics included in the estimated position θ_est and outputs the estimated position θ_out resulting from the erro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com